Exam 1 review (lecture 2)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Young nation years (1776-1865)/19th century (1800s)
Healthcare values & practices
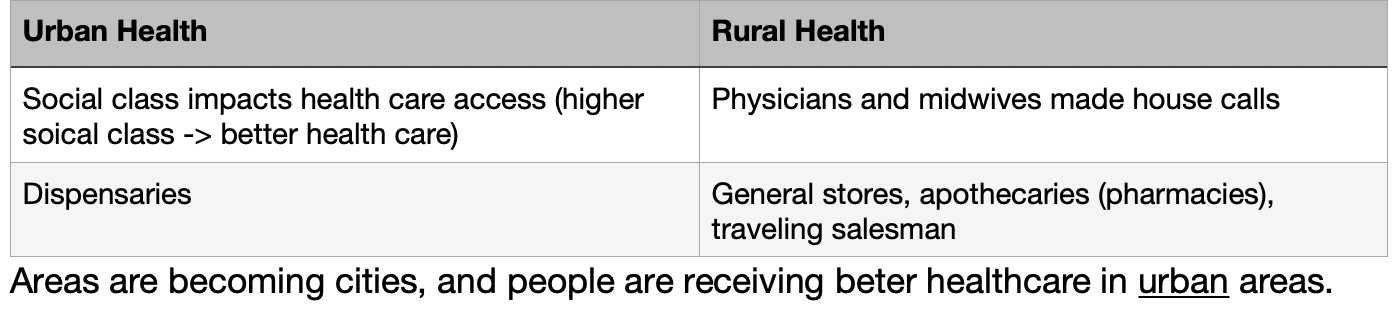
Urban vs Rural health
Self reliance
Many theories of disease causation:
Contagion:
Supernatural cause:
Proper personal behavior:
Miasma:
Humoral (Humoral Theory):
Contagion: being near others with illnesses
Supernatural cause: God/religion
Proper personal behavior: smoking/drinking/etc
Miasma: environment
Humoral (Humoral Theory): imbalance of the humors = disease
The body contains a mix of four humors (fluids): black bile, yellow bile, blood, and phlegm
To restore health: purging, blister, bleed, bloodletting, leeches
Major medical discovery:
Other medications used were:
Late 1800s:
anesthesia
Other medications used were calomel, rhubarb, opium, medicinal alcohol, quinine
Late 1800s: ether, cocaine, aspirin, codeine, iodine
Quackery:
Quackery: term to denote patent medicines deemed to be dangerous and/or fraudulent in their claims
Typical patent or quack medicines were marketed in colorful distinctive bottles.
Transformation of the hospital
Transformation of the hospital
Increase in hospital construction (late 1800s post civil war)
New types of hospitals: tuberculosis sanatorium, children, mental
Improvements: lighting, ventilation, supplies and instruments
More hospitals overall
Transition from healing arts to
science of medicine
Practicioners
orthodox vs sectarian
Practicioners
Types of “physicians”
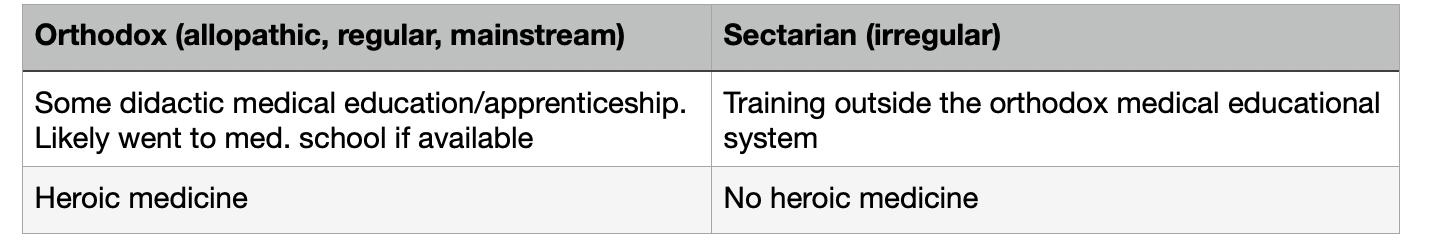
Heroic medicine:
Heroic medicine: draconian medical practices in the 18th/19th centuries that included bleeding, blistering, purging, and the use of mercury/arsenic-based medicines
Sectarian medicine:
Thromsonianism:
Hydropathy:
Homeopathy:
Electicism:
Temperance:
Kellogg/Graham:
Sectarian medicine:
Thromsonianism: botanical medicine
Hydropathy: water therapy
Homeopathy: use of plants, minerals or animals in “infinitesimal” (very small) doses to stimulate body’s own defenses
Electicism: combination of therapies above
Temperance: movement for no alcohol
Kellogg’s corn flakes/Graham crackers
Financing
Financing
Some insurance towards the end of the 1800s
Covered accident and/or sickness
Wasn’t like todays insurance, as most people didnt have insurance
Government involvement
Government involvement
Similar to colonial times
Lack of legislation regulating patent medicines, wasn’t addressed til Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) due to quackery, making sure everything in bottles was safe and accurate.
Early 20th century (1900-1945)
Healthcare values & practices -> boom of the medical sciences
Flexner report (1910):
More drugs:
WWI -
1920-30s:
Antibiotcs and sulfa drugs were…
Healthcare values & practices -> boom of the medical sciences
Flexner report (1910): evaluation of 157 med schools in US and 8 in Canada based on different criteria
More drugs
WWI - epinephrine
1920-30s: insulin, antibiotics, and sulfa drugs
Antibiotcs and sulfa drugs were the first drugs to bring real improvement in morbidity (decreased the number of days sick)
Practicioners (early 20th century)
Heroic medicine was …
Practicioners (early 20th century)
Heroic medicine was rejected
Sought private, paying patients from the middle to upper classes
Finance early 20th century
Finance early 20th century
More insurance
Private insurance plans, bluecross - hospitals, blue shield plans (1930) - physicians
Government involvement (don’t worry about years, just know these were in the Early 20th century)
Increased role of …
Federal government:
Legislations:
Government involvement (don’t worry about years, just know these were in the Early 20th century)
Increased role of government policy making at the local, state, and federal level
Federal government: US Public health service
Legislations:
Pure food and drug act, Sheppard towner maternity, infacy act, national cancer act
National institues of health (NIH), veterans administration (VA)
America since 1940
Healthcare values and practices
WWII had a…
Hill-Burton Act of 1946:
America since 1940
Healthcare values and practices
WWII had a medical aftermath, as there were international medical consequences. There were new trends related to healthcare, new patterns of disease, and advancements to prolong lifespan.
Hill-Burton Act of 1946: Hospital boom
Federal funding for assisting in construction of new hospitals/health centers
America since 1940 Practicioners: changes in …
Practicioners: changes in demographics
Financing since 1940
Financing since 1940
Most people finally get health insurance
Growth of private plans (Blue Cross, Blue Shield)
Medicare/Medicaid
Health Maintainence Organization (HMO) act -> prepaid healthcare and managed care, essentially healthcare for employees
Government involvement since 1940
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) -> privacy
Obamacare -> tried for universal healthcare coverage
Health: definition
Health: state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
Health demographic trends*
Most important trends throughout the 20th century were
Health demographic trends*
Most important trends throughout the 20th century were
Decline in infant mortality rate
Increase in life expectancy
Changes in causes of death and disease (1900s was infectious diseases, 2000s are chronic diseases)
Healthcare system developed for acute disease (fix/leave, not chronic)
21st century focus on health promotion and disease prevention
Health demographic factors*
Health demographic factors*
Changes in standard of living/lifestyle
Advances in public health measures
Progress in medical practice, including therapeutic interventions in treatment of patients