Psych 101 JMU Final Exam
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Personality trait
durable disposition to behave in a particular way across a variety of situations
Five factor model of personality
-neuroticism
-extraversion
-openness to experience
-agreeableness
-conscientiousness
Freud's psychoanalytic theory
grew out of his therapeutic work with clients and emphasized the importance of the unconscious
Personality structure
Id, superego, ego
Id
instinctive component that follows the pleasure principle
Ego
decision-making component that follows the reality principle
Superego
moral component
Three levels of awareness
-conscious(current awareness)
-preconscious(material just beneath the surface of awareness)
-unconscious(material well below the surface of awareness)
Defense mechanisms
-repression
-projection
-Displacement
-regression
-Denial
Repression
keeping distressed thoughts and feelings buried in the unconscious
Projection
Attributing one's own thoughts, feelings, or motives to one another
Displacement
Diverting emotional feelings (usually anger) from their original source to a substitute target
Regression
A reversion to immature patterns of behavior
Children evolve through 5 stages of psychosexual development
-oral
-anal
-phallic
-latency
-genital stages
Maslow's theory
human motives are organized into a hierarchy of needs
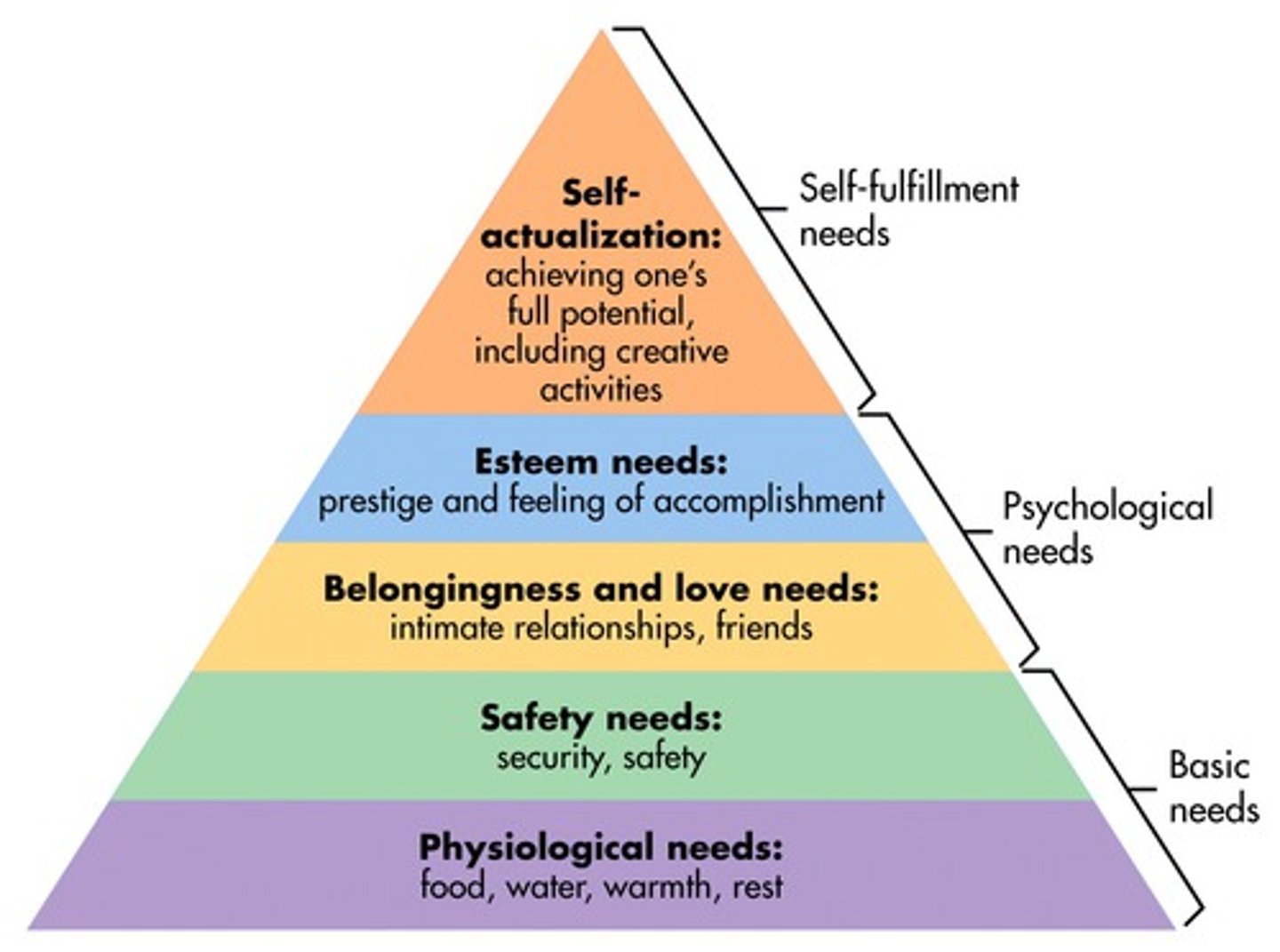
Self-actualization
the need to fulfill one's potential
Self-actualizing persons
people with very healthy personalities, marked by continued personal growth
Three assumptions of Freuds psychoanalytic
-Psychic determination
-Symbolic meaning
- unconscious motivation
Psychic determination
All psychological events have a cause
Symbolic meaning
Behaviors are symbolic
Unconscious motivation
unconscious mind is the reason you do certain behaviors