Properties of Sound
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I recommend reviewing the Electromagnetic Spectrum and waves unit before reviewing this one.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
1
New cards
What is a vibration?
The complete back-and-forth motion of an object. The picture shows one way sound is made by vibrations.
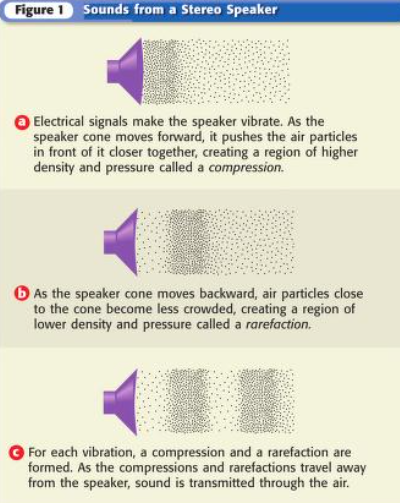
2
New cards
What are longitudinal waves?
Waves that are made of compressions and rarefactions.
3
New cards
What is a sound wave?
A longitudinal wave caused by vibrations and carried through a substance/a material medium. Particles of the substance, such as air particles, vibrate back and forth along the path that the sound wave travels.
4
New cards
How is sound transmitted?
Sound is transmitted through the vibrations and collisions of the particles. Sound travels as longitudinal waves because particles vibrate back and forth along the paths that sound travels.
5
New cards
Where do sound waves travel to?
All directions away from their source. However, air or other matter does not travel with the sound waves. The particles of air only vibrate back and forth.

6
New cards
The speed of sound depends only on…
the medium in which the sound is traveling. Sound travels quickly through air, but it travels even faster in liquids and even faster in solids.
7
New cards
What affects the speed of sound?
Temperature. In general, the cooler the medium is, the slower the speed of sound. Particles of cool materials move more slowly and transmit energy more slowly than particles do in warmer materials.
*A medium is a substance through which a wave can travel/a physical environment in which phenomena can occur. Most of the sounds that you hear travel through air at least part of the time- but sound waves can also travel through other materials, such as water, glass, and metal.*
*A medium is a substance through which a wave can travel/a physical environment in which phenomena can occur. Most of the sounds that you hear travel through air at least part of the time- but sound waves can also travel through other materials, such as water, glass, and metal.*
8
New cards
What is pitch?
A measure of how high or low a sound is perceived to be, depending on the frequency of the sound wave.
9
New cards
What is frequency of a wave?
The number of crests or throughs that are made in a given time. Frequency is expressed in hertz (Hz) where 1 Hz=1 wave per second.
*(image explains what crests and throughs are)*
*(image explains what crests and throughs are)*
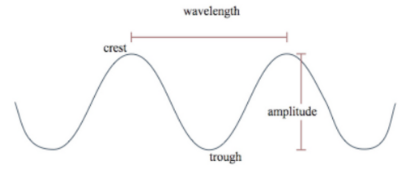
10
New cards
What is the Doppler Effect?
The doppler effect is the apparent change in the frequency of a sound caused by the motion of either the listener or the source of the sound.
For example, if you have ever passed a car with its horn honking, you probably heard the sudden change in pitch as the car passed you. The pitch you heard was higher as the car moved toward you than it was after the car passed. This was a result of the doppler effect.
For example, if you have ever passed a car with its horn honking, you probably heard the sudden change in pitch as the car passed you. The pitch you heard was higher as the car moved toward you than it was after the car passed. This was a result of the doppler effect.
11
New cards
In a moving sound source, such as a car with its horn honking, sound waves that are moving forward are going…
In the same direction that the car is moving. As a result, the compressions and rarefactions of the sound wave will be closer together than they would be if the sound source was not moving.

12
New cards
How would the frequency and the pitch of the sound of the horn sound to someone in front of the car?
The frequency and the pitch would sound high. After the car passes, it is moving in the opposite direction that the sound waves are moving.

13
New cards
How would the frequency and the pitch of the sound of the horn sound to someone in the back of the car?
The frequency and pitch of the sound seem low. The driver always hears the same pitch because the driver is moving with the car.
14
New cards
What is loudness?
A measure of how well a sound can be heard.
15
New cards
What happens if you strike a drum very hard?
The sound it produces is higher, so more energy is transferred to the drum. The drum moves with a larger vibration and transfers more energy to the air around it. This increase in energy causes air particles to vibrate farther from their rest positions.
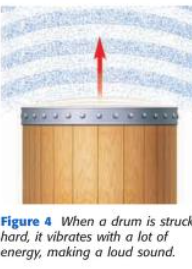
16
New cards
What is the amplitude of a wave?
The amplitude of a wave is the largest distance the particles in a wave vibrate from their rest positions. The larger the amplitude, the louder the sound. The smaller the amplitude, the softer the sound. When you strike a drum harder, you are increasing the amplitude of the sound waves being made.
17
New cards
What are decibels?
The most common unit used to express loudness and is represented with “dB”. The softest sounds an average human can hear are at a level of 0 dB. Sounds that are 120 dB or higher can be painful.
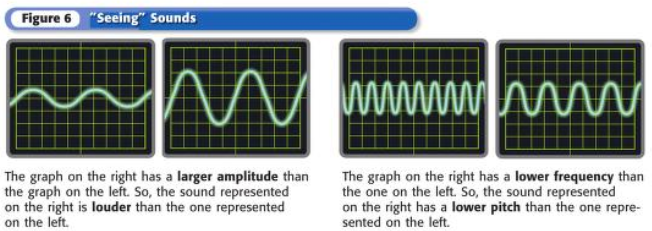
18
New cards
At the same temperature, in which medium does sound travel the fastest?
air, liquid, or solid
air, liquid, or solid
solid
19
New cards
In general, how does the temperature of a medium affect the speed of sound through that medium?
Molecules in higher temperature have more energy, thus, vibrate faster. Since they vibrate faster, the sound travels quicker. Therefore, the higher the temperature of the medium, the faster the speed of sound.
20
New cards
What property of waves affects the pitch of a sound?
frequency
21
New cards
Will a listener notice the Doppler effect if both the listener & the source of the sound are traveling toward each other? Explain
Yes, the sound waves in front of the source will become closer together as the source moves forward. Also, the listener will "meet" the sound waves more rapidly by moving toward the source. The movements of both the source & the listener will make the pitch of sound higher.
22
New cards
A drum is struck gently, then is struck harder. What will be the difference in the amplitude of the sounds made? What will be the difference in the frequency of the sounds made?
The amplitude of the sound will be higher when the drum is struck harder. The frequency will not change.