Business SCHSM Test Review
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Leadership
The process of inspiring others to work hard to accomplish important tasks.
Integrity
The quality of being honest and having strong moral principles.
Emotional Intelligence
The ability to understand and manage one's own emotions and the emotions of others.
Self Awareness
Understanding one's emotions, motivations, strengths, and weaknesses, and how they are perceived by others.
Self Regulation
The ability to control harmful urges and emotions, ensuring they do not negatively affect behavior.
Motivation
A passion to pursue, achieve, and progress towards goals, characterized by discipline and drive.
Empathy
Understanding others' emotions and treating them according to their emotional makeup.
Social Skill
The ability to build connections and be memorable in interactions with others.
Drucker’s Old Fashioned Leadership
A leadership approach emphasizing clear vision, responsibility, and integrity.
Moral Leadership
Leadership that begins with personal integrity and promotes an ethical organizational culture.
Visionary Leadership
A leader who provides a clear and compelling sense of the future and the actions needed to achieve it.
Servant Leadership
A leadership style focused on empowering others and prioritizing their needs.
Transactional Leadership
Leadership that uses tasks and rewards to influence and direct others' efforts.
Transformational Leadership
Inspirational leadership that arouses extraordinary effort and performance through vision and empowerment.
Ways to Build Leadership Skills
Practice discipline
Take on more projects
Learn to follow
Inspire others
Keep learning
Resolve conflicts
Ways to Build Confidence
Adopt a growth mindset
Practice Gratitude
Confront your fear
Lean into your strengths
Grow your competence
Autocratic-Authoritarian Style
A leadership style with centralized authority and low participation.
Democratic-Participative Style
A leadership style that involves high participation and feedback from team members.
Laissez-faire Style
A hands-off management approach that empowers self-motivated individuals.
Fielder’s Contingency Model
A theory suggesting effective leadership depends on matching style to situational demands.
Task Oriented Leader
A leader who excels in very favorable or unfavorable conditions.
Relationship-Oriented Leader
A leader who thrives in situations of moderate control.
Hersey-Blanchard Situational Leadership Model
A model suggesting leaders adjust their styles based on follower maturity.
Path-Goal Leadership Theory
A theory where leaders clarify goals and provide rewards to facilitate goal accomplishment.
Leader-Member Exchange Theory (LMX)
A theory recognizing that leaders treat members differently based on performance.
Leader-Participation Model
A model where leadership success is influenced by the decision-making method used.
Position Power
Power derived from formal authority and the ability to reward or punish.
Personal Power
Power based on individual characteristics such as expertise and relationships.
Team
A collection of people who regularly interact to pursue common goals.
Synergy
The combined effect of teamwork that is greater than the sum of individual efforts.
Teamwork
The process of actively working together to achieve common goals.
Team Success
Achieving more collectively than individuals could alone, demonstrating synergy.
Pros of Teamwork
Benefits such as improved creativity, decision-making, and commitment.
Problems with Teamwork
Challenges like social loafing and personality conflicts.
Recipe for Success
Elements like diversity of skills, clear goals, and good communication.
Stages of Team Development
Phases including forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning.
Forming
The initial stage of team orientation and interpersonal testing.
Storming
A stage characterized by conflict and competition within the team.
Norming
A stage where team members consolidate around tasks and build community.
Performing
A stage of focused teamwork and high productivity.
Adjourning
The final stage of task completion and team disengagement.
Aspects of Fiedler’s Contingency Theory
Quality of leader-member relations = the degree to which the group supports the leader (good to poor)
The degree of task structure = how clearly task goals, procedures and guidelines are spelled out (high to low)
The amount of position power = the degree to which the position gives the leader power to reward and punish subordinates (strong to weak)
When will task-oriented leader be needed (Fielder’s Contingency Theory)
Will work best in very favorable conditions (i.e. high control) or unfavorable conditions (i.e. low-control) situations.
When will relationship-oriented leader be needed (Fielder’s Contingency Theory)
Will be most successful in situations of moderate control
Telling Style (Hersey Blanchard Model)
Low readiness (unable and unwilling/insecure)
Selling Style (Hersey Blanchard Model)
Moderate to high readiness (unable but willing/confident)
Participating Style (Hersey Blanchard Model)
Low to moderate readiness (able but unwilling or insecure)
Delegating Style (Hersey Blanchard Model)
High readiness (able, willing or confident)
Directive Leadership (Path-Goal Leadership Theory)
Letting subordinates know what is expected, giving directions, scheduling work to be done, maintaining standards for performance etc (Good when assignment is unclear)
Supportive leadership (Path-Goal Leadership Theory)
Doing things to make work pleasant, treating group members as equals, being friendly and approachable, showing concern for well being etc (Good when worker self confidence is low)
Achievement-Oriented Leadership(Path-Goal Leadership Theory)
Setting challenging goals, expecting high levels of performance with work, emphasizing continuous improvements, show confidence is meeting high standards (Good when performance incentives are low)
Participative Leadership (Path-Goal Leadership Theory)
Involving subordinates in decision making, asking for suggestions, using suggestions when making decisions etc (Good when task challenge is insufficient and goals needed to be set)
In Group (Leader-Member Exchange Theory)
Considered the best performers
They enjoy special and trusted high-exchange relationships with the leader (might look like special assignments, privileges and access to info)
Out group (Leader-Member Exchange Theory)
Excluded from benefits
Low exchange relationship with the leader
Authority Decision: (Leader-Participation Model)
Made by the leader then communicated to the group
Consultative Decision: (Leader-Participation Model)
Made by the leader after receiving information, advice or opinions from group members.
Group Decision: (Leader-Participation Model)
Made by the group members themselves
Reward Power: Position
The capacity to offer something of value as a means of influencing other people ie. a raise, a promotion, a great office, a bonus etc
Coercive Power: Position
The capacity to punish or withhold positive outcomes as a means of influencing other people ie. termination, verbal or written reprimands, no bonus pay out, demotion
Legitimate Power: Position
The capacity to influence other people by virtue of formal authority, or the rights of the office ie. CEO, project manager, supervisor
Expert Power: Personal
The capacity to influence other people because of specialized knowledge ie. experience, specialized training, or talent
Referent Power: Personal
The capacity to influence other people because of their desire to identify personally with you ie. rich people, celebrities, inspiring boss
Relational Power: Personal
The ability to function well as part of a team working toward a collective goal while putting other team members’s need above your own ie. people who put the team members first
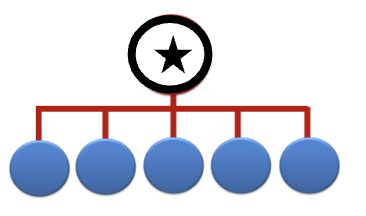
Supervisor: Serving as the appointed head of a formal work unit
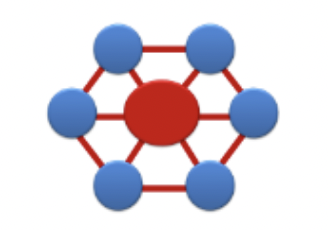
Network Facilitator: Serving as the peer leader network hub for special task force
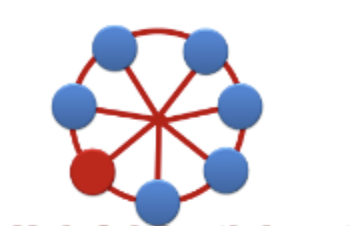
Helpful Participant: Serving as a helpful, contributing member of a project team.

External Coach: Serving as the external convener or sponsor of a problem-solving team staffed by others.

Email Format