Week 4 weather forecasting
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Describe the evolution of cyclones
Midlatitudes→ from jet stream (W to E) disturbances
→ low pressure w circulation that lead to comma shaped patterns
-> move along w jet stream (W to E), comma shape more obvious as it evolves
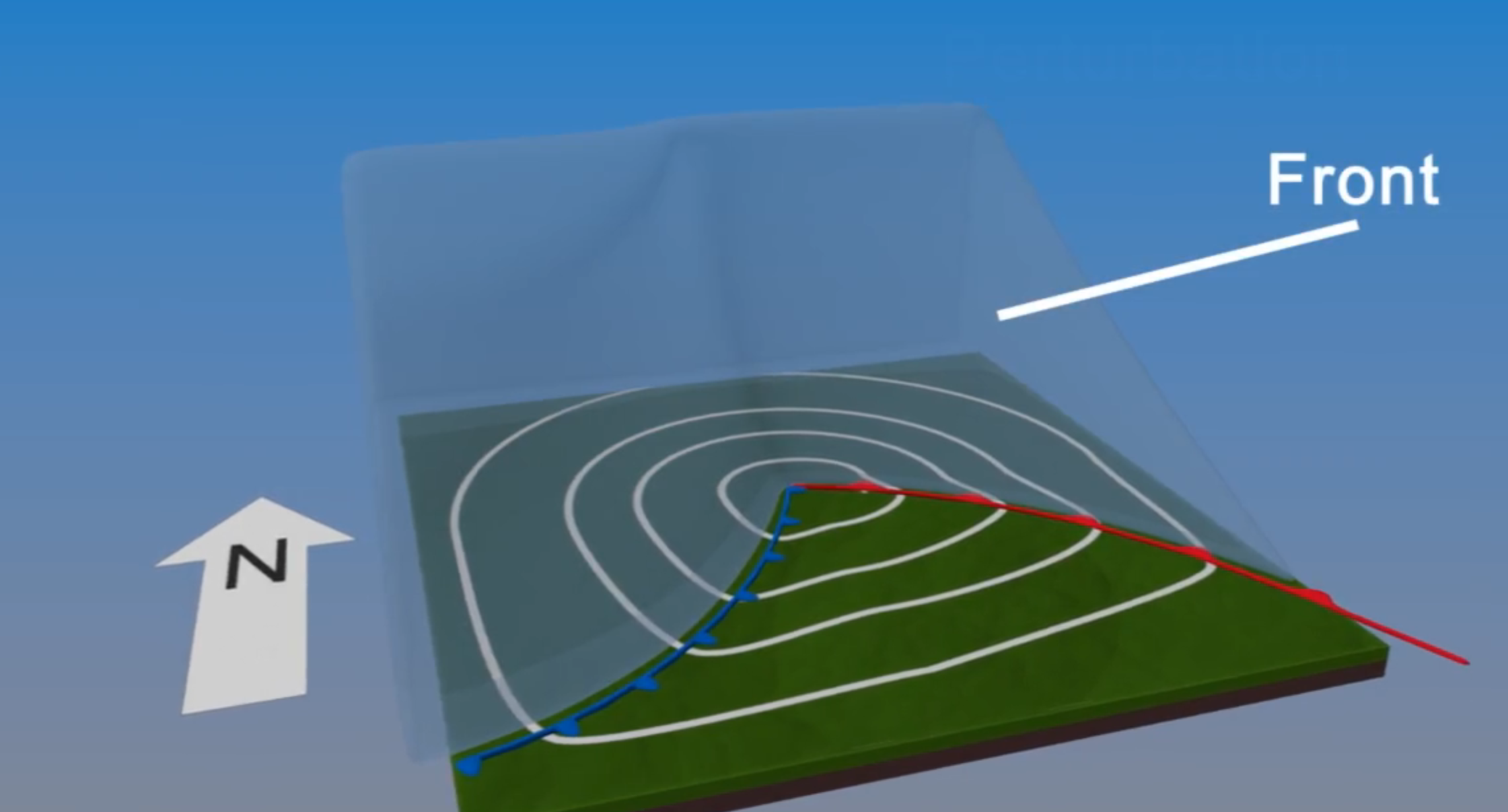
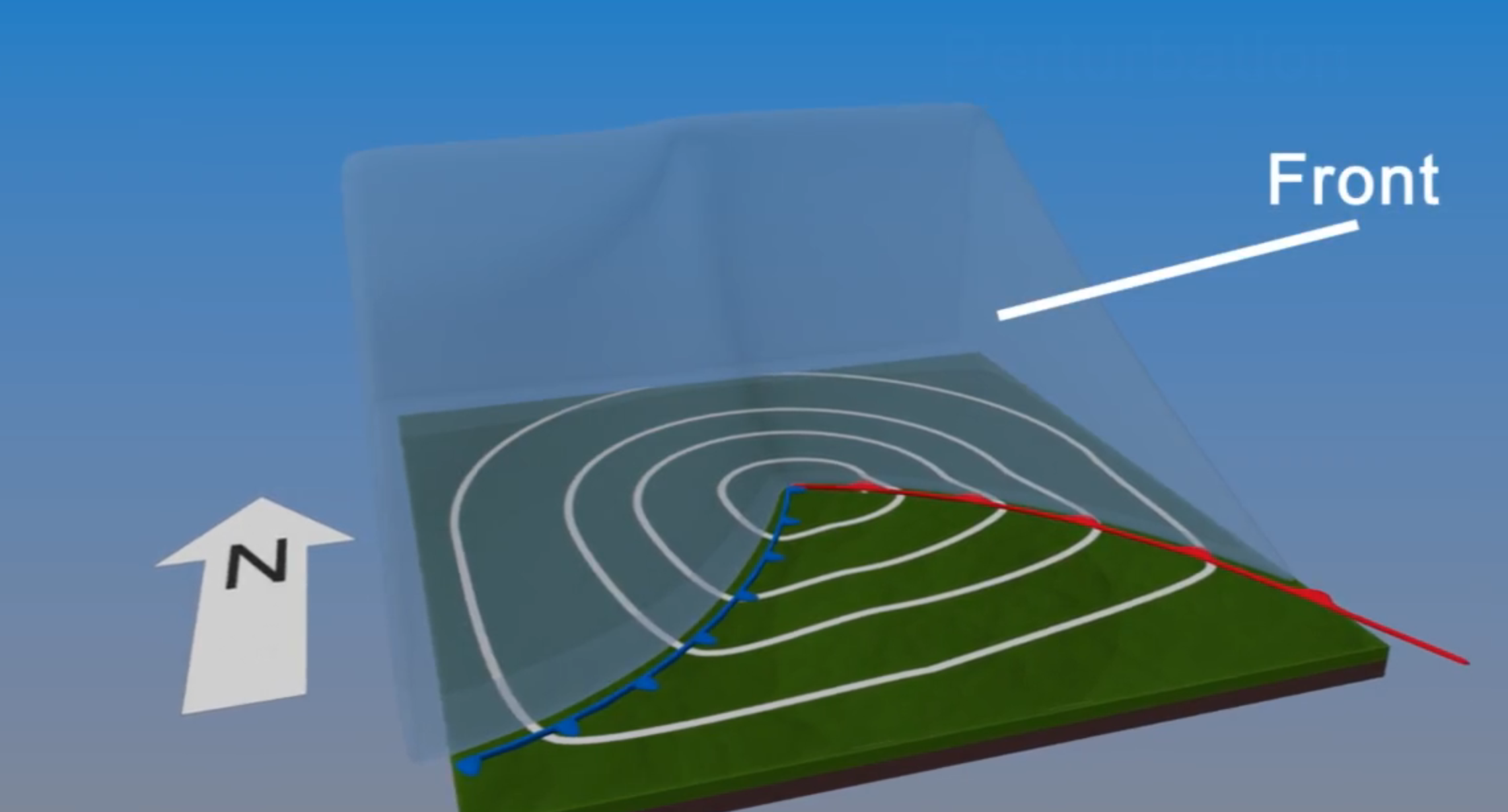
Describe the formation setting of cyclones with fronts and jetstreams
Forms due to temperature gradients
Occurs at front→ boundary between hot/cold air, is a slope
Low pressure region at middle (the perturbation), where counter clockwise winds flow
Frontal slope deforms over time, warm front→ warm air advances poleward, cold front→ cold air towards equator
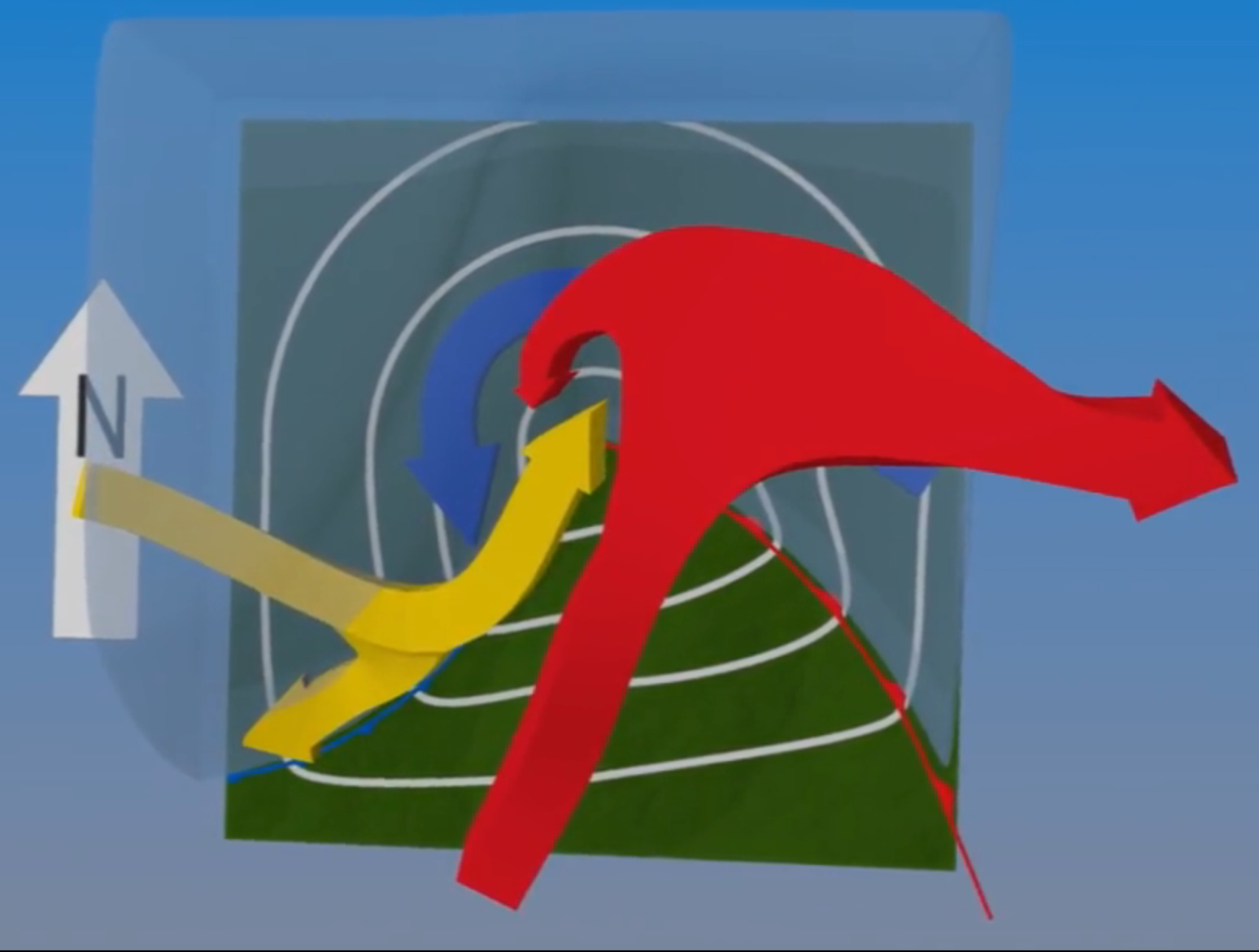
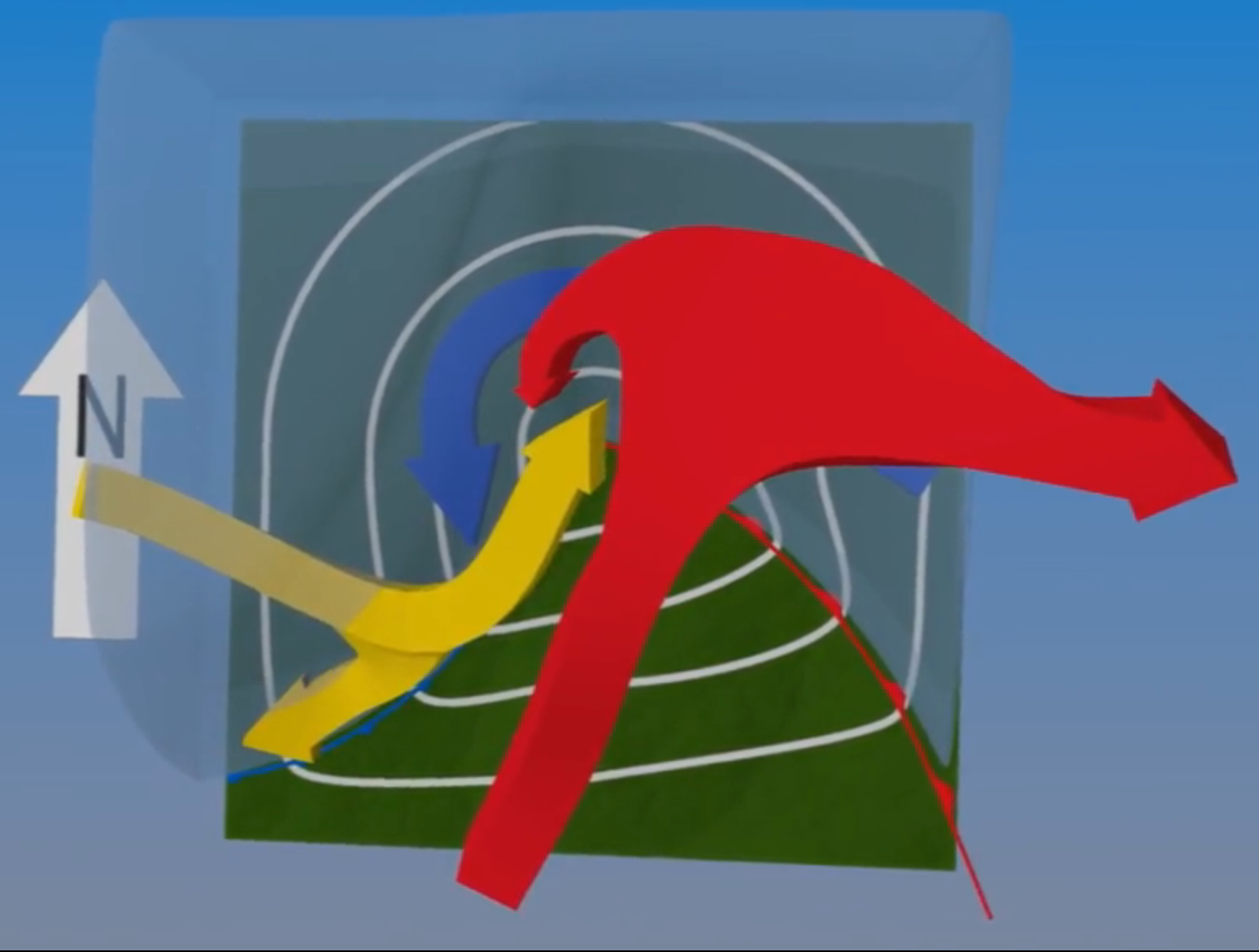
Describe the three airstreams which lead to the formation of cyclones
First airstream a warm conveyor belt from south
→ hits front and rises into jetstream
→ splits in two, towards east + west, forms comma shape
Second cold conveyor belt from east/north
→ stays near surface under warm belt
Third dry airstream, is dry
→ descends from upper atmosphere
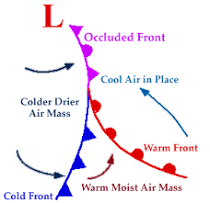
Describe the formation of a cyclone
warm air is lifted as cyclone evolves (less warm area)
→ cyclone intensified circulation
→ cold air expands,
→ dry air becomes more wrapped up
Surface fronts wrap up to form occluded front
→ cold + warm front merged
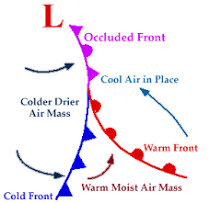
Why do jet streams exist?
due to temperature differences between polar region and mid-latitudes
blows from west to east
acts as a steering mechanism for storms + weather conditions
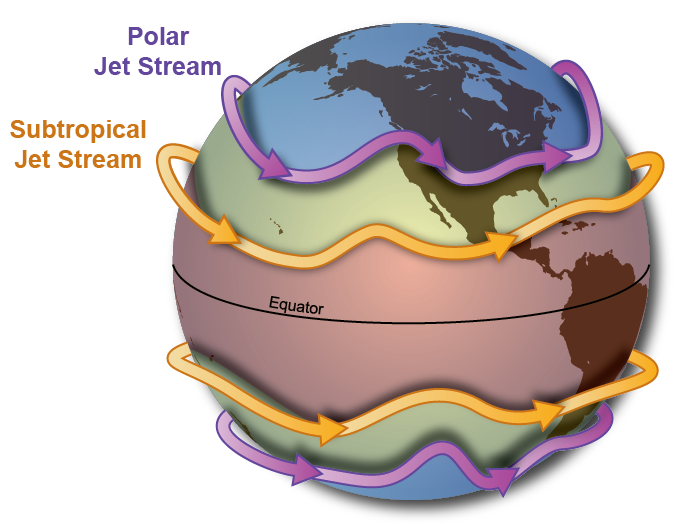
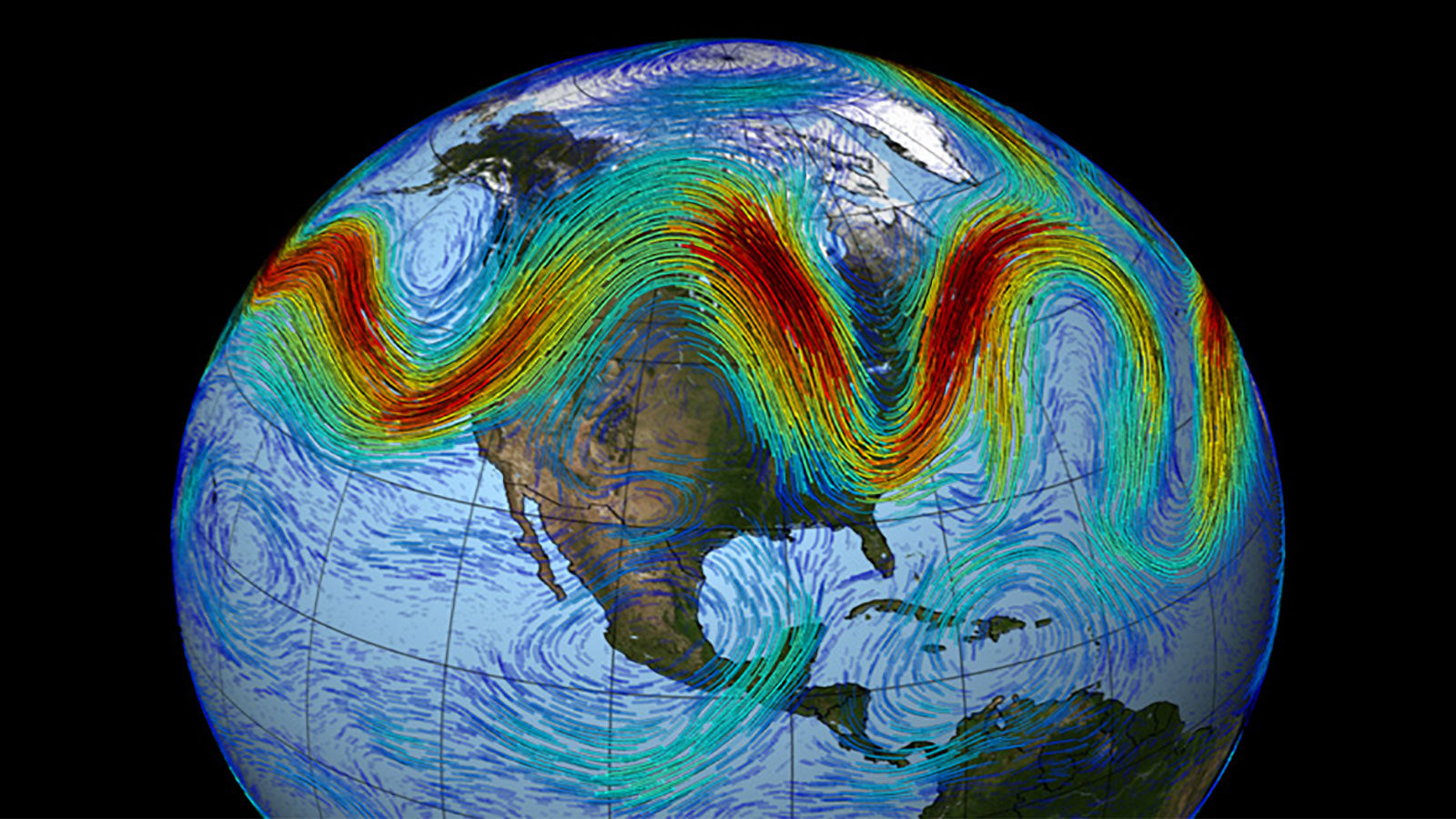
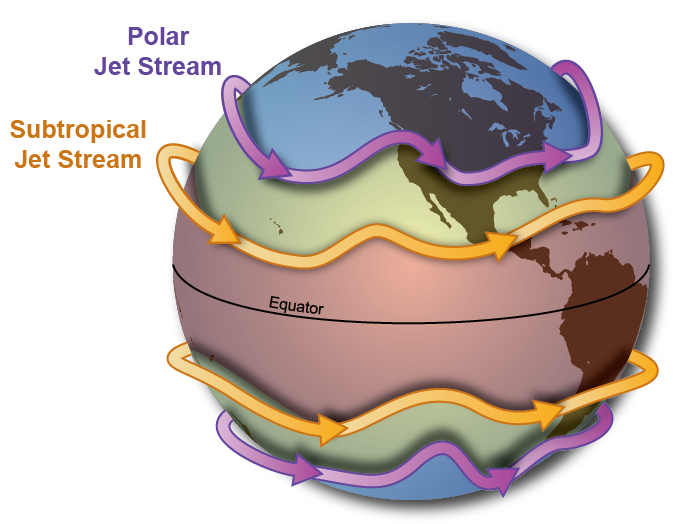
How do jetstreams control the direction warm and cold air moves?
Undulations (rising and falling motion) in jet stream called Rossby waves
→ when jetstream moves toward equator these waves bring cold air
→ towards poles, bring hot air
these waves show boundary between warm + cold
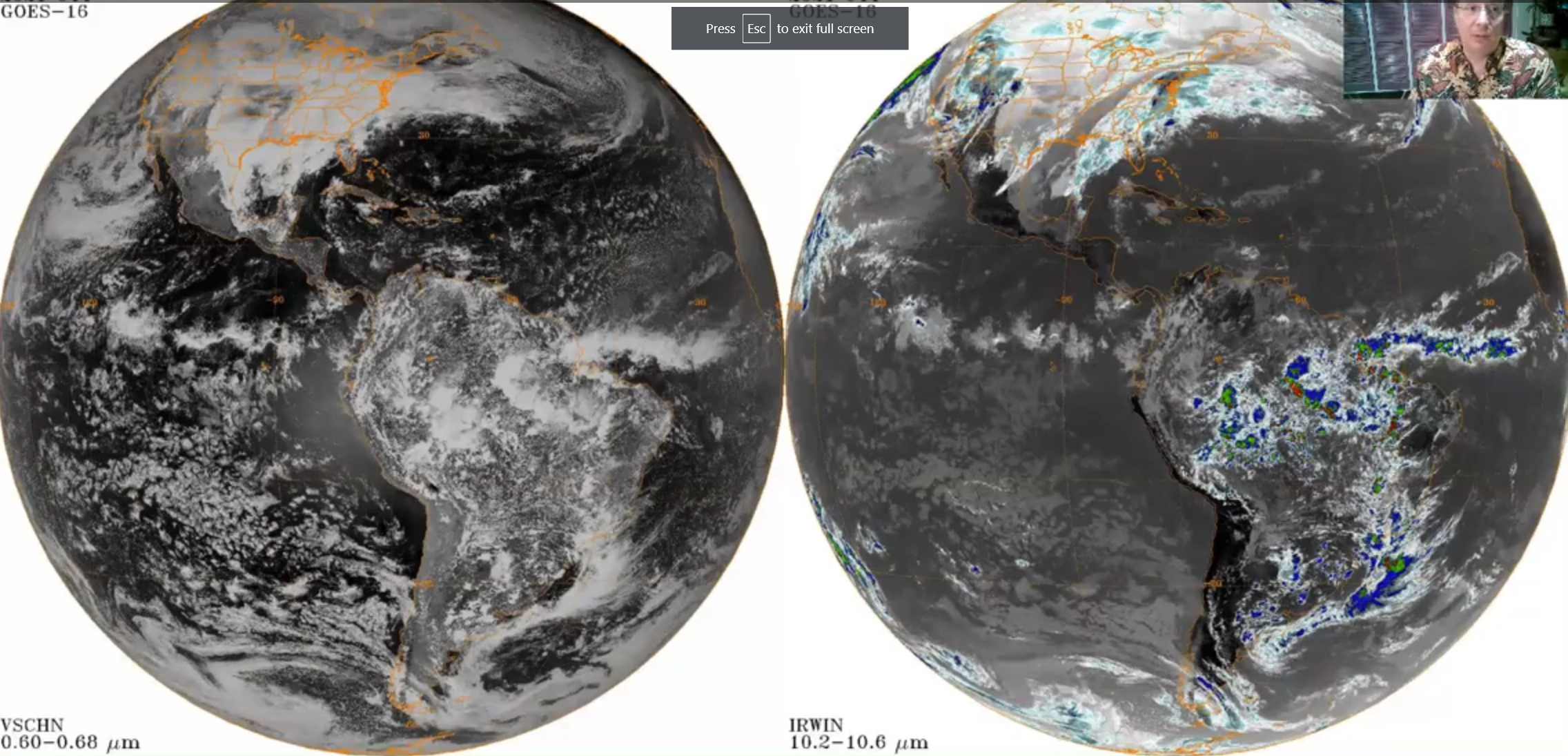
Describe the differences between satellite vs radio imagery
Satellite (space)
detects reflected visible light/ emitted infrared by earth
Mainly clouds
Radar (ground)
scattered microwaves
Mainly precipitation sized particles
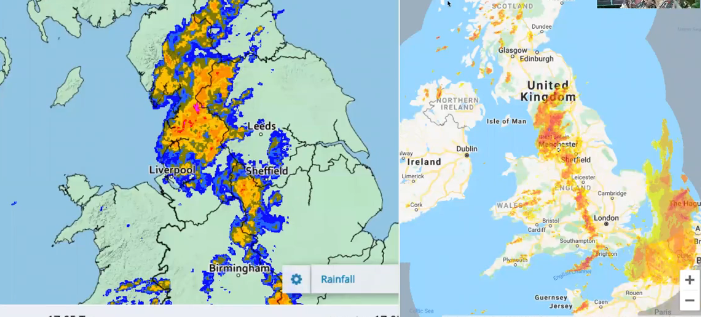
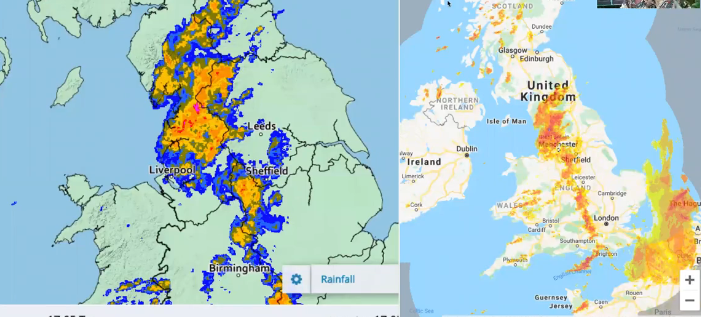
Reading radar imagery
Orange means more intense precipitation in intense storms
Blue opposite
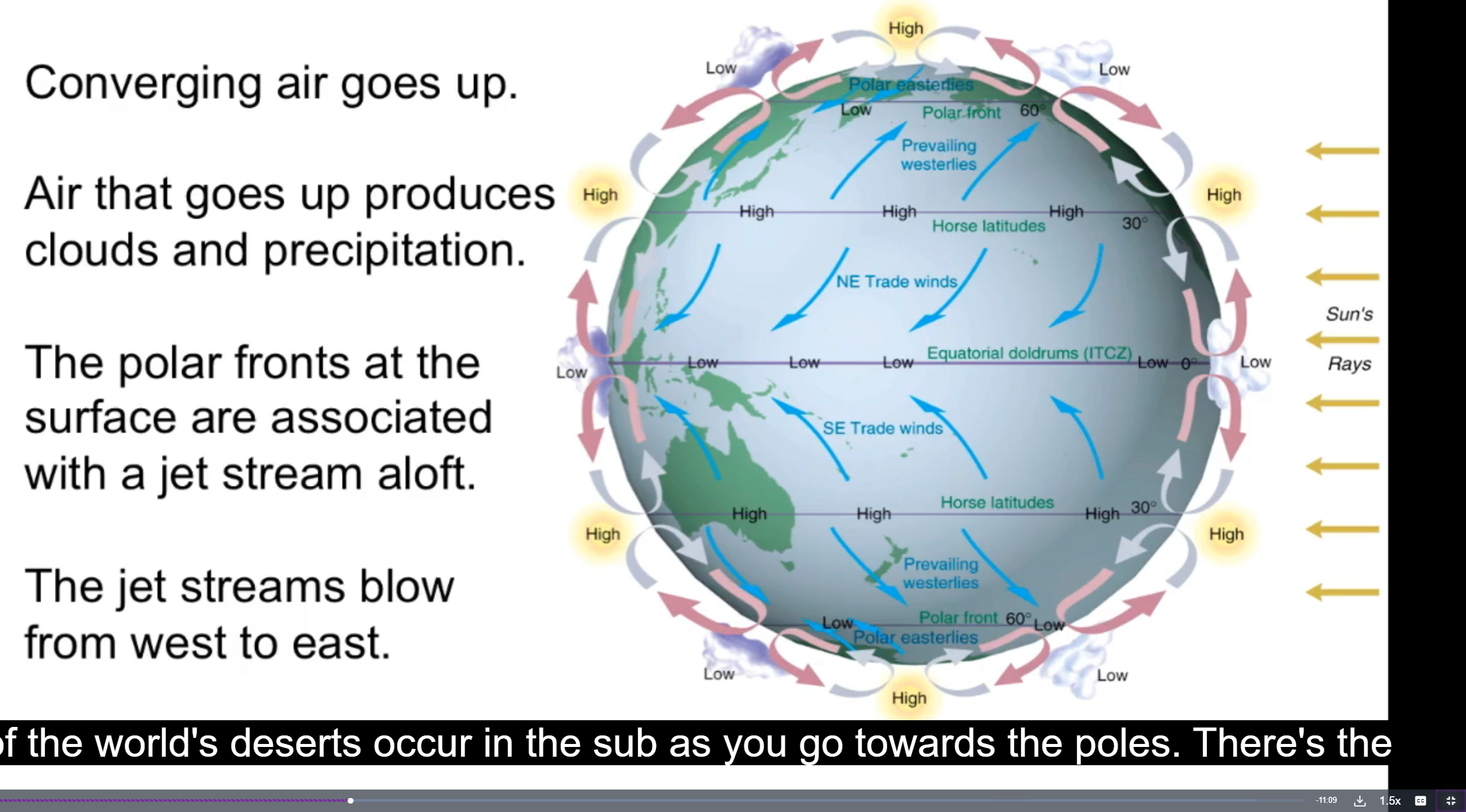
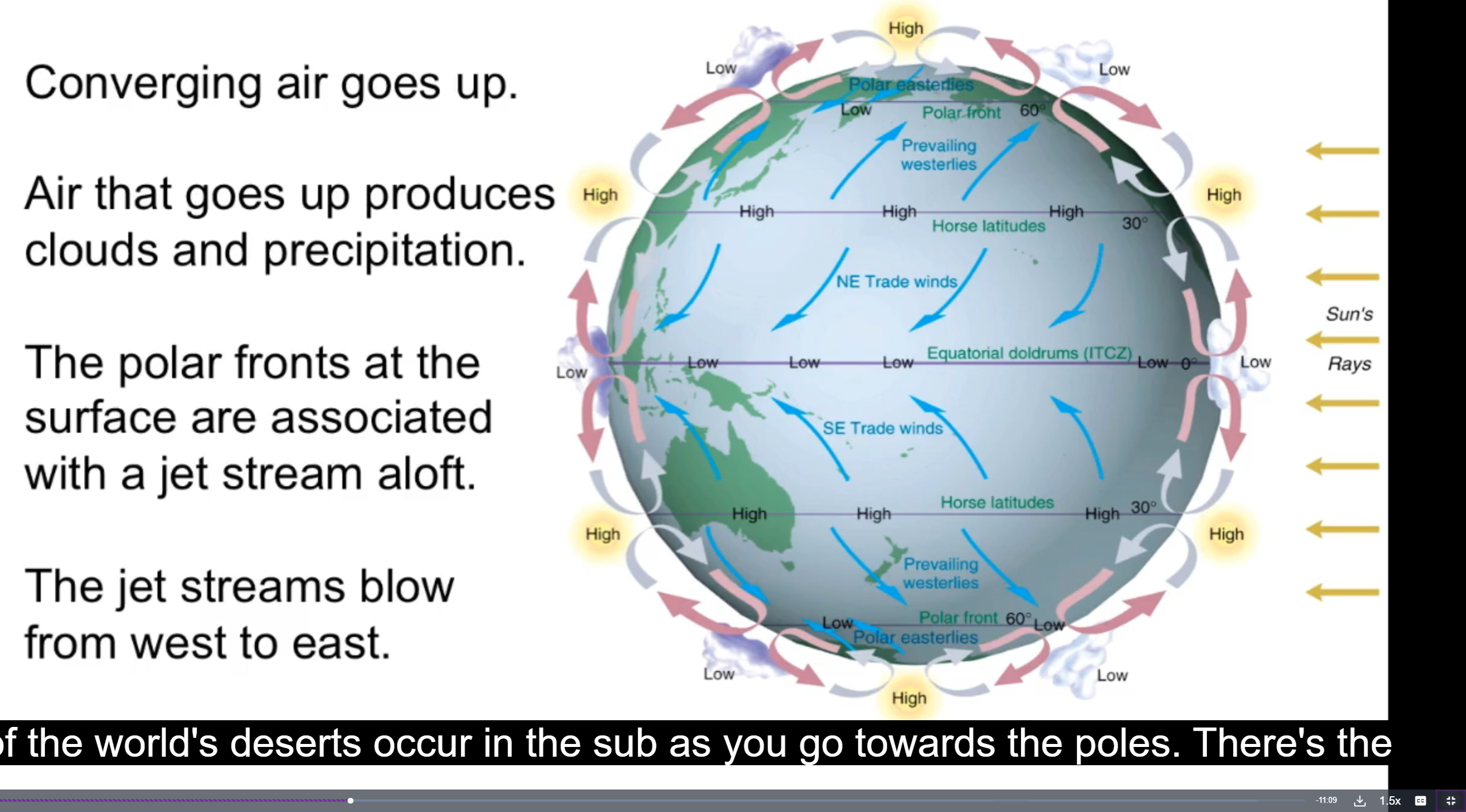
Explain atmosphere circulation and how it affects weather
Imbalance in heat between tropics + pole lead to circulation around equator, more rain in equator
→ this rising air descends at subtropics, less clouds + rain
Cold air near poles which goes towards equator
→ meets w westerlies (from hemispheres) to form front which forms jet streams and weather variability

Describe cumulus clouds + environment which it forms
Fluffy, individual
Flat base w dome shaped top
Formed in unstable environments by convection, warm air rises and cools
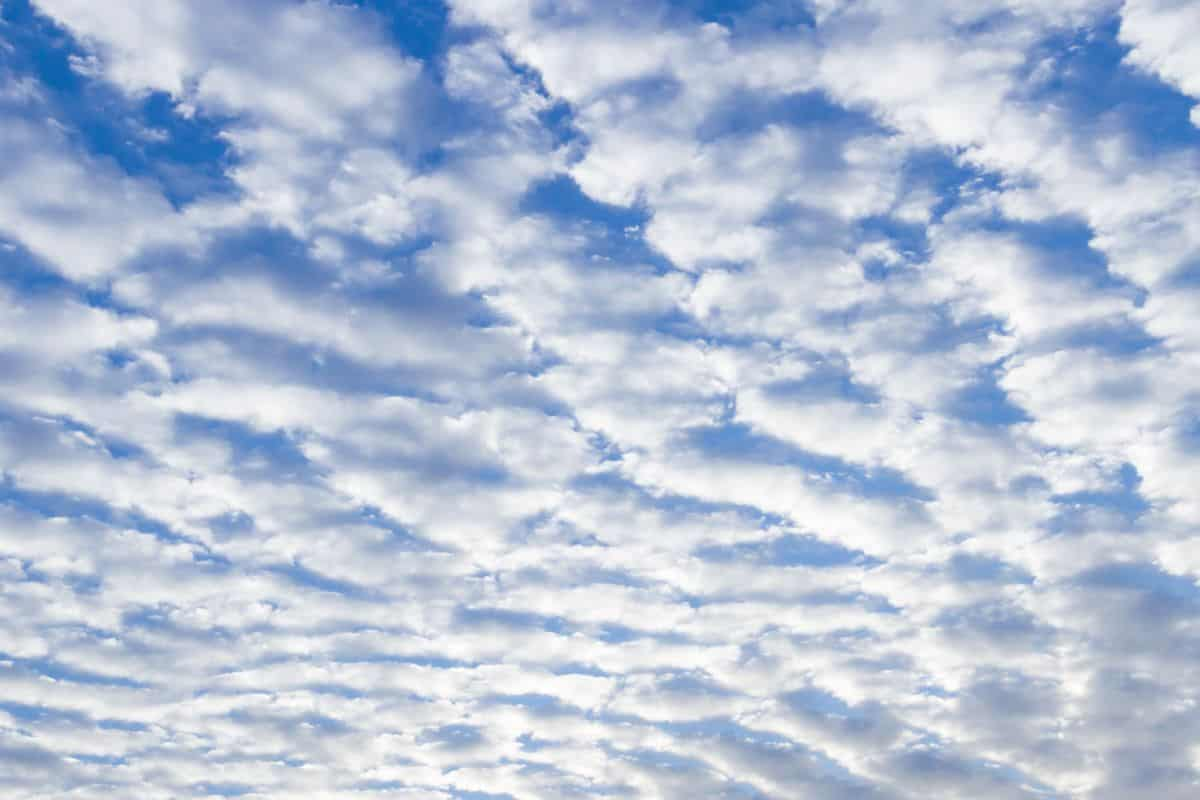


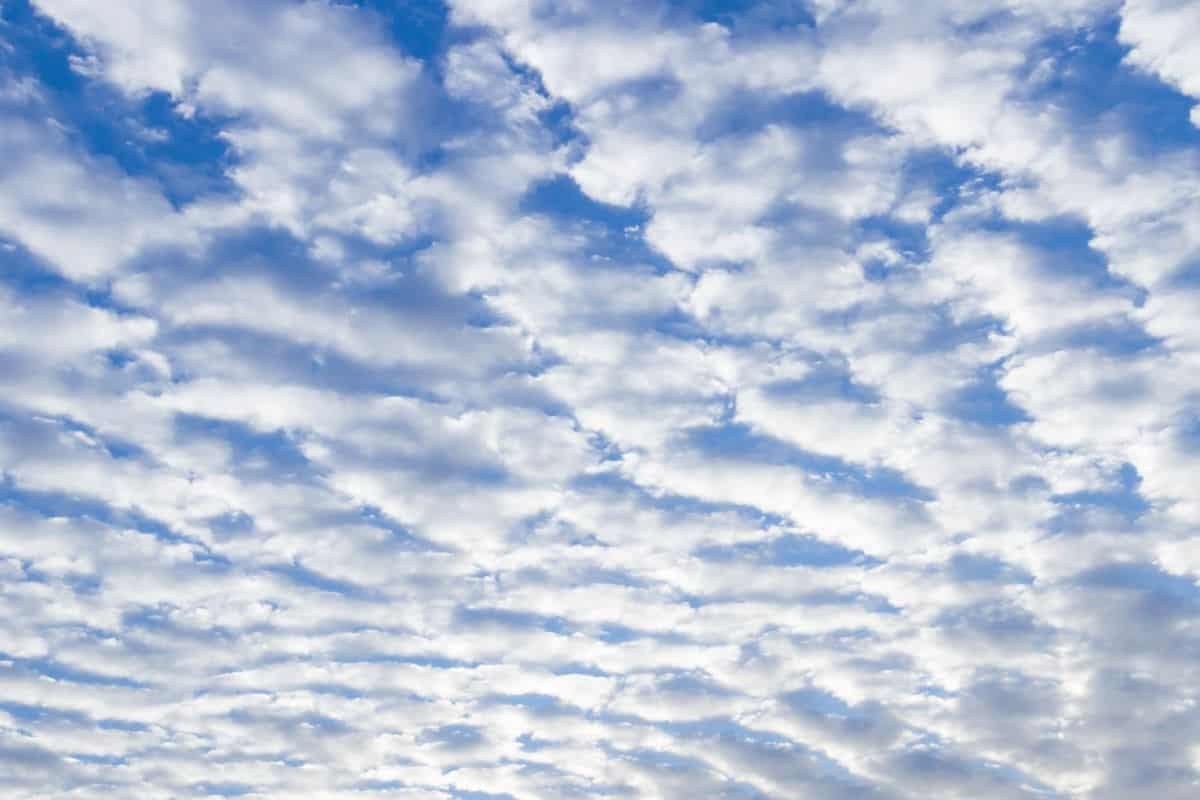
Describe stratus clouds + environment which it forms
low level, uniform, continuous layer
occur in stable conditions w little vert air movement
leads to overcast skies + light drizzle
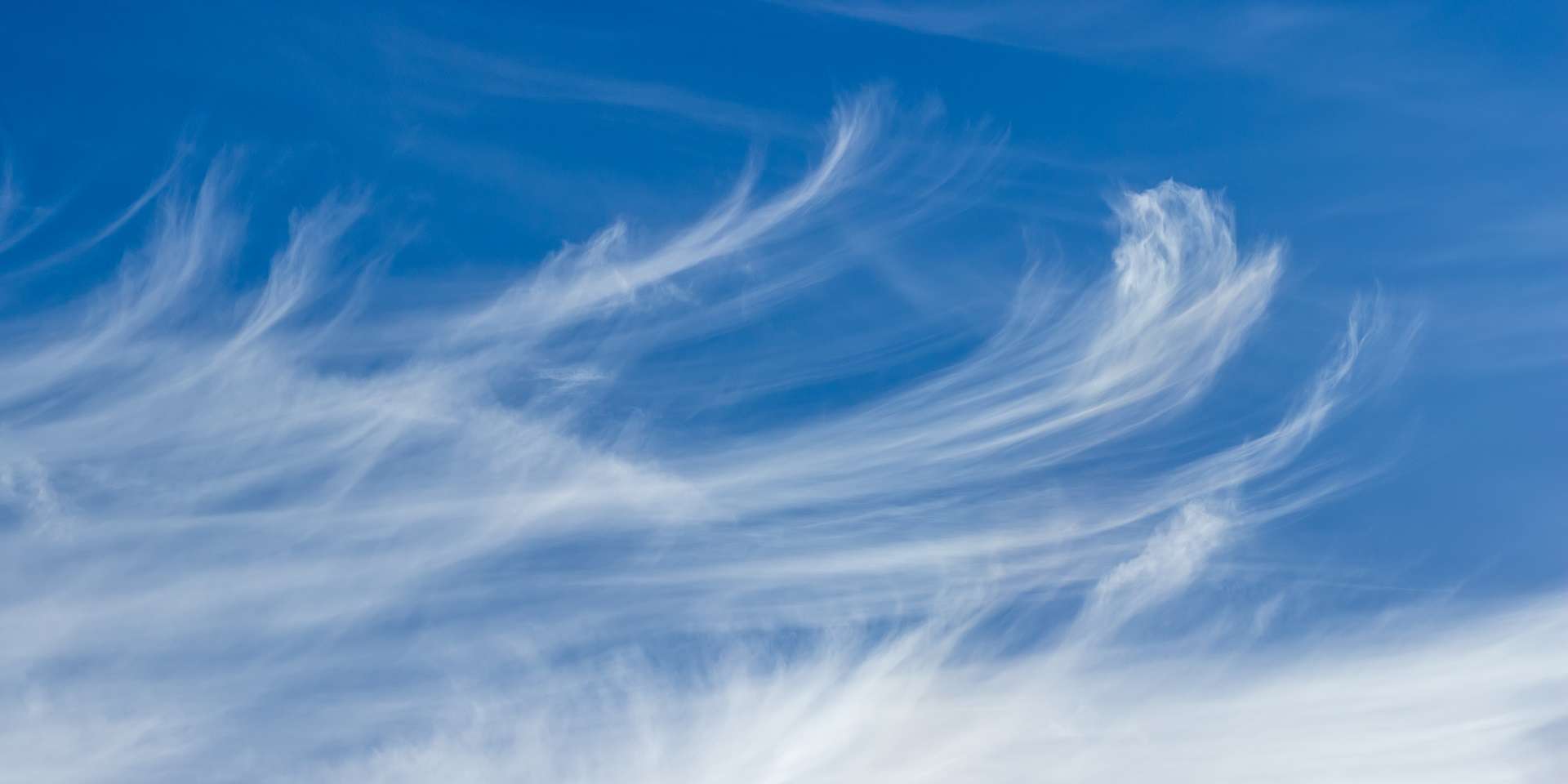


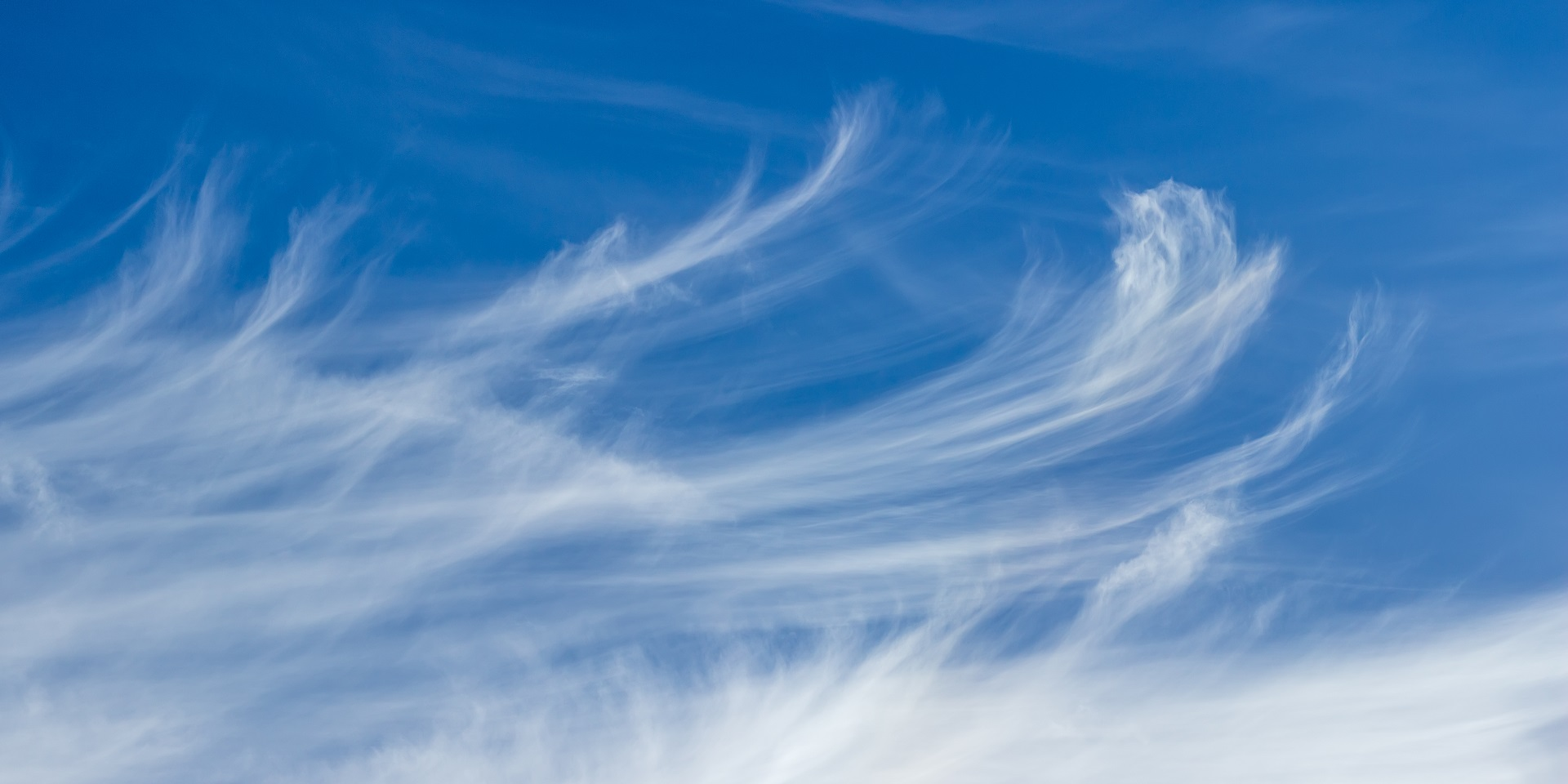
Describe cirrus clouds + environment which it forms
High level, made of ice crystals
Thin, feathery
Forms in stable + cold environments (front of warm fronts or high up)
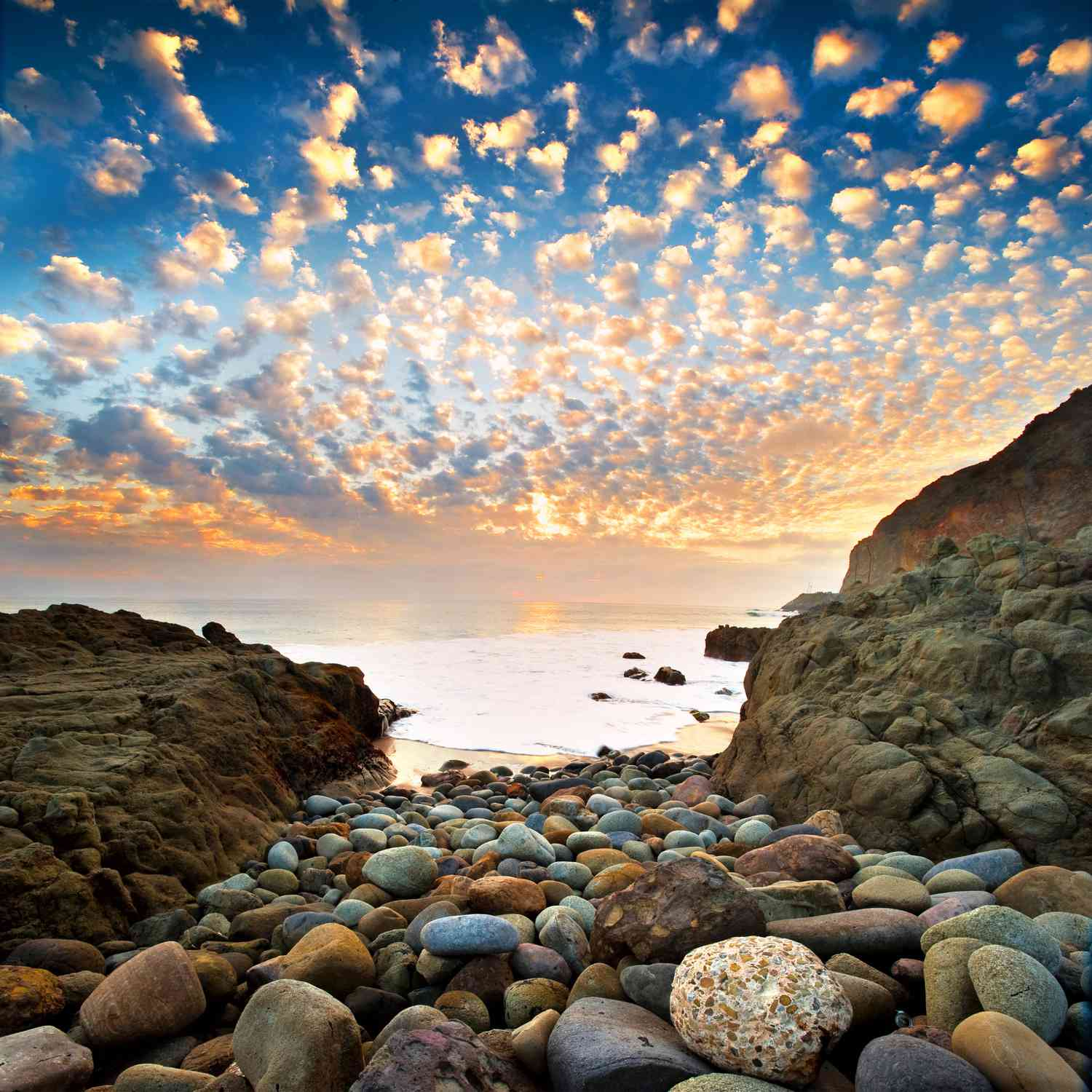


Describe altocumulus clouds + environment which it forms
mid level, wavy or globular shape
white or gray
indicates stable weather conditions, before weather change
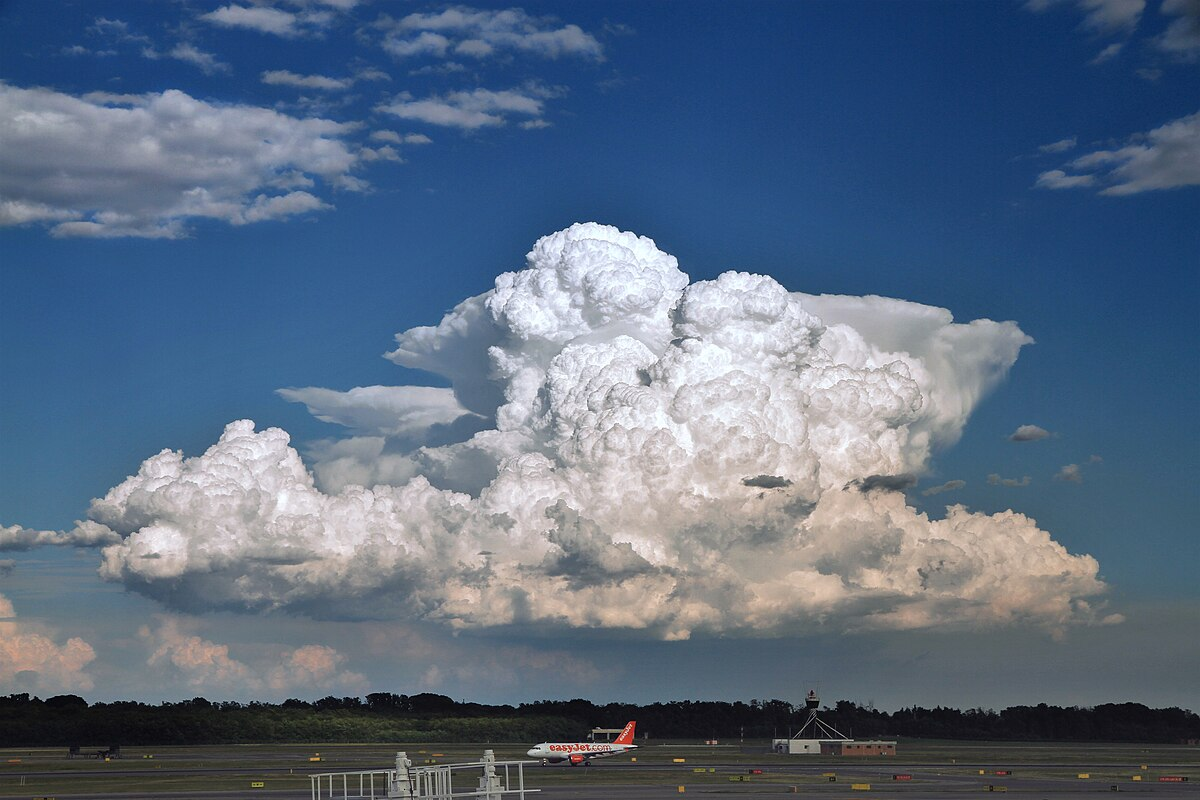


Describe cumulonimbus clouds + environment which it forms
Mushroom shaped w dark dense base
forms in unstable conditions w moisture + strong vert air
extreme weather

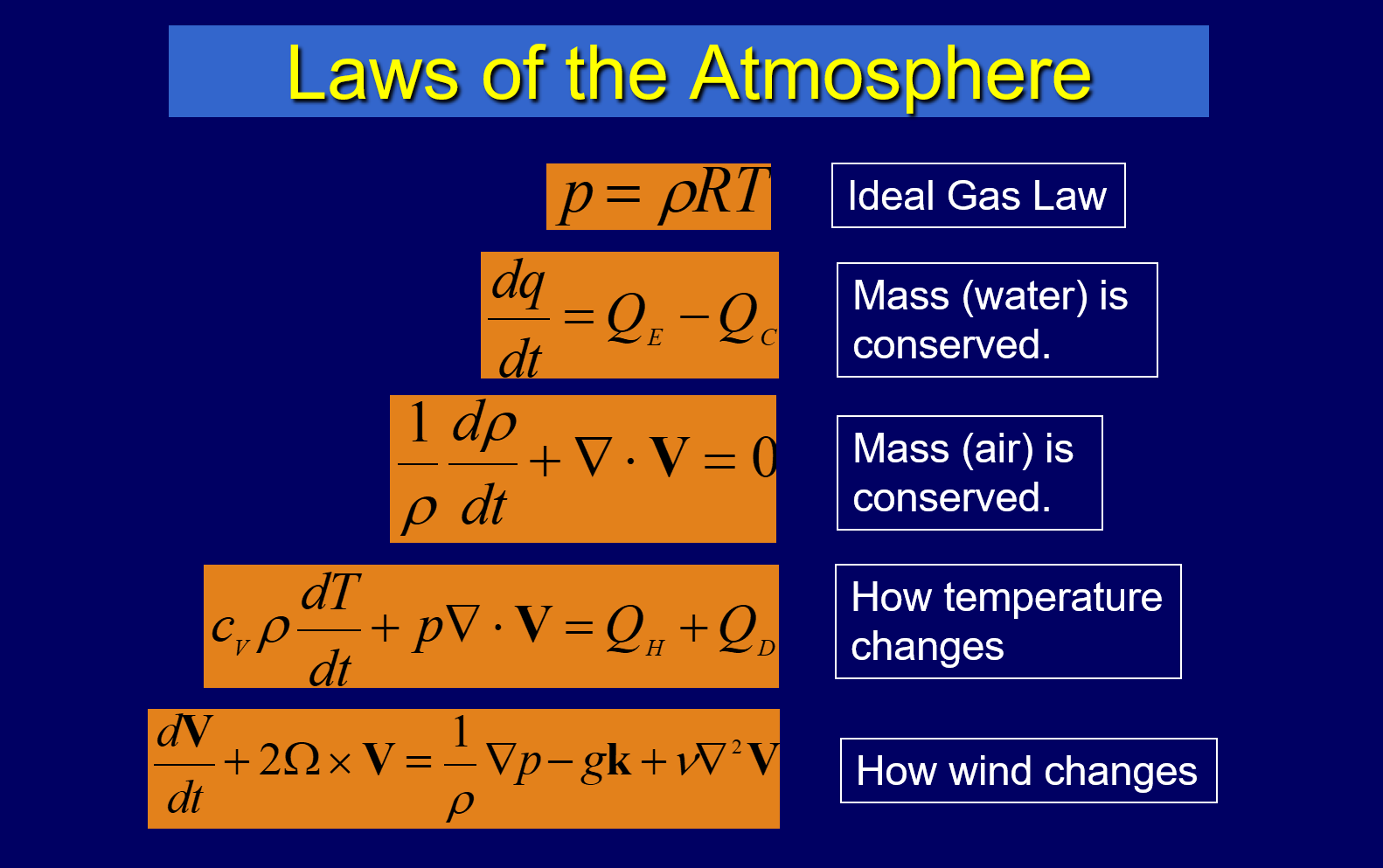
Explain the scientific basis for weather forecasting and how weather forecasts are made.
Using the laws of atmosphere
→ ideal gas law, conservation of mass, wind/temp changes
→ computer models it
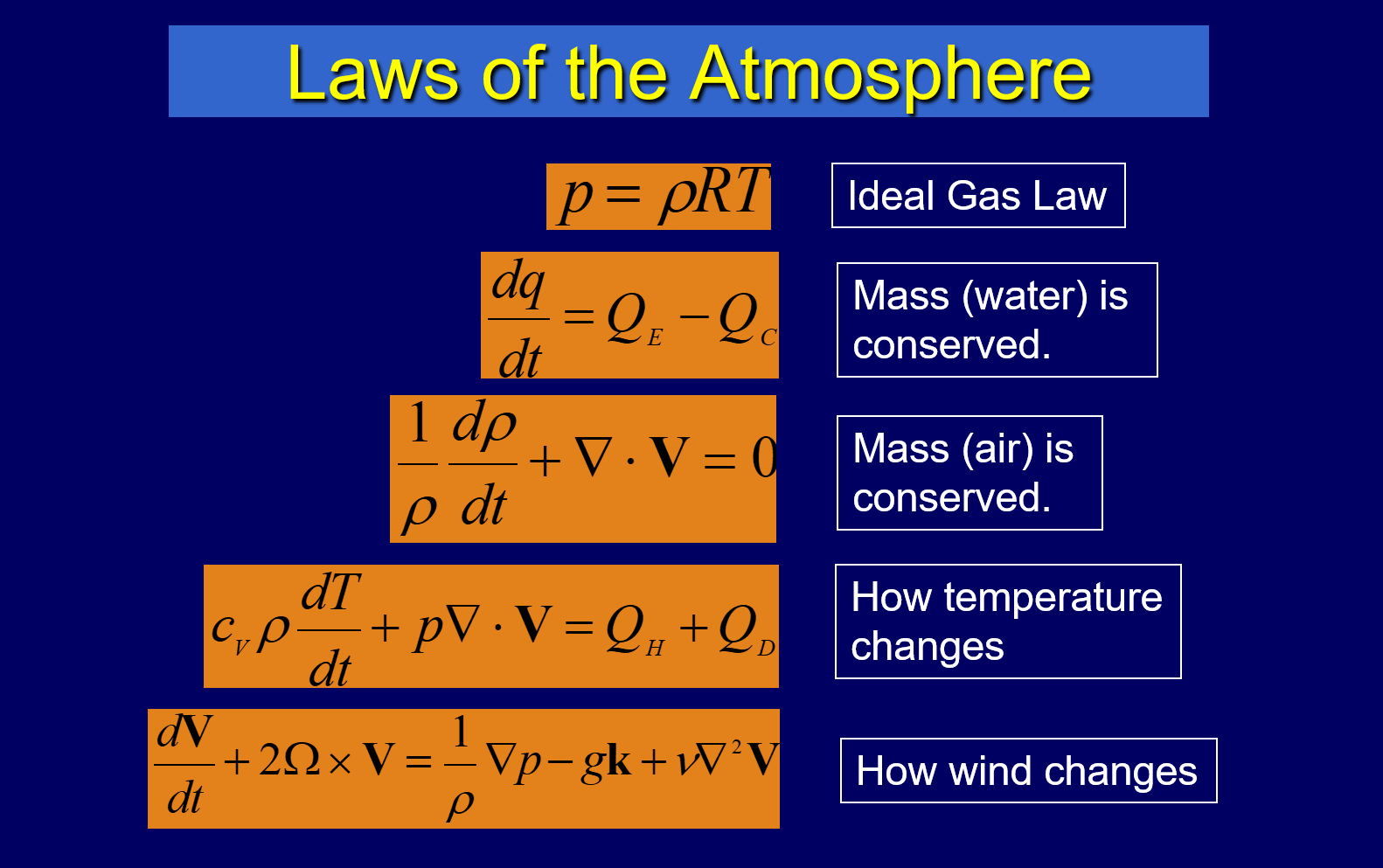
According to