Unit 4: Muscular System Notes
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Naming of muscles
direction, size, location, shape, action, number of origins
Function of muscle
Movement
Maintain posture
Stabilize joints
Generate heat
Muscle terminology
Myo; muscle
Mys; muscle
Sarco: flesh
Connective tissue of SKELETAL muscle
Fascia: outermost layer
Epimysium: covers entire muscle
Perimysium: around a fascicle(bundle of fibers)
Endomysium: around a single muscle fiber(cell)
Muscle attachment
Tendon: cord-like structure
Aponeuroses: sheet-like structure
Sites of muscle attachment
Bone, cartilages, connect tissue coverings
Sarcolemma
cell membrane
Sarcoplasm
cytoplasm
Thick filament
Myosin(mayo)
Thin filament
Actin
SKELETAL muscle fibers are made up of
Myofibrils
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
where we get calcium
Sarcomeres
striated patterns formed by filaments
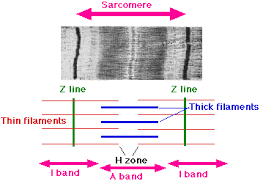
I band
thin filament
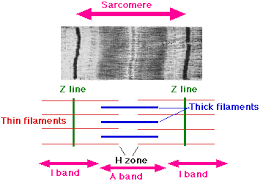
A band
thick and thin filament
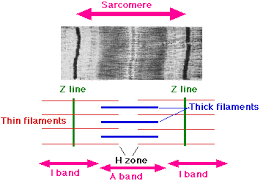
H zone
thick filament
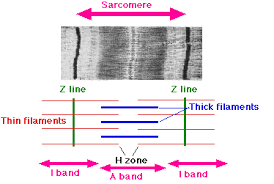
Z line
sarcomere boundary line
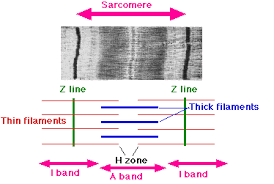
M line
center of A band
Muscle contraction
Results from actin and myosin filaments sliding past one another, shortening of sarcomeres.
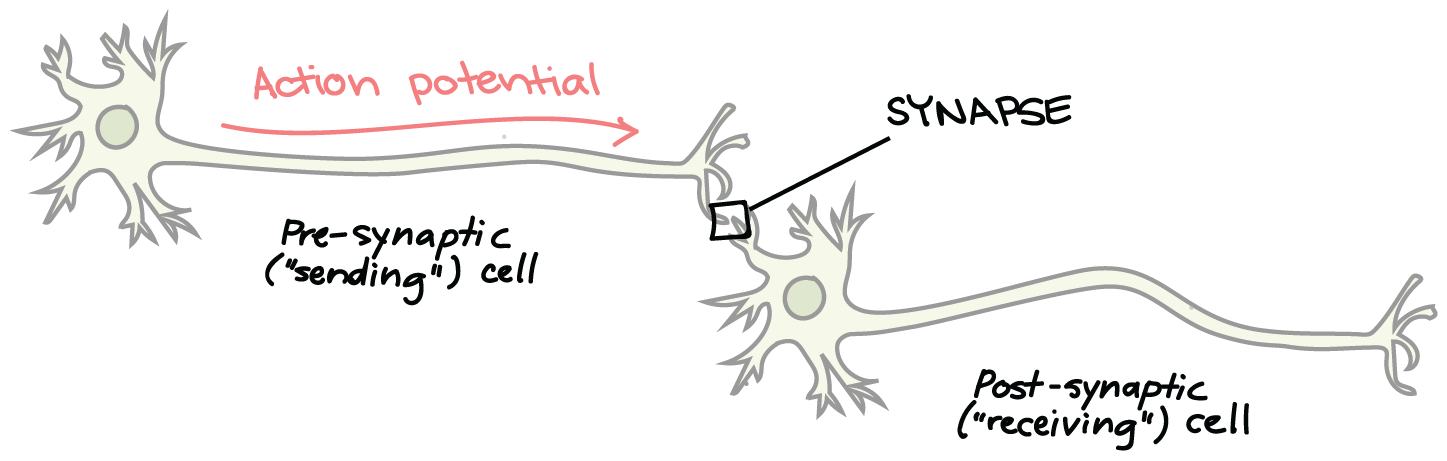
Neuromuscular Junction
A type of synapse, motor neuron and muscle cell interact
Motor neuron
nerve cell that carries a signal to the muscle cell
Motor end plate
cell membrane of muscle cell
Synaptic cleft
the gap between the neuron and muscle cell
Synaptic vesicles
carry neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitter
THE signal
Stimulus for contraction
Acetylcholine releases and binds to muscle receptors. Sarcolemmas permeability increase to let Na+(sodium) and K+(potassium) ions create action potential. Impulse causes the SR to release calcium, which leads to muscle contraction.
Acetylcholine
the signal
Muscle relaxation
Ca+2 ions are stored in SR
Troponin-tropomyosin cover actin bind sites
Cross-Bridging Cycle
Myosin attached to actin, forming the cross-bridges
Myosin cross-bridge pulls actin
ADP and P are released from myosin
New ATP binds to myosin
Actin and myosin cross-bridge breaks
ATP spilts into ADP and phosphate
Energy sources for Contraction
ATP reserves
Creatine phosphate: initial source of energy to regenerate ATP from ADP and P.
Cellular respiration: creates large amounts of ATP(36-38)
Cellular Respiration
creates lactic acid
Anaerobic(lactic acid) threshold
shift from aerobic, during strenuous muscle activity. When not enough oxygen is supplied, lactic acid is produced.
Oxygen debt
amount of oxygen needed to convert lactic acid to glucose and restore muscle ATP and creatine concentrations.
Muscle fatigue
inability to contract muscle
Common causes of muscle fatigue
decreased blood flow
Ion imbalances across the sarcolemma
Loss of desire to continue exercise
Accumulation of lactic acid
Muscle cramp
sustained, involuntary muscle contraction.
may be caused by changes in electrolyte concentration in extraceullular fluids in the area
Smooth Muscle
Lack striations
Slow and tireless
Short
Cardiac muscle
Branched cells
Cells joined by intercalated discs
Self-exciting and rythmic
Skeletal muscle
voluntary
Multi-nucleated
cylindrical shapes
Muscle Characteristics
Contractibility: shorten and thicken
Extensibility: ability to stretch
Elasticity: return to og length
Irritability: respond to stimuli
Muscle tone: tension/resistance, even at rest