Chapter 13- Blood vessels
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
tunica media
Which layer of the blood vessel wall is labeled "A"?
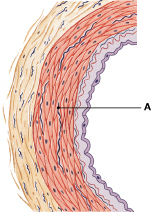
permits exchange with interstitial fluid
What is the most specific physiological function of the blood vessel labeled "C"?
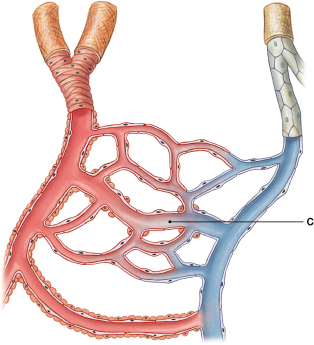
arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, veins
If you were to follow the flow of blood after it leaves the heart, what is the correct order of blood vessels it would travel through?
Arteries always carry oxygenated blood.
Which of the following statement is NOT correct regarding blood vessels?
tunica media.
The muscular layer of blood vessels is the
muscular
Arteries with a thick tunica media are ________
arteries.
capillaries
The vessels that permit exchange of materials between the blood and the surrounding interstitial fluid are called
atherosclerosis
Which condition is described as the formation of lipid deposits in the tunica media associated with damage to the endothelial lining?
elastic arteries
Which blood vessels are able to absorb the pressure changes that occur during the cardiac cycle?
arteriole/controls blood pressure
Identify the correct match between the blood vessel and its corresponding characteristic.
It slows blood flow, allowing sufficient time for capillary exchange to occur.
What is the advantage of the small diameter of capillaries?
media
The layer of the blood vessel that contains smooth muscle is the tunica __________.
tunica intima
Arteriosclerosis is a thickening and toughening of arterial walls. Many people know it as "hardening of the arteries." Complications related to it account for about half of all deaths in the United States. The effects of arteriosclerosis are varied. For example, arteriosclerosis of coronary vessels is responsible for coronary artery disease (CAD). Arteriosclerosis of arteries supplying the brain can lead to strokes. Arteriosclerosis takes two major forms:
1. Focal calcification is the deposition of calcium salts following the gradual degeneration of smooth muscle in the tunica media. 2.
Atherosclerosis is the formation of lipid deposits in the tunica media and is the most common form of arteriosclerosis. What is name of the innermost layer of an
artery?
decrease in blood viscosity
Which of the following would increase the rate of blood flow?
axillary artery
Which of the following locations is NOT used to check the pulse?
Both numbers are high. There is an increase in blood pressure even when the ventricles are relaxed.
Your patient's blood pressure is 150/99. How would you explain to your patient what the numbers mean?
lymphatic vessels
Water and solutes that are not reabsorbed by capillaries ultimately return to the bloodstream by way of
blood osmotic
The force that tends to reabsorb or pull water back
into a capillary is called ________ pressure.
capillary hydrostatic pressure
The force that pushes fluid out of the capillaries is called ________.
Total peripheral resistance
________ refers to the factors that oppose blood flow in the entire cardiovascular
system.
The transition causes the resistance to drop further so that the flow rate of blood increases.
As blood travels through the venous system toward the heart, why do the veins become larger in diameter?
peripheral resistance
Which of the following has the greatest effect on blood flow to the tissues?
turbulence
The third and fourth heart sounds are generated by
Under normal circumstances, blood flow equals cardiac output.
Considering the factors affecting blood flow, choose the correct relationship.
a vessel 1 cm in diameter
In which of the following would vascular resistance be the least?
cardiovascular pressure decreases.
As blood travels from the aorta toward the capillaries,
blood pressure
Chemoreceptors are to oxygen as baroreceptors are to ______________.
Renin & ADH
Which of the following hormones are released in response to a decrease in blood volume?
venoconstriction
A decrease in peripheral vein diameter is called
relaxation of precapillary sphincters & increased vessel diameter
Which of the following changes will result in increased blood flow at an injury site during inflammation?
sensory neurons on the surface of the medulla oblongata
Which of the following monitors the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid?
hypotension and inadequate peripheral blood flow.
Shock is an acute circulatory crisis marked by
extensive vasodilation
As exercise begins, ________ occur(s) as the rate of oxygen consumption in skeletal muscles increases.
right pulmonary arteries.
Label C represents the
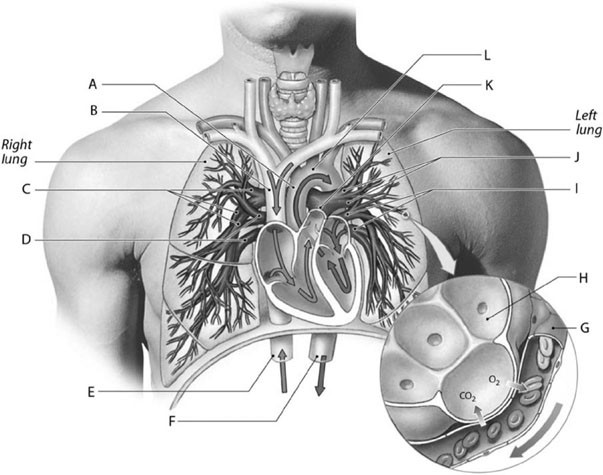
descending aorta.
Label F represents the
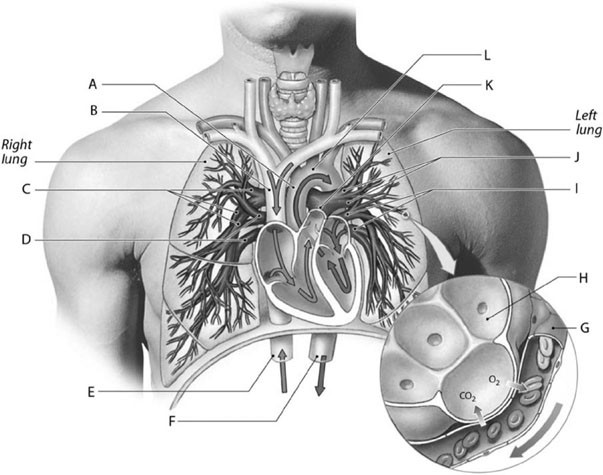
left pulmonary arteries.
Label J represents the
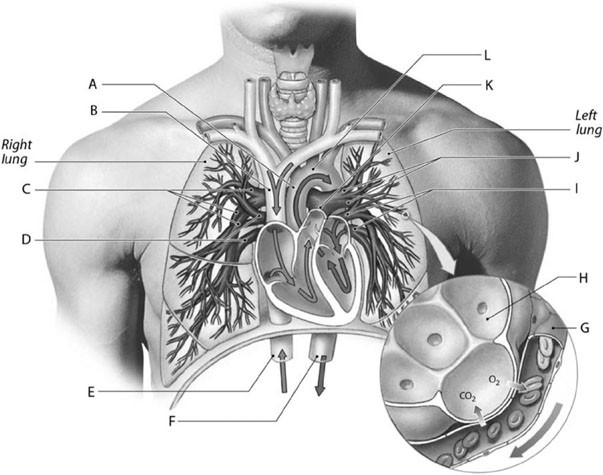
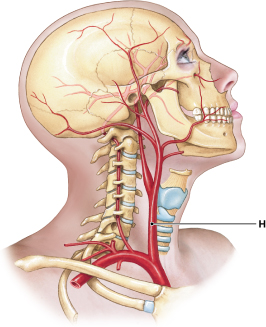
internal and external carotid
The blood vessel labeled "H" splits to become the __________ and __________ arteries.
diaphragm
The ________ divides the aorta into a superior thoracic aorta and an inferior abdominal aorta.
inferior vena cava.
The vessel that receives most of the blood from organs inferior to the diaphragm is the
brachiocephalic vein.
After merging with the external and internal jugular veins, the subclavian vein becomes the
external carotid artery.
The vessel that supplies blood to the face is the
internal carotid; vertebral
Blood reaches the brain by two routes: through the ________ and the ________ arteries.
external carotid artery
The strong pulse that is felt by pressing gently along either side of the trachea usually indicates the location of the ________.
drain the posterior surface of the skull, descending within the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae.
Vertebral veins
organs inferior the diaphragm; upper limbs and head
The inferior vena cava would receive blood from the _____________________ whereas the superior vena cava would receive blood from the
________________________.
brachial artery.
After crossing the axilla, the axillary artery becomes the
inferior vena cava.
The two common iliac veins form the
basilar artery
Inside the cranium, the vertebral arteries fuse to form the ________, which continues along the ventral surface of the brain.
hepatic portal system
Blood leaving the capillaries supplied by the celiac, superior mesenteric, and inferior mesenteric arteries flows to the liver through the ________.
superior mesenteric artery
Which of the following supplies blood to major sections of the intestinal tract and the pancreas?
deliver blood to the diaphragm.
The phrenic arteries
internal jugular veins
Most of the blood leaving the brain passes through one of the dural sinuses and leaves the skull in one of the ________, descending parallel to the common carotid artery in the neck.
brain
When one exercises at maximal levels, only the blood supply to the ________ is
unaffected.
A typical vein does not need to withstand much pressure.
Why do veins have relatively thin walls?
external jugular vein.
Blood from the superficial structures of the head and neck is collected by the
media
The layer of the blood vessel that contains smooth muscle is the tunica __________.
autoregulation
When blood flow in a capillary bed decreases in response to locally high oxygen levels, it is caused by
tunica externa.
The outermost layer of the arterial wall is the
pulse pressure
The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is the
subclavian artery
The vessel that supplies blood to the arm, shoulder, chest wall, back, and spinal cord is called the ________.
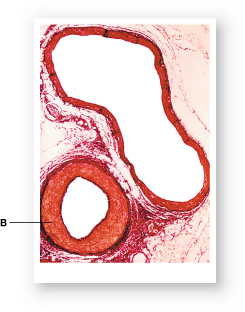
artery
Which type of blood vessel is labeled "B"?
internal thoracic artery
A blockage in the ________ would greatly interfere with blood flow to the pericardium and anterior wall of the chest.
common iliac arteries.
Near the level of vertebra L4, the abdominal aorta branches to form the
peak systolic
The pressure at which the pulse can first be heard corresponds to the ________
pressure.
sphygmomanometer
The instrument used to measure blood pressure is the ________.
carotid sinus.
Baroreceptors that function in maintaining adequate blood flow to the brain are located in the
Arteries contain a tunica media, whereas veins do not.
When comparing arteries and veins, which of the following statements is NOT
correct?
inferior vena cava
Which of the following vessels of the systemic circuit has the lowest
pressure?
both blood pools in the veins and varicose veins are correct
When the venous valves become weak and lose elasticity, which of the following events will most likely occur?
venules
Blood flowing out of a capillary bed first enters structures called ________.