Comprehensive Guide to Causal and Qualitative Research Methods in Social Sciences
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
What is the basic difference between idiographic and nomothetic explanations?
Idiographic explanations focus on individual cases and specific contexts, while nomothetic explanations seek general laws applicable across cases.
What type of reasoning is associated with idiographic explanations?
Narrative reasoning, which involves telling a story about the sequence of events leading to an outcome.
What is a key characteristic of idiographic explanations?
They are deterministic, focusing on what caused a specific event to occur.
What does the term 'counterfactual' refer to in nomothetic explanations?
The situation that describes what would have happened in the absence of variation in the independent variable.
What is required to establish a causal relationship?
Time order, nonspuriousness, empirical association, identifying a causal mechanism, and specifying the context.
What does 'nonspuriousness' mean in causal relationships?
It means that the relationship between two variables is not caused by variation in a third variable.
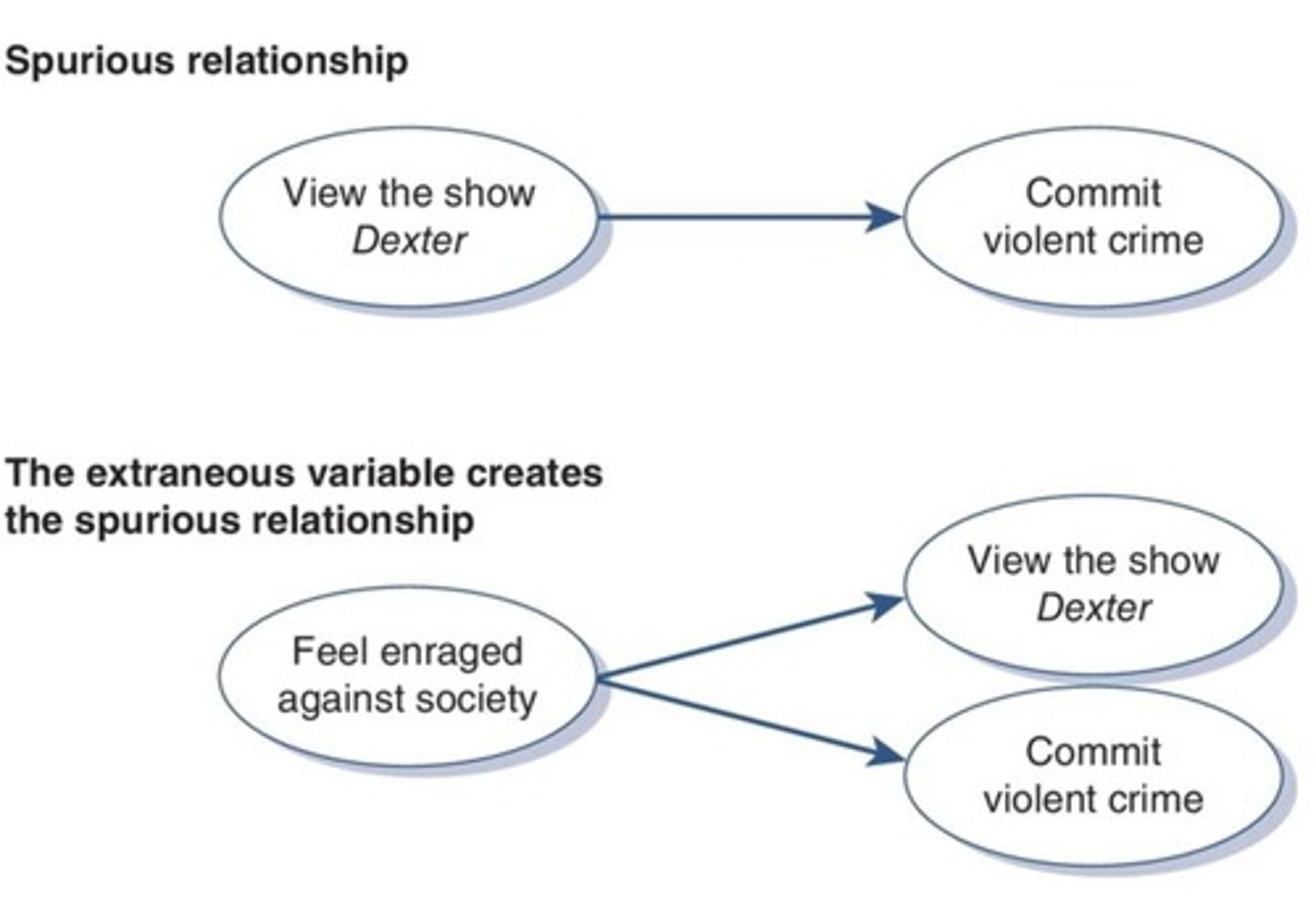
What is an example of a spurious relationship?
The relationship between shoe size and academic knowledge, where age is the third variable affecting both.
What are the three criteria for establishing causality in a true experiment?
Time order, nonspuriousness, and empirical association.
What is a true experiment?
A research design that includes two or more comparison groups, random assignment, and pretest/posttest assessments.
What is a cross-sectional design?
A research design where data is collected at one point in time, making it difficult to establish time order.
What is a key limitation of cross-sectional designs?
They cannot reliably determine the sequence of events or causal relationships.
What are demographic variables, and why are they significant in causal analysis?
Demographic variables like sex, race, and age are fixed at birth and can help establish time order in causal analysis.
What is the role of reliable reports in cross-sectional studies?
Respondents' reliable reports can help establish time order if they accurately recall past events.
What is the significance of identifying a causal mechanism?
It strengthens confidence in the conclusion that two variables have a causal connection.
What does 'ceteris paribus' mean in the context of nomothetic explanations?
It means 'all other things being equal' when considering the effects of an independent variable on a dependent variable.
What is one challenge of nonexperimental designs in establishing causality?
It is difficult to meet criteria for valid nomothetic causal explanations without experimental designs.
What does empirical association refer to in causal relationships?
It refers to the observed correlation between variables, which strengthens but is not required for causal conclusions.
How can researchers improve causal conclusions in nonexperimental designs?
By designing research that creates comparable conditions to isolate the effects of the independent variable.
What is the importance of specifying the context in which a causal effect occurs?
It helps understand how relationships among variables may differ across different settings or populations.
What is a key feature of true experiments that enhances causal validity?
Random assignment of participants to experimental and control groups.
What is the purpose of pretests and posttests in true experiments?
To assess changes in the dependent variable after the experimental condition has been applied.
What is a potential issue when using surveys to establish causality?
Surveys conducted at a single point in time cannot confirm the order of cause and effect.
What is the significance of the extraneous variable in causal relationships?
It can cause variation in both the independent and dependent variables, leading to spurious relationships.
What is a major weakness of sloppy record taking in research?
It can lead to inconsistencies in data.
What is a challenge when using cross-sectional data for causal analysis?
Identifying the time order of effects can be insurmountable.
What is longitudinal research?
Research that collects data over time to examine changes.
What is a repeated cross-sectional design?
A design that uses different samples from the same population at two or more points in time.
What are fixed sample panel designs?
Designs that follow the same individuals over time to identify changes.
What are the difficulties associated with fixed sample panel designs?
Expense and attrition, as tracking individuals over time can be costly and lead to participant dropout.
What are event-based cohort studies?
Studies that focus on a group of people sharing a common characteristic, such as birth year.
How can comparing findings between different cohorts be beneficial?
It helps reveal the importance of social or cultural contexts experienced by different cohorts.
What distinguishes true experiments from quasi-experiments?
True experiments involve random assignment and comparison groups, while quasi-experiments do not.
What is the significance of random assignment in true experiments?
It ensures that the only difference between experimental and comparison groups is the treatment received.
What is a counterfactual in the context of true experiments?
The outcome that would have occurred if subjects had not been exposed to the treatment.
What is the difference between random assignment and random sampling?
Random assignment determines group placement, while random sampling selects cases for the sample.
What is the purpose of pretests in true experiments?
To measure the dependent variable prior to the experimental intervention.
What are the advantages of using pretests?
They provide direct measures of change and verify the success of randomization.
What characterizes quasi-experimental designs?
They may lack comparison groups or random selection, making them less robust than true experiments.
What is a time series design?
An evaluation of before and after events without a comparison group.
What is an ex post facto design?
A design where treatment and comparison groups are designated after the treatment has occurred.
What is the benefit of ex post facto designs?
They allow researchers to use existing data to develop research questions without conducting a formal experiment.
What is a nonequivalent control group design?
A design where experimental and comparison groups are selected before treatment without random assignment.
How can matching be used in research studies?
To create comparable groups for treatment and control in studies where random assignment is not possible.
What is individual matching in quasi-experimental design?
A method where individual cases in the treatment group are matched with similar individuals in the comparison group.
What are the benefits of individual matching?
It can create a comparison group that is very similar to the experimental group.
What are some issues with individual matching?
Determining which variables to use for matching and the possibility that matches may not be found for all cases.
What is aggregate matching?
Finding a group with similar distributions on key variables, such as average age or percentage of females, rather than matching individuals.
What is a requirement for a study to be considered quasi-experimental?
Individuals cannot choose which group to join or where to seek services.
What is selection bias?
When characteristics of the experimental and comparison group subjects differ, potentially affecting the outcomes.
What is differential attrition?
When subjects are more likely to drop out of one group than another, causing differences between the groups.
What are endogenous effects in quasi-experimental designs?
Changes that occur naturally among subjects during the experiment that are independent of the treatment.
What are the three threats to internal validity in quasi-experimental designs?
Testing, maturation, and regression effects.
What is the testing threat to internal validity?
Subjects may respond differently in the posttest due to sensitization from the pretest.
What is the maturation threat to internal validity?
Changes in outcome scores may occur due to natural maturation rather than the treatment.
What is the regression threat to internal validity?
Subjects chosen for low scores may improve in the posttest simply due to random fluctuations.
What are external or historical effects?
Events occurring during the experiment that influence outcome scores, unrelated to the treatment.
What is contamination in experimental research?
When either the experimental or comparison group is aware of the other and is influenced as a result.
What is treatment misidentification?
When the treatment does not cause the outcome directly but through an unidentified intervening process.
What is the placebo effect?
When subjects improve due to their expectations of the treatment rather than the treatment itself.
What is the Hawthorne effect?
When subjects alter their behavior because they know they are being observed in a study.
What ethical issue involves deception in experiments?
Misleading subjects about research procedures to create realistic treatment conditions.
What is informed consent in research?
Consent must be given voluntarily by competent individuals who are fully informed about the research.
What are the benefits of using surveys in research?
Efficiency, generalizability, and versatility in collecting data from many people at a low cost.
What is generalizability in survey research?
The ability to apply findings from a sample to a larger population.
What challenges can affect survey generalizability?
Surveys not being available in multiple languages and lack of internet access among certain demographics.
What should researchers avoid when developing a survey?
Including too many irrelevant questions and failing to include crucial questions.
What is a key consideration when formulating survey questions?
Ensure questions are clear and avoid confusing phrasing or vagueness.
What should be the time frame for questions about day-to-day activities?
No longer than 'in the past month'.
What is a recommended time frame for questions about rare events?
Between 6 months to 12 months.
What type of grammar should be used in survey questions?
Good grammar is essential for clarity.
What is a common issue with double-barreled questions?
They ask more than one question at once, making it unclear which part the respondent agrees or disagrees with.
What is the problem with using negative wording in questions?
It confuses respondents and makes it difficult to answer accurately.
What is a 'fence sitter' in survey responses?
A respondent who sees themselves as neutral on an issue.
What is a 'floater' in survey responses?
A respondent who chooses an answer even when they lack knowledge about the question.
How should demographic questions be handled in surveys?
Place them at the end if not sensitive; at the beginning if they are sensitive.
What is a major drawback of mailed self-administered surveys?
They rely on voluntary return, leading to low response rates.
What is a benefit of telephone surveys?
Most families have phones, allowing for broader reach.
What is a significant drawback of in-person interviews?
They are costly and time-consuming.
What is a benefit of electronic (web-based) surveys?
They can increase measurement validity and elicit more honest responses.
What is a drawback of electronic surveys?
Coverage bias, as not everyone has internet access.
What is a benefit of group-administered surveys?
High response rates due to participants feeling compelled to join.
What is a drawback of group-administered surveys?
It can be challenging to assemble a group of willing participants.
What is the purpose of mixed-mode surveys?
To combine strengths of different survey methods to maximize data collection.
What should be avoided when asking about sensitive behaviors?
Questions should be framed to seem acceptable to encourage honest responses.
How can survey questions be made more appealing?
Incorporate visuals like pictures and graphics to enhance understanding.
What is a common issue with telephone surveys?
Respondents may tire and refuse to answer all questions.
What should be done to avoid agreement bias in surveys?
Impartially present both sides of the attitude scales in the questions.
What is the impact of telemarketing on survey responses?
It has led to people being less likely to answer unknown phone numbers.
What is a potential issue with demographic questions on income?
They can be perceived as intrusive.
What is an important aspect of the interviewer's role in in-person surveys?
They must create a personal, engaging, and non-reactive environment.
What should be done if a survey includes sensitive topics?
Demographic questions should be placed at the beginning to ensure confidentiality.
What is a drawback of relying on self-administered surveys?
Respondents may skip questions or stop answering partway through.
What is a potential drawback of interviewing nonresponders over the phone?
Respondents may give different answers based on the mode they are interviewed in.
What are the four types of errors that a successful survey must minimize?
Poor measurement, nonresponse, inadequate coverage of the population, and sampling error.
What is poor measurement in surveys?
When respondents interpret questions superficially and provide acceptable answers rather than truthful ones.
What is the primacy effect in survey responses?
The tendency of respondents to choose responses that appear earlier in a list.
What is nonresponse in surveys?
The decline in perceived benefits of survey participation and increased perceived costs, leading to fewer responses.
What can invalidate the results of a survey?
A poor sampling frame that inadequately covers the population.
What is sampling error?
The difference between the characteristics of a sample and the characteristics of the population from which it was selected.
What is a complete observer in research?
A researcher who observes without disrupting participants, but may miss the meaning behind behaviors.