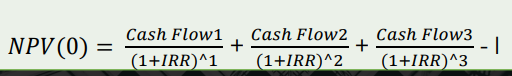PROJECT MANAGEMENT 2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Strategy
is making a decision how the organization will compete its rivals in the industry where it is participating
It is vital for success of the project to be parallel with strategic goals of the organization
Strategy Management
is responding to changes in the external environment for competitive position
A key requisite for survival to always keep updated to external changes through continuous scan of the political-legal, economic, socio-cultural, technological, and natural (PESTN) environment of the organization
Project Management Maturity
is the progressive advancement of project and multi-project management proficiency in approach, methodology, strategy, and decision-making process.
Project Maturity Model
reflects that maturity is a continuous process of improvement via identifiable incremental steps.
High Maturity
Institutionalized, seeks continuous improvement
Moderate Maturity
Defined practices, training programs organizational support
Low Maturity
Ad hoc process, no common language, little support
Project Selection
the process of appraising a project or groups of projects and afterward deciding to execute some of them in order to realize the objectives of the organization.
It appraises each project proposal and decides on the premier priority project/s for more analysis
• Follows a four-stage process namely identification of project/s, evaluation and prioritizing project/s selection and initiation of project/s and review of projects.
1 Identify projects that support the strategy
2 Evaluate and prioritize projects
3 Select and initiate projects
4 Review projects regularly
4 GENERIC PROCESS OF PROJECT SELECTION
FIRST STEP
Calls for the naming of the project concepts or ideas with a written brief description of a project
SECOND STEP
Each project is evaluated using different criteria and models and the outcomes become the basis of prioritization
THIRD STEP
Selection and initiation that logically follows evaluation and prioritization focusing mainly on the delicate decision of staffing the project teams
FOURTH STEP
A regular review of project/s which is imperative to find out if they are still in-line with the strategy of the firm
model
offers an abstraction of a more intricate reality \
• A fractional version of the certainty it intended to replicate and cannot produce an optimal decision
NONNUMERIC
Do not utilize numbers as inputs; older and simpler
NUMERIC
Make use of numbers to measure both objective and subjective criteria
Sacred Cow
A project recommended by a senior and influential official in the organization. "Sacred" in a sense that it will be maintained until the boss personally, identifies the idea as a failure and terminates it
Operating Necessity
A project is obligatory to keep the system operating; does not necessitate a great extent of formal evaluation
Competitive Necessity
A project which is founded on a desire to preserve the company's competitive position in the market 4. Product Line Extension A project to develop and distribute
Product Line Extension
A project to develop and distribute new products evaluated in the level to which it fits the firm's present product line, fill a gap, strengthens a weak link, or extends the line in a fresh, advantageous direction
Comparative Benefit Model
Often used to select from a list of projects that are complex, difficult to assess and often non comparable. The one with the most benefit to firm is selected.
. Sacred Cow\
Operating Necessity
Competitive Necessity
Product Line Extension
Comparative Benefit Model
5 NONNUMERIC MODELS
REALISM
The model should mirror the reality of manager’s decision situation together with the various objectives of both the firm and its managers
EASE OF USE
The model should be realistically convenient, not require to carry out, and be simple to employ and comprehend
CAPABILITY
The model should be complicated enough to deal with numerous time periods, simulate different situations both inside and external to the project and optimize the decision
COST
The data gathering and modelling costs should be low in relation to the cost of the project and must certainly be less than the probable benefits of the project.
FLEXIBILITY
The model should offer convincing outcomes among the conditions that the firm may experience
EASY COMPUTERIZATION
The model should be simple and suitable to collect and accumulate the information in a computer database, and to maneuver data in the model by using a commonly accessible, standard computer package programs
Payback Period
Measures the time it will take to recover the project investment Formula:
A shorter payback period, the better

Payback Period Interpretation
A shorter payback period, the better
. Internal rate of Return interpretation
The discount rate which equates the present value of the future cash flows of an investment with the initial investment. It is the discount rate at which the net present value of an investment becomes zero.
Internal rate of Return
A project should only be accepted if its IRR is NOT less than the target internal rate of return. When comparing two or more mutually exclusive projects, the project having highest value of IRR should be accepted.