Chapter 19- Supply Chain Management Within the Sterile Processing Department
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Operational supplies
Supplies needed for SPD operations. Examples include detergents, sterilization wrap, sterilization testing products, etc.
Patient care supplies
Supplies dispensed for patient treatment and care. Examples include catheters, implants, bandages, etc.
Inventory
Reusable equipment and consumable items used to provide healthcare services for patients.
(inventory)Reusable
Assets, such as medical devices and sterilization containers, that can be reused as healthcare services are provided to patients. Ex: mechanical washers and sterilizers.
consumable (inventory)
Assets, such as wrapping supplies, processing chemicals, and other items that are consumed as healthcare services are provided to patients. Ex: detergents, disposable wraps, and sterility assurance products.
Distribution
The movement of supplies
Periodic Automatic replenishment (PAR)
An inventory replenishment system in which the desired amount of products that should be available is established, and inventory replenishment returns the quantity of products to this level
Automated supply replenishment system
Replenishment system in which items removed from inventory are automatically identified and tracked. When a reorder point is reached, item information is generated on a supply pick list in the central storeroom, or with a contracted vendor. Items are then issued and transferred to the appropriate user area.
Exchange cart system
An inventory system where desired inventory items are placed on a cart assigned to a specific location. A second duplicate cart is maintained in another location and exchanged on a scheduled basis to ensure sufficient supplies are available at all times
Requisition system
A method of inventory distribution where items needed are requested by user department personnel and removed from a central storage location for transport to the user department
Non-stock items
Items not carried in the central storeroom or in the sterile processing area but that are purchased from an outside vendor, as needed, and then delivered to the requesting department
Sustainability
Processes designed to reduce harm to the environment or deplete natural resources, thereby supporting long-term ecological balance.
Sterilizers, mechanical washers and other expensive items are examples of
capital equipment
(workbook) Which of the following system provides supplies and instruments for individual surgical procedures?
Case Cart
(workbook) The inventory system that stock supplies by per-established stock levels is called a/an:
PAR system
(workbook) The inventory system that uses two identical carts to facilitate supply replenishment is called the
exchange cart system
(workbook) Automated supply replenishment systems are:
Computerized
(workbook) The movement of supplies throughout the healthcare facility is called:
Distribution
(workbook) Supply inspection should include
checking for excessive handling
(workbook) Items like disposable wraps are called
consumable supplies
(workbook) Capital equipment items are
items with a higher purchase price

Reference number

Product serial number
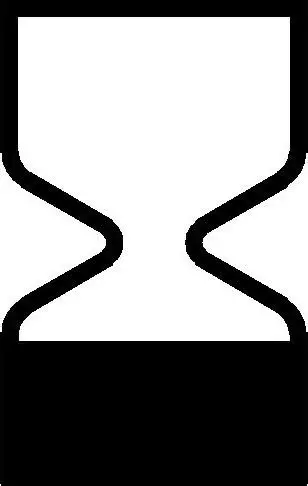
Use by date

Do not reuse
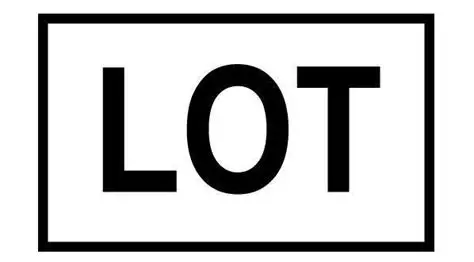
Lot number/batch code

Date of manufacturer

The CE mark is an identification mark that indicates that a product has complied with the health and safety requirements, as published by european directives
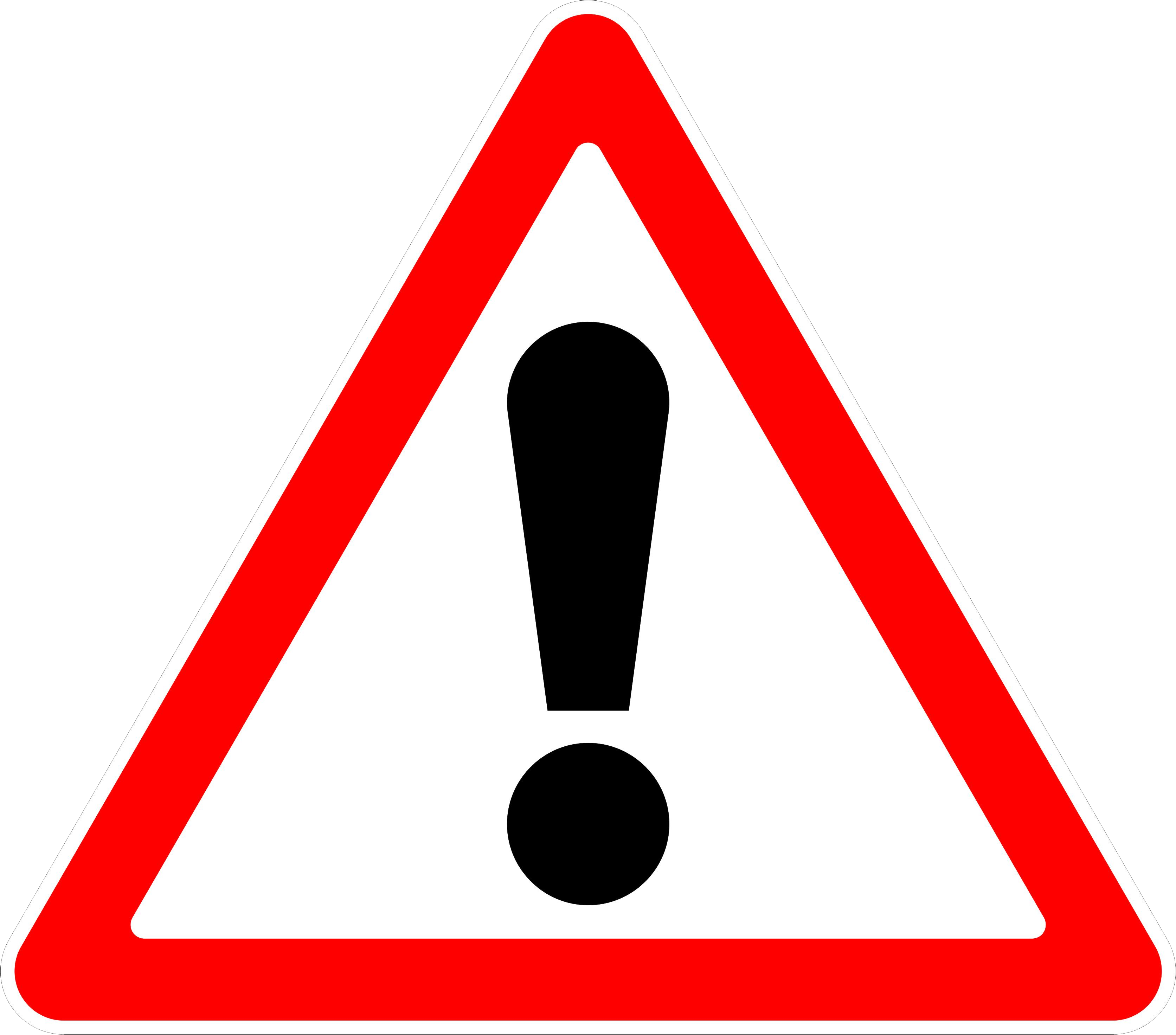

Attention: see instructions
Who is responsible for the supply purchasing, receiving and distribution?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) department
Consumable and reusable items are considered…
Assets. They represent a significant financial investment by the healthcare facility and must be managed in a way that enables the facility to benefit from them at the lowest cost possible.
Group purchasing organizations (GPOs)
Negotiate contracts for products and services that enable facilities to receive special, reduced pricing.
Where are a large portion of inventory items stored?
In the SCM department
Consignment
An inventory system where items are provided to the healthcare by the vendor but not charged to the facility until the items are used.
Any implant not accounted for
Will be charged
What do commercially sterilized packages come with?
Printed instructions. Most product packaging contains information regarding product manufacturer, sterility, storage, and safe use.
Manufacturer information
Manufacturer’s name
Product name and specifics
Product reference number
Date of manufacturer
Batch number
product serial number
expiration information
Sterility information
Sterility statement
Expiration date
Storage information
Storage temperature limits
Moisture or humidity limits
Fragility
Safe use instructions
Identification of single-use items
Notification of latex contents
References to product instructions for use
Do all packages have an expiration date?
No. Such items do not have materials that will degrade or decompose in an established normal-use time frame. The packages will have a statement indicating that the package is sterile, unless opened or damaged.
What should inspections include?
Visual checks to ensure that the packages has no holes, tears, signs of moisture, dust, or other visible damage.
The unique device identifier (UDI) system will allow
Tracking of medical devices
Easy identification of an item being recalled
more accurate reporting and analysis of adverse events caused by a medical device
Identification of counterfeit medical devices
What are the common causes for the loss of sterile items?
Expiration
Contamination
Obsolescence
Loss
Theft
What is the best method of transport?
Closed case carts
What is the goal of distribution?
To move the correct items in appropriate quantities to the right places at the right times and in the most cost-effective manner possible.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the exchange cart system?
It’s automatic
It’s labor intensive and requires adequate space to stage the carts.
Benefits of the case cart system:
Reduces the amount of space needed for supply storage in the user department
Promotes standardized infection prevention practices
reduces operational costs associated with supply and instrument management
Allows more efficient equipment and supply tracking
STAT orders are time consuming and costly to fill because…
They disrupt routine inventory management activities.
[workbook] Product expiration dates are located on this part of each purchased sterilized package:
There is no standard placement for expiration dates