Translation of mRNA and Protein Synthesis Overview
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
What disease did Archibald Garrod study to connect genes to enzymes?
Alkaptonuria
What did Garrod propose was missing in patients with alkaptonuria?
A particular enzyme, specifically homogentisic acid oxidase.
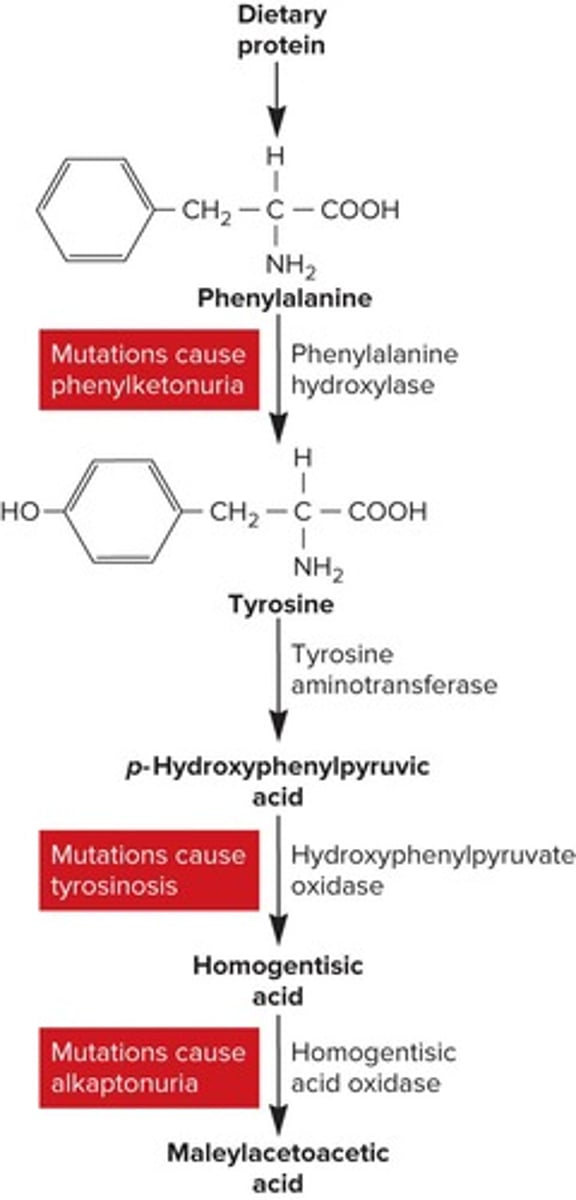
How did Garrod describe alkaptonuria?
As an inborn error of metabolism.
What was the main focus of Beadle and Tatum's experiments in 1941?
To create mutations in chromosomes and verify their Mendelian behavior.
What organism did Beadle and Tatum study for their experiments?
Neurospora crassa.
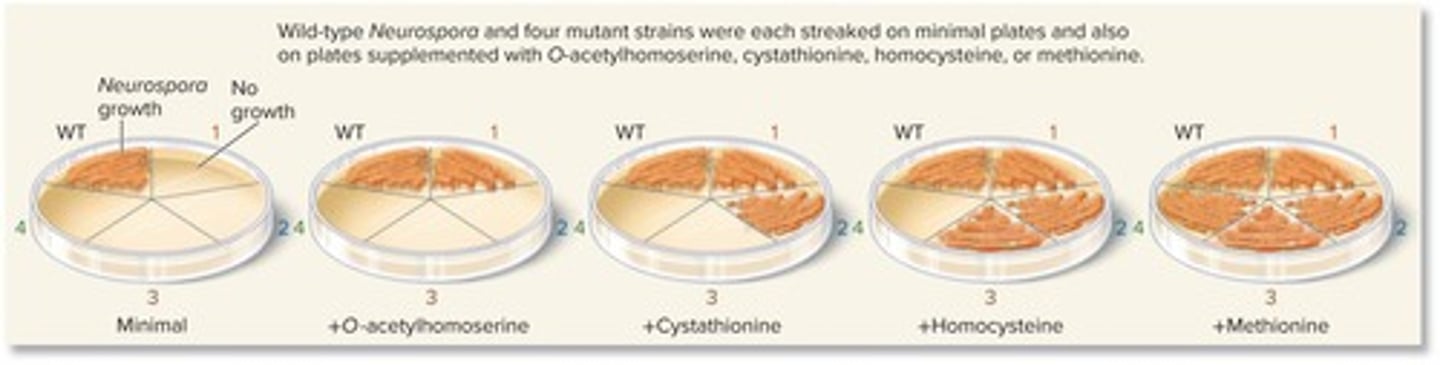
What method did Beadle and Tatum use to induce mutations?
X-rays to damage DNA.
What was the original hypothesis proposed by Beadle and Tatum regarding genes and enzymes?
The one-gene/one-enzyme hypothesis.
What modification was made to the one-gene/one-enzyme hypothesis?
It was modified to the one-gene/one-polypeptide hypothesis.
What did Beadle and Tatum identify in their analysis of mutant strains?
Mutants deficient in each enzyme of the biochemical pathway for synthesizing arginine.
What was the conclusion drawn by Beadle and Tatum regarding gene function?
A single gene controls the synthesis of a single enzyme.
What are the four modifications of the one-gene-one-enzyme theory?
1. Enzymes are only one category of proteins. 2. Some proteins are composed of two or more different polypeptides. 3. Many genes do not code polypeptides (e.g., functional RNA). 4. One gene can code multiple polypeptides through alternative splicing.
What is the role of codons in the genetic code?
Codons are groups of three nucleotides in mRNA that code for amino acids.
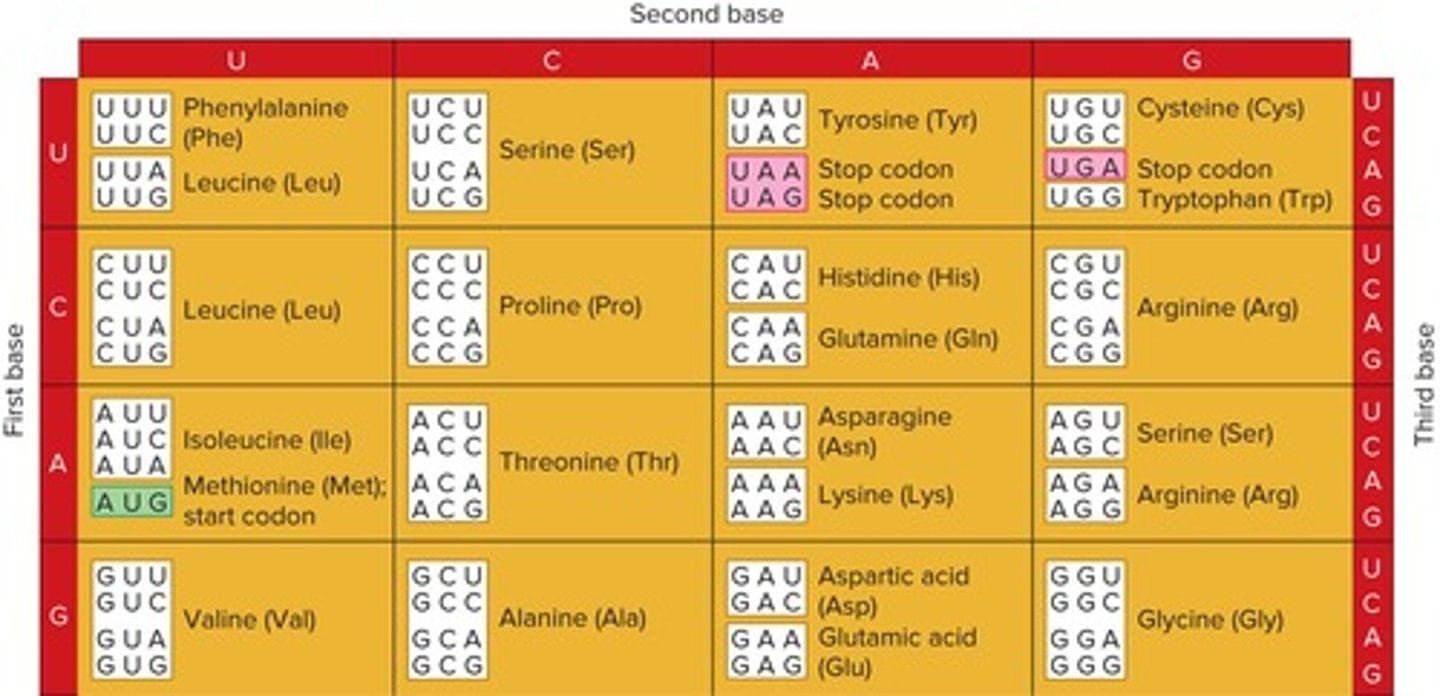
How many codons are there in the genetic code?
64 codons.
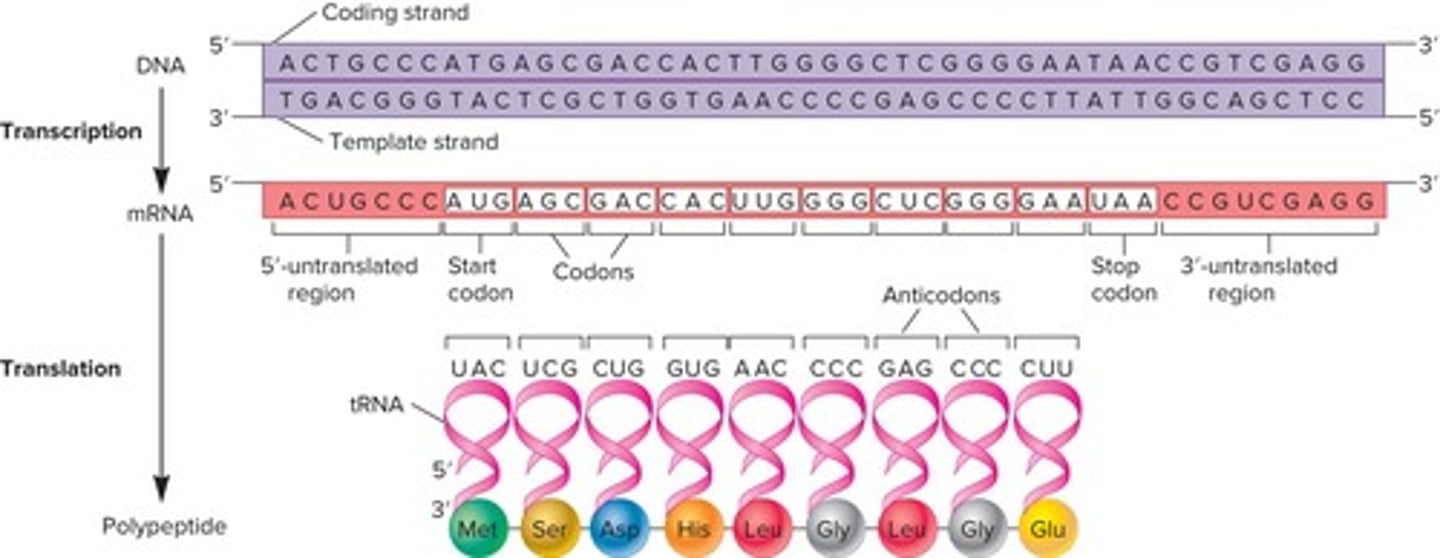
What does translation in genetics involve?
The interpretation of the nucleotide language of mRNA into the amino acid language of proteins.
What was the purpose of using minimal media in Beadle and Tatum's experiments?
To grow fungal cells that lacked specific enzymes.
What was the significance of the mutant strains of Neurospora in Beadle and Tatum's research?
They were unable to grow on plates lacking certain amino acids, indicating a genetic defect.
What does the term 'polypeptide' denote?
Structure of a protein.
What does the term 'protein' denote?
Function of a polypeptide.
What is the relationship between the genetic code and protein synthesis?
The genetic code is used to translate mRNA into proteins.
What is the significance of alternative splicing in gene expression?
It allows one gene to code for multiple polypeptides.
What did Beadle and Tatum's experiments contribute to our understanding of genetics?
They provided evidence linking genes to specific enzymes and metabolic pathways.
What is meant by 'functional RNA molecules'?
RNA molecules such as tRNA and rRNA that do not code for polypeptides.
What is the start codon in the genetic code?
AUG, which specifies methionine.
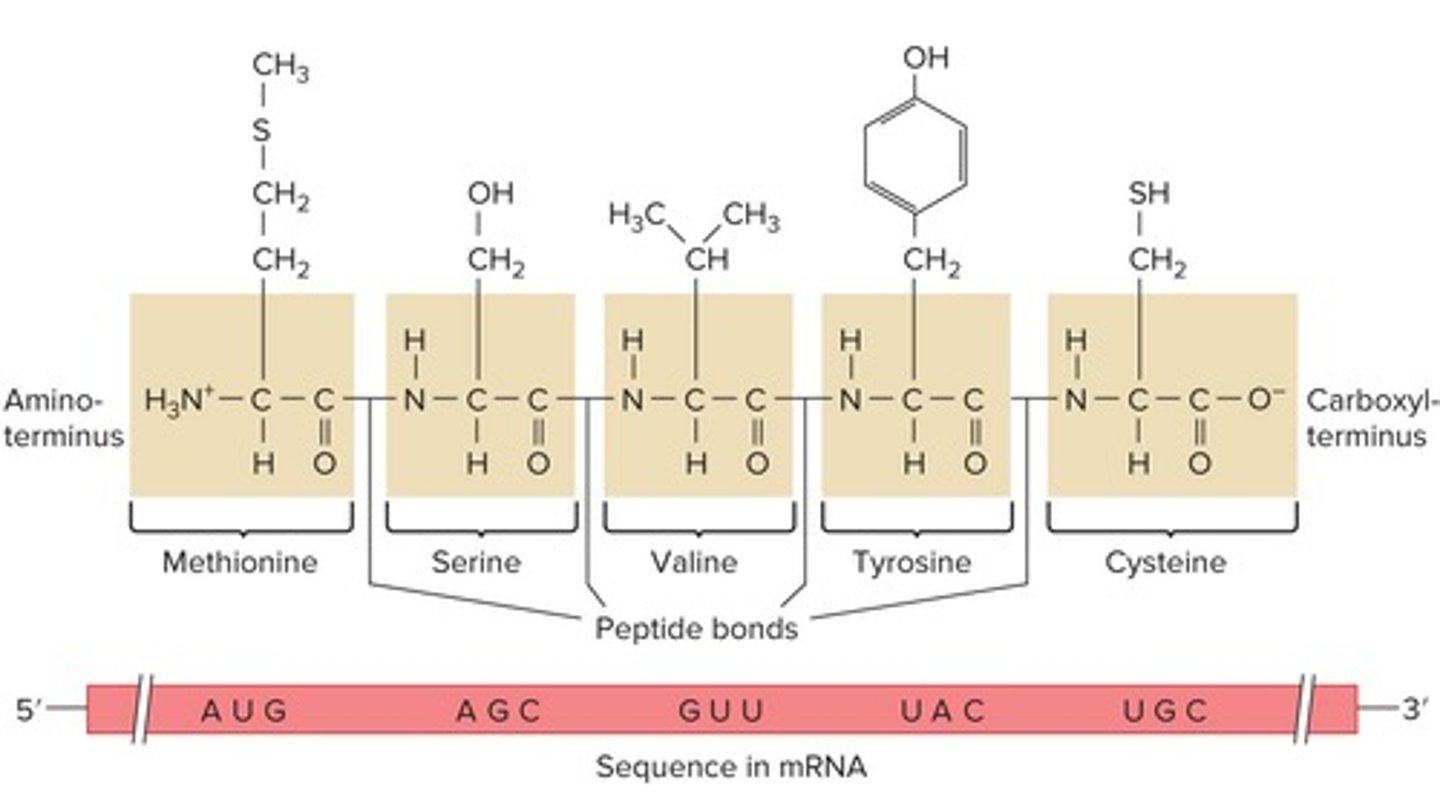
What do UAA, UAG, and UGA codons signify in the genetic code?
They are termination or stop codons.
What does degeneracy in the genetic code mean?
More than one codon can specify the same amino acid.
Give an example of synonymous codons for glycine.
GGU, GGC, GGA, and GGG all code for glycine.
What is a key characteristic of the genetic code?
It is nearly universal, with only a few rare exceptions.
What are the 21st and 22nd amino acids sometimes referred to as?
Selenocysteine (Sec) and pyrrolysine (Pyl).
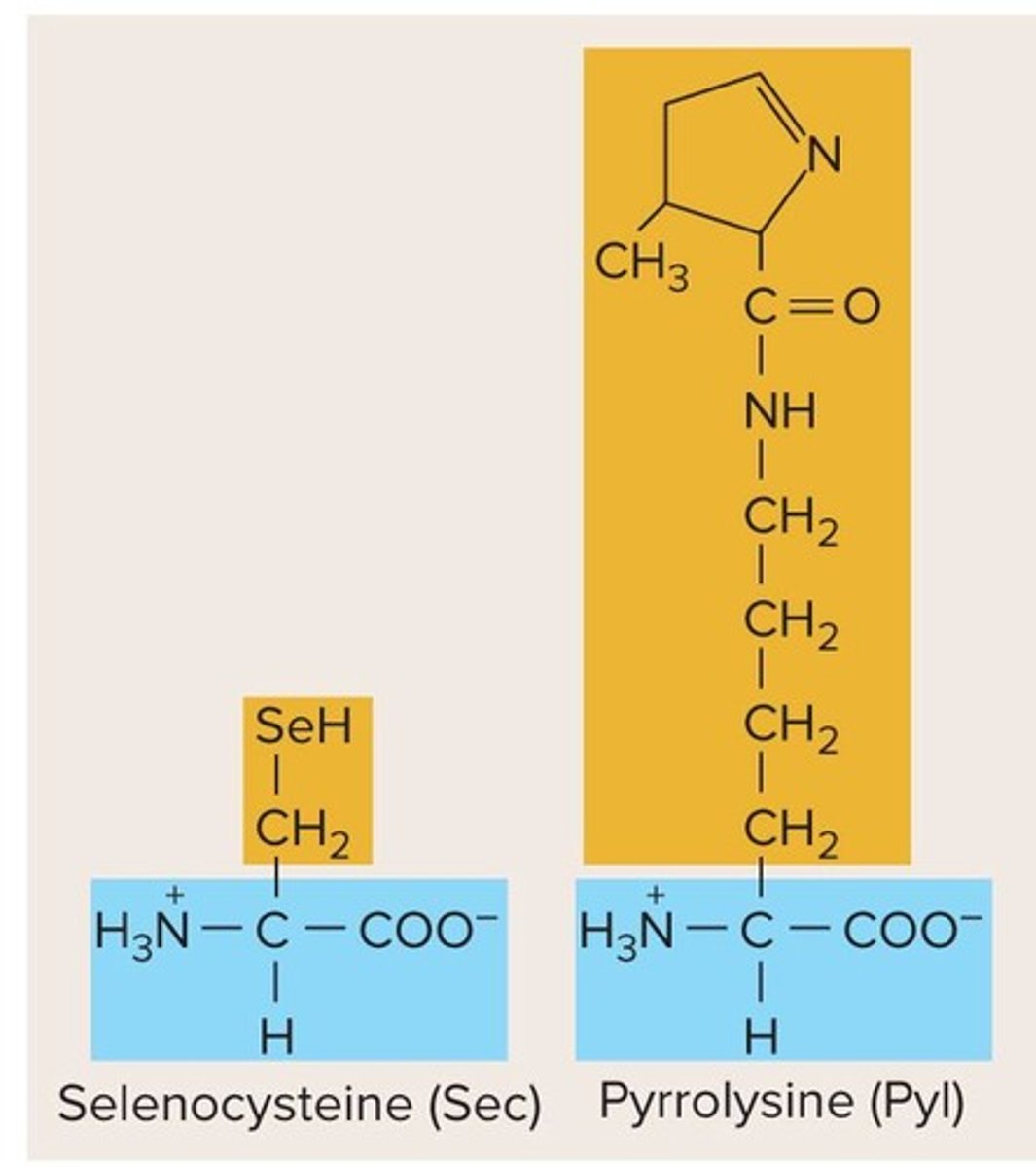
Which codons code for selenocysteine and pyrrolysine?
UGA codes for selenocysteine and UAG codes for pyrrolysine.
What is required to incorporate selenocysteine and pyrrolysine into proteins?
Codon and downstream sequences in mRNA are needed.
What is the effect of deleting a nucleotide in the reading frame of mRNA?
It changes the reading frame and alters the amino acid sequence.
What is the directionality of polypeptide synthesis?
It parallels the 5' to 3' orientation of mRNA.
What is formed during each cycle of elongation in polypeptide synthesis?
A peptide bond between the carboxyl group of the last amino acid and the amino group of the new amino acid.
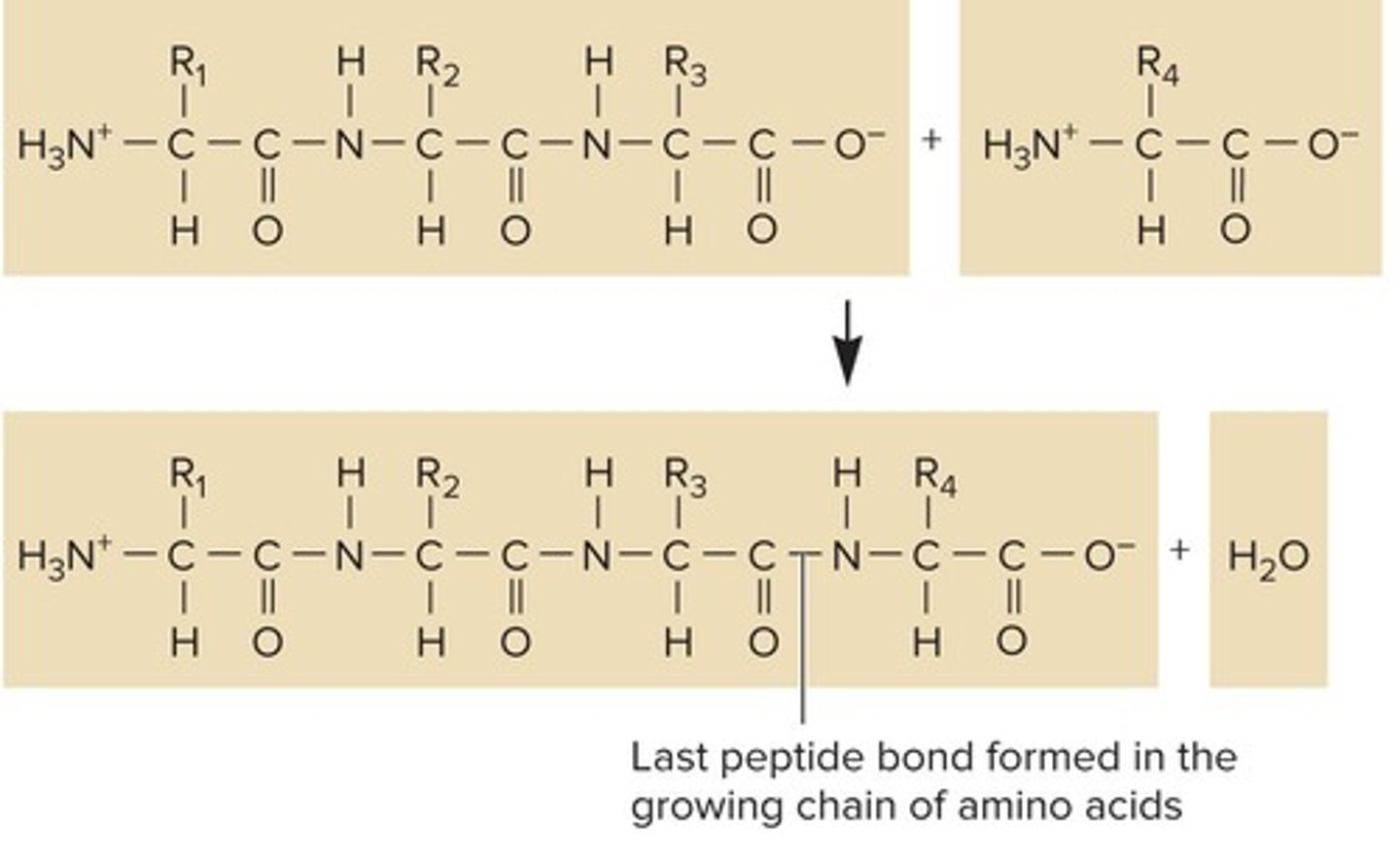
What are the N-terminus and C-terminus of a polypeptide chain?
The N-terminus is the end with an exposed amino group, and the C-terminus is the end with an exposed carboxyl group.
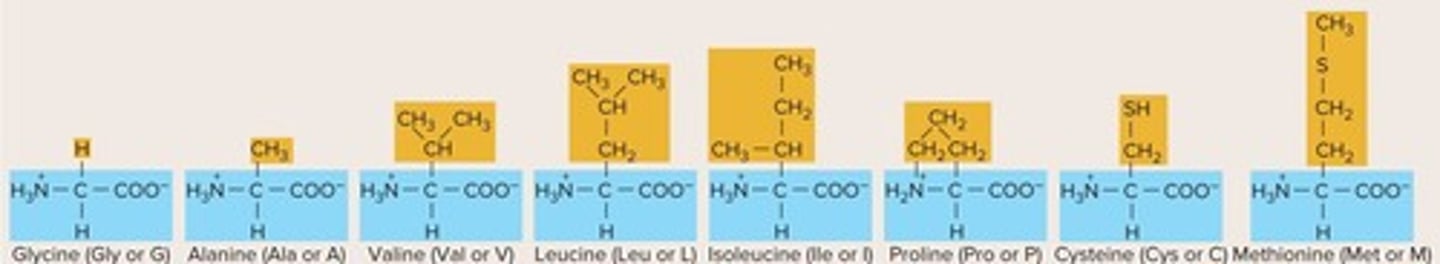
How many standard amino acids are commonly found in polypeptides?
There are 20 standard amino acids.
What determines the structure and function of proteins?
The amino acid sequences of polypeptides.
What is unique about each amino acid?
Each contains a unique side chain, or R group, with distinct chemical properties.
What role do the chemical properties of amino acids play in proteins?
They help determine the function of the proteins they build.
What are nonpolar, aliphatic amino acids known for?
They are hydrophobic and often buried within the interior of a folded protein.
What are the four categories of amino acids mentioned?
Nonpolar, aliphatic; aromatic; polar, neutral; and polar, acidic.
What happens if the reading frame is altered?
It can lead to a completely different sequence of amino acids.
What is the role of tRNA in protein synthesis?
tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome and match them to the codons in mRNA.
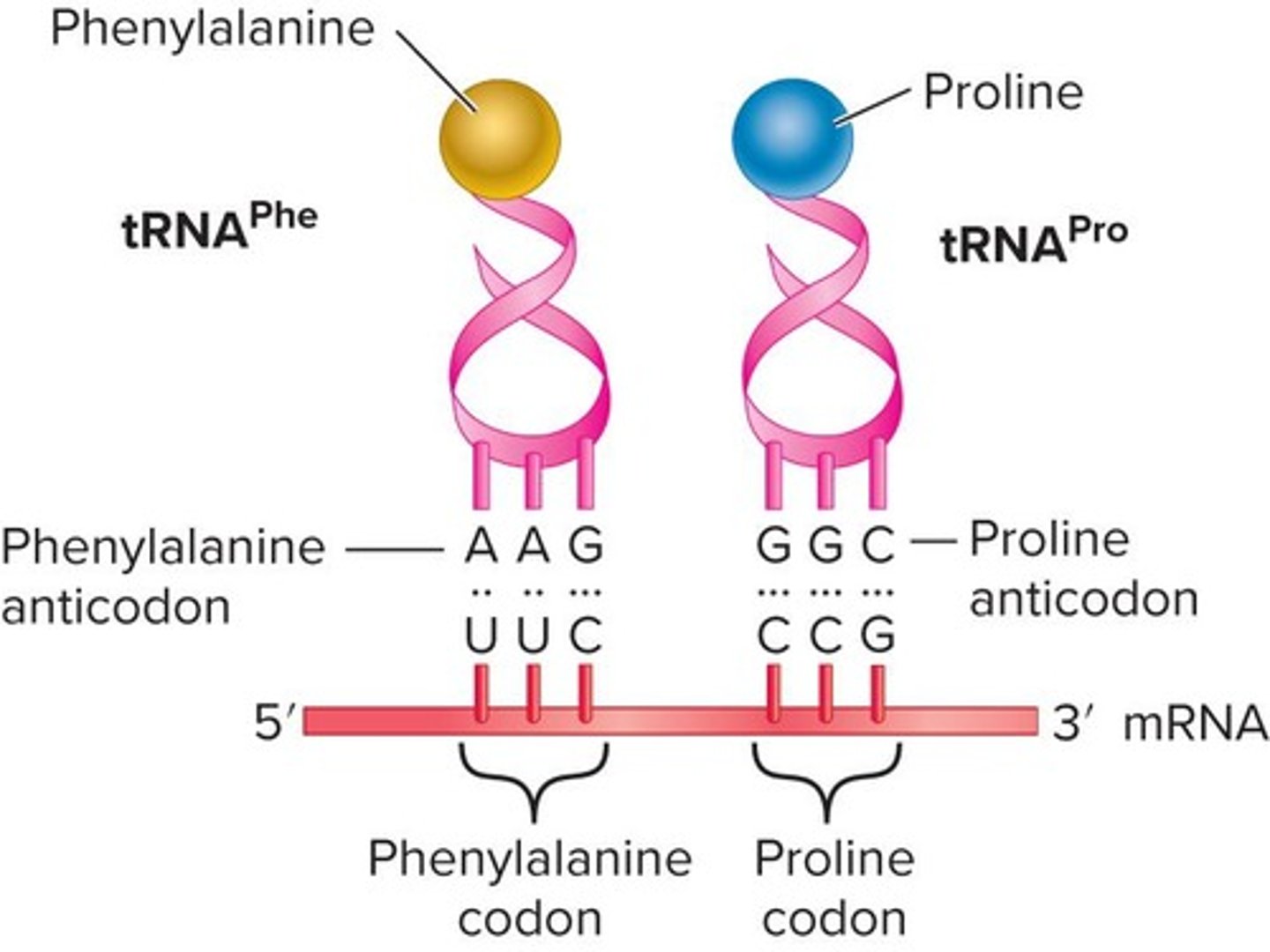
What is the significance of the reading frame in the genetic code?
It defines how codons are grouped into amino acids.
What is the relationship among DNA, mRNA, and polypeptides?
There is a sequence relationship where DNA is transcribed to mRNA, which is then translated into polypeptides.
What are some exceptions to the universal genetic code?
Certain codons may code for different amino acids in specific organisms, such as methionine in yeast mitochondria.
What are the four levels of protein structure?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary.
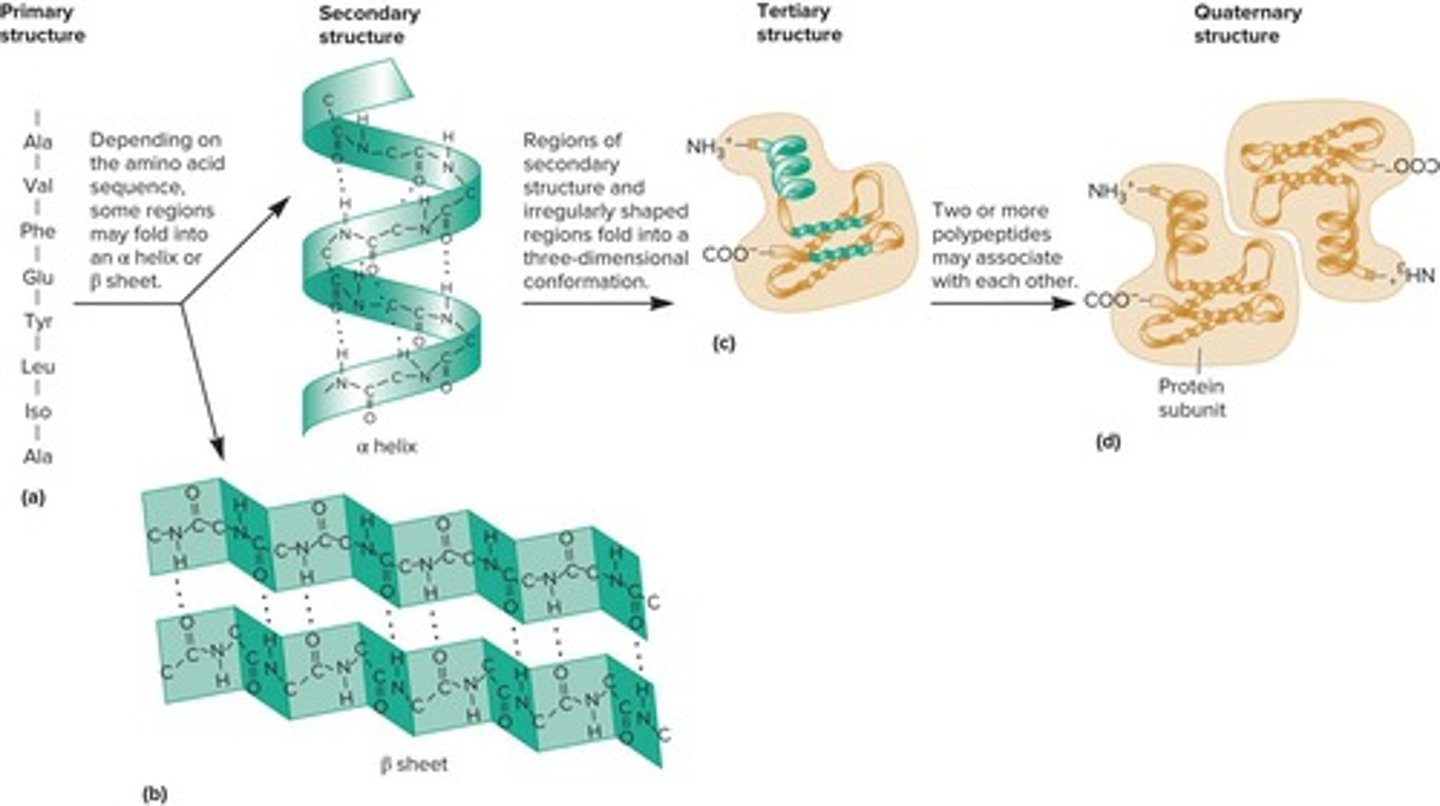
What defines a protein's primary structure?
A protein's primary structure is its amino acid sequence.
What are the two types of secondary structures in proteins?
α helix and β sheet.
How are secondary structures stabilized in proteins?
By the formation of hydrogen bonds between atoms in the polypeptide backbone.
What characterizes the tertiary structure of a protein?
It is the final conformation of proteins composed of a single polypeptide, determined by hydrophobic and ionic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and van der Waals interactions.
What is quaternary structure in proteins?
It is formed when two or more polypeptides associate to make a functional protein.
What role do chaperones play in protein folding?
Chaperones may aid in the folding of proteins during translation.
What are the functions of proteins in a cell?
Transport & Movement, Cell shape and organization, Cell signaling & Cell surface recognition, and as enzymes that accelerate chemical reactions.
What is the function of tubulin in cells?
It forms cytoskeletal structures known as microtubules.
How does hemoglobin function in the body?
It transports oxygen in red blood cells.
What is the role of insulin in cellular function?
It is a hormone that influences cell metabolism and growth.
What does hexokinase do in cellular metabolism?
It phosphorylates glucose during the first step in glycolysis.
What is the function of β-Galactosidase?
It cleaves lactose into glucose and galactose.
What is the role of RNA polymerase?
It synthesizes RNA using ribonucleotides as building blocks.
What does DNA polymerase do?
It synthesizes DNA using deoxyribonucleotides as building blocks.
What type of amino acids are polar and charged?
They are hydrophilic and more likely to be on the surface of a protein.
What is the significance of the genetic code deciphered in the early 1960s?
It was crucial for understanding how genetic information is translated into proteins.
What are the characteristics of polar, basic amino acids?
They are hydrophilic and can interact with water.
What is the importance of protein folding?
Proper folding is essential for the protein's function and stability.
What interactions determine the tertiary structure of proteins?
Hydrophobic interactions, ionic interactions, hydrogen bonds, and van der Waals interactions.
What is the relationship between protein structure and function?
The characteristics of a cell depend on the types of proteins it makes, which perform various functions.
What is the role of integrins in cells?
They bind to large extracellular proteins, contributing to cell shape and organization.
What was the goal of the experiment conducted by Gobind Khorana?
To decipher the relationship between base composition and particular amino acids.
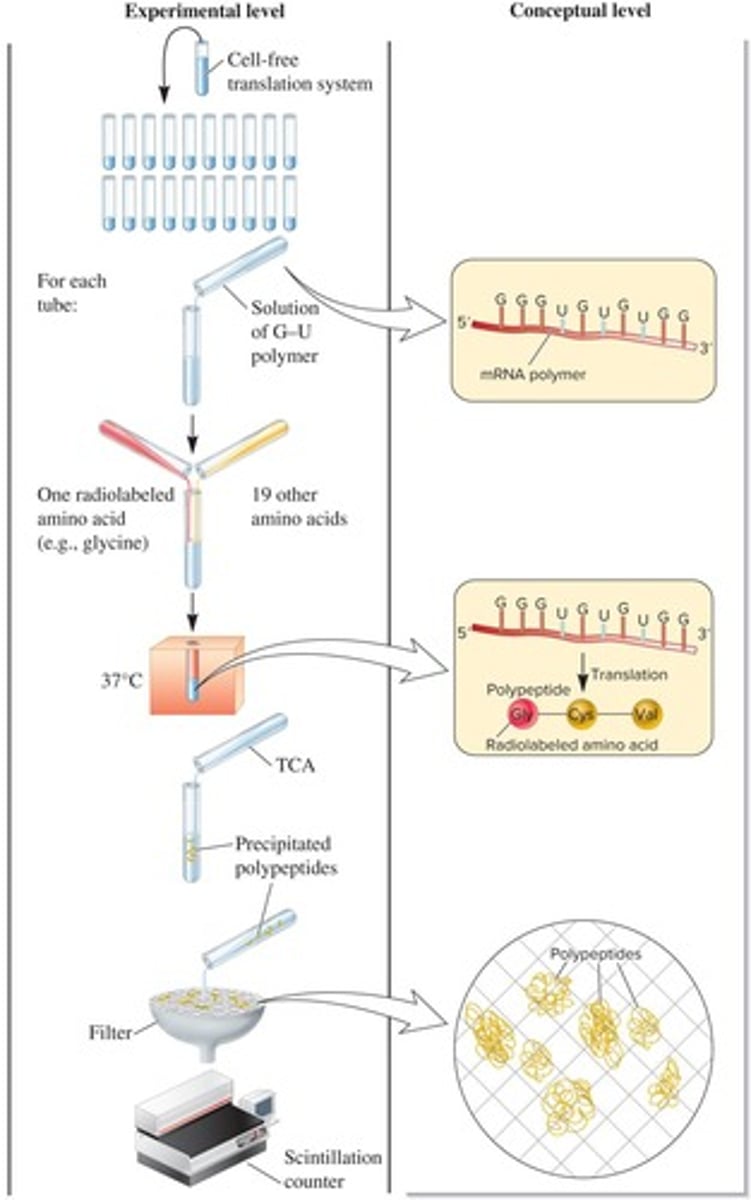
What system did Nirenberg and his colleagues use to help elucidate the genetic code?
A cell-free translation system.
How did Nirenberg's team detect synthesized polypeptides in their experiments?
By adding radiolabeled amino acids to the extracts.
What enzyme was used to create synthetic RNA in the experiments?
Polynucleotide phosphorylase.
What is a key characteristic of the synthetic RNA produced in the experiments?
It does not use a template, resulting in a random order of nucleotides.
How can an experimenter control the composition of synthetic RNA?
By controlling the amounts of nucleotides added.
What was the composition of nucleotides used in the example for synthetic RNA?
70% G and 30% U.
What are the codon possibilities derived from a mixture of 70% G and 30% U?
Examples include GGG (34%), GGU (15%), GUU (6%), UUU (3%), UUG (6%), UGG (15%), UGU (6%), GUG (15%).
What components are included in the cell-free translation system?
Ribosomes, tRNAs, and enzymes that attach amino acids to tRNA molecules.
What is the first step in the elucidation of the genetic code using the cell-free translation system?
Place the cell-free translation system into 20 tubes.
What is the purpose of adding trichloroacetic acid (TCA) in the experiments?
To precipitate polypeptides but not amino acids.
What happens to amino acids that are not incorporated into polypeptides during the experiment?
They pass through the filter.
What method is used to count the radioactivity of the precipitated polypeptides?
Using a scintillation counter.
What was the relative amount of glycine incorporated into the translated polypeptides?
49%.
Which amino acid had a 21% incorporation rate in the experiments?
Valine.
What was the incorporation rate of tryptophan into the translated polypeptides?
15%.
What was the incorporation rate of phenylalanine into the translated polypeptides?
3%.
What conclusion can be drawn from the expected codon frequencies for glycine?
The codons GGG and GGU corresponded to the high incorporation of glycine (49%).
What does the inability to distinguish codons imply about the genetic code?
The code could not be deciphered in a single experiment and required data from multiple experiments.
What was the incorporation rate of leucine and cysteine in the experiments?
Both had an incorporation rate of 6%.
How many amino acids had a 0% incorporation rate in the experiment?
14 amino acids.
What is the significance of the experiments conducted by Nirenberg and Khorana?
They were crucial in cracking the genetic code.
What novel method did Gobind Khorana and his collaborators develop?
A method to synthesize RNA.
What lengths were the short RNAs created by Khorana's team?
2 to 4 nucleotides long.
How were the short RNAs linked together in Khorana's synthesis method?
Enzymatically to create long copolymers.
What was the purpose of the RNA copolymers synthesized by Khorana and colleagues?
They helped to crack the genetic code.
What is an example of a synthetic RNA used by Khorana's team?
Synthetic RNA 'UC'.
What codon possibilities does the synthetic RNA 'UC' form?
UCU, CUC.
Which amino acids are incorporated by the synthetic RNA 'UC'?
Serine and leucine.
What were the codon possibilities and amino acids for the synthetic RNA 'AG'?
Codon possibilities: AGA, GAG; Amino acids: Arginine, glutamic acid.
What were the codon possibilities and amino acids for the synthetic RNA 'UG'?
Codon possibilities: UGU, GUG; Amino acids: Cysteine, valine.
What were the codon possibilities and amino acids for the synthetic RNA 'AC'?
Codon possibilities: ACA, CAC; Amino acids: Threonine, histidine.
What were the codon possibilities and amino acids for the synthetic RNA 'UUC'?
Codon possibilities: UUC, UCU, CUU; Amino acids: Phenylalanine, serine, leucine.