Lab Packets 5-8 BIO172L
1/135
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MU
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
(LAB 5) Generalized Blood Vessel pathway
Arteries
Arterioles
Capillaries
Venules
Veins
In which generalized blood vessel does exchange occur?
Capillaries
In which of the generalized blood vessels is blood pressure highest?
Arteries
In which generalized blood vessels is blood pressure lowest?
Veins
What is the signifigance of the pressure gradient that exists along the circulation route listed above?
Promotes blood flow
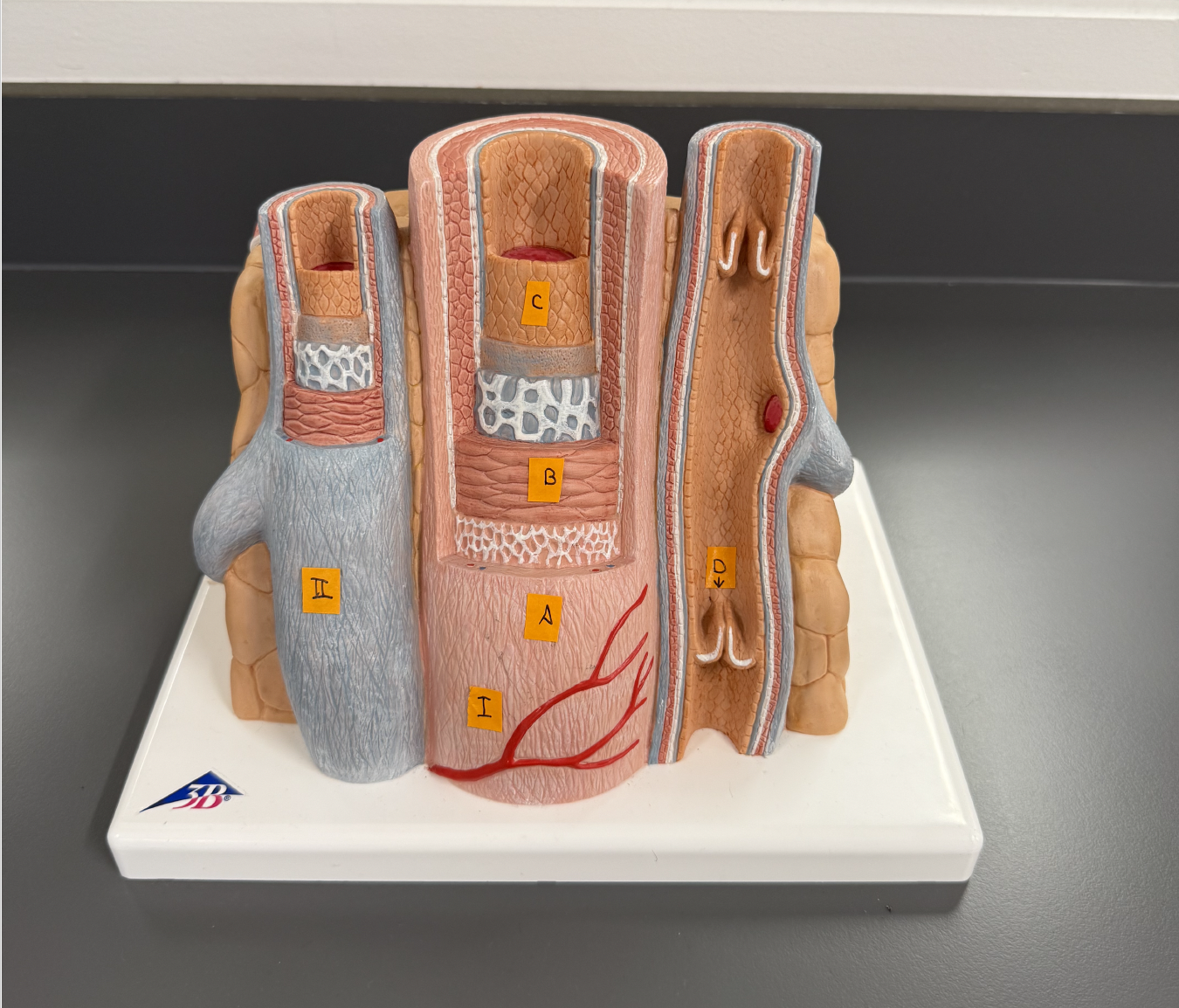
Use this for the next few questions
I. (Blood Vessel Type)
Artery
II. (Blood Vessel Type)
Vein
A. (Wall Layer)
Tunica exterina
B. (Wall Layer)
Tunica media
C. (Wall Layer)
Tunica interina
D. (Specific structure)
Venous Valve
Anatomically, how are these blood vessels alike? Different?
They both have the same layers, but only the veins have valves.
The innermost layer of these blood vessels consist of a single layer of epithelium called the ___.
Endothelium
The walls of which type of blood vessel (Not shown on the model) is essentially just this layer of cells?
Capillary
Use this image for the next few questions.
If you cant find the numbers then study the structures on google.
10.
Aorta
7.
Brachiocephalic trunk
4.
Right Common Carotid Artery
3a.
Right Subclavian Artery
C.
Left Common Carotid Artery
S.
Left Subclavian Artery
Right Subclavian Vein
II.
Left Subclavian Vein
Right Internal Jugular Vein
V.
Left Internal Jugular Vein
Right Brachiocephalic Vein
X.
Left Brachiocephalic Vein
21.
Superior Vena Cava
C. and S. supply blood to which side of the body
Left
supplies blood to which side of the body
Right
branches into two main arteries, ____
Right Subclavian Artery
Right Common Carotid Artery
17.
Pulmonary Trunk
Left Pulmonary Artery
Left Pulmonary Veins
Be able to identify:
Left Axillary Artery
Left Brachial Artery
Left Radial Artery
Left Ulnar Artery
Where must blood flow before flowing into the axillary artery?
Subclavian Artery
Be able to identify: (Not as important)
Ulnar Vein
Radial Vein
Brachial Vein
Cephalic Vein
Basilic Vein
Median Cubital Vein
Axillary Vein
Subclavian Vein
Identify the following systemic blood vessels on the model of the left leg:
Femoral Artery
Popliteal Artery
Anterior Tibial Artery
Posterior Tibial Artery
Femoral Vein
Popliteal Vein
Posterior Tibial Vein
Identify the following veins: (Not as important)
Great Saphenous Vein
Anterior Tibial Vein
Femoral Vein
Common Iliac Vein
Use this image for the next few questions:
1.
Thoracic Aorta
2.
Abdominal Aorta
3.
Celiac Trunk
4.
Right Renal Artery
5.
Superior Mesenteric Artery
6.
Inferior Mesenteric Artery
7.
Right Common Iliac Artery
8.
Left Common Carotid Artery
9.
Left Internal Carotid Artery
10.
Left External Carotid Artery
11.
Left Common Iliac Vein
Right Renal Vein
13.
Inferior Vena Cava
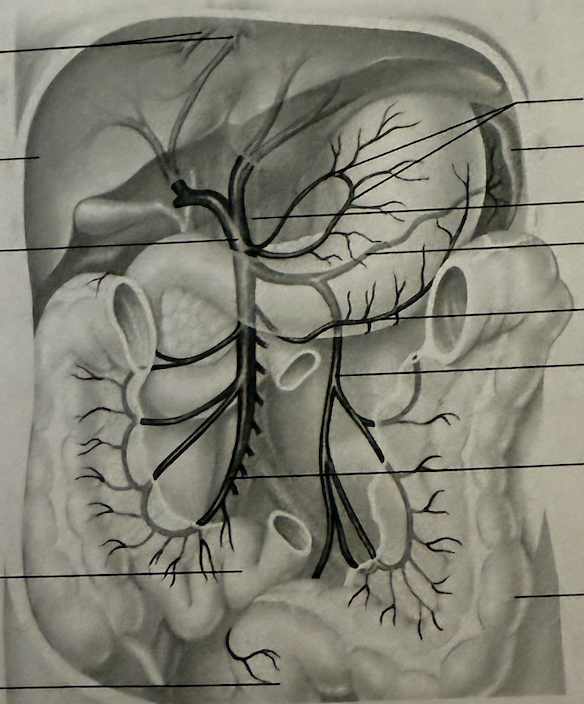
Identify the following: (Not as important)
Hepatic Portal Veins
Hepatic Portal vein
Splenic Vein
Superior Mesenteric Vein
Inferior Mesenteric Vein
Gastric Veins
What is the function of the hepatic portal vein?
Drain the digestive viscera, spleen, and pancreas and deliver this blood to the liver for processing.
(Lab 6) Explain what as pulse is.
Pressure in arteries that occurs with each contraction and relaxation of the left ventricle.
Explain what blood pressure is.
Pressure the blood exerts against any unot area of the blood vessel walls.
In most clinical situations, what blood vessel of the arm is used to take BP measurements?
Brachial Artery
How do you calculate Mean Arterial Pressure? (MAP)
DP + 1/3 (PP)=
How do you calculate Pulse Pressure? (PP)
SP-DP=
How do you calculate Cardiac Output?
Heart Rate x Stroke Volume=
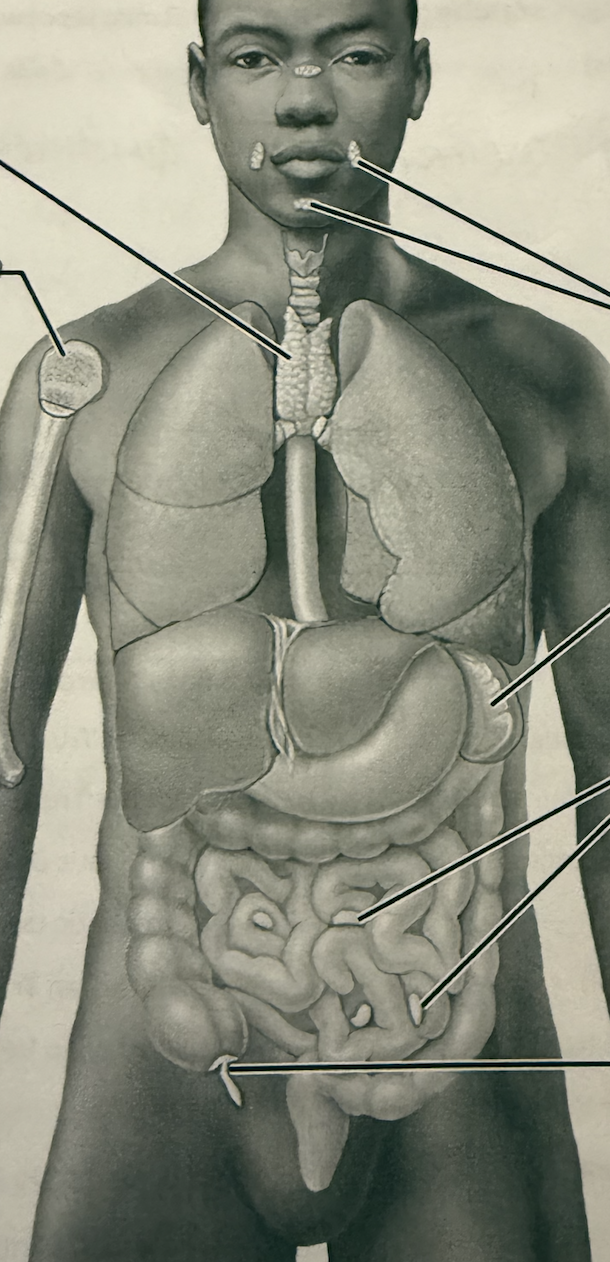
Identify the following:
Thymus
Reb Bone Marrow
Tonsils
Spleen
Peyers Patches
Appendix
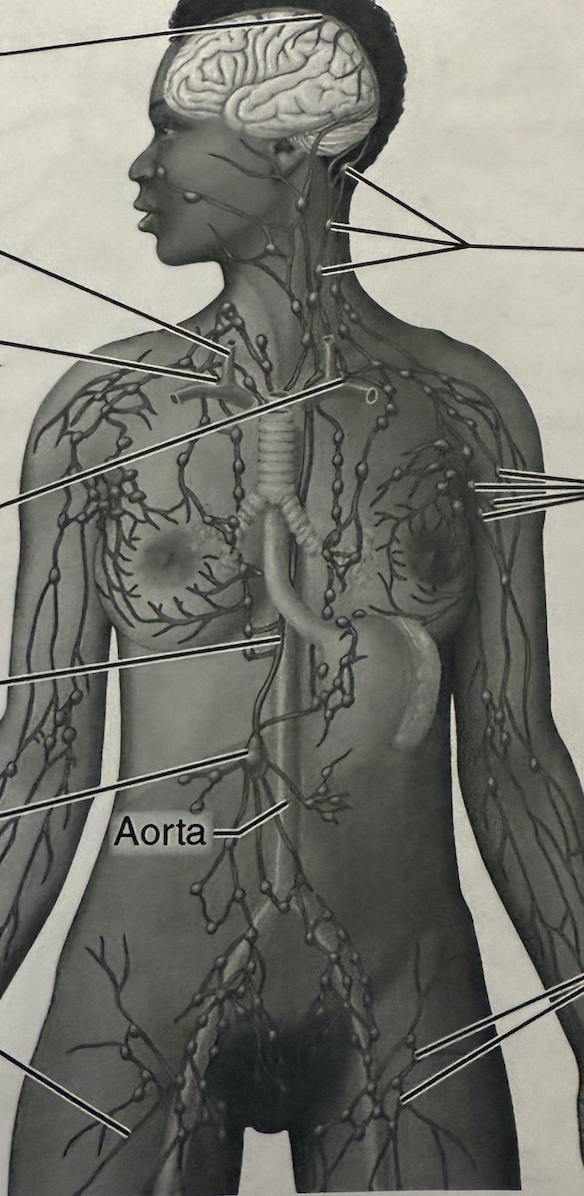
Identify the following:
Right Internal Jugular Vein
Right Lymphatic Duct
Thoracic Duct
Cisterna Chyli
Cervical Lymph Nodes
Axillary Lymph Nodes
Inguinal Lymph Nodes
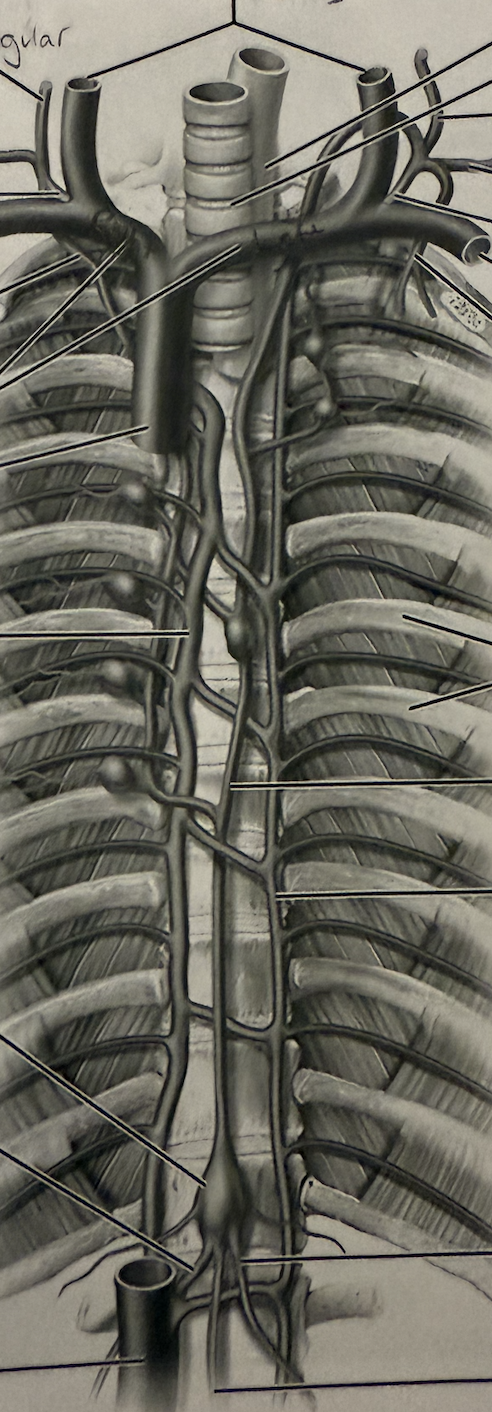
Identify the following:
Internal Jugular Veins
Right Jugular Trunk
Right Subclavian Trunk
Right Lymphatic Duct
Right Subclavian Vein
Brachiocephalic Veins
Superior Vena Cava
Cisterna Chyli
Right Lumbar Trunk
Left Jugular Trunk
Left Subclavian Trunk
Left Subclavian Vein
Thoracic Duct
Left Lumbar Trunk
Why is the lymphatic system one-way, whereas the blood vascular system is two-way?
Lymphatic system doesn’t have arteries so it only goes one-way.
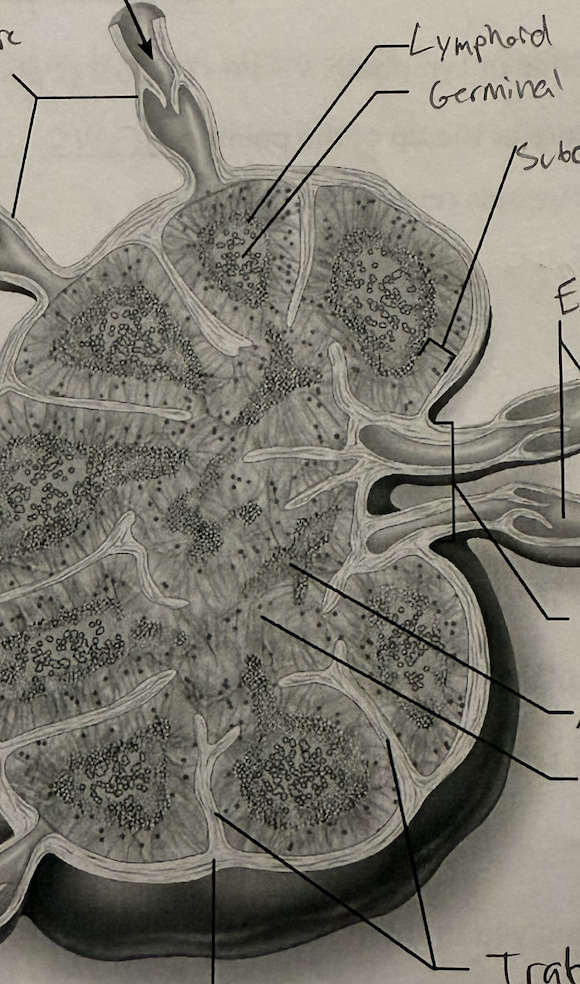
Identify the following structures:
Afferent Lymphatic Vessel
Lymphatic Follicle
Germinal Center
Subcapsular Sinus
Efferent Lymphatic Vessels
Hilum
Medullary Cord
Medullary Sinus
Trabeculae
Capsule
Lymphedema is insufficient movement of lymph, why would exercise help counter this condition?
Skeletal muscle contractions move lymph throughout the body/back to the heart.
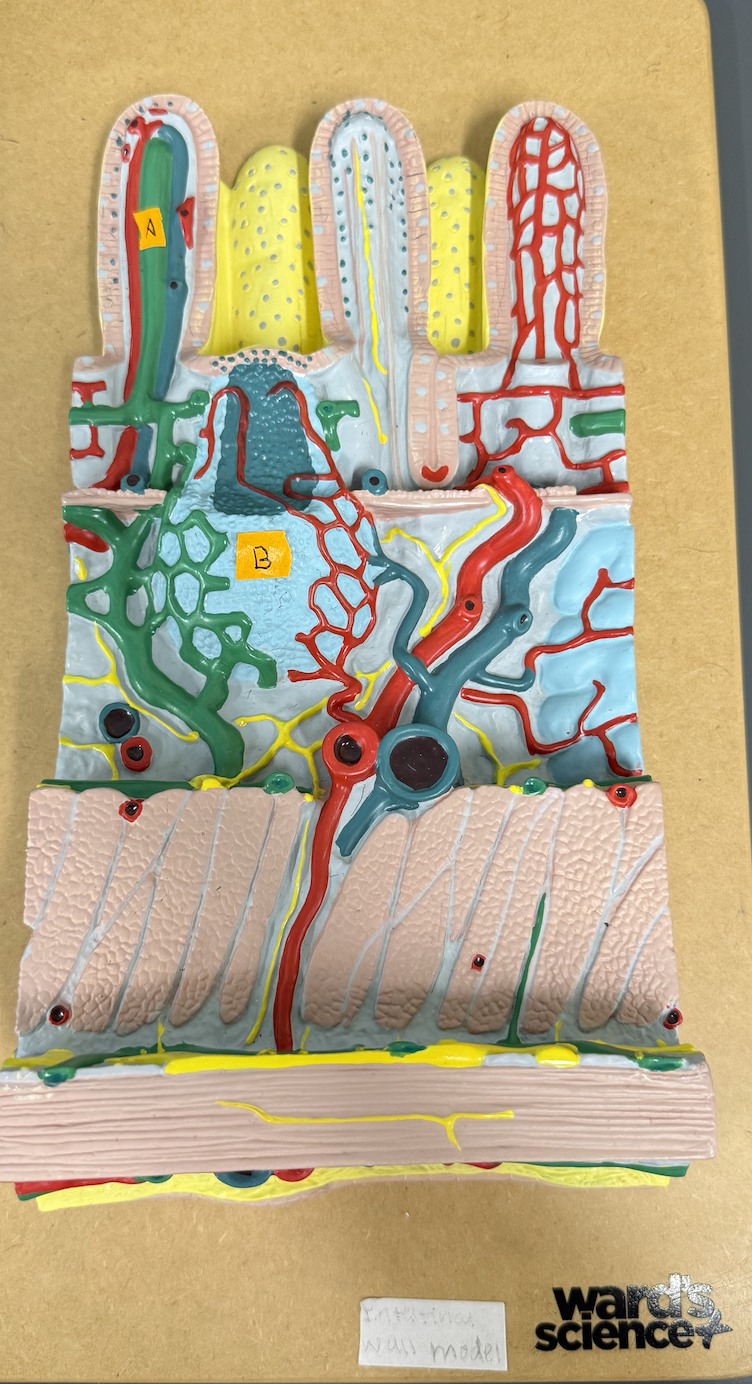
Identify structures of the intestinal wall: A and B
A: Lacteal
B: Peyer’s Patches
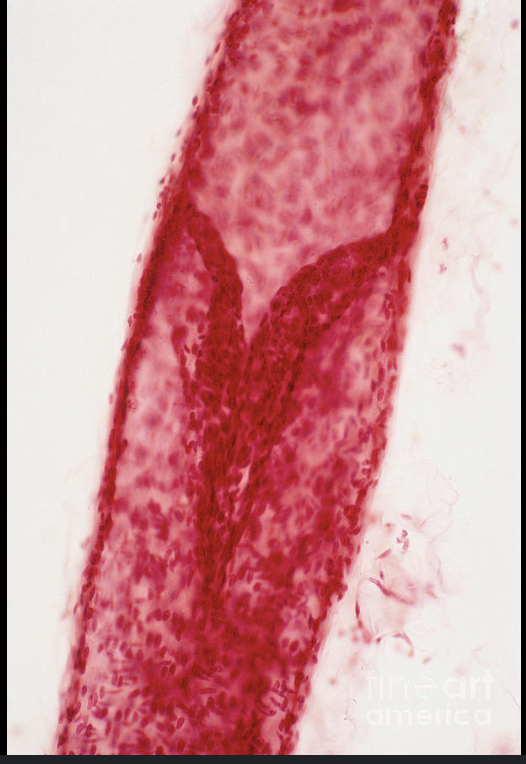
What is this structure of a lymphatic vessel?
Valve Leaflets
How do lymphatic vessels resemble veins?
They both have valves
What is the function of lymphatic vessels?
To carry lymph from the nodes to the veins
What is lymph?
Fluid absorbed by the lymph vessels from the interstical fluid
What factors contribute to lymph movement?
Valves: Control direction
Skeletal Muscle Contraction: Move it
What is the cisterna chyli?
A large lymph node in the abdomen
Which portion of the body is drained by the right lymphatic vessel?
Right arm and right chest
Identify Structures: X. Y. Z.
X: Thoracic Duct
Y: Thoracic Duct
Z: Right Lymphatic Duct
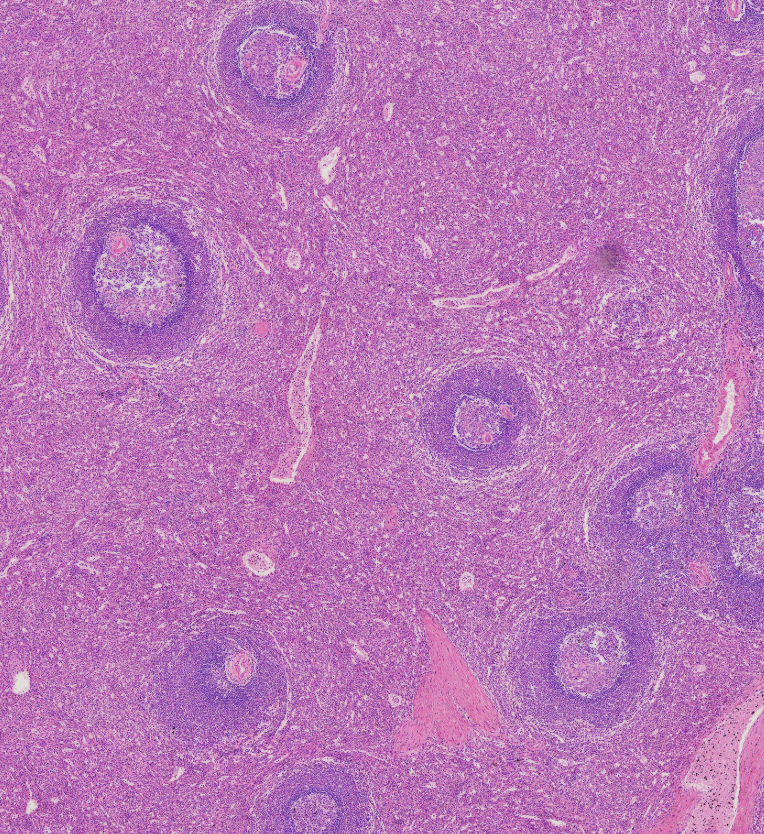
Identify Red vs. White pulp in the spleen
White: Purple Bubbles
Red: Everything Else
Which pulp is responsible for immune function?
White Pulp
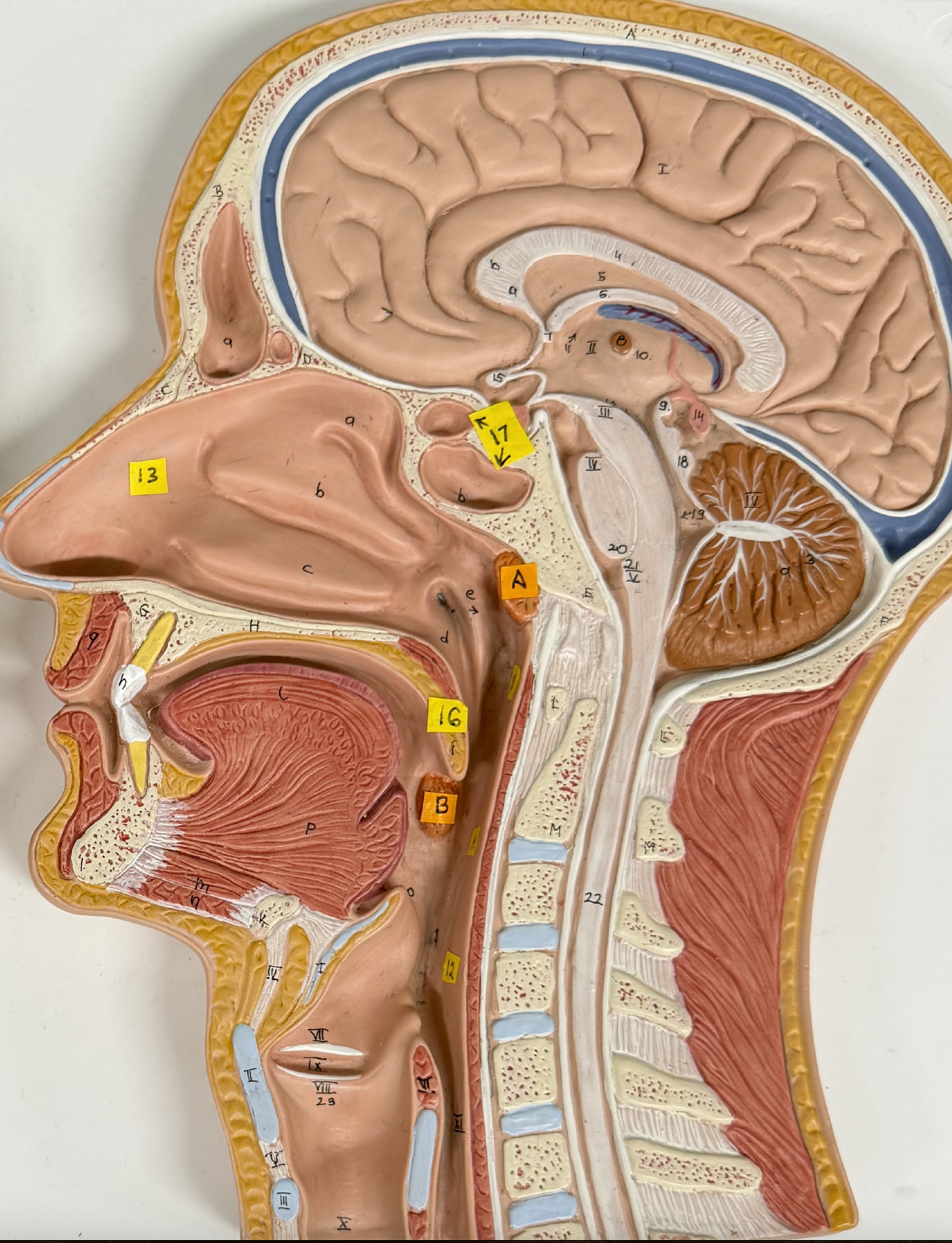
Identify tonsil structures: A. B.
A. Pharyngeal Tonsils
B. Palatine Tonsils
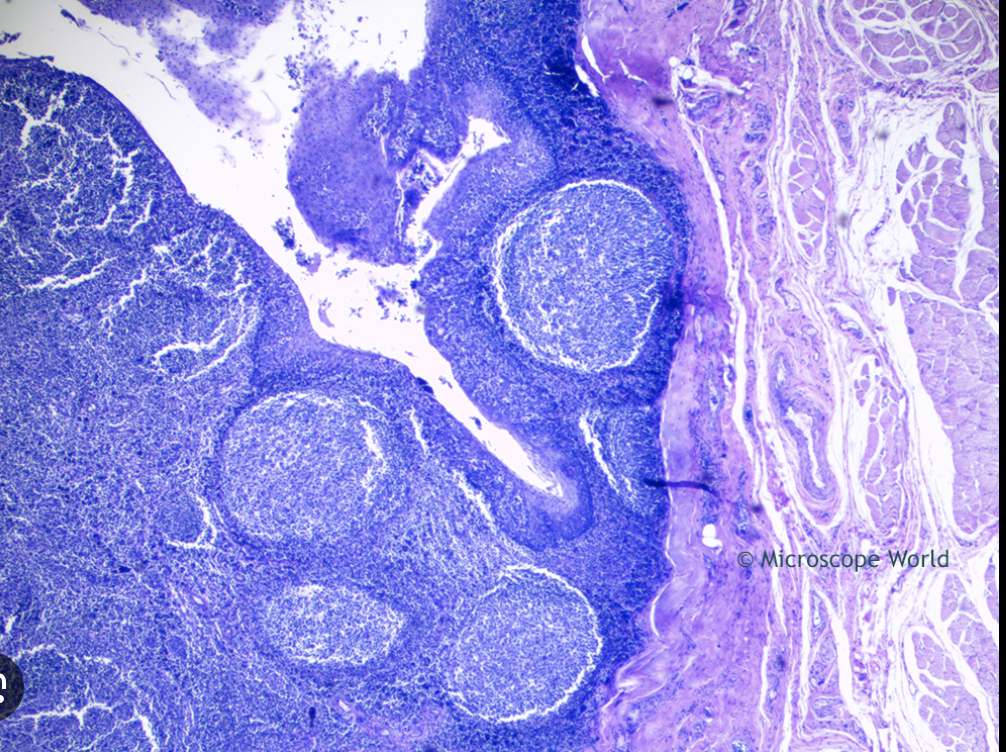
Identify the Tonsillar Crypt
The white streak going from top left to the center
What is a tonsil stone
A culmination of food, bacteria, and dead cells that calcify into a rock in your tonsils
What is the effector cell of humoral immunity?
B Cells, they create antibodies in the lymph nodes
What is the effector cell of cell-mediated immunity?
Cytotoxic T Cells, they purge infected host cells
Define Immunological memory:
The memory B and memory T cells created when exposed to a pathogen in preparation for next time.
Define specificity:
Cytotoxic T cells and B cell antibodies only react with a particular antigen/cell receptor.
Define self-tolorance:
Cytotoxic T cells and B cell antibodies recognize self antigens and don’t attack them.
(Lab 7) Major role of the respiratory system is to:
Supply the body with oxygen and dispose of CO2
List the 4 distinct process that must occur in respiration
Pulmonary Ventilation
External Respiration
Transport of Respiratory Gases
Internal Respiration
Upper respiratory structures include:
External Nose
Nasal cavity
Pharynx
Pharyngotympanic Membrane
Paranasal Sinuses
The ___ is the largest laryngeal cartilage.
Thyroid Cartilage
All but the smallest branches of the bronchial tree have ___ reinforcements in their walls.
Cartilaginous
The structural and functional units of the lungs are ___.
Alveoli
How many lobes in the left lung?
2
How many lobes in the right lung?
3
Why is it important that the trachea is reinforced with cartilage?
To keep the airway open and prevent it from sticking shut.
Why is it important that the tracheal cartilage is incomplete posteriorly?
So that the esophagus isn’t compressed.
What is the function of pleural fluid?
To lower resistance and allow the lungs to glide as they expand in the thoracic cavity.
Pathway of air:
Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Primary Bronchus
Secondary Bronchus
Tertiary Bronchus
Bronchioles
Alveoli
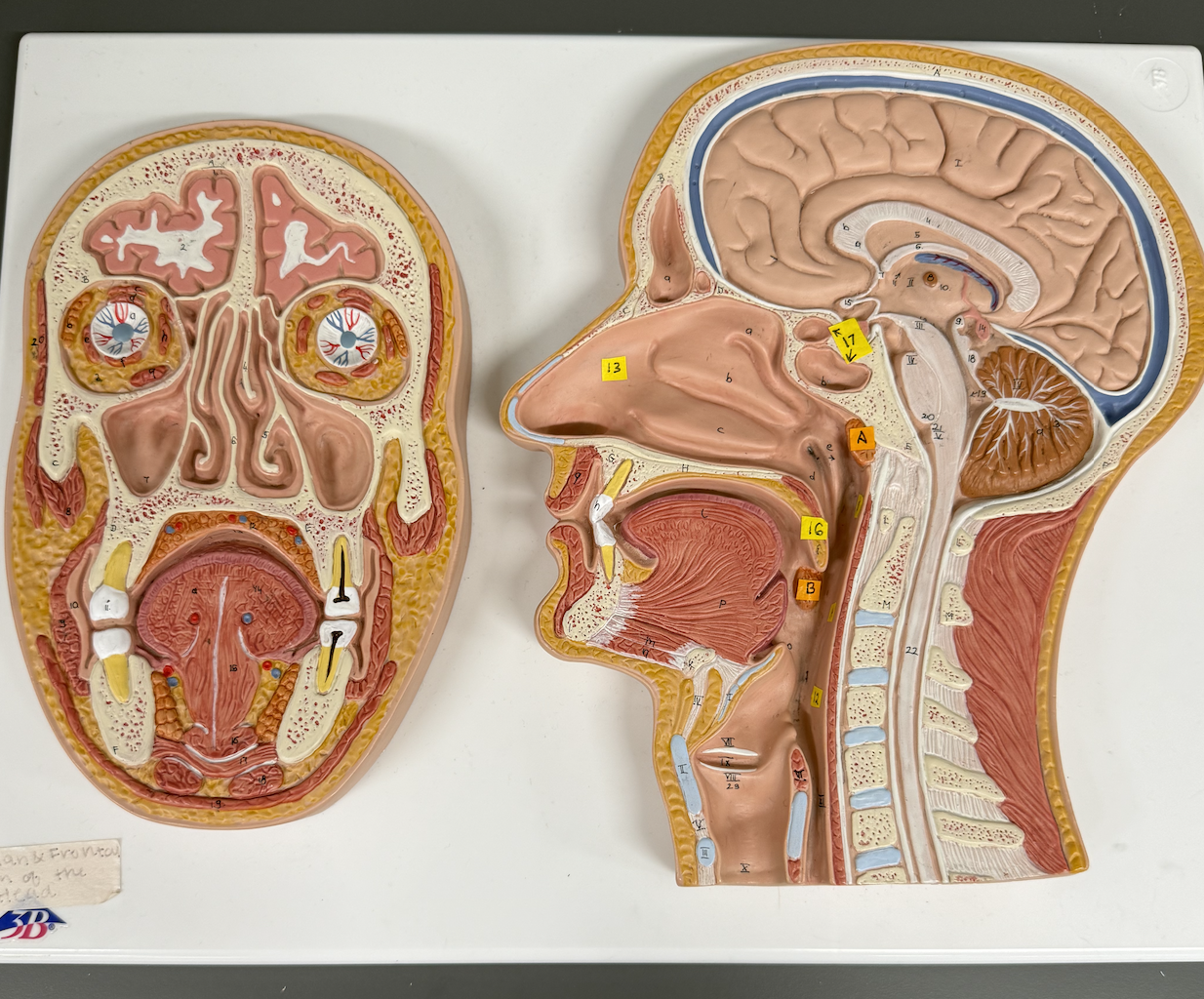
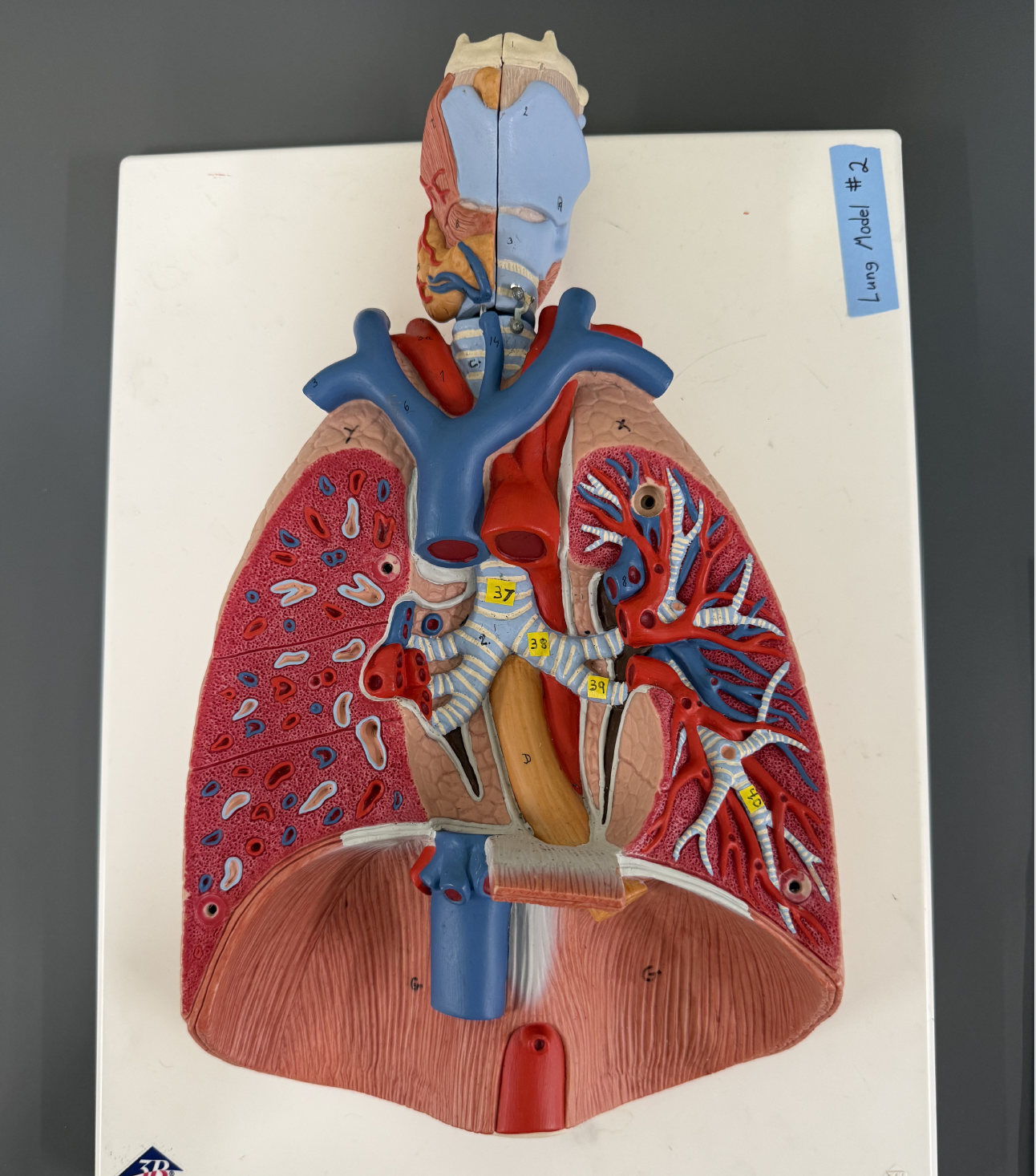
Use image to Identify the following structures: