Attribution Theory and Person Perception in Social Psychology
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Social Psychology
Study of how individuals' thoughts, feelings, behaviors are influenced by others.
Person Perception
Process of forming impressions of others.
Mere-Exposure Effect
Repeated exposure increases liking of novel stimuli.
Attribution Theory
Explains behavior by crediting situation or disposition.
Situational Attribution
Behavior attributed to external factors or situations.
Dispositional Attribution
Behavior attributed to internal factors or personality.
Explanatory Style
How people explain good or bad events in life.
Optimistic Explanatory Style
Attributing positive outcomes to internal factors.
Pessimistic Explanatory Style
Attributing negative outcomes to internal factors.
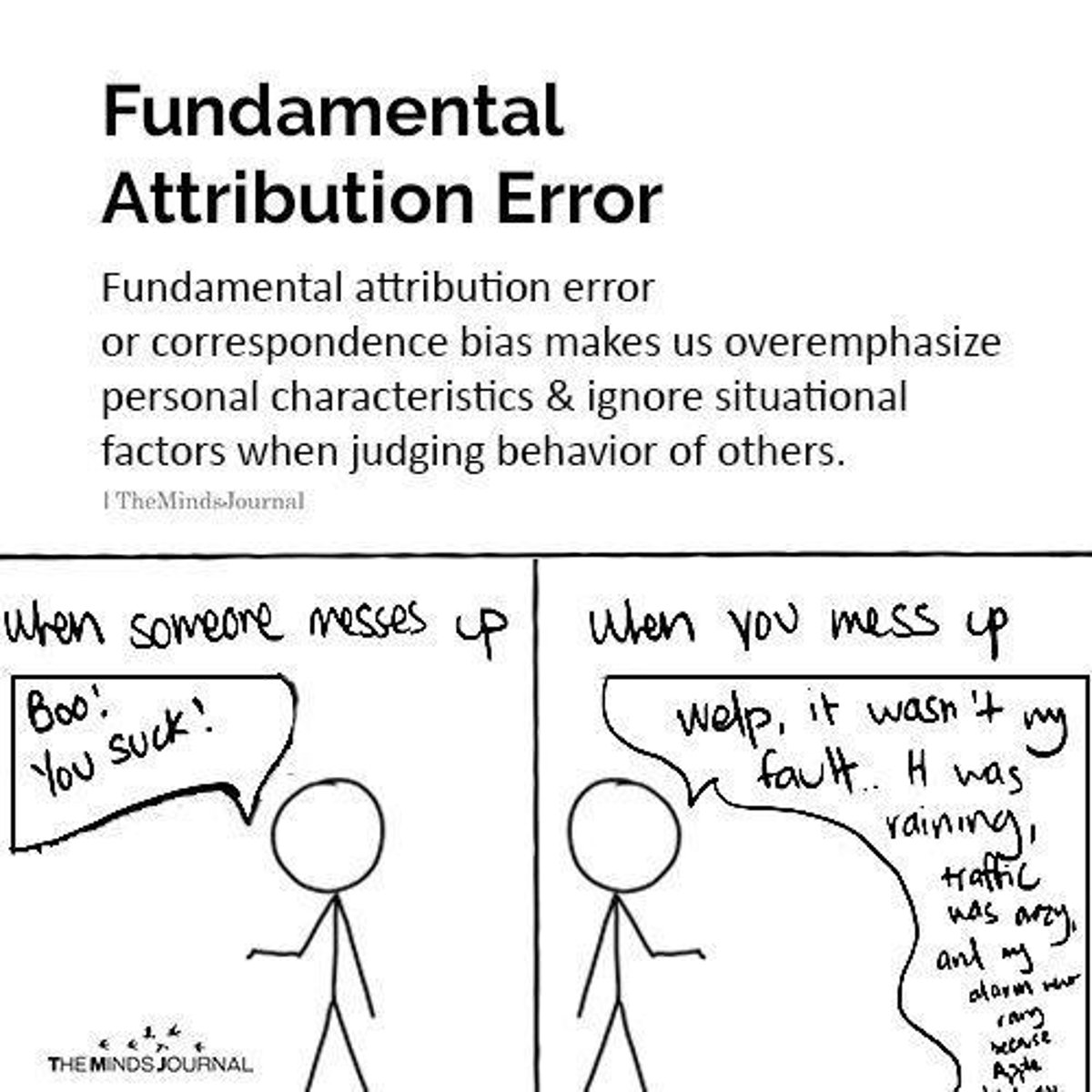
Fundamental Attribution Error
Over-attributing others' behavior to internal factors.
Actor-Observer Bias
Attributing own actions to external, others' to internal factors.
Self-Serving Bias
Attributing successes to self, failures to external factors.
Cognitive Bias
Systematic pattern of deviation from norm in judgment.
Bias of Behavior
General tendency to misattribute causes of actions.
Impression Formation
The process of developing opinions about others.
Stereotyping
Overgeneralized belief about a group of people.
Social Influence
Effects of others on individual behavior and thoughts.
Cognitive Dissonance
Mental discomfort from holding conflicting beliefs or behaviors.
Groupthink
Decision-making process where group harmony overrides realistic appraisal.
Confirmation Bias
Favoring information that confirms existing beliefs.

Social Comparison
Evaluating oneself in relation to others.
Normative Social Influence
Conforming to be accepted or liked by others.
Actor-Observer Bias
Differential attribution of actions based on perspective.
Self-Serving Bias
Attributing successes to internal, failures to external factors.
Internal Locus of Control
Belief that one controls their own fate.
External Locus of Control
Belief that fate is determined by external forces.
Learned Helplessness
Feeling of helplessness due to lack of control.
Personal Control
Sense of controlling one's environment and outcomes.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Belief that leads to its own fulfillment.
Social Comparison Theory
Evaluating oneself based on others' abilities.
Upward Comparison
Comparing to someone perceived as better off.
Downward Comparison
Comparing to someone perceived as worse off.
Relative Deprivation
Feeling deprived compared to others in social group.
Perception of Control
Influence of control beliefs on behavior and mental processes.
Impact on Self-Esteem
Social comparisons significantly affect self-esteem levels.
Cultural Influence on Perception
Social groups shape treatment and perception of others.
Attribution Theory
How individuals explain causes of behavior.
Motivation from Upward Comparison
Can inspire self-improvement despite potential inadequacy feelings.
Boost from Downward Comparison
Can enhance self-esteem by feeling superior.
Consequences of Learned Helplessness
Lower morale and increased stress from lack of control.
Role of Environment in Control
Limited control in settings like prisons reduces morale.
Behavioral Confirmation
Behaviors elicited by others confirming beliefs.
Seligman's Research
Studies on learned helplessness and control perceptions.
Social Reference Group
Group used for social comparison assessments.
Cognitive Dissonance
Mental discomfort from conflicting beliefs or behaviors.
Attitude
A feeling influenced by beliefs, guiding responses.
Cognitive Component
Beliefs about an object's attributes.
Affective Component
Feelings associated with an object.
Behavioral Component
Actions taken towards an object.
Stereotype
Generalized concept about a group.
Implicit Attitudes
Unconscious biases individuals may not acknowledge.
Explicit Prejudice
Conscious negative beliefs about a group.
Implicit Prejudice
Unconscious biases measured by tools like IAT.
Discrimination
Unjustifiable negative behavior towards a group.
Prejudice
Unjustifiable negative attitude towards a group.
Just-World Phenomenon
Belief that actions lead to deserved outcomes.
Social Unrest
Protests driven by perceived unfair deprivation.
Attitude Formation
Process of developing feelings towards objects.
Advertising Tactics
Strategies to evoke feelings for product connection.
Social Movements
Collective efforts to address perceived injustices.
Out-Group Homogeneity Bias
Perception that out-group members are similar.
In-Group Bias
Preference for members of one's own group.
Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's own culture.
Cognitive Load
Mental effort required to process information.
Negative Evaluations
Unfavorable judgments about others based on biases.
Stereotype Function
Reduces cognitive load in decision-making.
Criminal Behavior
Actions driven by feelings of unfair deprivation.
Social Movements Examples
Protests arising from perceived social injustices.
Just-world phenomenon
Belief that actions yield deserved consequences.
Victim-blaming
Assigning fault to victims for their misfortunes.
Ingroup
Group sharing a common identity, referred to as 'us'.
Outgroup
Group perceived as different, referred to as 'them'.
Ingroup bias
Favoring one's own group over others.
Outgroup Homogeneity Bias
Seeing outgroup members as more similar than ingroup.
Stereotypes
Oversimplified beliefs about a group of people.
Prejudice
Negative attitudes toward individuals based on group membership.
Social Roots of Prejudice
Prejudice arises from group identity and favoritism.
Scapegoat Theory
Prejudice serves as an outlet for anger by blaming others.
Belief Perseverance
Clinging to beliefs despite contradictory evidence.
Confirmation Bias
Seeking information that supports existing beliefs.
Cognitive Dissonance
Tension from conflicting attitudes and behaviors.
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
Theory explaining how we reduce dissonance.
Alleviating Cognitive Dissonance
Change action, attitude, or perception of action.
Example of Cognitive Dissonance
Feeling guilt after shoplifting despite self-image.
Leon Festinger
Psychologist who proposed Cognitive Dissonance Theory.
Order vs. Chaos
Humans prefer structured environments over chaotic ones.
Us vs. Them Mentality
Dividing people into favored ingroup and outgroup.
Historical Prejudice Examples
Japanese internment, Nazi scapegoating, post-9/11 backlash.
Diversity Recognition
Acknowledging differences within one's own group.
Behavior Change Difficulty
Changing beliefs is often easier than changing actions.
Social Norms
Group expectations for appropriate attitudes and behaviors.
Conformity
Adjusting behavior to align with group standards.
Obedience
Following direct commands from an authority figure.
Automatic Mimicry
Unconscious imitation of others' behaviors.
Chameleon Effect
Tendency to mimic behaviors of others.
Social Influence Theory
Explains reasons for conformity under social pressure.
Normative Social Influence
Conforming to avoid rejection or gain approval.
Informational Social Influence
Conforming due to perceived valuable information.
Solomon Asch's Line Study
Experiment testing levels of conformity with lines.
Conformity Conditions
Factors influencing likelihood of conforming behavior.