Infections of the Urinary and Reproductive Systems
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What are the components of the urinary system?
Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
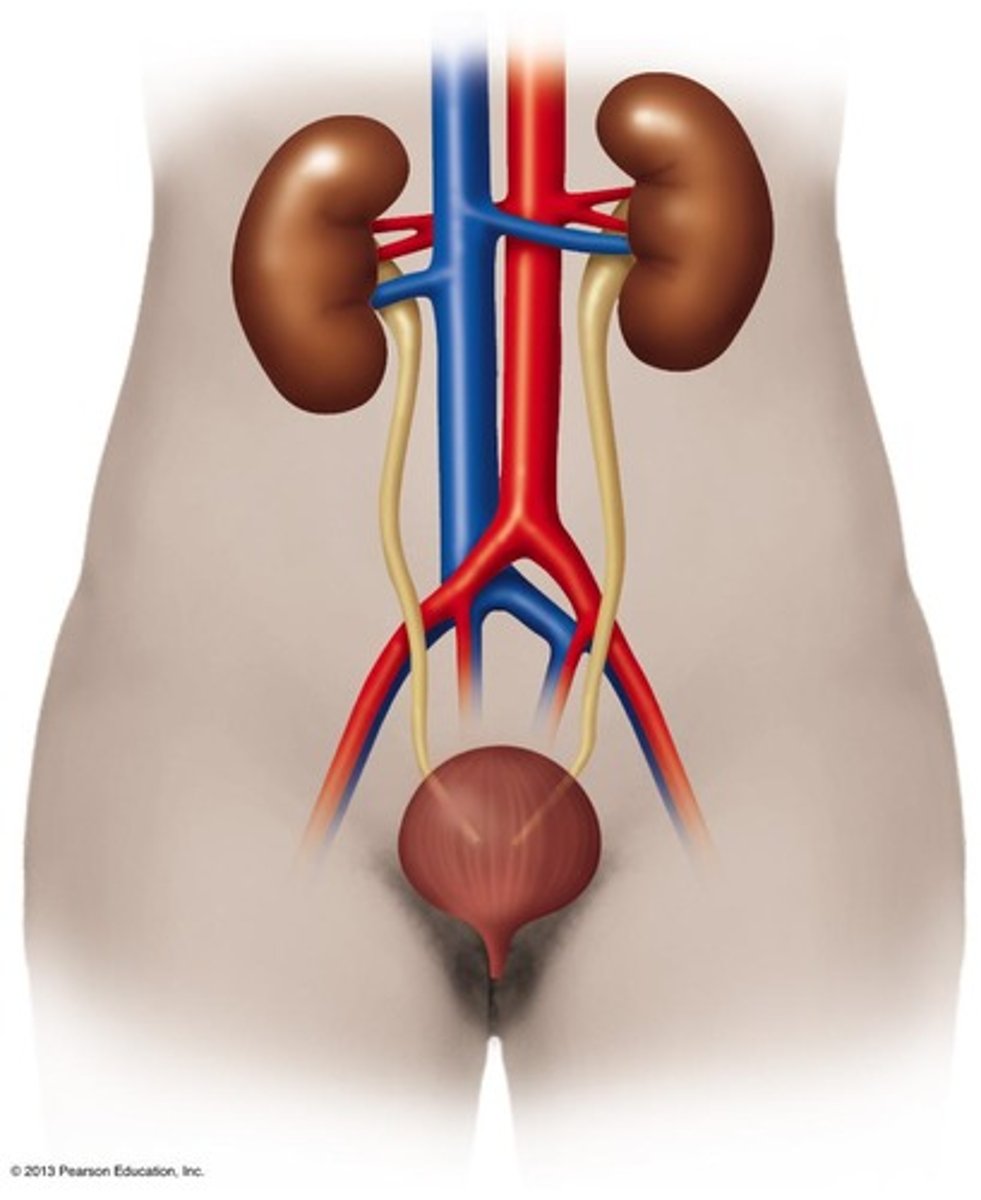
What mechanisms help prevent urinary tract infections?
Valves that prevent backflow to kidneys, acidity of urine, and mechanical flushing.
What is cystitis?
An inflammation of the urinary bladder. (more common in women)
What is urethritis?
An inflammation of the urethra.
What is pyelonephritis?
An inflammation of one or both kidneys.
What is the most common causative agent of urinary tract infections?
Escherichia coli.
Symptoms of pyelonephritis
fever, back or flank pain (generally results in bacteremia)
Treatment of pyelonephritis
cephalosporin
causative agents of cystitis
E. coli and S. saprophyticus
What are the symptoms of cystitis?
Dysuria (painful urination) and pyuria (pus in urine).
How is pyelonephritis diagnosed?
>100,000 CFUs/ml of a single species and a positive leukocyte esterase test.
What is leptospirosis and its causative agent?
caused by Leptospira interrogans, a spirochete; obligate aerobe
What are the symptoms of leptospirosis?
Headaches, muscular aches, fever, kidney failure (Weil's disease), and pulmonary hemorrhagic syndrome.
what are the reservoirs for leptospirosis
dogs, cats, and rats
how is leptospirosis transmitted
skin/mucosal contact from urine contaminated water from domestic or wild animals
What is the treatment for leptospirosis?
Doxycycline.
how is leptospirosis diagnosed
serological test
what is predominant in the vagina and what does it produce
lactobacilli produce H2O2 and lactic acid
What are sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
Infections that often have no signs or symptoms and include over 30 types. (between 15-24 year olds)
How can STIs be prevented?
condoms
What are the pros of at-home testing for STIs?
More cases diagnosed, better access for patients, and quicker treatment.
What are the cons of at-home testing for STIs?
Cost, privacy concerns, and concerns about accuracy.
What is the causative agent of gonorrhea?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a gram-negative diplococcus.
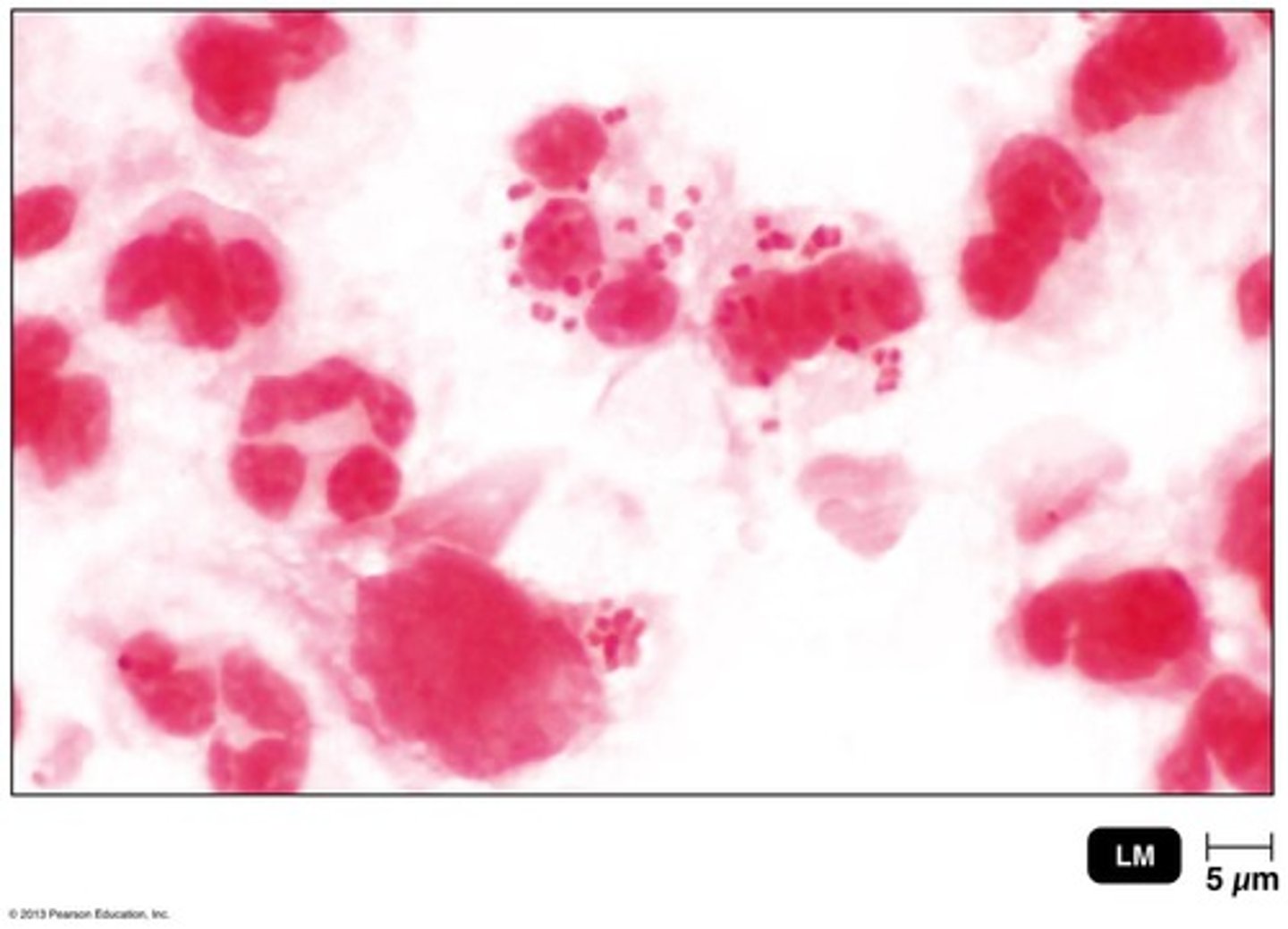
What are the symptoms of gonorrhea in men?
Painful urination and discharge of pus; may also cause epididymitis.
What are the symptoms of gonorrhea in women?
Fewer symptoms; may lead to pelvic inflammatory disease.
if gonorrhea is left untreated it may
disseminate and become systemic endocarditis, meningitis, arthritis
ophthalmia neonatorum
infant blindness due to a gonorrheal infection of the eyes
What is the diagnosis method for gonorrhea?
Gram stain, ELISA, or PCR.
What is the treatment for gonorrhea?
Cephalosporins, such as ceftriaxone and azithromycin.
What is nongonococcal urethritis (NGU)?
An infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, or Ureaplasma urealyticum.
symptoms of Nongonoccal urethritis
painful urination and watery discharge; (women =possible complications, PID)
diagnosis of Nongonoccal urethritis
culture, PCR
treatment for Nongonoccal urethritis
doxycycline and azithromycin
causative agent of Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Polymicrobic; usually N. gonorrhoeae and C. trachnomatis
What are the symptoms of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)?
Chronic abdominal pain and potential infertility due to scarring.
salpingitis
infection of uterine tubes; scarring an cause infertility or ectopic pregnancy
treatment for Pelvic inflammatory disease
doxycycline and cefoxitin
What is the causative agent of syphilis?
Treponema pallidum, a gram-negative spirochete.
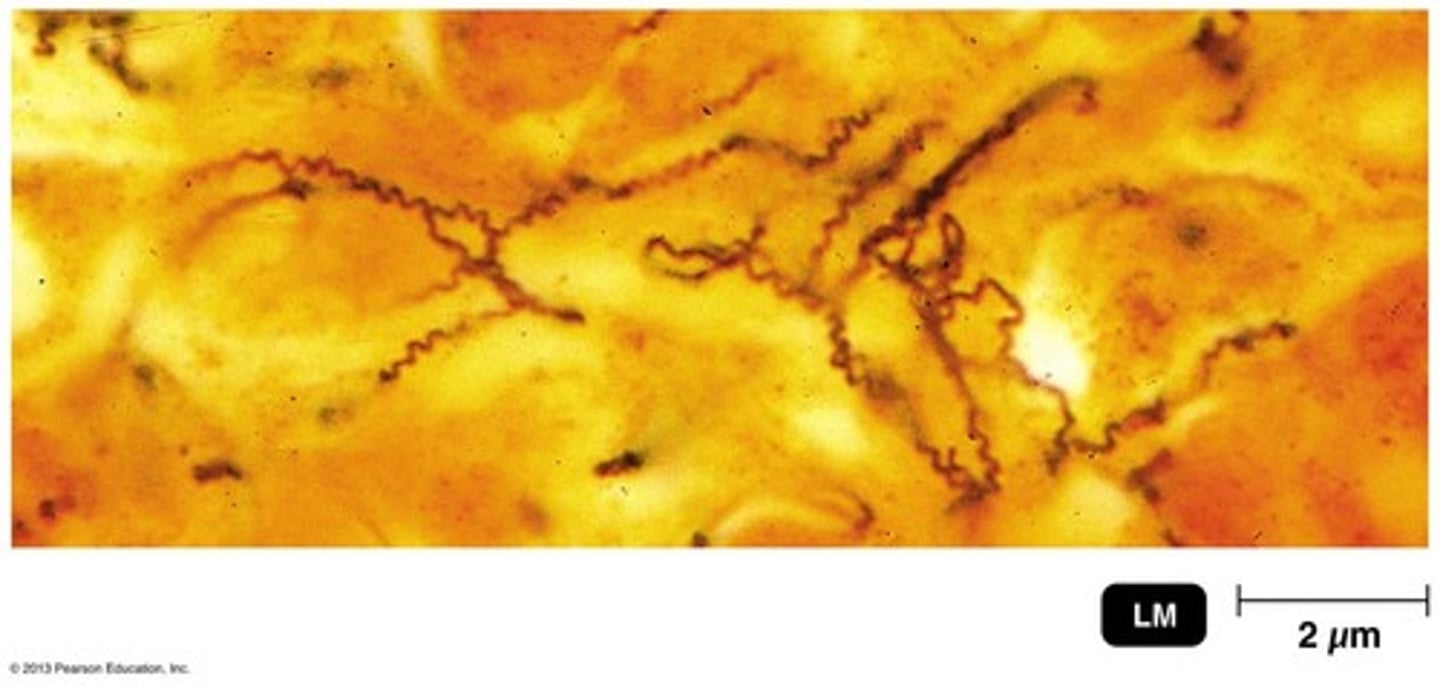
transmission of syphilis
invades the mucosa or through skin breaks and enters the bloodstream; induces inflammatory response
yaws
skin disease that is not sexually transmitted
What occurs during the primary stage of syphilis?
A painless chancre appears at the site of infection about 3 weeks after exposure
What are the symptoms of secondary syphilis?
Skin and mucosal rashes, especially on the palms and soles; due to inflammatory responses
latent period of syphilis
has no symptoms
What is the tertiary stage of syphilis?
Symptoms appear years after latency, including gummatous syphilis, cardiovascular syphilis, and neurosyphilis
Congenital Spyhilis
neurological damage to the fetus
What is the treatment for syphilis?
Benzathine penicillin.
What is lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)?
An infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, characterized by swelling in lymph nodes.
symptoms of lymphogranuloma venereum
initial lesion on genitals heals, bacteria spread through lymph, swelling in lymph nodes in groin
diagnosis of lymphogranuloma venereum
microscopic identification and culture
treatment for lymphogranuloma venereum
doxycycline
What is genital herpes and its causative agent?
caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2).
What are the symptoms of genital herpes?
Painful vesicles on the genitals and painful urination. (heals within 2 weeks)
What is the treatment for genital herpes?
no cure; uses Acyclovir, famciclovir, and valacyclovir for management/suppression
What causes genital warts?
Human papillomaviruses (HPV), particularly serotypes 6 and 11.
diagnosis of genital warts
via culture or PCR
what serotypes of genital warts cause visible warts
serotypes 6 and 11
what serotypes of genital warts cause cervical cancer
serotypes 16 and 18 (kills 4,000 women annually in US)
treatment for genital warts
removal of warts; podofilox and imiquimod
prevention of genital warts
quadrivalent or nine-valent HPV vaccines
What is candidiasis?
An overgrowth of Candida albicans, causing yeasty discharge and vaginitis.
where does candidiasis grow
on the mucosa of the mouth, the intestinal tract, and the genitourinary tract
oral candidiasis
thrush; white patches or plaques on the tongue & other oral mucous membranes
vulvovaginal candidiasis
vaginitis. yeasty, thick, yellow discharge
treatment for candidiasis
clotrimazole or fluconazole
What is Trichomoniasis and its causative agent?
caused by Trichomonas vaginalis, leading to irritation and foul discharge.
when does Trichomoniasis grow
when normal acidity of the vagina is disturbed
symptoms of Trichomoniasis
irritation and a profuse, frothy, greenish yellow, foul odor discharge
diagnosis and treatment for Trichomoniasis