CH.18 The Cardiovascular System
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
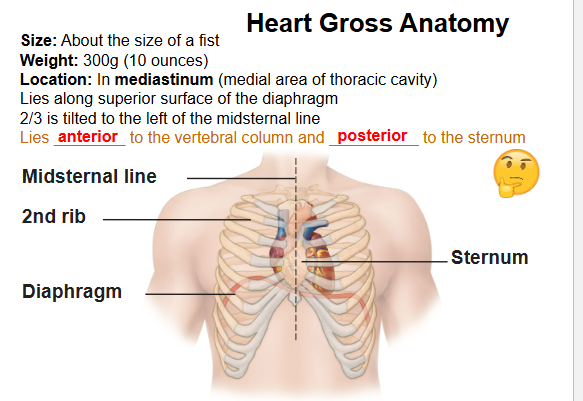
Where is the heart located?
Mediastinum, above the diaphragm tilted 2/3 to the left
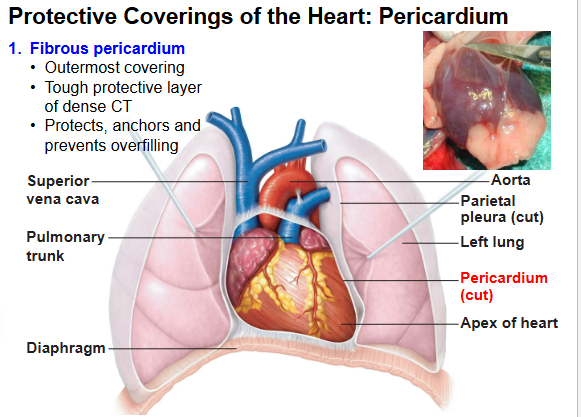
What protects the anchors of the heart?
Fibrous pericardium
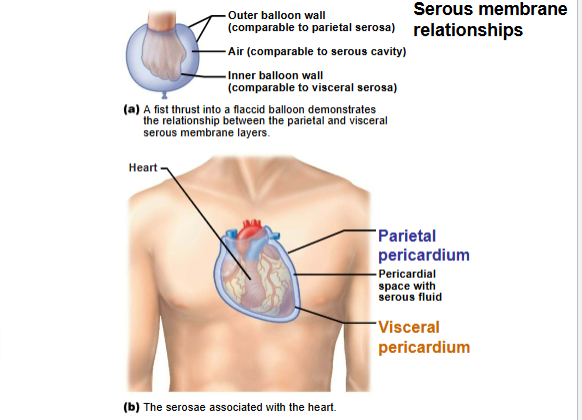
What are the two layers of serous pericardium?
Parietal (lines fibrous pericardium) & Visceral (epicardium, covers heart).
What fluid reduces friction between heart layers?
Serous (pericardial) fluid.
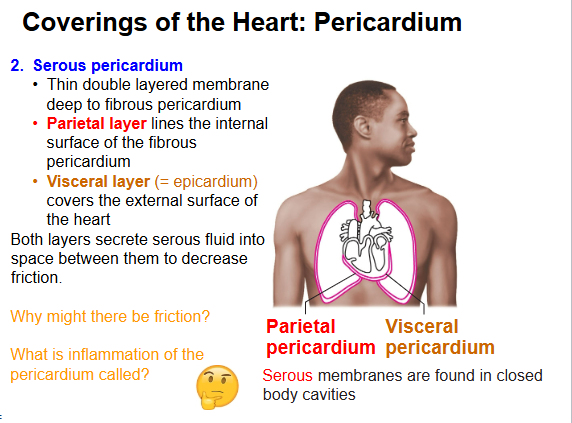
Inflammation of the pericardium is called?
Pericarditis.
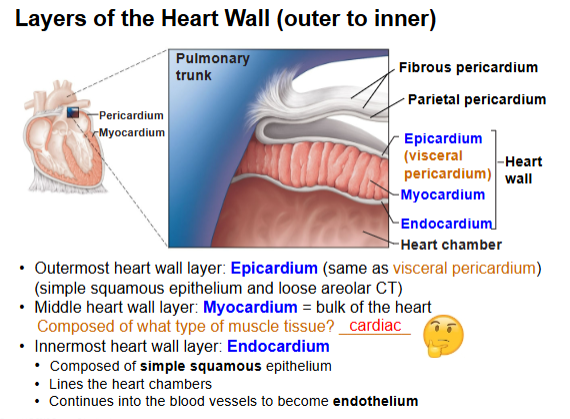
What are the 3 heart wall layers (outer → inner)?
Epicardium → Myocardium (cardiac muscle) → Endocardium.
Which layer is the thickest and responsible for pumping?
Myocardium.
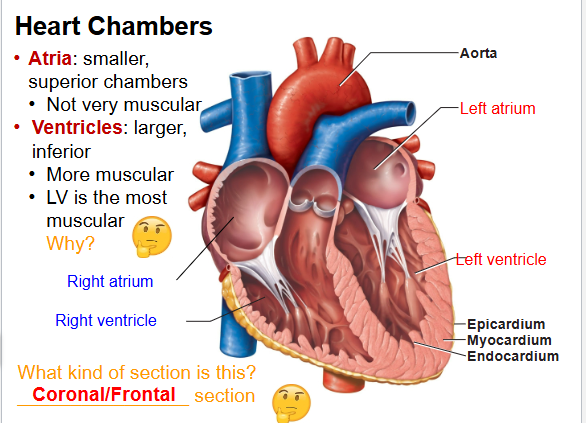
Name the 4 heart chambers.
Right atrium, Right ventricle, Left atrium, Left ventricle.
Which chamber is most muscular? Why?
Left ventricle, pumps blood to whole body.
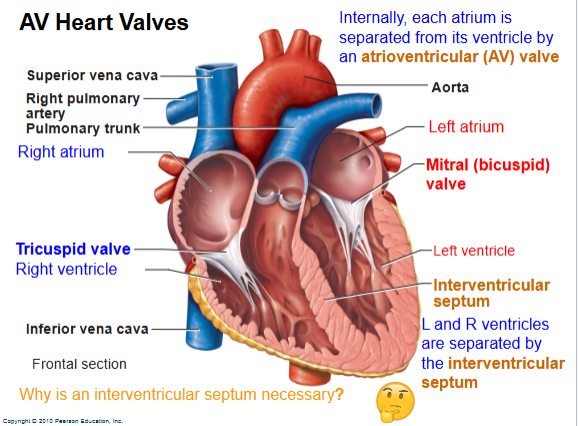
What are the AV valves?
Tricuspid (RA→RV), Bicuspid/Mitral (LA→LV).
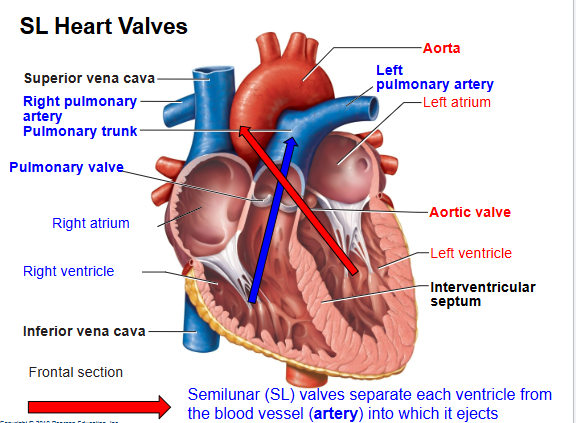
What are the SL valves?
Pulmonary (RV→lungs), Aortic (LV→body).
What prevents AV valves from flipping backward?
Chordae tendineae + papillary muscles.
Right side of heart pumps blood where?
To lungs (pulmonary circuit).
Left side of heart pumps blood where?
To body (systemic circuit).
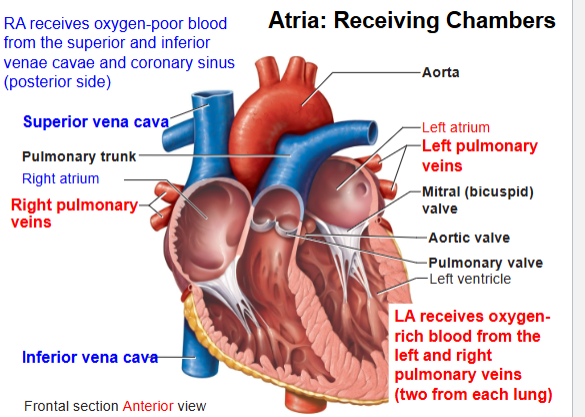
What kind of blood do pulmonary arteries carry?
Oxygen-poor blood (to lungs).
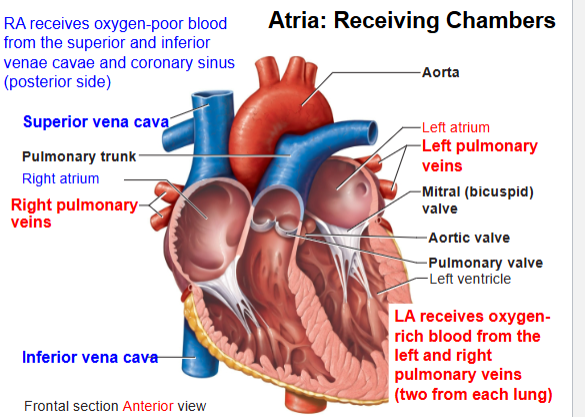
What kind of blood do pulmonary veins carry?
Oxygen-rich blood (to heart).
What makes the “Lub” sound?
AV valves closing.
What makes the “Dup” sound?
SL valves closing.
Systole = ?
Contraction.
Diastole = ?
Relaxation.
What is the heart’s pacemaker?
SA node (sinoatrial node).
What delays impulse to allow atria to contract first?
AV node.
Order of conduction pathway?
SA node → AV node → Bundle of His → Bundle branches → Purkinje fibers.
What does P wave represent?
Atrial depolarization.
What does QRS complex represent?
Ventricular depolarization (atrial repolarization hidden).
What does T wave represent?
Ventricular repolarization.