AP BIO UNIT 2: cell structure and function
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
1
New cards
topic 5.
**CELL ORGANELLES, MEMBRANES, AND TRANSPORT**
**CELL ORGANELLES, MEMBRANES, AND TRANSPORT**
**OVERVIEW:**
* **cell organelles and their functions**
* **endosymbiosis hypothesis**
* **the advantages of compartmentalization**
* **the importance of surface area to volume ratios**
* **structure of the plasma membrane**
* **what can (and cannot) cross the plasma membrane**
* **passive transport**
* **active transport**
* **cell organelles and their functions**
* **endosymbiosis hypothesis**
* **the advantages of compartmentalization**
* **the importance of surface area to volume ratios**
* **structure of the plasma membrane**
* **what can (and cannot) cross the plasma membrane**
* **passive transport**
* **active transport**
2
New cards
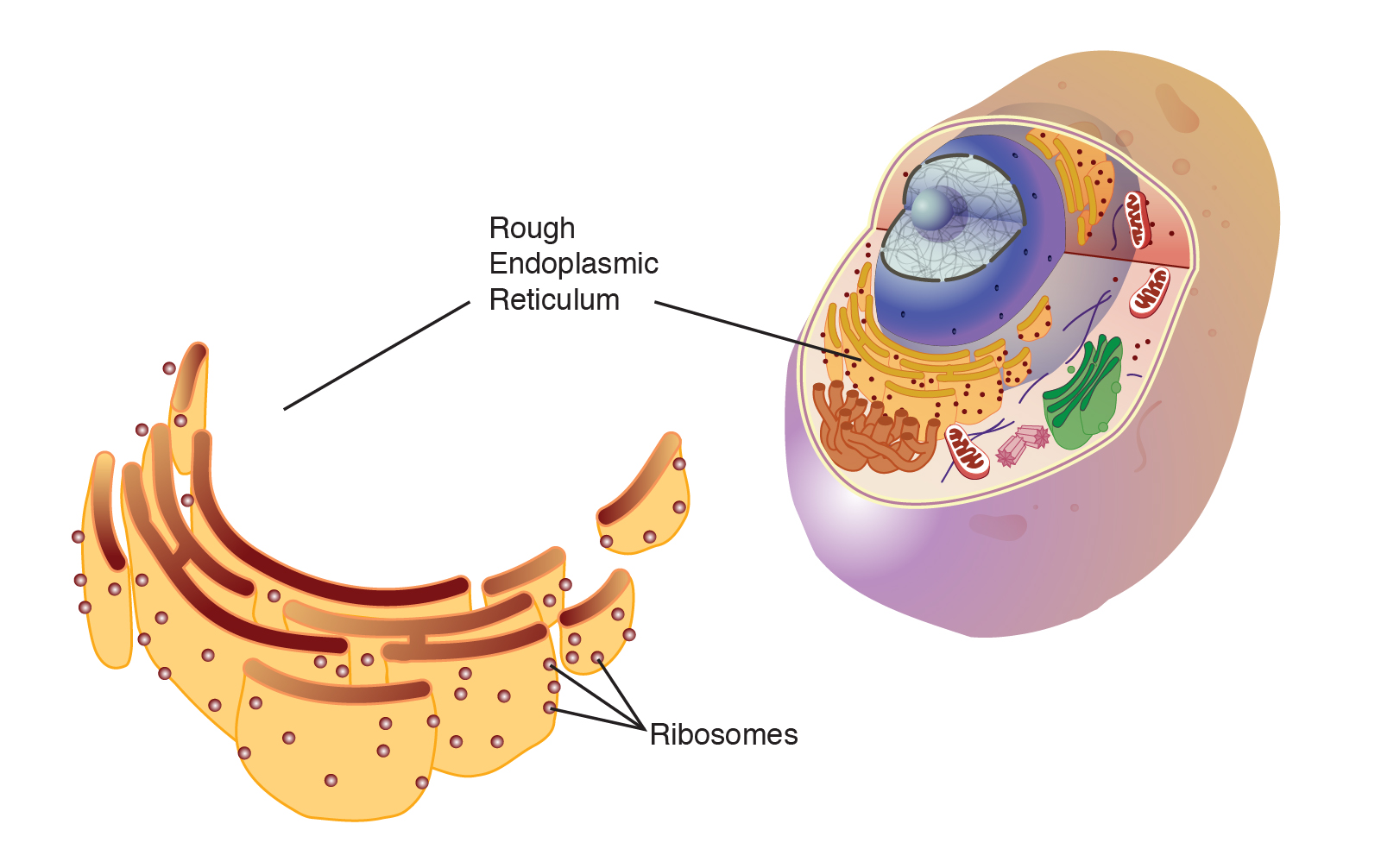
ribosomes
function in protein synthesis and are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
* made of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
* made of proteins and ribosomal RNA (rRNA).
3
New cards
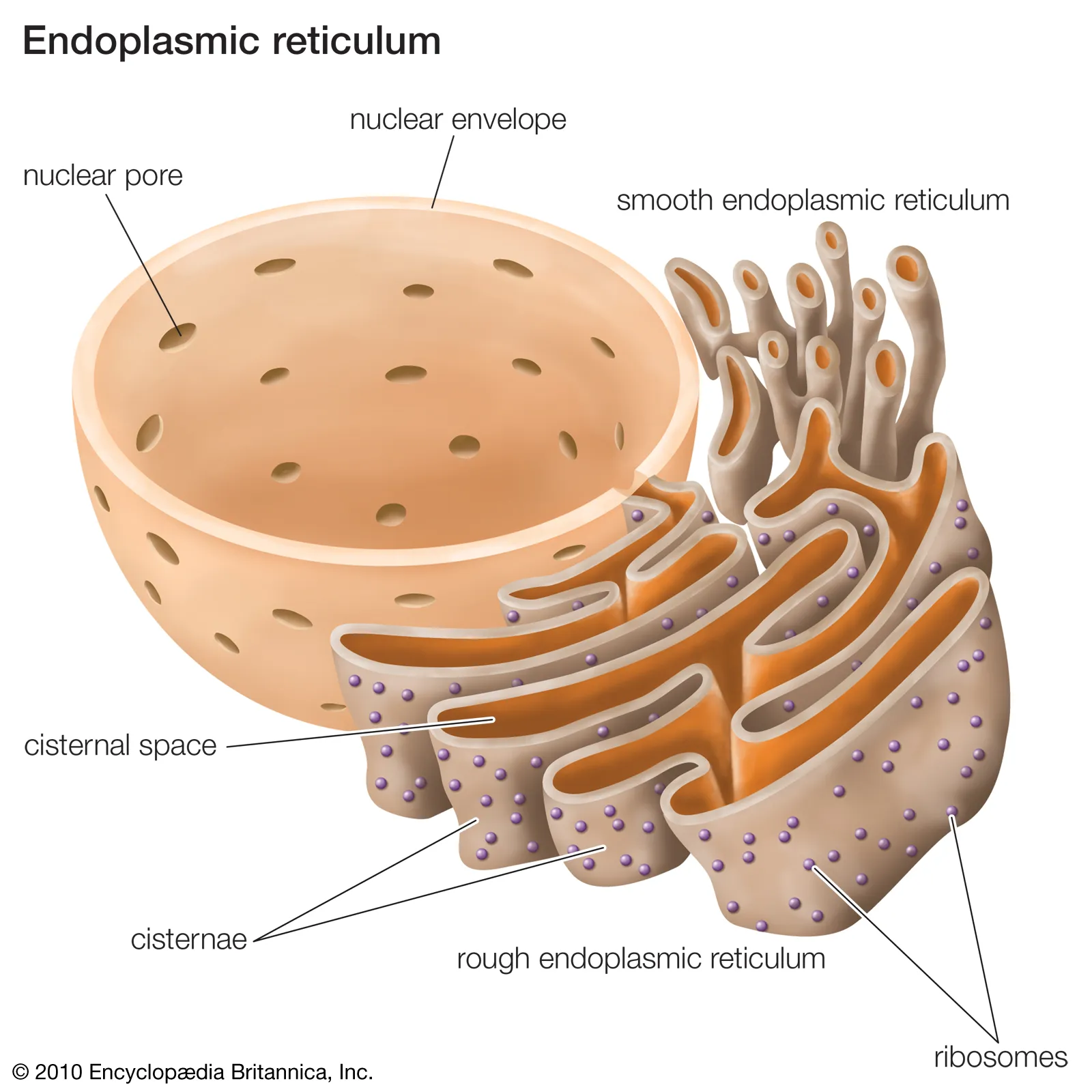
endoplasmic reticulum
is a series of membrane channels in eukaryotic cells.
* **rough endoplasmic reticulum:** has ribosomes bound to its membranes and functions in protein synthesis.
\
* **smooth endoplasmic reticulum:** does not contain ribosomes and functions in the synthesis of lipids and the detoxification of harmful substances in the cell.
* **rough endoplasmic reticulum:** has ribosomes bound to its membranes and functions in protein synthesis.
\
* **smooth endoplasmic reticulum:** does not contain ribosomes and functions in the synthesis of lipids and the detoxification of harmful substances in the cell.
4
New cards
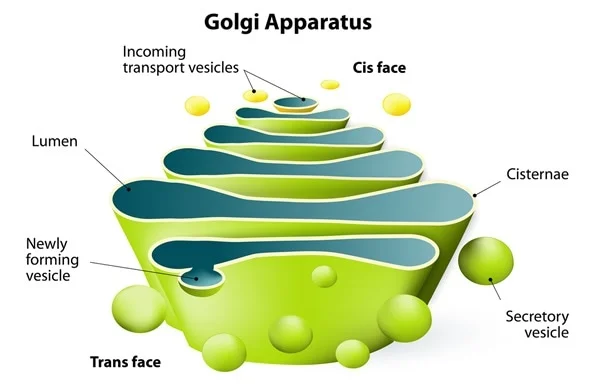
golgi complex
is a stack of flattened membrane sacs (called cisternae).the interior of each cisternae is called the lumen and contains the enzymes necessary for the golgi complex to function. the golgi complex controls the modification and packaging pf proteins for transport.
5
New cards
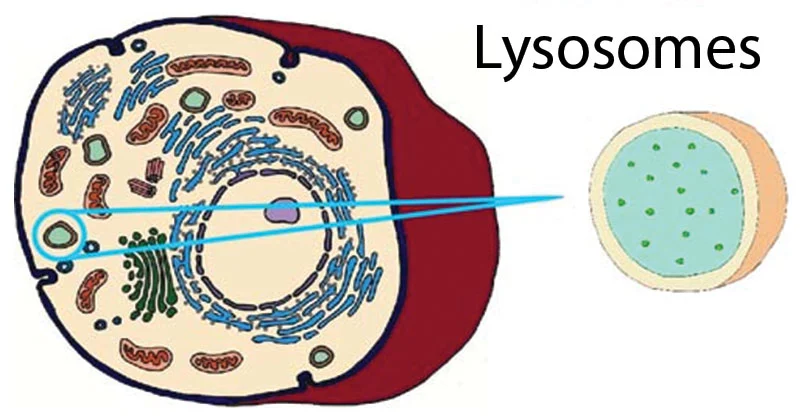
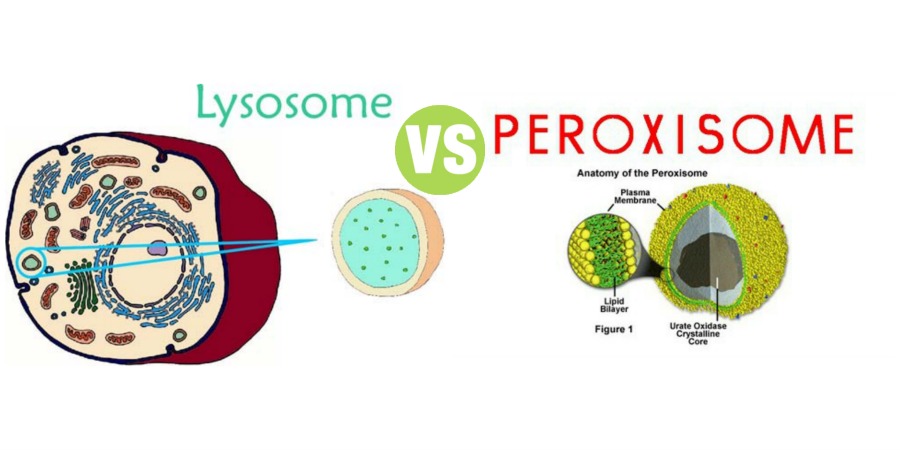
lysosomes
are membrane-bound sacs, containing hydrolytic enzymes, that function in variety of cell processes. lysosomes can help digest macromolecules, break down worn-out cell parts, function in apoptosis, or destroy bacteria and viruses that have entered the cell.
6
New cards
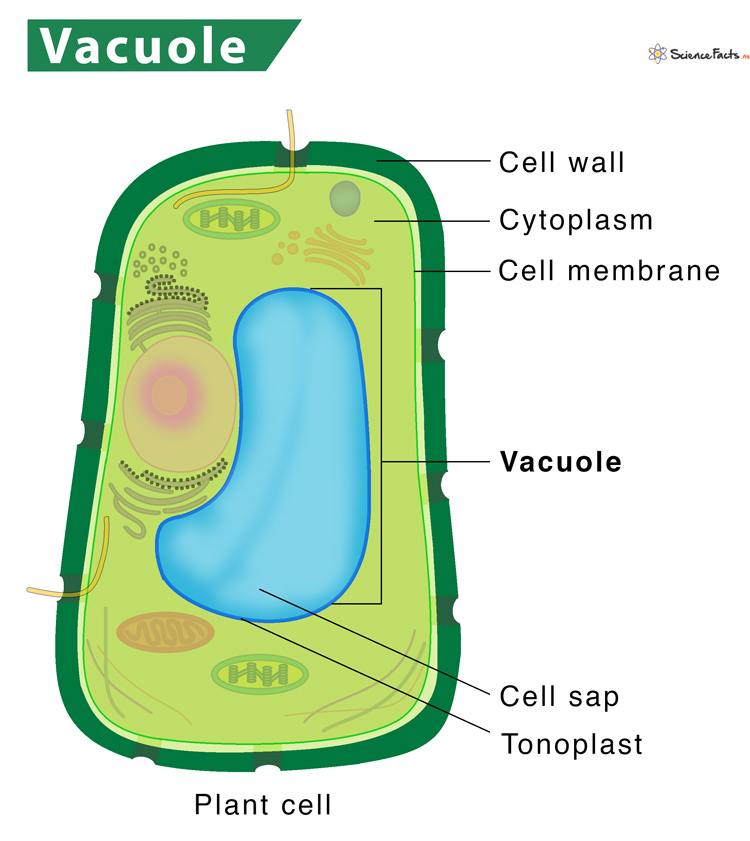
vacuole
a membrane-bound sac in eukaryotic cells. vacuoles function in food or water storage, water regulation in a cell, or waste storage until the waste can be eliminated from the cell.
7
New cards
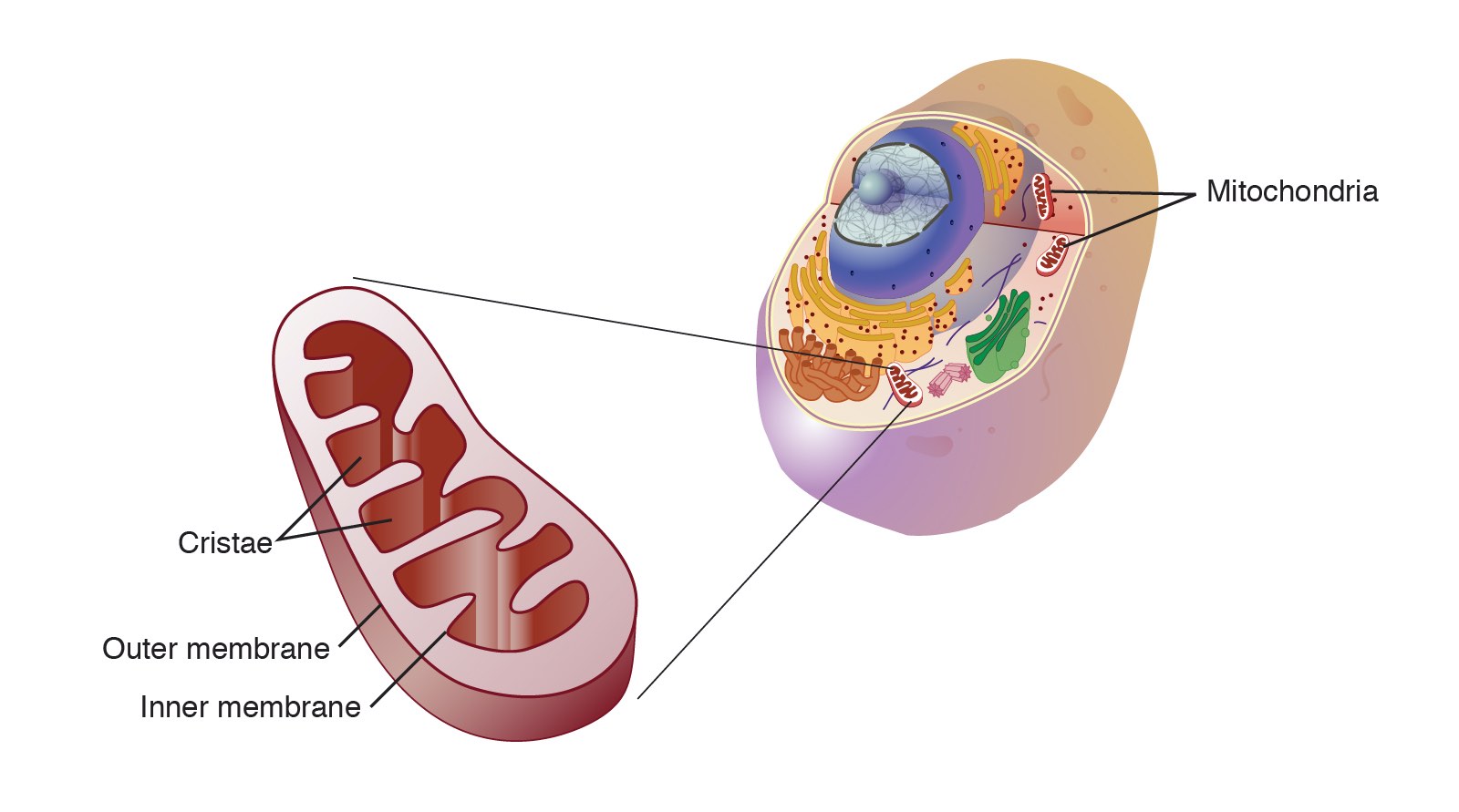
mitochondria
produces energy for the cell. the mitochondria have double-membranes, with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. mitochondria also contain their own mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
* **matrix:** an enzyme-containing fluid located in the center of the mitochondria.
* **matrix:** an enzyme-containing fluid located in the center of the mitochondria.
8
New cards
chloroplasts
are found in plants and algae that carry out photosynthesis. like mitochondria, chloroplasts also have a double-membrane structure.
* **thylakoids:** a smooth outer membrane and pancake-shaped membranous sacs.
* **grana:** stacked thylakoids.
* **stoma:** the liquid inside the chloroplast that surrounds the grana.
* **thylakoids:** a smooth outer membrane and pancake-shaped membranous sacs.
* **grana:** stacked thylakoids.
* **stoma:** the liquid inside the chloroplast that surrounds the grana.

9
New cards
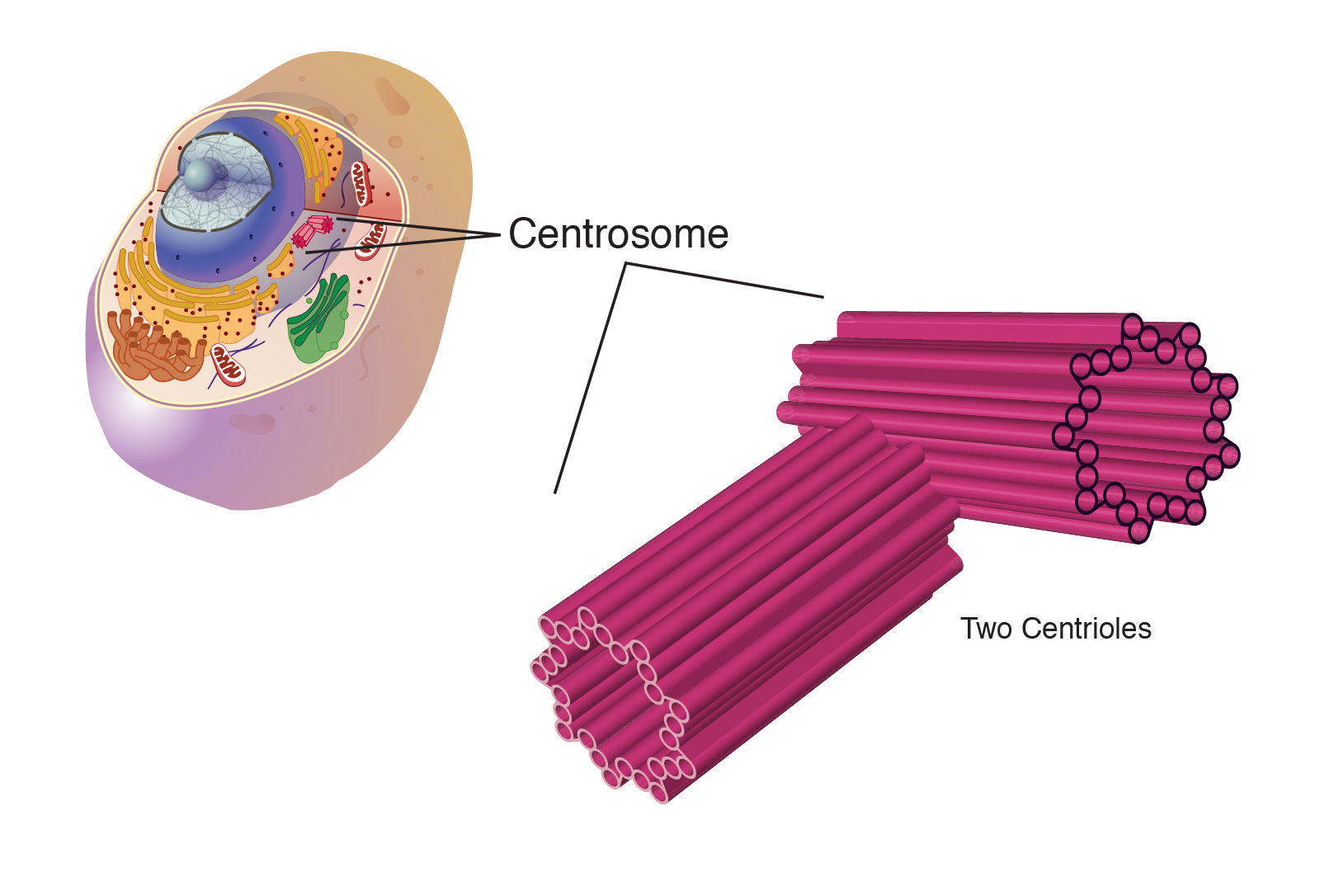
centrosome
is found in animal cells and helps the microtubules assemble into the spindle fibers needed in cell division.
\
**fun fact:** defects in centrosome function have been associated with dysregulation of the cell cycle in some cancers.
\
**fun fact:** defects in centrosome function have been associated with dysregulation of the cell cycle in some cancers.
10
New cards
amyloplasts
plant cells may contain amyloplasts. excess glucose produced by photosynthesis is stored as starch molecules in the amyloplasts. amyloplasts are frequently found in the root and tubers of starchy vegetable, such as potatoes!

11
New cards
peroxisome
helps oxidize molecules and break down toxins in the cell.
12
New cards
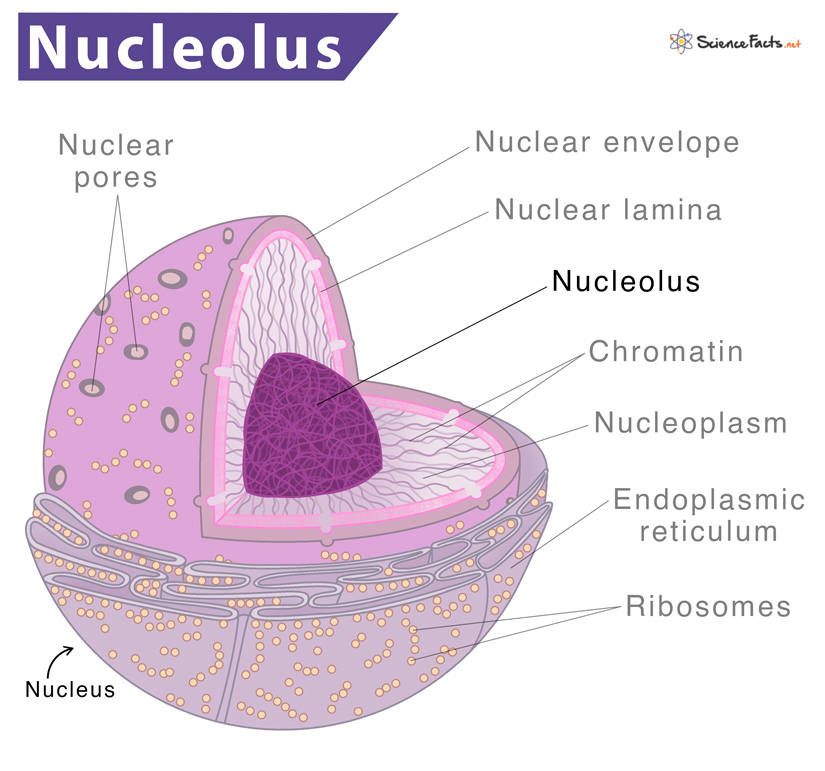
nucleolus
it is not a membrane-bound organelle; that term refers to the region in the nucleus where ribosomes are assembled.
13
New cards
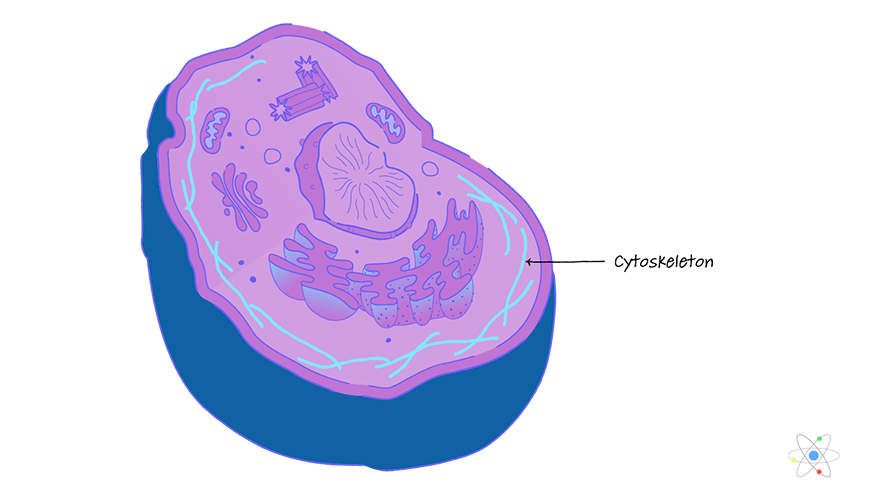
cytoskeleton
are fibers that help give cells their shape and can be used to move items in the cell.
14
New cards
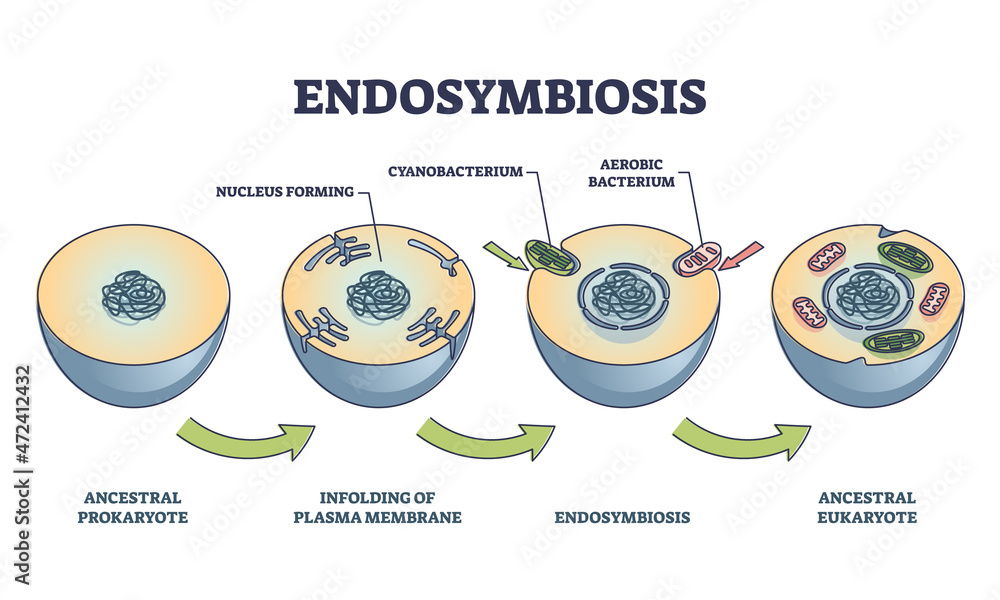
endosymbiosis hypothesis
states that membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, were once free-living prokaryotes that were absorbed into other larger prokaryotes.
15
New cards
surface area to volume ratios
as the radius *increases*, the surface area to volume ratio will *decrease*. *(the amount of surface are available per unit volume for exchange of materials gets smaller and smaller.)*
16
New cards
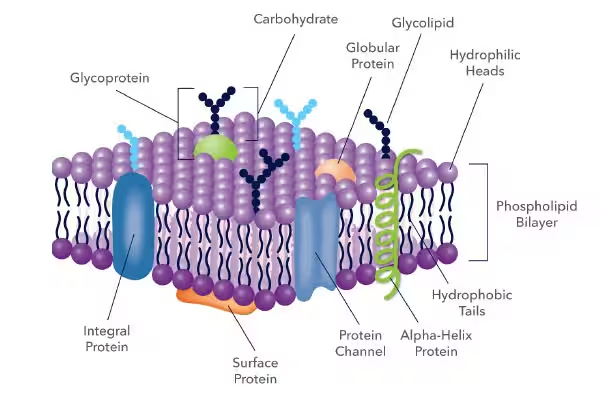
plasma membrane
are selectively permeable, which means that some materials can cross the membrane while other materials cannot.
17
New cards
bilayer
the plasma membrane is made of a bilayer of phospholipids. phospholipids have a hydrophilic (or polar) phosphate “head” and two hydrophobic (or nonpolar) “tails.”
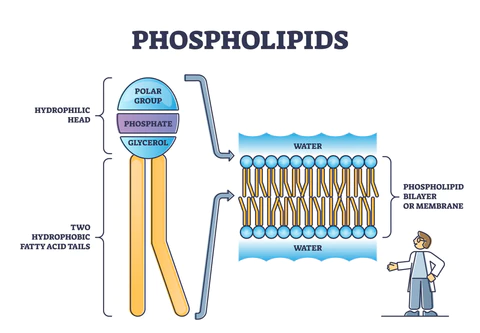
18
New cards
glycoproteins & glycolipids
membrane, modified proteins that are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer. these components of the membrane are mobile and can flow throughout the surface of the plasma membrane, allowing the cell to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
**proteins in the plasma membrane have many functions:**
* transporting materials
* participating in cell signaling processes
* anchoring the cell to its surroundings
* catalyzing chemical reactions
**proteins in the plasma membrane have many functions:**
* transporting materials
* participating in cell signaling processes
* anchoring the cell to its surroundings
* catalyzing chemical reactions
19
New cards
aquaporins
are specialized proteins that allow for most of the passage of water in and out of the cell.
20
New cards
cell wall
are composed of large carbohydrates (cellulose in plants, glucans in fungi, and peptidoglycan in prokaryotes). the cell walls provide rigidity to the cell and are an additional barrier to substances entering or exiting the cell.
*plants, fungi, and prokaryotic cells are surrounded by a cell wall.*
\
*plants, fungi, and prokaryotic cells are surrounded by a cell wall.*
\
21
New cards
passive transport
the movement of molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
*molecules move “down” their concentration gradient.*
*molecules move “down” their concentration gradient.*
22
New cards
diffusion
the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient without the input of energy.
23
New cards
facilitated diffusion
the process of passive transport that uses a membrane protein.
*ex.) the specialized membrane proteins called aquaporins that allow large quantities of water to move down their concentration gradient.*
*ex.) the specialized membrane proteins called aquaporins that allow large quantities of water to move down their concentration gradient.*
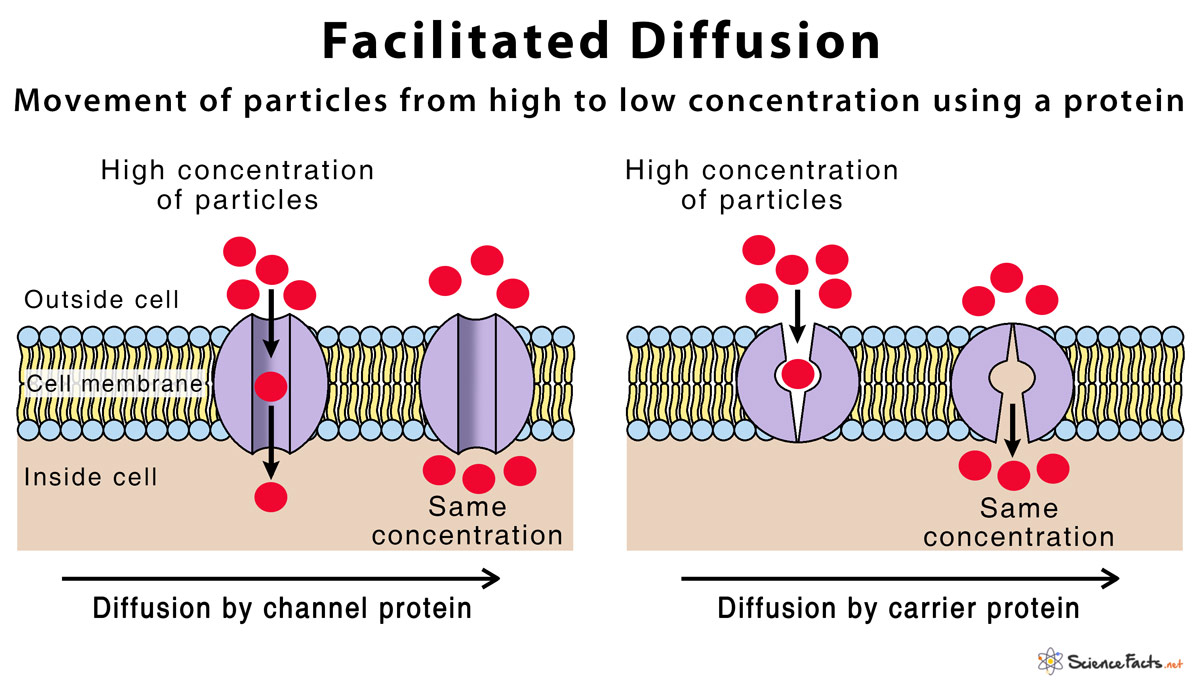
24
New cards
channel proteins
can allow the passive transport of ions, such as Ca^+2 or Cl^-1, down their concentration gradients.
25
New cards
active transport
moves molecules from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration.
*ex.) Na^+/k^+ pump. this membrane protein requires the input of ATP to pump Na^+ ions from their lower concentration outside the cell to an area with higher concentrations of k^+ ions inside the cell.*
***3 Na^+ pumped out of the cell, 2 k^+ions are pumped into the cell***
this movement of molecules “against” their gradient requires the input of energy.
*ex.) Na^+/k^+ pump. this membrane protein requires the input of ATP to pump Na^+ ions from their lower concentration outside the cell to an area with higher concentrations of k^+ ions inside the cell.*
***3 Na^+ pumped out of the cell, 2 k^+ions are pumped into the cell***
this movement of molecules “against” their gradient requires the input of energy.
26
New cards
endocytosis
is used bu the cell to take in water and macromolecules by enfolding them into vesicles formed from the plasma membrane.
27
New cards
exocytosis
vesicles (that contain molecules to be expelled) are fused with the plasma membrane, which then allows these molecules to be expelled from the cell. this movement of large molecules into or out of the cell requires the input of energy.
28
New cards
topic 6.
**MOVEMENT OF WATER IN CELLS**
**MOVEMENT OF WATER IN CELLS**
**OVERVIEW:**
* **water potential**
* **osmolarity and its regulation**
* **water potential**
* **osmolarity and its regulation**
29
New cards
hypotonic solution
has a lower concentration of solute.
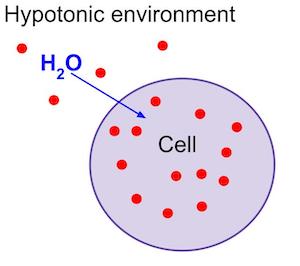
30
New cards
hypertonic solution
has a higher concentration of solute.
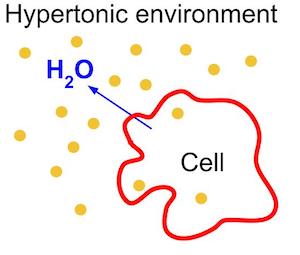
31
New cards
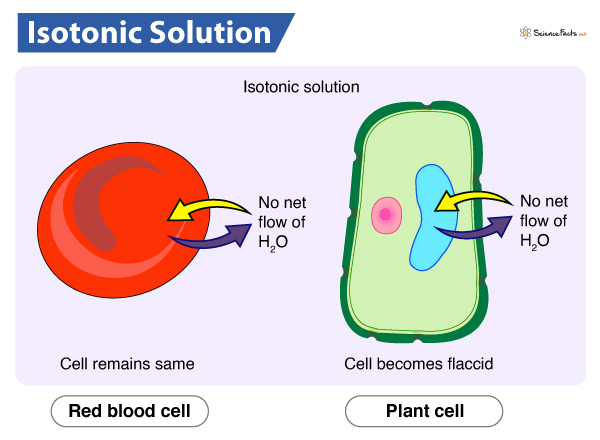
isotonic solution
has the same concentration of solute as that of another solution.
32
New cards
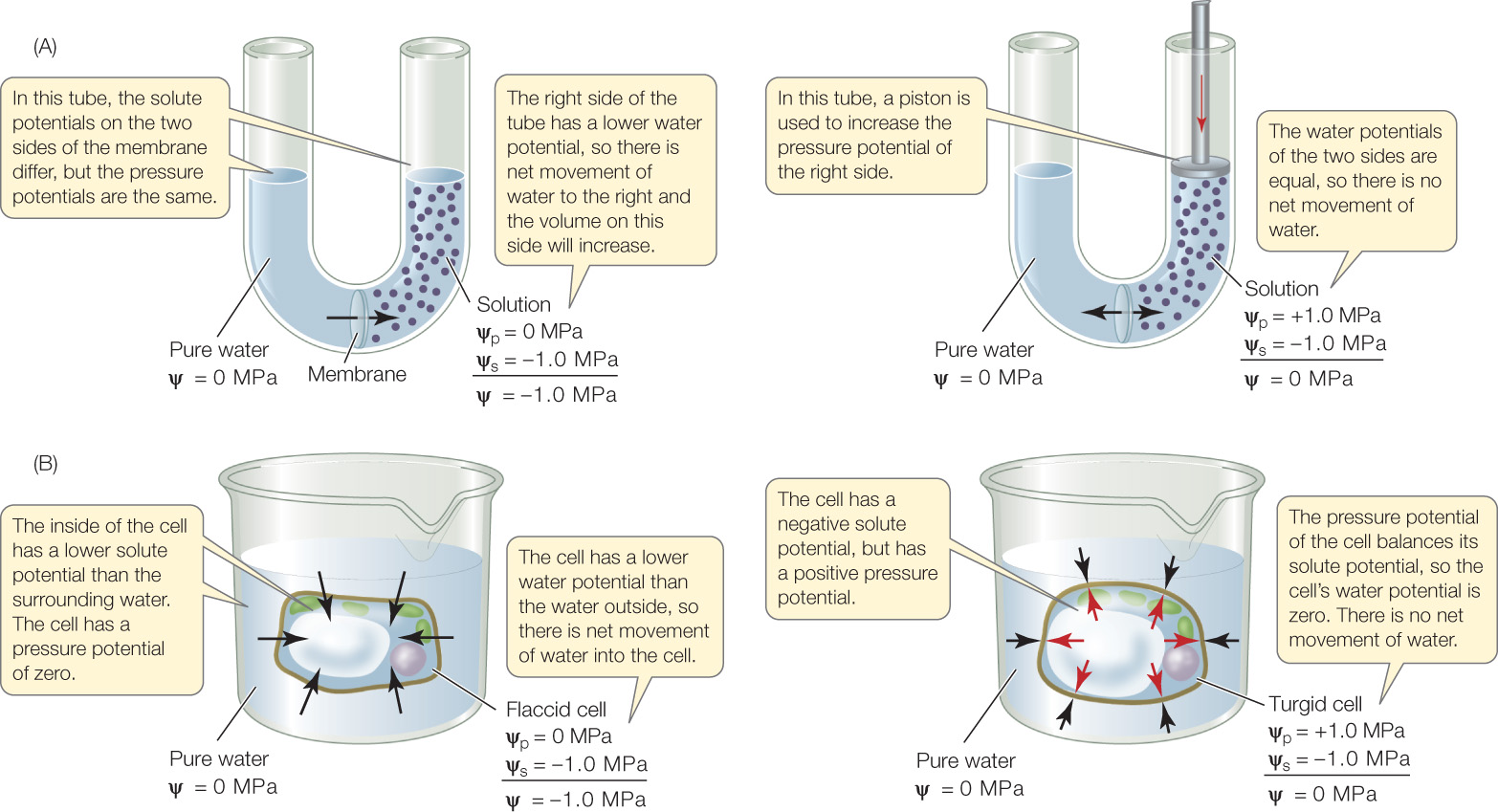
water potential
can be defined as the potential energy of water in a solution, or the ability of water to do work.
33
New cards
osmolarity
the total concentration of solutes in a solution.