3.5 - CompTIA A+ Core 1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Motherboard
The main circuit board in a computer responsible for connecting all components such as CPU, memory, storage, and peripherals.
Advanced Technology Extended (ATX)
A standard motherboard form factor established by Intel in 1995, commonly used in laptops and desktops.
microATX
A smaller motherboard form factor designed to be a more compact version of the ATX standard.
Mini Information Technology eXtended (Mini ITX)
A low-power motherboard form factor developed by VIA Technologies in 2001, suitable for compact systems.
Small form factor
Refers to motherboards that are designed to fit into smaller cases, optimizing space and cooling.
Power connectors
The main power for ATX motherboards typically uses a 20-pin or 24-pin connector and may include additional 4/8-pin connectors for the CPU.
Screw-compatible with ATX
Refers to the ability of smaller ITX motherboards to use screws designed for ATX motherboards.
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)
Standard for connecting external devices (i.e., expansion slots) to a computer.
Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe)
Newer and faster standard used to connect external devices to a motherboard, utilizing a serial interface.
SATA
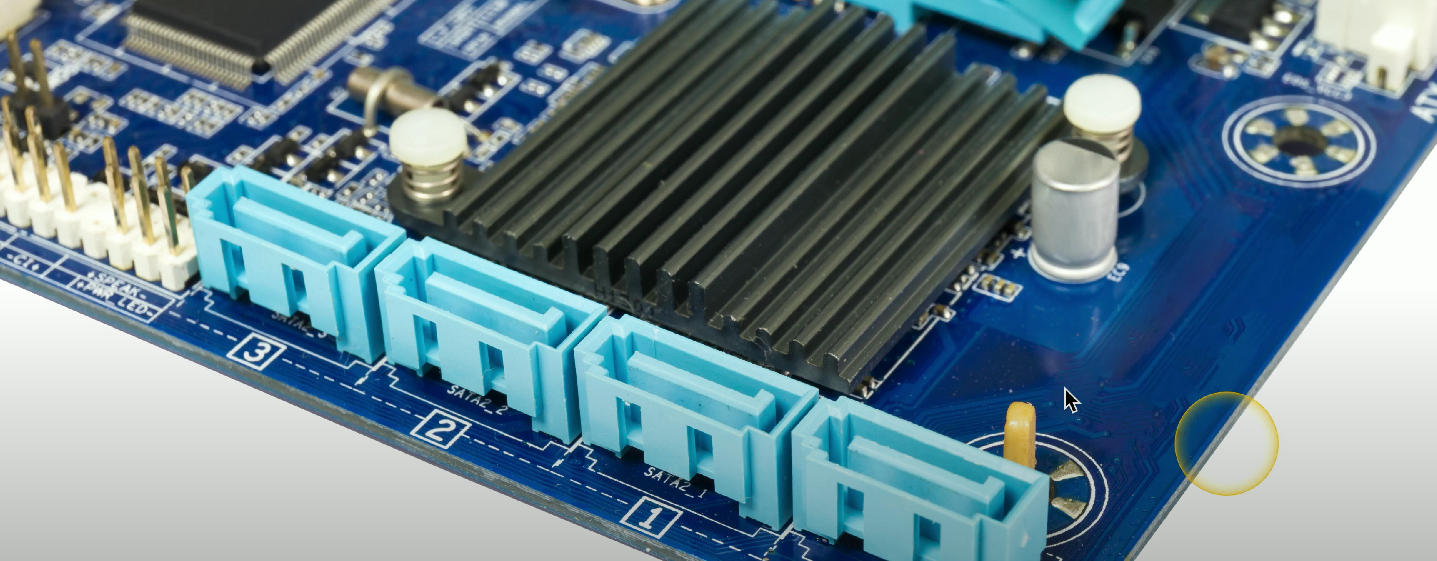
Connector/communication interface used to connect storage devices like HDDs and SSDs.
eSATA
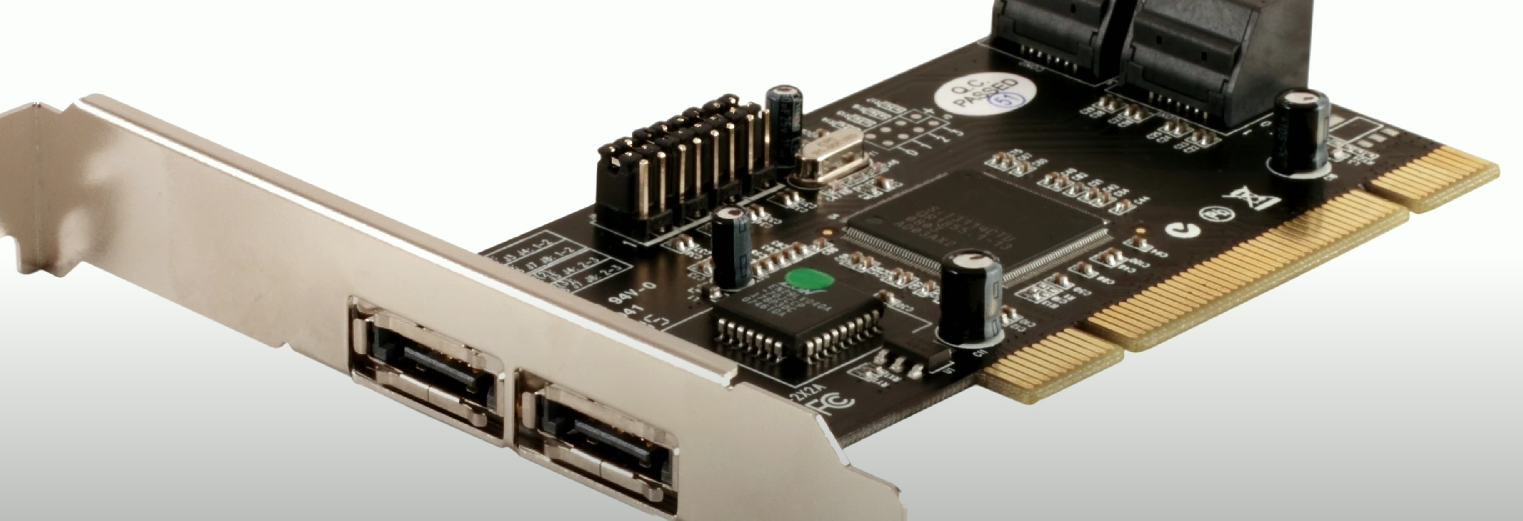
External form of SATA used for connecting external hard drives and solid-state drives.
Pin headers
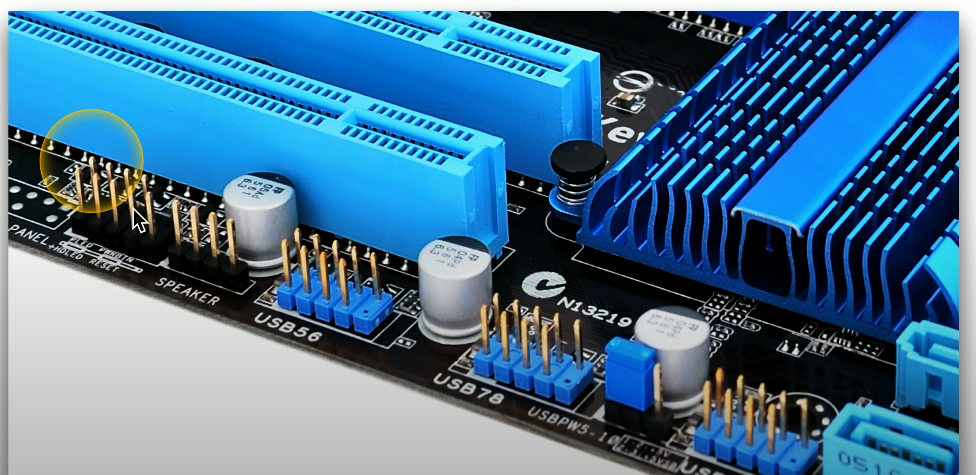
Simple electrical interfaces used to attach connectors for various functions such as power, peripheral connections, lights, and buttons.
M.2

Smaller form factor hard drive for SSDs that allows for high-speed data transfer with modular installation into the motherboard.
Desktop Motherboard
A full-size motherboard for desktops, typically featuring a single CPU and 2-4 memory slots.
Laptop Motherboard
A compact motherboard designed to be small, light, and portable, with limited modification options and usually proprietary.
24-pin Motherboard Connector

The main source of power for the motherboard, which connects to the power supply and provides power to internal components.
4-pin ATX 12V Connector
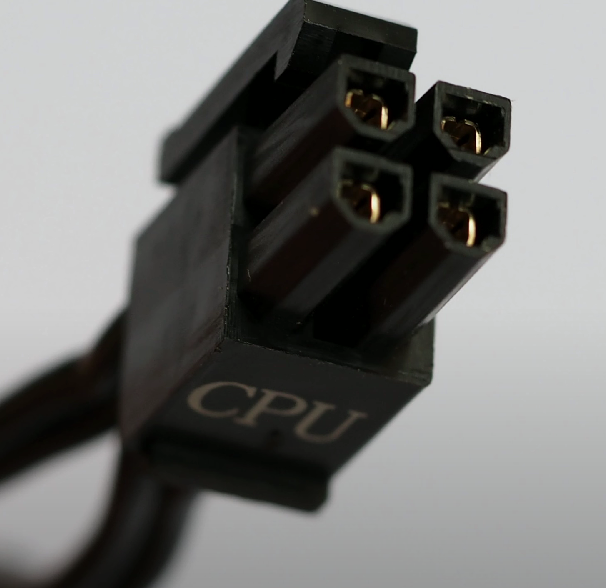
An additional power connector providing 12V to older motherboards, often labeled as ATX12V, P4, or CPU.
Multi-Socket
A motherboard configuration that allows support for multiple physical CPU packages to handle higher loads.
AMD (Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.)
Historically known as the more cost-effective CPU vendor.
Intel
Typically recognized as the higher-performance CPU vendor.
Thermal Throttling
A mechanism that reduces CPU speed to prevent overheating, commonly experienced in laptop CPUs.
Expansion Slots
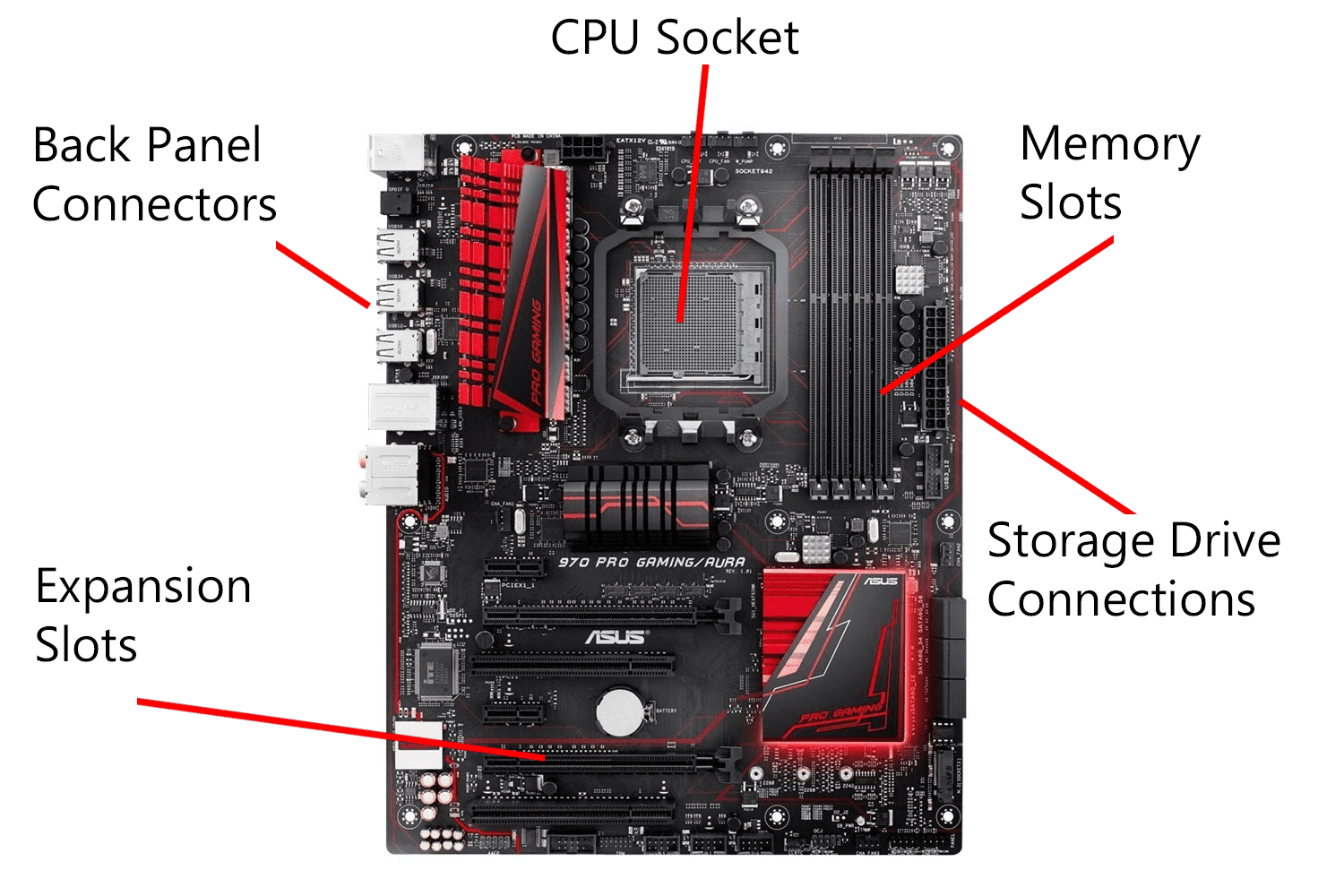
Slots on a motherboard that allow additional hardware components to be added, with more available on desktops than laptops.
Server Motherboard
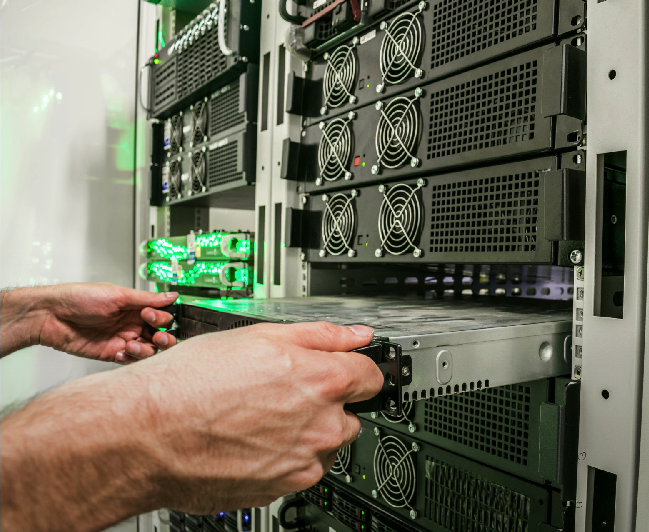

A type of motherboard designed for servers, often featuring multiple CPU support and larger ATX form factors.
BIOS
Basic Input/Output System - software used to start your computer.
POST
Power-On-Self-Test - checks for the memory, CPU, and input devices during startup.
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
Standard form of BIOS that can be used across multiple manufacturers; designed to replace legacy BIOS systems.
CMOS battery
Legacy BIOS component used for date/time configuration, not required in modern flash-based storage.
USB permissions
Security settings that restrict USB device use to maintain security, configured in UEFI/BIOS.
Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
Hardware designed for encryption on hard drives, generating keys with a cryptographic processor.
Secure Boot
A UEFI feature that checks digital signatures to prevent unauthorized BIOS updates.
Boot/BIOS password
Prevents system startup without the user password; the supervisor password is needed for configuration changes.
Temperature monitoring
Process of tracking computer heat, essential for ensuring appropriate cooling.
Fan considerations
Different cooling fans are used for CPU and chassis to manage heat generated by computing power.
Virtual computing capabilities
It allows other operating systems to be run within a single hardware platform.
Virtualization addition to CPU
It is typically added to hardware components like the CPU for faster and easier management.
Intel Virtualization Technology (VT)
Technology that supports virtualization for Intel CPUs.
AMD Virtualization (AMD-V)
Technology that supports virtualization for AMD CPUs.
x86
Alternate name for a 32-bit CPU architecture
x64
Alternate name for a 64-bit CPU architecture
Data access for a 32-bit processor
A 32-bit processor can access up to 2³² bits of information, which is 4,294,967,296 values.
Data access for a 64-bit processor
A 64-bit processor can access up to 2^64 bits of information, which is 18,446,774,073,709,551,616 values.
What is the maximum memory capacity a 32-bit OS can manage?
A 32-bit OS can only support up to 4 GB of memory.
64-bit OS application support
A 64-bit OS can support both 32-bit and 64-bit applications.
Benefits of Advanced RISC (ARM) architecture
It includes efficient/fast processing, less power use, and less heat production.
Deices that use ARM architecture
Traditionally mobile and IoT devices.
Core configurations in motherboards
Motherboards can have multiple CPU cores that distribute processing demands.
Different core types
They are referred to as dual-core, multi-core, or quad-core.
Purpose of CPU caches
Caches are designed to speed up information processing to and from the CPU.
Expansion Card
A hardware component that allows extended computer functionality, requiring insertion into a motherboard slot and possibly driver installation.
Sound Card
An expansion card that outputs high-end audio for applications like headphones or home theaters and allows multiple inputs for music capture or podcasting.
Video Card
Also known as a discrete graphics card, this component provides higher performance graphics than integrated options and is typically used for gaming and high-performance applications.
Capture Card
A device that allows video input and capture into a system, commonly used for live streaming or connecting external cameras.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
An expansion card that provides Ethernet or wireless connectivity, used when the motherboard lacks a functional onboard NIC.
PCI Express
A high-speed interface standard used for connecting expansion cards like video cards due to its high bandwidth capabilities.
Check the manufacturer documentation for ___ installation
driver
Some expansion cards may require old drivers to be removed via ____
Windows Device Manager
You can also manually install drivers via ______
Windows Device Manager
Cooling
The process of removing heat from computer components to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Active Cooling
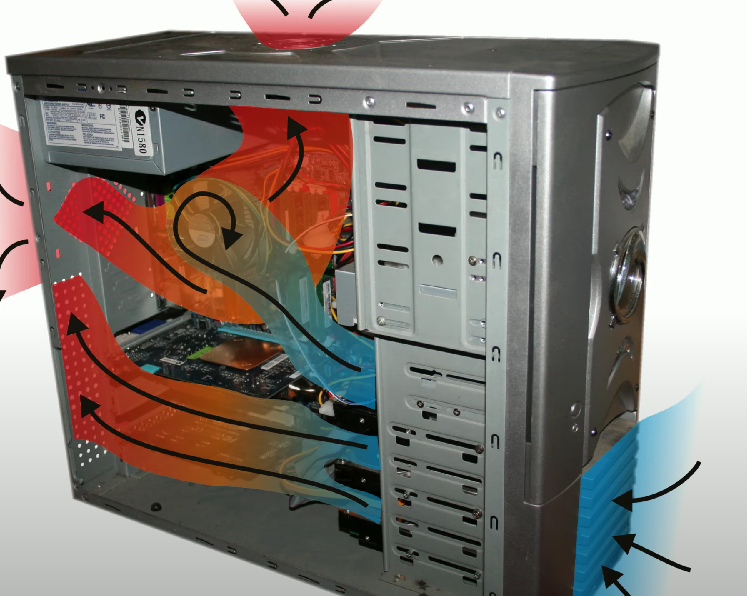

A method that uses fans or liquid coolants to actively remove heat from components in a computer.
On-board fans
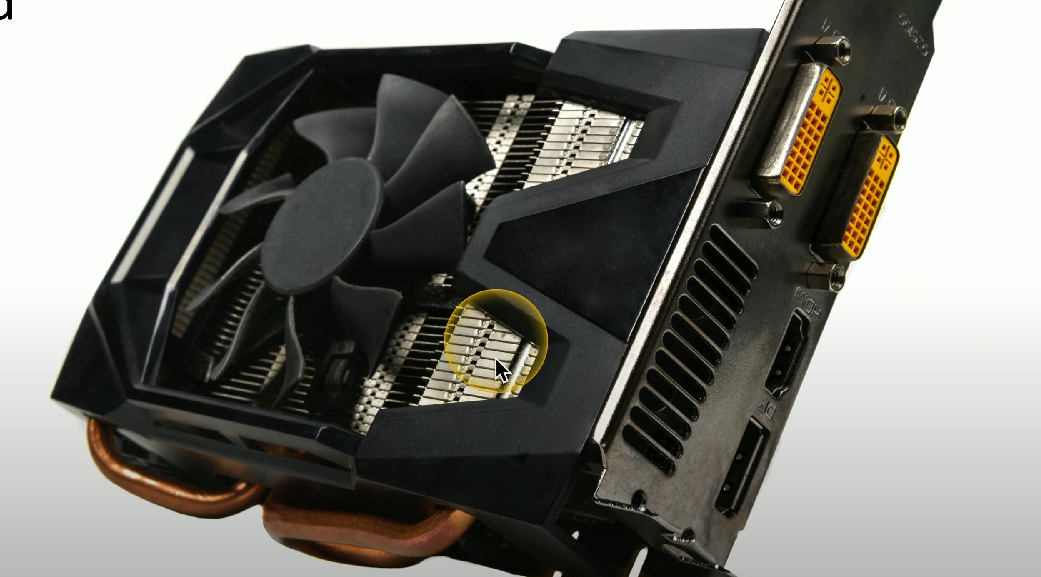

Fans designed to cool an entire adapter or expansion card, often bulky and typically seen on high-end graphics cards.
Heat Sink
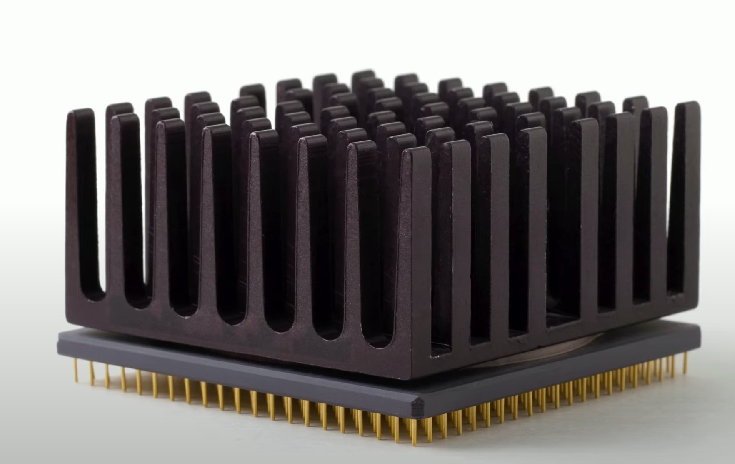

A component made of copper or aluminum that transfers heat away from internal components and dissipates it into a medium.
Passive Cooling
Cooling method that relies on heat sinks and does not use fans or active components.
Thermal Paste
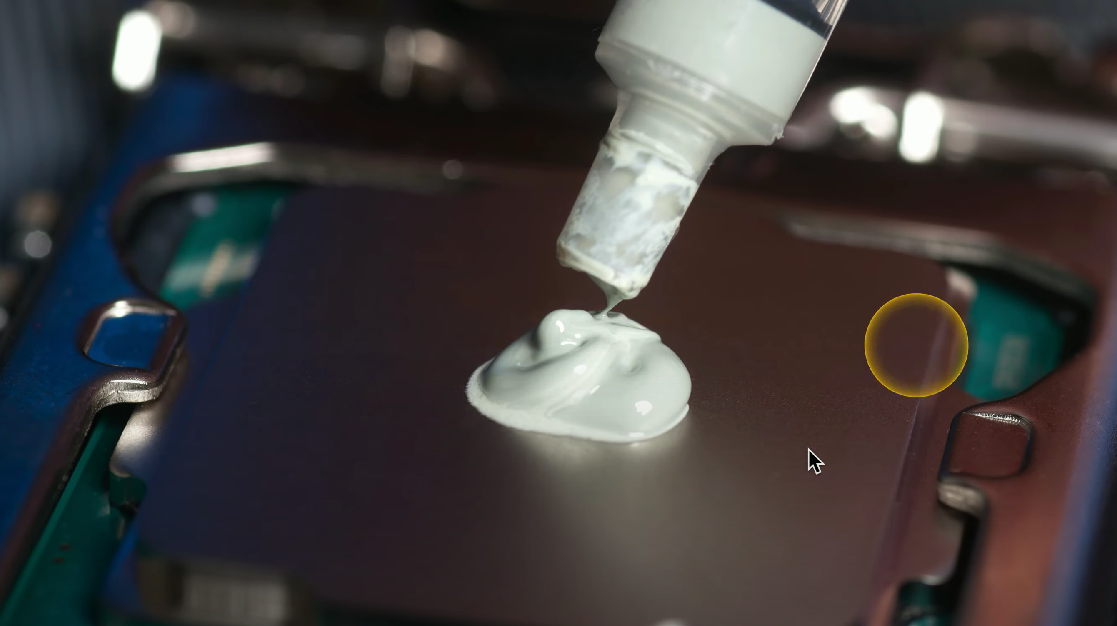

A conductive grease placed between a heat sink and a component to enhance thermal conductivity.
Thermal Pads
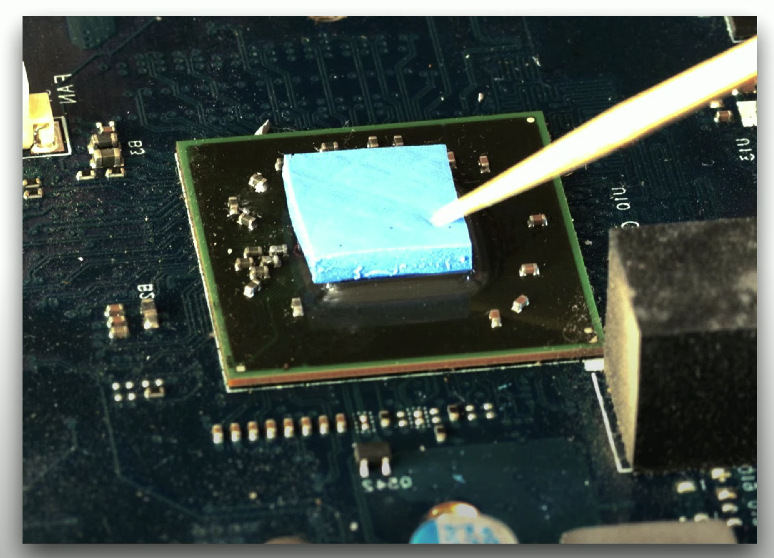
Non-reusable materials placed between heat sinks and components, requiring replacement each time a heat sink is removed.
Liquid Cooling
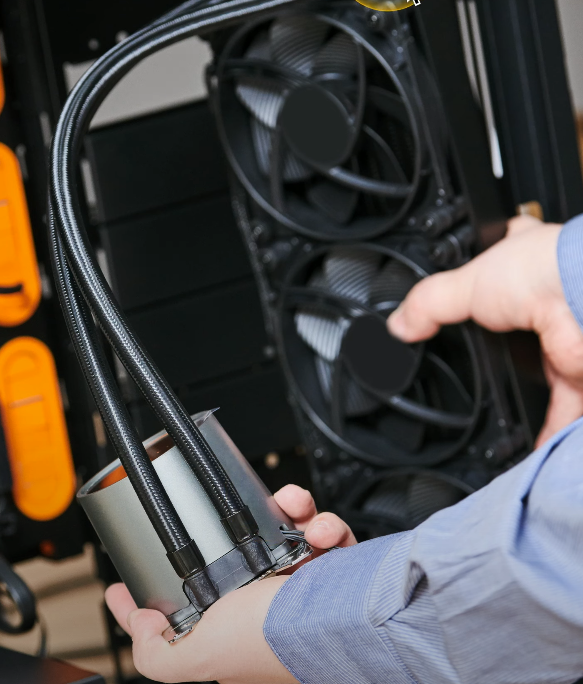

A type of active cooling that uses liquid coolant to circulate through a computer for enhanced cooling.