Operations Management
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What does operations management use?
resources to appropriately create outputs that fulfil defined market requirements
What is operations management?
The activity of managing the resources which are devoted to the production and delivery of products and services
The people who are responsible for managing some or all resources that comprise the operations function
Who are operations managers?
Inputs are used to transform something or themselves into outputs of services and products.
What is the transformation process model?
Resources that are treated transformed or converted in the process to produce goods or services
What are transformed resources?
What are the 4 types of operations and processes?
Volume
Variety
Variation in demand
Visibility
Can you describe what it’s like to have low volume?
The product or service is tailored to customer needs. Low repetition, each staff member performs more of each task, less systemisation and high unit costs.
Describe having a high volume?
High repeatability, specialisation, capital intensive and low unit costs
What are some examples of low volume operations?
Food chains and car manufacturing assembly lines
Explain operations that offer a low variety of products/services.
Offers a limited range of products, focuses on efficiency and standardisation, predictability and has routine tasks
Explain operations that offer a high variety of products/services.
Allows customisation and differentiation. Flexible, matches customer needs and has high unit costs.
Explain operations that have low variation in demand.
Demand is stable and there are low unit costs. It is easier to plan capacity, workforce and inventory.
Explain operations that have high variation in demand.
Changing capacity,anticipation, flexibility, in touch with demand, high unit costs.
What are examples of operations with high variation in demand?
Hotels
Ski resorts
Hospitals
Explain low visibility within an organisation.
Customers have little or no direct contact with the production process. They only see the output
Explain high visibility within an organisation.
Customers are directly involved. Satisfaction is governed by customer perception and there are high unit costs.
Examples of high-visibility operations.
Restaurants- customers expect quick service
Call centers- Customers hang up if waiting for too long
Retail checkouts- long lines reduce customer satisfaction
What are the key features of high visibility operations?
Customers experience the process in real time
Customer satisfaction depends on both service quality and interaction quality
Operations must handle short waiting tolerance
What are the key features of low visibility operations?
Customers don’t see how the work is done so efficiency and consistency matter the most
Easier to standardise processes and focus on cost reduction
Lower pressure from customers during the process itself
What are the key features of low variety operations?
Processes are routine, repetitive and standardised
Easier to forecast demand and plan resources
Operations achieve efficiency and lower costs
Limited ability to customise for individual customers
What are the key features of high variety operations?
Processes must be flexible and adaptable
More complex scheduling, planning and inventory management
Unit costs are higher (less repetition, smaller batch sizes)
Greater opportunities for customisation and differentiation
What are the examples of transformed resources?
Materials
Information
Customers
What are transforming resources?
The resources that convert the transformed resources into outputs
What is the operations function?
The part of an organisation responsible for producing the goods or providing the services a company sells in its markets.
Explain why it is important when a product is designed how choices made shape it?
Choices made at the stage of design shape how it is produced and in turn the design of the production process influences what is feasible in the product or service itself.
Should the design of products/services and the design of processes be interrelated and treated together?
Yes
What are project processes?
A one time set of coordinated activities aimed at creating a unique product or service often involving high customization complex planning and defined start and end points.
What is a jobbing process?
products are made in small quantities often as one-off items or in very low volumes
they are tailored to meet specific customer requirements.
What are some examples of jobbing processes?
Custom furniture
producing specialist machinery
tailoring clothing
In jobbing processes the focus is on what?
customisation and quality rather than speed or low cost
What is a batch process?
higher volumes but lower variety than for jobbing
What is an example of a batch process?
Bakery bakes 200 loaves in one batch stops then produces some more
Explain a mass (line) process?
standardised products are made in very large volumes but with a low variety.
What are some examples of mass production processes?
Car assembly lines
electronics manufacturing
Explain a continuous process.
Extremely high volume and low variety where production is never stopped
High volume allows them to reduce production costs which reduces the cost of the goods
What are the manufacturing process types?
Project
Jobbing
Batch
Mass
Continuous
What is professional service?
High contact customized and knowledge intensive operations where skilled professionals use their expertise to deliver tailored solutions to individual clients.
What are service shops?
service shops handle a range of services that can be partly standardised but still tailored to each customer’s situation
sits in between professional and mass services
What are mass services?
It aims to deliver the same or very similar standardised service repeatedly to many people
What are the five performance objectives ?
Quality
Speed
Dependability
Flexibility
Cost
What are the two important things you must remember for manufacturing businesses?
Volume
Variety
What happens to variety when we have a high volume and vice versa?
High volume- low variety
High variety- low volume
What are the 3 service process types?
Professional service
Service shop
Mass service
What is process mapping?
Understanding the journey of those goods and services
What can be done to improve that (reflecting upon the five performance objectives)
What are the seven types of waste that exist?
Transportation
Inventory
Motion
Waiting
Overproduction
Overprocessing
Defects
What are the 3 ways of categorising waste?
Value add (VA) activities
Non-value add (NVA) activities
Necessary NVA (NNVA) activities
What are value add activities (waste)?
Anything a customer is willing to pay for because it transforms the product in a meaningful way
What are non value add activities (waste)?
activities that consume resources but do not add value from the customer’s perspective
customer is not willing to pay for these activities
What are necessary NVA activities (waste)?
Essential for us to pay
What are the primary examinations of each activity?
Purpose- What is achieved
Place- Where is it done
Sequence- When is it done
Person - Who does it
Means- How is it done
What are the secondary examinations of each activity?
Purpose- What else could/should be done
Place- Where else could/should it be done
Sequence - When else could/should it be done
Person - Who else could/should do it
Means - How else could/should it be done
What are the ways in which operations differ?
volume variety variation in demand visibility of their output
What is a project?
A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result, characterized by a defined beginning and end, specific objectives, and constraints such as time, budget, and resources.
What is a general characteristic of a project?
Projects are building blocks in the design and execution of organisational strategies.
What are the principal outcomes of a project?
The satisfaction of customer requirements and the delivery of project objectives on time and within budget.
When are projects terminated?
Projects are terminated upon achieving their objectives, when they are no longer viable, or when they are deemed unnecessary by stakeholders.
What are the differences between process and project management?
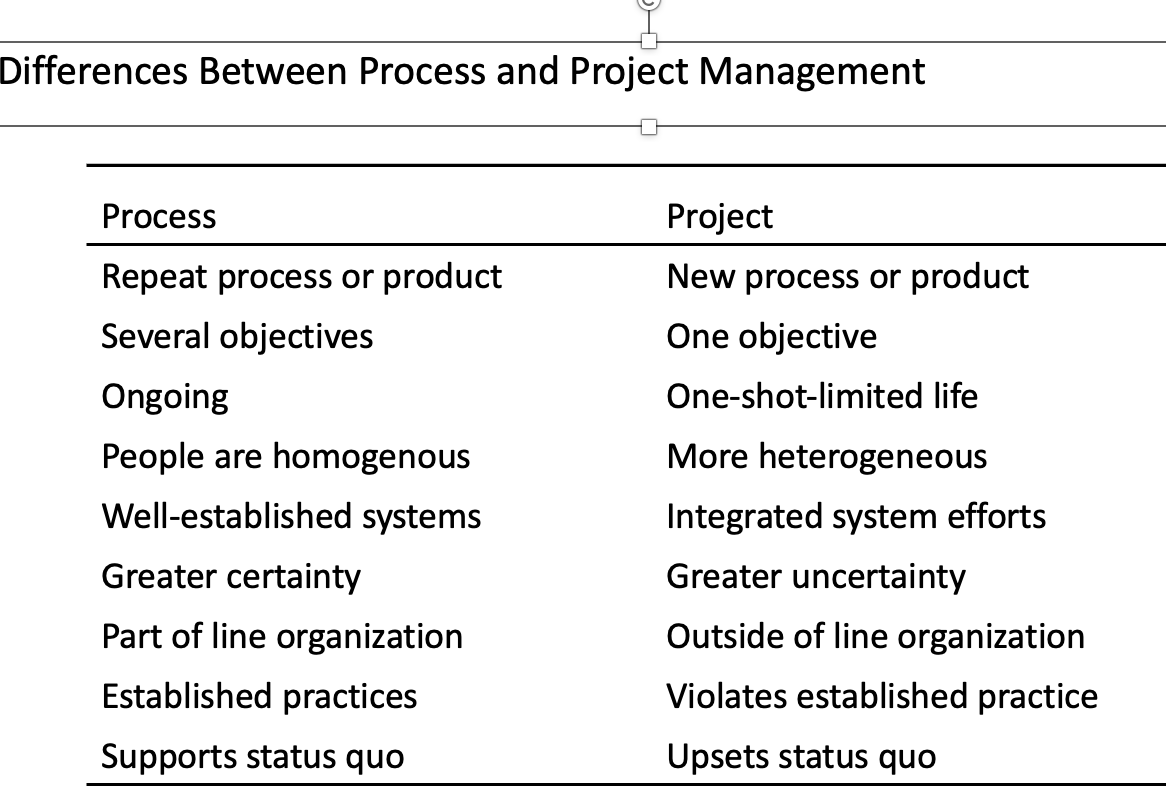
Why are projects important?
Shortened product life cycles
Narrow product launch windows
Increasingly complex and technical products
Emergence of global markets
An economic period marked by low inflation
What is the diagram for project life cycle stages?
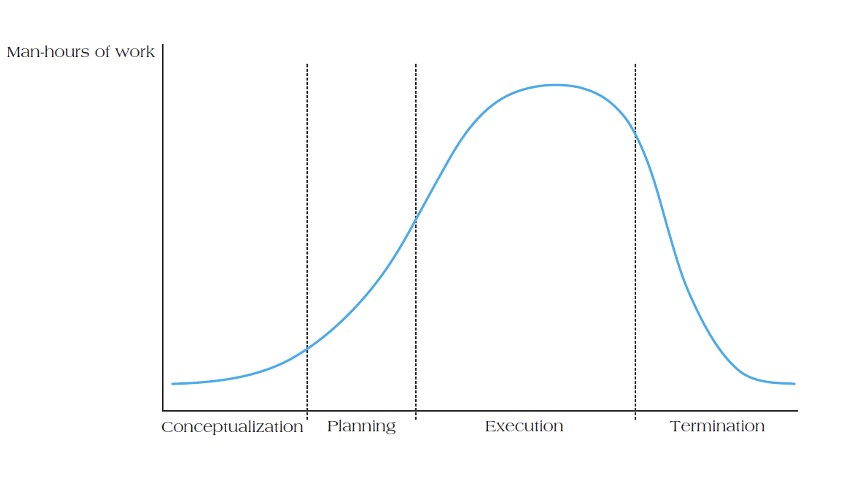
What is a project life cycle?
the stages in a project’s development
What are the four distinct phases of a project’s life cycle?
Conceptualization
Planning
Execution
Termination
Explain conceptualisation in a projects life cycle.
development of the initial goal and technical specifications of the project
Explain Planning in a projects life cycle.
All detailed specifications, schedules, schematics and plans are developed.
Explain execution in a projects life cycle.
The actual “work” of the project is performed.
Explain termination in a projects life cycle.
The project is transferred to the customer, resources reassigned and the project is closed out.
What is the quadruple constraint of project success?
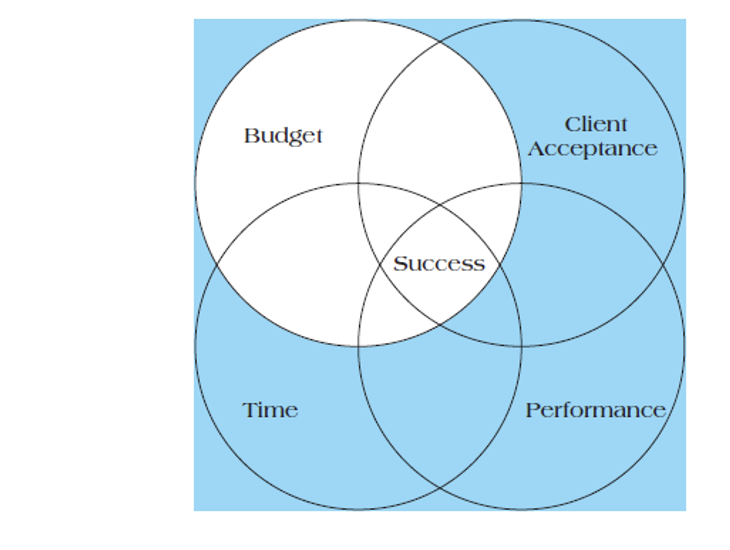
What is the iron triangle when it comes to success in a project?
cost
quality (scope)
time
What must a project meet in order to be successful?
iron triangle
What is a project scope?
what is and isn’t included in a project
What is scope management?
The process of controlling all the work required within a project
What is conceptual development?
The process that addresses project objectives by identifying and evaluating the best ways to meet them.
What is a statement of work?
A formal document that contains
Introduction and background
Technical description of the project
Timeline and milestones
What is a project charter?
A document issued by the project initiator or sponsor formally sanctioning existence of the project and authorises the project manager to begin applying organisational resources to project activities.
What is included in a scope statement?
Establish project goal criteria to include: cost, schedule,performace,deliverables
Develop management plan for project
Establish a work breakdown structure
Create a scope baseline
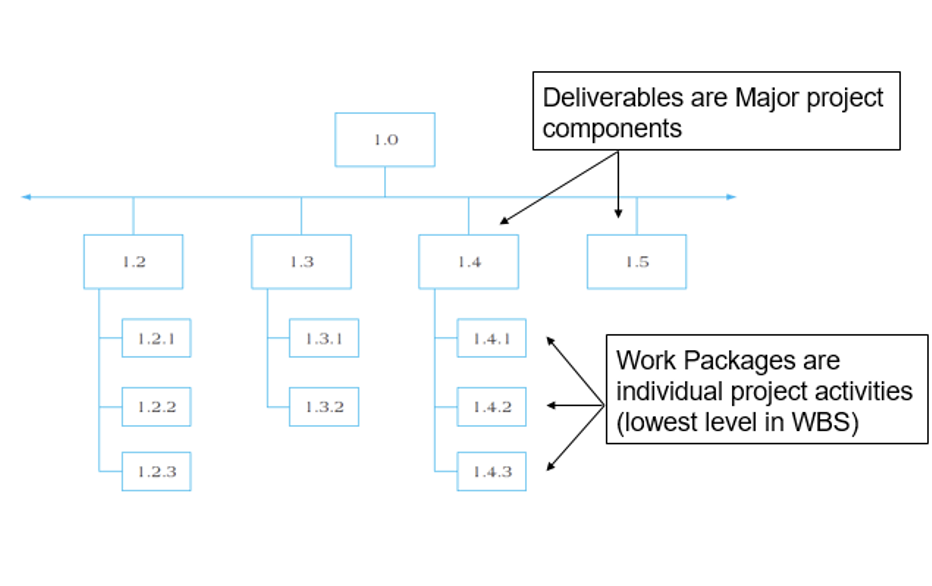
What is a work breakdown structure?
A hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the project deliverables.
What is the logic of hierarchy the WBS follows?
Project
Deliverable
Subdeliverable
Work package
What is a work package?
It is the lowest level in the work breakdown structure.
Deliverable result
One owner
Miniature projects
What is the partial work breakdown structure?
What is the organizational breakdown structure?
It acts as a blueprint to project managers.
What is work authorisation?
The formal “go ahead” to begin work.
What is scope reporting?
Monitoring how well the project is staying within its defined boundaries of work, deliverables and objectives
Why may projects fail?
Poor planning
Unclear objectives
Poor communication
Inadequate resources
Unrealistic timeframes and budgets
Why may there be project changes?
Initial planning errors, either technological or human
Additional knowledge of project or environmental conditions
Uncontrollable mandates
Client requests
What does it mean if a service is standardized?
Not tailored individually
What are some examples of mass services?
Banking Airlines Retail
What is Breakeven Analysis in the context of production planning?
It addresses the decision of whether to make or buy a product.
When making a product what are the two costs involved?
Fixed costs
Variable costs
What must firms operate above to achieve profitability?
above the breakeven point
What is the formula for Breakeven point?
BEP: revenue= total cost
What are profit/loss corridors?
profit corridor- area between revenue and total cost line to right of BEP
loss corridor- area between revenue and total cost line to left of BEP
When buying a product as to making one what happens to fixed costs and variable costs?
Buying usually decreases fixed costs but increases variable costs
Breakeven analysis can be used to decide what?
Whether a business venture will succeed or not
Type and capacity of equipment needed
Whether to produce a product or outsource it
What are the steps to the decision making process?
Define problem
Identify alternatives
Determine decision making criteria
Evaluate alternatives using criteria
Choose an alternative
What are the 4 decision types?
Certain decisions
Uncertain decisions
Risky decisions
Competitive decisions
What are the 4 stages under decision making under uncertainty?
What decision alternatives do we have?
What are all the possible scenarios including future events?
What are the payoffs for each decision and state of nature?
What do I value?
What is the maximax decision rule?
Determine the best possible payoff for each scenario
Choose alternative with highest maximum payoff
What is the maximin decision rule?
Determine the worst possible payoff for each choice
Choose “best worst” alternative
What is laplace decision making rule?
Determine average payoff for each option
Choose alternative with best average benefit
What is the minimax decision making rule?
Calculate regret for each alternative under each source
Choose alternative with the smallest regret
What is the maximum likelihood decision making rule?
Choose the option with highest payoff for state of nature deemed most likely to occur