CHEM1161: Functional Groups
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
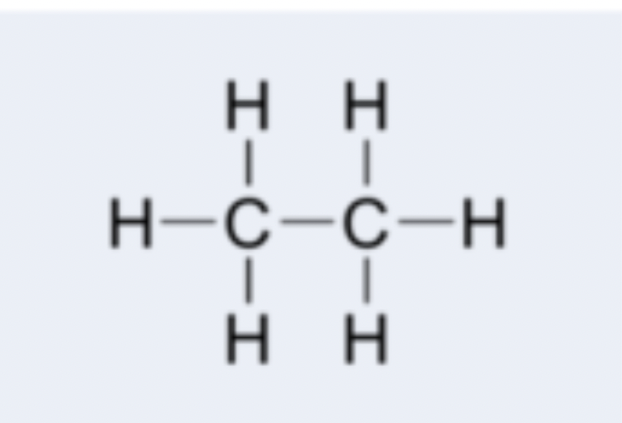
alkane
hydrocarbon containing only single carbon-carbon bonds; examples: methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8)
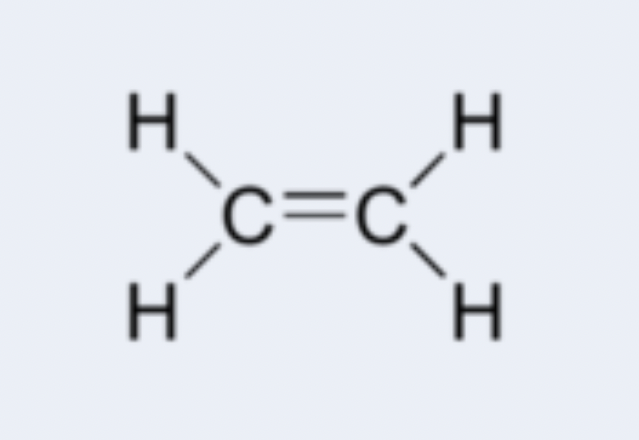
alkene
hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon-carbon double bond; examples: ethene (C2H4), propene (C3H6)
alkyne
hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon-carbon triple bond; examples: ethyne (C2H2), propyne (C3H4)
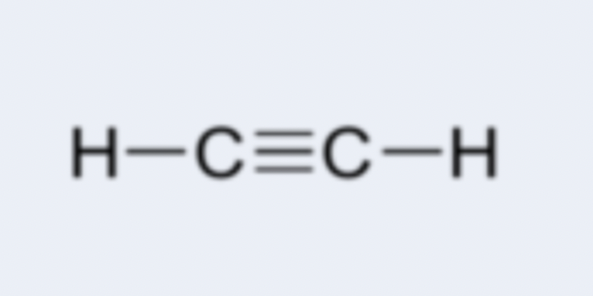
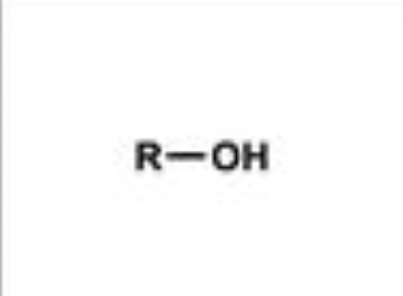
alcohol
organic compound containing a hydroxyl (-OH) functional group bonded to a saturated carbon atom; examples: methanol (CH3OH), ethanol (C2H5OH)
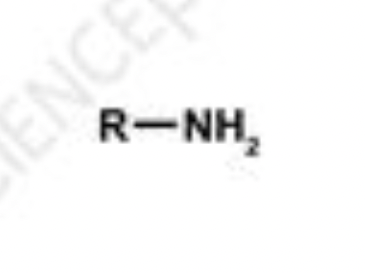
amine
organic compound derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacing one or more hydrogen atoms with alkyl or aryl groups; examples: methylamine (CH3NH2), dimethylamine ((CH3)2NH)
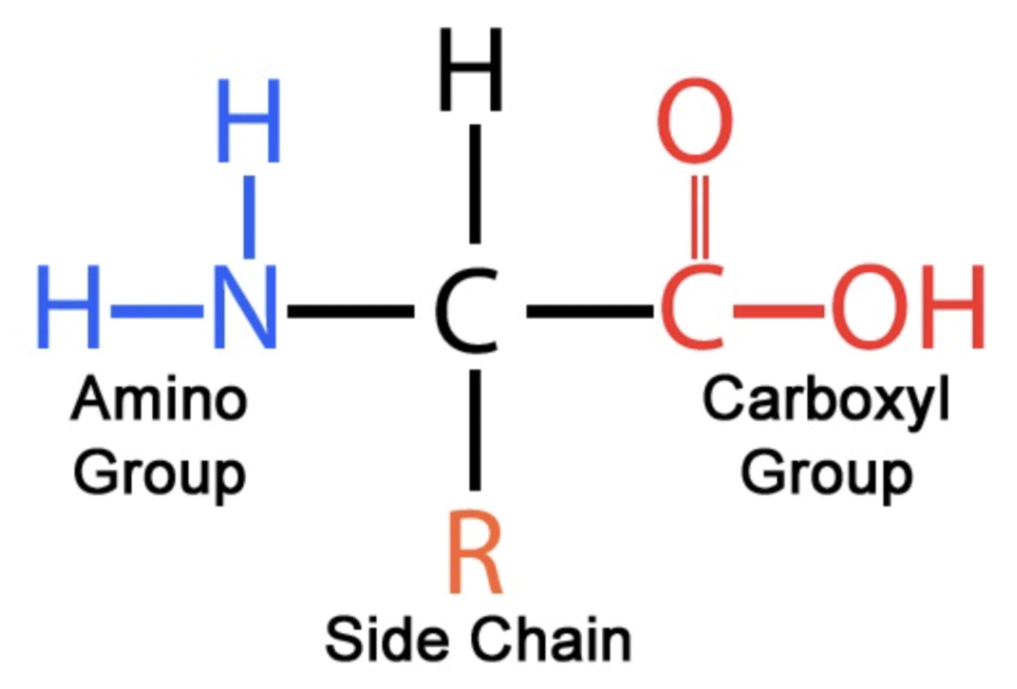
amino acid
organic compound containing both an amino (-NH2) group and a carboxyl (-COOH) group; examples; glycine (C2H5NO2), alanine (C3H7NO2)
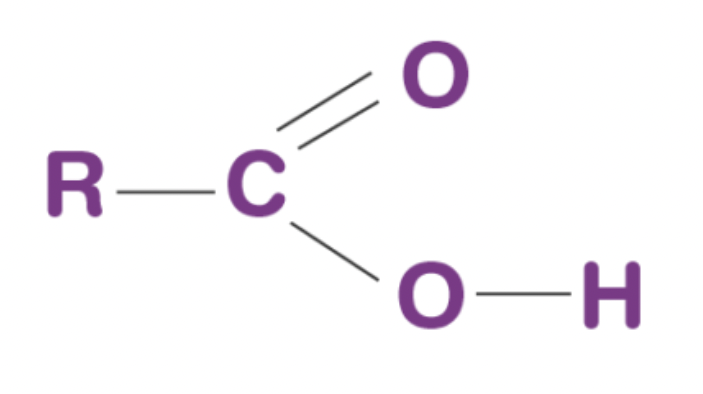
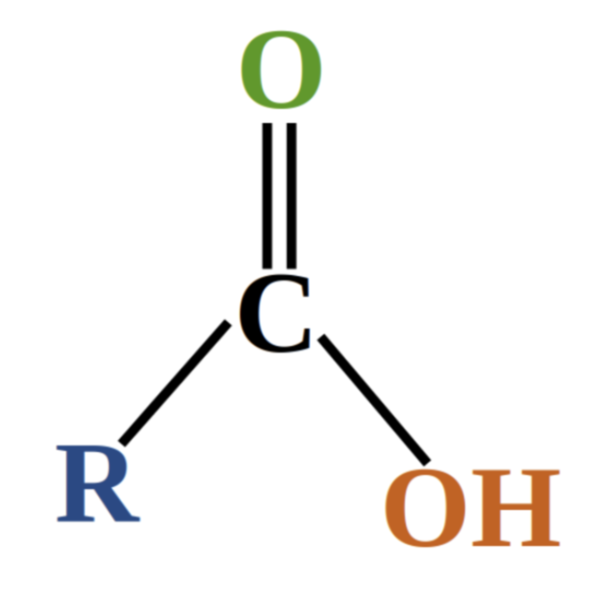
carboxylic acid
organic compound containing a carboxyl (-COOH) functional group
hydroxyl
functional group consisting of an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (-OH); characteristic of alcohols and carboxylic acids
carbonyl
functional group consisting of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O); present in ketones and carboxylic acids
aromatic
cyclic (ring-shaped) hydrocarbon with alternating double and single bonds (conjugated pi system) that exhibits special stability; example: benzene (C6H6)
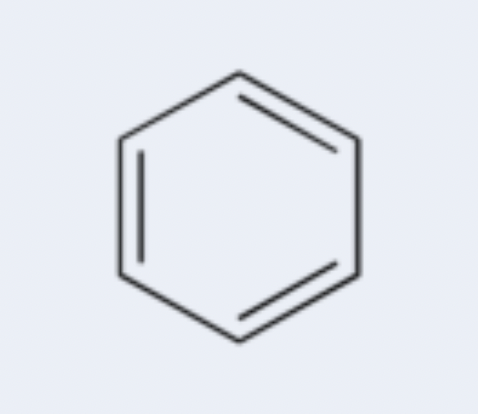
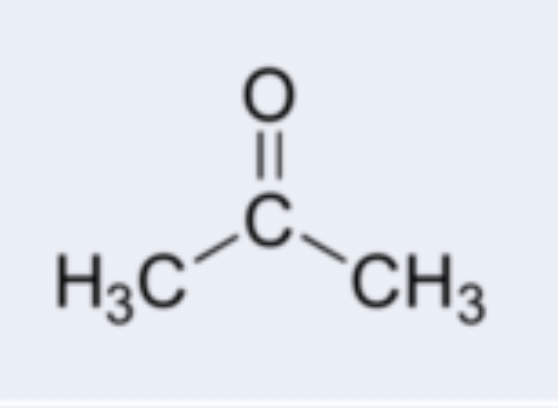
ketone
organic compound containing a carbonyl (C=O) functional group where the carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms; examples: acetone (CH3COCH3), butanone (CH3COCH2CH3)
hydrocarbon
organic compound composed of ONLY C and H atoms; insoluble in water; nonpolar
carboxyl group
functional group consisting of a carbonyl (C=O) group with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to the carbon (-COOH)