the ultimate AP Psych exam study guide
1/202
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2024/2025 AP psych
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
203 Terms
Hypothesis
Tentative explanation - must be falsifiable (able to be supported or rejected). ends with period instead of question mark. Ex) People who get at least 8 hours of sleep per night will perform better on memory recall tasks than those who get less than 6 hours.
Operational definition
clear, precise, quantifiable definition of your variables –allows replication and collection of reliable data. ex) rating on a 1–10 sleep quality scale each morning.
Qualitative data
descriptive data (eye color), describes qualities or characteristics.
Quantitative data
Numerical data - ideal and necessary for statistics
population
everyone the research could apply to
sample
the people (or person) specifically chosen for a study
correlation
identify relationship between two variables. Advantage: useful when experiments are unethical. Disadvantage: CORRELATION DOES NOT EQUAL CAUSATION
directionality problem
which direction does it go? (does depression cause low self esteem or does low self esteem cause depression?)
3rd variable problem
diff. variable is responsible for the relationship (ice cream and murder)
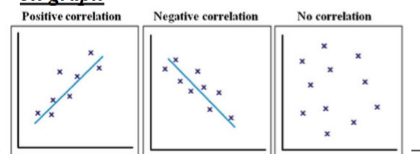
positive correlation
variables increase and decrease together
Negative correlation
as one variable increases, the other decreases
Correlations cannot be ____ or ____ than 1/-1
Greater or less than 1/-1 , the stronger the number, the stronger the relationship, regardless of the pos/neg sign. Stronger relationships = tighter clusters on graph
experiments
purposefully manipulate variables to determine cause/effect. Advantage: only method that establishes cause/effect Disadvantage: can be unethical, too artificial
independent variable
purposefully altered by researcher to look for effect
experimental group
received the treatment (part of the IV); can have multiple exp groups
control group
gets placebo or nothing, baseline (part of the IV), can only have 1
dependent variable
measured variable (is DEPENDENT on the independent variable)
placebo effect
any observed effect on a behavior that is “caused” by the placebo (shows effectiveness of exp. treatment) usually fixed w/ blinded studies
double-blind
experiment where neither the participant or the experiment are aware of which condition people are assigned to (drug studies)
single-blind
only participant blind- used if the experimenter can’t be blind (gender, age, etc)
confounding variable
error/flaw in study that is accidentally introduced. ex ind: amount of time studying dep: test scores confound: prior knowledge
random assignment
assigns participants to either control or experimental group at random - increases chance of equal representation among groups (spreads the lefties across both groups) - allows you to say cause /effect
naturalistic observation
observe people in their natural settings. adv: real world validity disadv: no cause and effect
case study
studies one person (usually) in great detail. adv: collect lots of info. disadv: no cause/effect
meta-analysis
combines multiple studies to increase sample size and examine effect sizes
descriptive statistics
show shape of the data (mean, median, mode)
mean
average (use in NORMAL distribution)
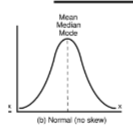
median
middle number (used in SKEWED distribution)
mode
number that occurs most often
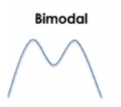
bimodal
has two modes - usually indicates good bad scores
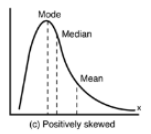
skews
usually created by outliers
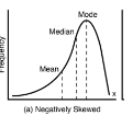
neg skew
mean is to the left (neg side) WHALE TAIL POINTS TO THE NEGATIVES!!
pov skew
mean is to the right. WHALE TAIL POINTS TO THE POSITIVE NUMBERS!!
how to find median
arrange your numbers in ascending order (from smallest to largest). Find middles number if u have odd set of numbers
For example, in the list [3, 5, 7], the median is 5.
If you have an even number of values, the median is the average of the two middle numbers. For example, in the list [3, 5, 7, 9], the median is (5 + 7) / 2 = 6.
Odd Set: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] → Median is 6 (the middle number).
Even Set: [1, 3, 5, 7] → Median is (3 + 5) / 2 = 4.
range
distance b/w smallest number and biggest number
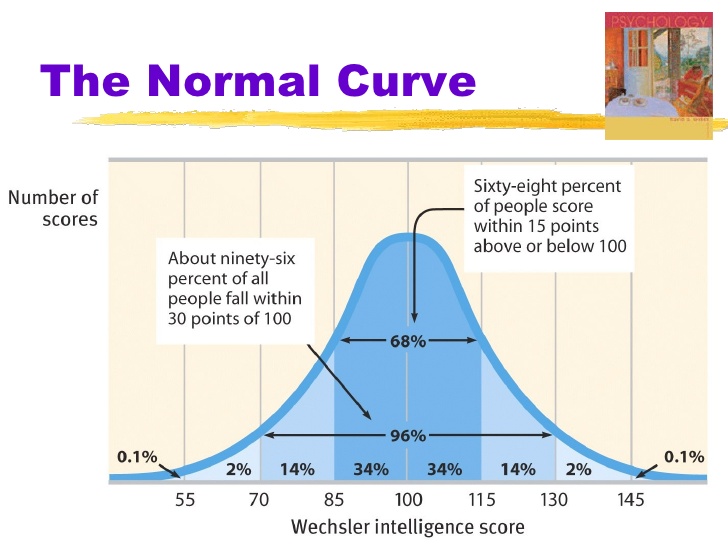
standard deviation
avg. amount the scores are spread from the mean (bigger number = more spread) 68-95-97.7
inferential statistics
establishes significance (meaningfulness) (stat significance, effect size)
statistical significance
results not due to chance, exp. manipulation caused the difference in mean. p<0.5=stat significance, smaller=better , says effect exists or not
p-value
says stat sig. needs to be less than 0.05
effect size
data has practical significance - bigger = better. may have stat sig (p) but the size not might be great, d: A small effect size is around 0.2, medium is 0.5, and large is 0.8. r (correlation): range from -1 to 1, where 0 indicates no correlation.
experiments that include people must be__ /EG
reviewed by an institutional review board
confidentiality (ethical guideline)
names/info kept secret
informed consent /EG
participants must agree to be part of study
informed assent / EG
minors and their parents must agree
debriefing / EG
must be told the true purpose of the study (done after it study needed deception)
no harm /EG
no harm to participants mentally or physically
surveys
usually turned into correlation bc subject to self report bias
self report bias
errors when collecting survey data due to social desirability or wording effects
social desirability effect
people lie to look good/ like a better person
wording effects in questions
how you frame the question can impact your answer
random sample/selection
method for choosing participants for your study - everyone has a chance to take part, increases generalizability
difference between random sample and random assignment
sample = generalize , assignment = cause/effect groups
representative sample
sample mimics the general pop (ethnic, gender, age)
convenience sample
select participants on availability/most easiest way - less representative and less generalizability this way
sampling bias
sample isn’t representative due to convenience sampling
cultural norms in experiments
behaviors of a particular group can influence research results
experimenter bias / participant bias
experimenter/participant expectations influences the outcome of study
cognitive bias
bias in thinking/judgment (usually implicit)
confirmation bias
find info that supports our preexisting beliefs
hindsight bias
“i knew it all along!!” (no you didnt)
overconfidence
overestimate our knowledge / abilities
hawthorne effect
people change behavior when watched
belief perseverance
people hold on to their beliefs even when faced with contradictory evidence
research needs ____ and ___
peer review and adequate sample sizes
evolutionary psych
study how natural selection influences behavior (think darwin)
heredity (nature)
how genes influence your behavior
environment (nurture)
how outside situations influence your behavior (ex school)
twin/adoption studies
genetics (nature): identical twin (monozygotic) will have a higher percentage of also developing a disease
environment: identical twins raised in different environments show differences in nuture
desirable subjects for twin studies
monozygotic (identical) twins cancels out most nature (genetic) factors and looks more at nurture.
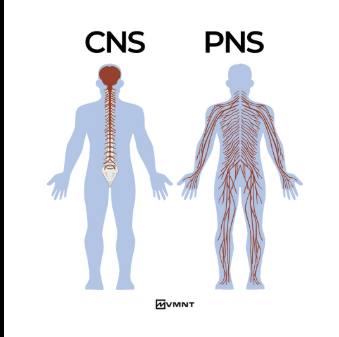
Central nervous system
Brain and Spinal cord
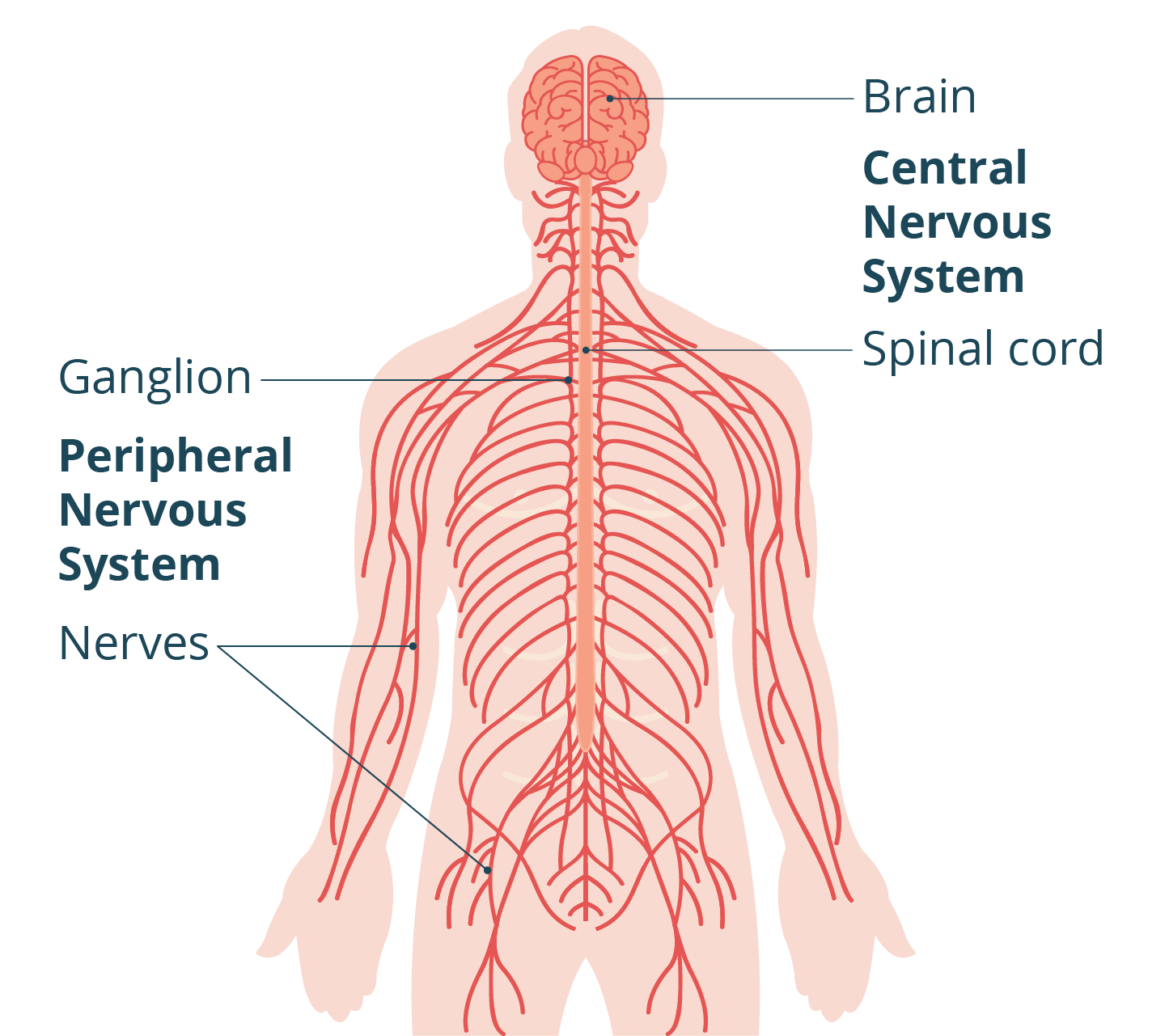
peripheral nervous system
rest of the nervous system and relays to central NS (includes somatic, autonomic - both branch out to more NS)
somatic nervous system
voluntary movement, has sensory and motor neurons
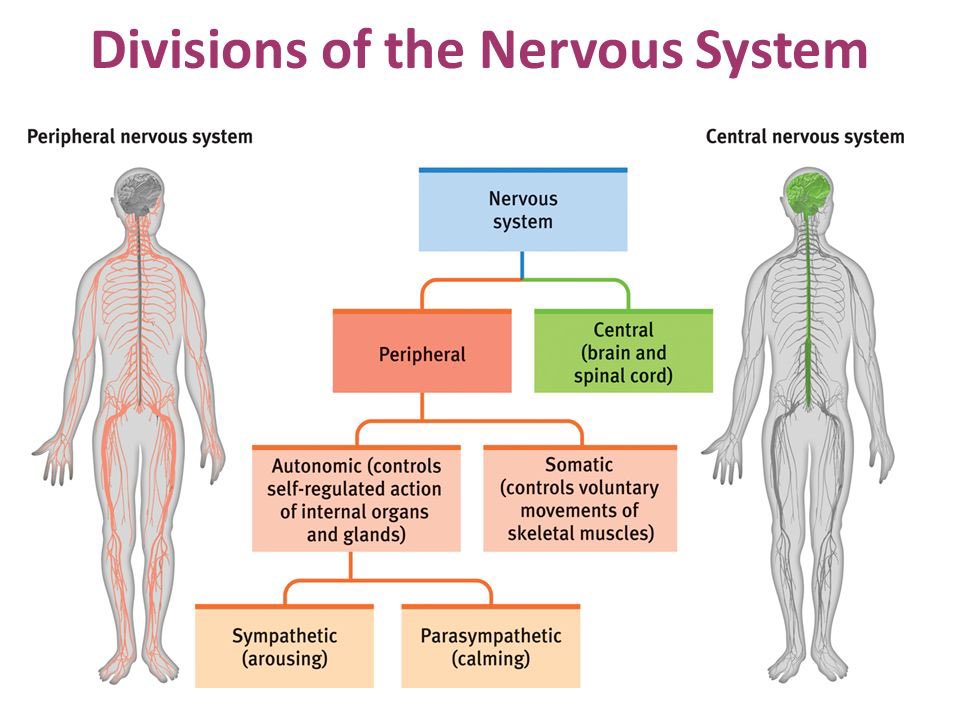
autonomic nervous system
involuntary organs ( controls heart, lungs, etc) - contains sympathetic and parasympathetic)
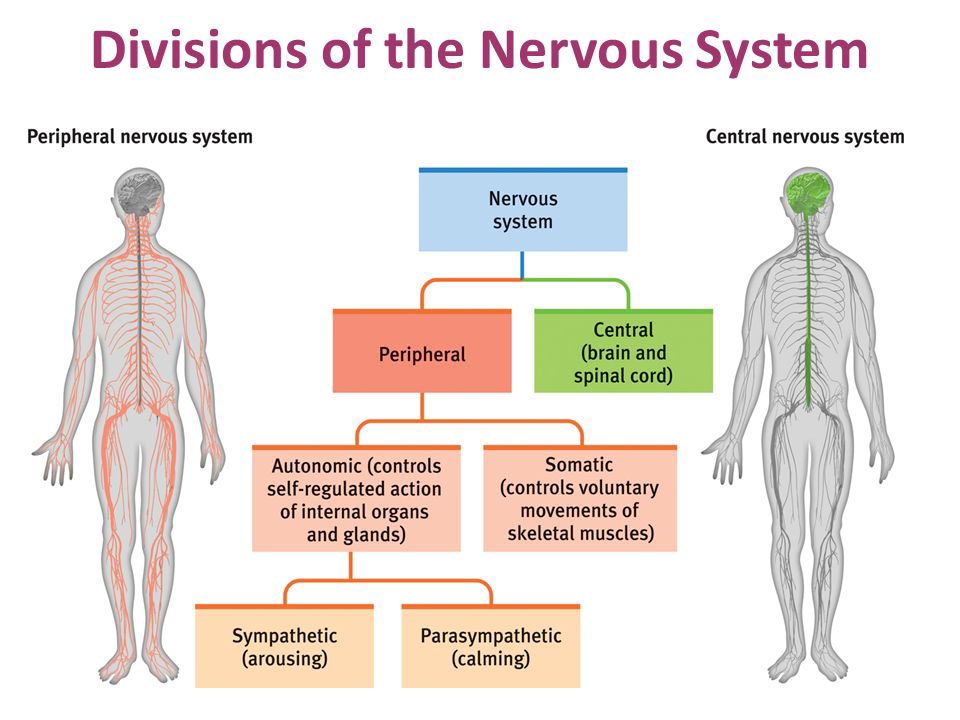
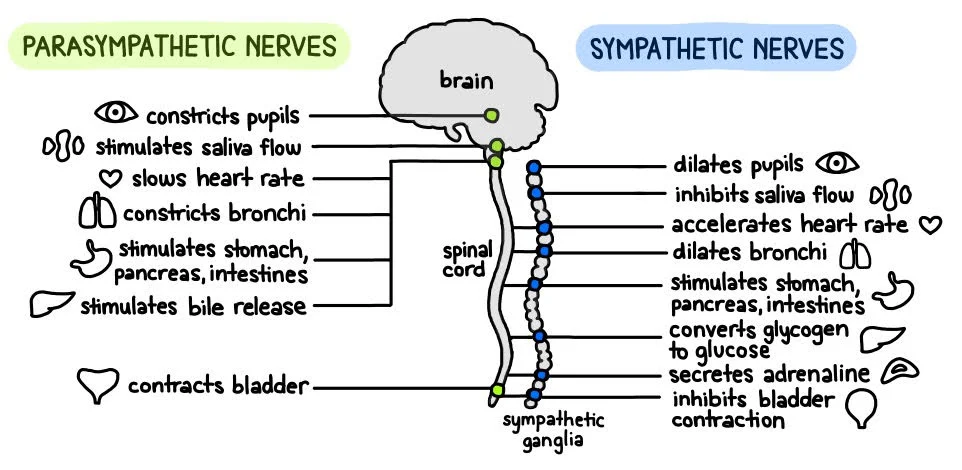
parasympathetic nervous system
rest/digest (generally inhibits - exception digestion which it activates), tries to calm
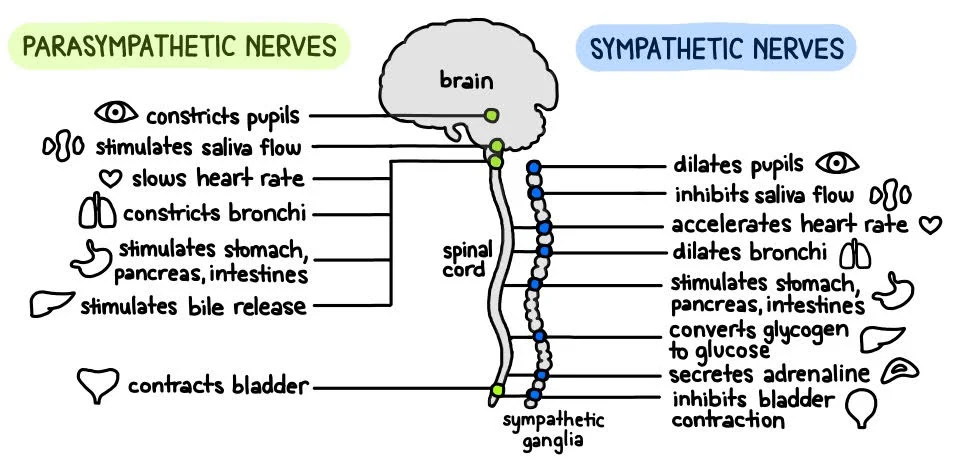
sympathetic nervous system
fight/flight (generally activates - except digestion which it slows)
neuron
basic cell of the nervous system
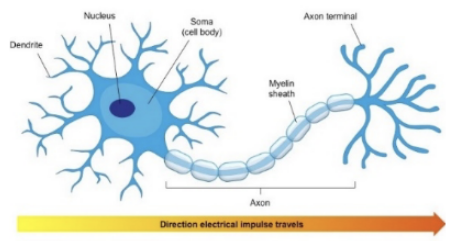
dendrites
receive incoming neurotransmitters
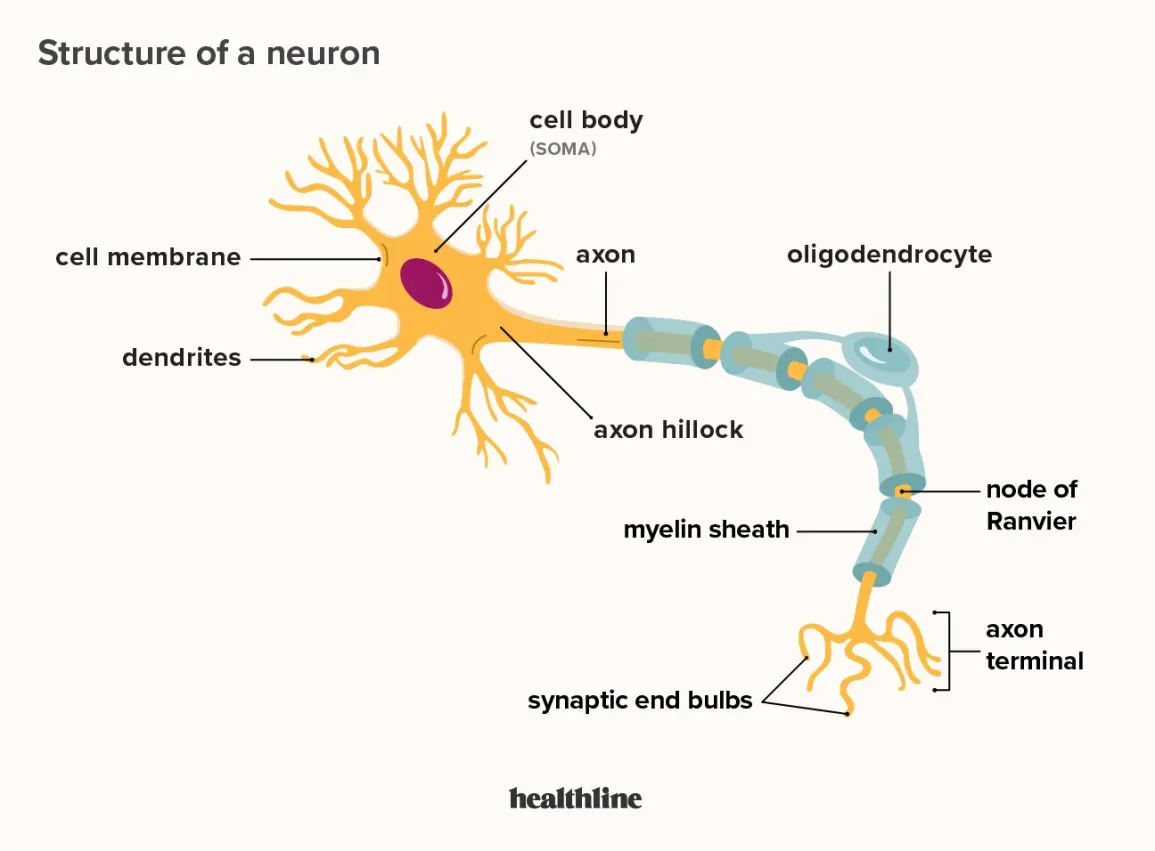
axon
action potential travels down this
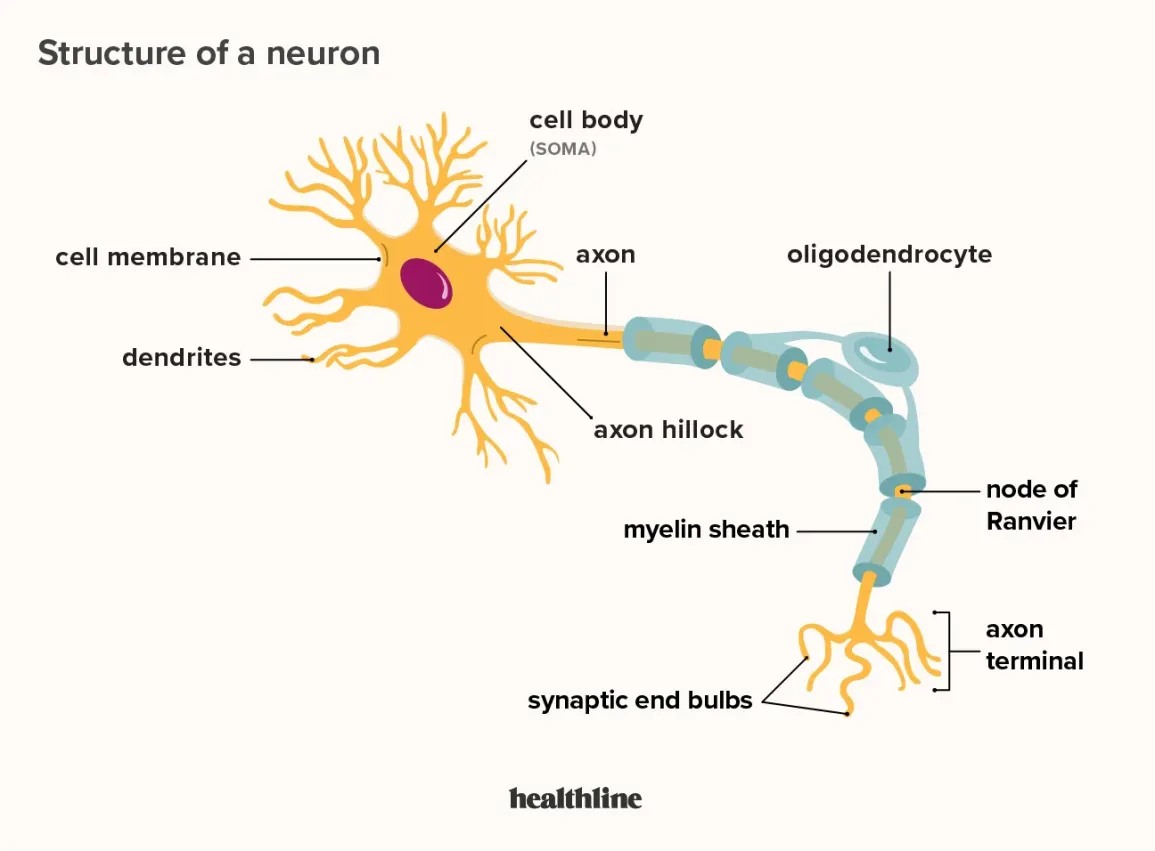
myelin sheath
speeds up action potential down axon, protect axon
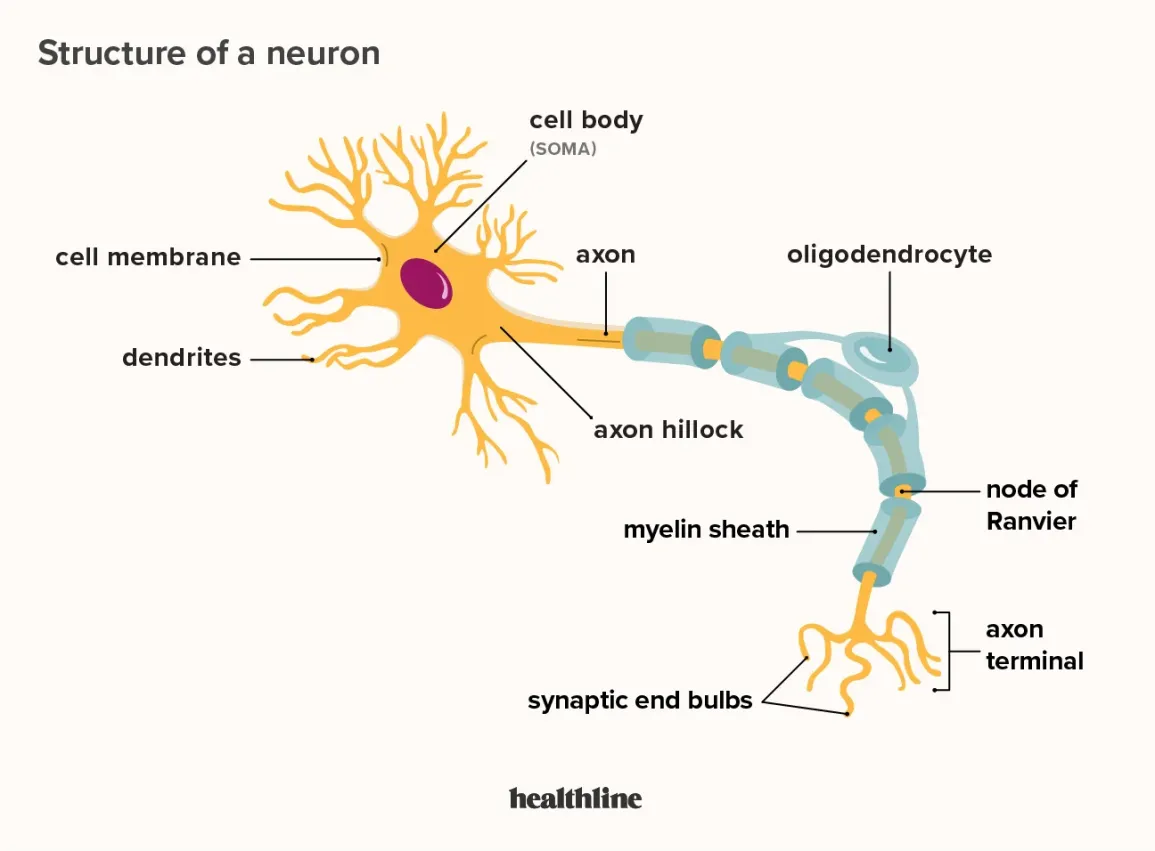
synapse
gap between neurons
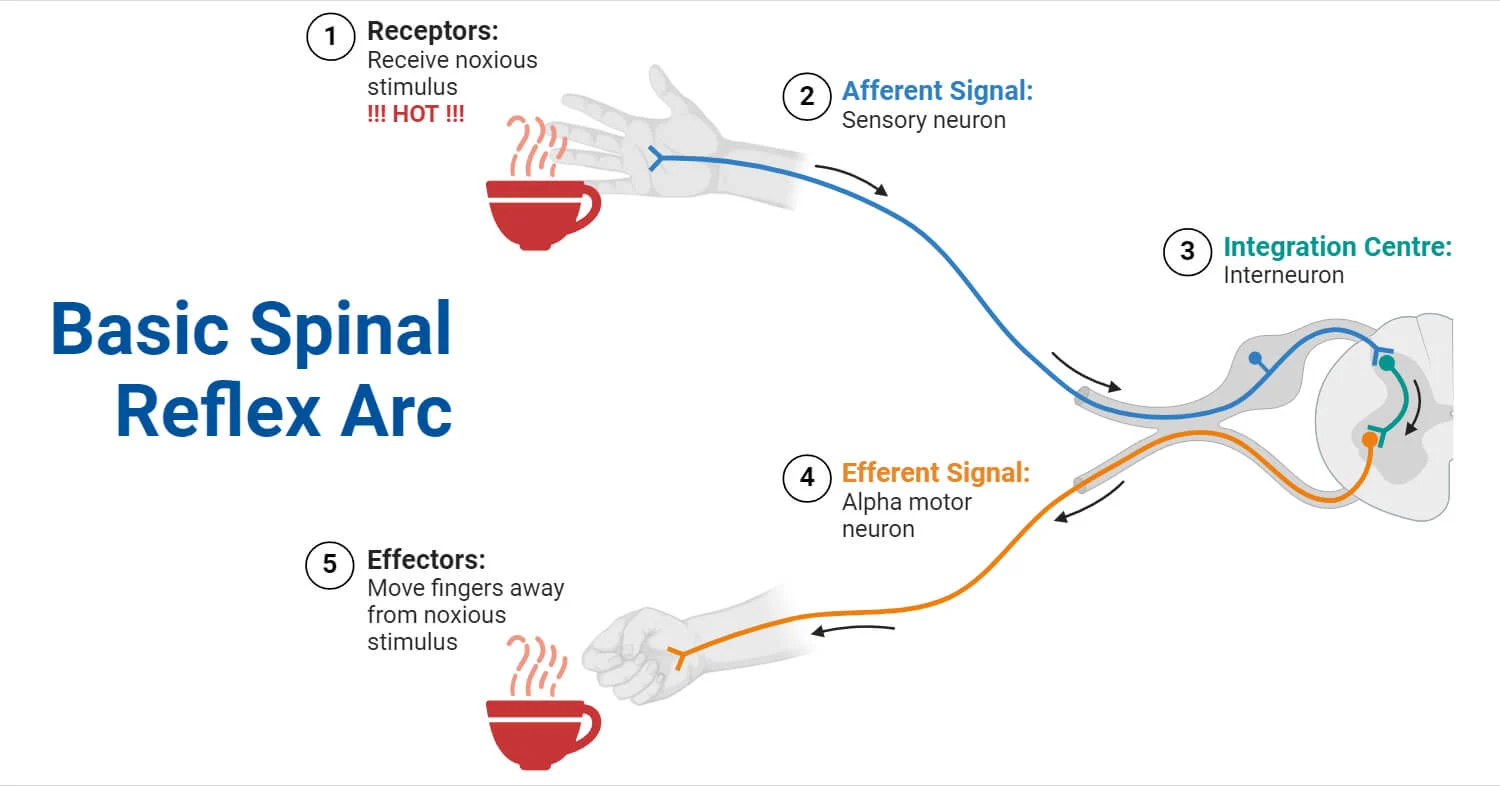
sensory neurons
receives sense signals from environment and send signals to the brain (ex. touch something hot, sensory neurons in your skin send a signal to your brain, telling you to pull your hand away quickly!)
motor neurons
signals to move send signals from the brain to your body (ex. decide to wave hello to a friend, your motor neurons send signals to the muscles in your arm)
interneurons
cells in the spinal cord/brain responsible for reflex art, help sensory neurons and motor neurons communicate within the brain and spinal cord. ex. helps when hand is on hot flame
reflex arc
important stimuli skips the brain and routes through the spinal cord for immediate reactions (hand on a hot flame)
GLIA
support cells that give nutrients and clean up around neurons
action potential
what fires neurons, ions move across membrane sends and electrical charge down the axon
resting potential
neuron maintains a -70mv charge when not doing anything
depolarization
charge of neuron briefly switches from neg to pov - triggers action potential
threshold of depolarization
stimulus strength must reach this point to start to action potential
all or nothing principle
stimulus must trigger the action potential past its threshold, but does not increase the intensity or speed of the response (think about flushing a toilet)
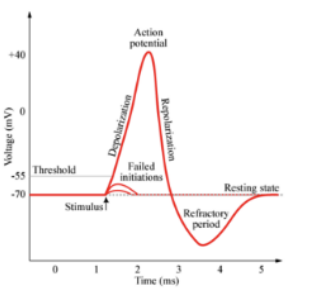
refractory period
A neuron must rest and reset before it can send another action potential (toilet has to reset!)
neruotransmitters
chemicals released in synaptic gap, received by neurons. classified as excitatory (increase Action potential in other neurons) or inhibitory (decrease action potential) (ex. GABA, dopamine, serotonin, etc)
GABA /NT
major inhibitory neurotransmitter - reduces anxiety and promotes relaxtation (yo! gaba gaba the show calms you down!)
Glutamate /NT
major excitatory NT (glutes excite you!) stimulates brain activity, learning, and memory. When you’re studying for a big test, glutamate is working hard to help you remember all those facts
Dopamine /NT
reward (short term - reinforcing behaviors that lead to rewards) and fine movement ( Low levels are associated with movement disorders - Parkinson's disease), in hypothalamus, assoc. w/ addiction.
serotonin /NT
moods regulation (long-term - low leads to anxiety/depression), regulates sleep wake cycles - in amygdala, too little assoc. with depression
acetylcholine (ACh) /NT
Memory and movement - in hippocampus, assoc. w/ alzheimer’s (A’s match)
Norepinephrine /NT
Sympathetic NS, fight or flight NT - too little assoc. w/ depression
endorphins /NT
decrease pain, natural euphoria (runners high)
substance P / NT
Pain regulation (abnormality increases pain and inflammation)