Topic 5: Chemical Equilibrium - Equilibrium Constants (K)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Chemical Equilibrium
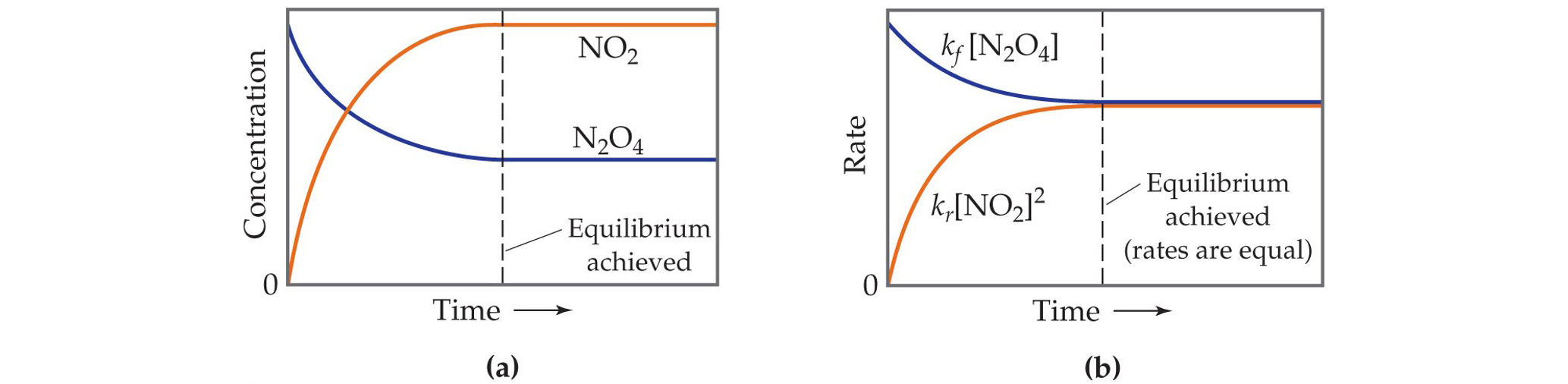
A state in which the concentrations of reactants and products no longer change because the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal
Reversible Reaction
A reaction in which reactants form products and products can reform reactants, indicated by the double arrow (⇌)
Example: H₂O (l) ⇌ H₂O (g)
Dynamic Equilibrium
A condition where the forward and reverse reactions occur at equal rates, so concentrations remain constant but reactions continue at the molecular level
Closed System
A system where no substances can enter or leave, allowing equilibrium to be established
Equilibrium Constant (K)
A fixed ratio of product concentrations to reactant concentrations at equilibrium for a given reaction and temperature
Kc
The equilibrium constant expressed in terms of concentrations (mol/L)
Temperature and K
The only factor that changes the equilibrium constant K is temperature
Equilibrium Position
Not affected by initial concentrations, the system shifts to re-establish the K ratio
Equilibrium Expression
An equation showing how K is calculated from the concentrations of products and reactants at equilibrium
General Equilibrium Expression
Where: aA + bB ⇌ dD + eE
Kc = [D]d[E]e/[A]a[B]b
Products in the numerator
Reactants in the denominator
Stoichiometric Coefficients
Used as powers on the concentration terms in the K expression
Heterogeneous Equilibrium
A reaction with species in multiple phases (solid, liquid, gas, aqueous)
Example: CaCO₃(s) ⇌ CaO(s) + CO₂(g)
Solids and Liquids in Equilibrium Expressions
Pure solids and liquids are excluded from the K expression because their concentrations do not change
Large K (K > 1)
Products are favored; high product concentration and low reactant concentration
Small K (K < 1)
Reactants are favored; low product concentration and high reactant concentration
K = 1
Neither direction is favored; significant amounts of both reactants and products
Reversing a Reaction
The new equilibrium constant is the reciprocal of the original: Kc' = 1/Kc
Example: If PCl₅ ⇌ PCl₃ + Cl₂ is reversed,
Kc = [PCl₃][Cl₂]/[PCl₅]
Changing Coefficients
If all coefficients in the balanced equation are multiplied by n, the new equilibrium constant becomes Kⁿ