SDSU Nutri201 Exam 3
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what are lipids & major types
“fats”
triglycerides
cholesterol
phospholipids
triglyceride
glycerol + 3 fatty acid
95% of dietary lipids
adipose fat
short triglyceride chain length
2-6 C’s
mostly supplements
water soluable
medium triglyceride chain lengths
6-10 Cs
long triglyceride chains
12+ C’s
Fat soluble, hard to break down
easiest to get in diet and not always saturated
22+ long chains are bad
determining unsaturated vs saturated fat
Amt of H (max 4) per 1 C
saturated fat - single bonds
monounsaturated - 1 double bond
polyunsaturated - 2 double bond
bends in fatty acid backbone
At room temp;
no bends = solid
bends = liquid
bends occur with
only for unsaturated fats
occur bc of a cis double bond making it bend
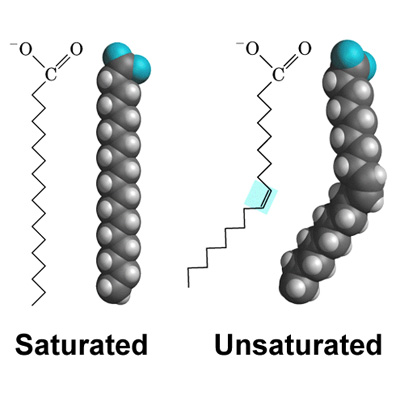
examples of saturated fat
animal fats and tropical oils
examples of unsaturated fat
plant fats (peanut, soybeans, olives) (l)
cis double bonds
H on same side of fatty acid backbone
most common
trans double bonds
H across fatty acid backbones
produced by fat into sat fat
top sources of omega fatty acid
slamon
herring
manhaden
anchovies
sardines
flaxseeds
canola oil
walnuts
eggs
fatty essential acid
means humans can’t make it so it has to be eaten
linoleic acid - 18 C , fatty acid Omega 6 , polyunsat fatty acid
alpha-linolenic acid - omega 3 fatty acid
omega 3 is bigger than omega 6
linolenic AMDRs
linoleic acid - 5-10% of kcals
linolenic acid/n-3s - .6-1.2 of kcals
Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency Symptoms
aka EFA
Reproductive failures
skin abnormalities
kidney & liver disorders
growth and vision impairment in infants
fatty acid nomenclature
example:
cis X - Y:Z like cis9-16:1
cisX - where the double bonds are located in the chain (i.g. X’th chain)
Y - amt of carbon atoms
Z - amt of double bonds
rmbr that sat fat has 0 double bonds, so no ‘cisX’ or Z values
Lauric Acid
12:0
Sat fat, 12 C, 0 db
Myristic Acid
14:0
Sat fat, 14 C, 0 db
Palmitic Acid
16:0
sat fat, 16 C, 0 db
Stearic Acid
18:0
sat fat, 18 C, 0 db
arachidic acid
20:0
sat fat , 20 C , 0 db
palmitoleic acid
cis9-16:1
unsat fat , db at 9th , 16 C , 1 db
Oleic Acid
cis9-18:1
unsat , db at 9th, 18 C, 1 db
Linoleic acid
cis9,cis12-18:2
unsat , db at 9th and 12th, 12 C , 2 db
linolenic acid
cis9,cis12,cis15-18:3
unsat fat , db at 9th 12th and 15th, 18 C , 3 db
arachidonic acid
cis 5, cis 8, cis 11, cis 14-20:4
unsat fat , db at 5th 8th 11th 14th , 20 C , 4 db
Eicosatetraenoic acid
cis 5 , cis 8 , cis 11, cis 14, cis 17-20:5
unsat fat , db at 5th 8th 11th 14th 17th , 20 C , 5 db
Docosahexaenoic acid
cis 4 cis 7 cis 10 cis 13 cis 16 cis 19 - 22:6
unsat , db at 4th 7th 10th 13th 16th 19th , 22 C , 6 db
Glycerol
not lipid soluble
prod in CHO metabolism
convert to CHO thru gluconeogensis
cholesterol
found strictly only in animals
chicken giblets have most
used for:
transmitting nerve impulses thru body
vit D source for skin
part of all cell membranes
makes sex hormones
forms bile acid in liver
olestra
fat substitute that is used in some food products to reduce their fat and calorie content with chemically modifying veggies oil
lipoprotein health issues
coronary hearth disease
plaque formation
olestra pros
0 kcals
0 fat , sat , and trans fat
0 cholesterol
withstands frying and baking
tastes like fat
olestra cons
vitamin loss
phytochemical losses
digestive sys upset
anal leakage
expensive
no long term study in children
fat replacers effectiveness
can assist but easily negligent if later compensated
less kcal
less sat fat
more nutrients
random tips to decrease fat
grill , roast , bake , microwave , stir fry , poach
light dressing & large green portions
reduce butter , creamy sauces , cheese , bacon
only use lean meats
home made prep > premade & prepacked
benefits of the Mediterranean diet
reduced blood clotting
reduced LDL cholesterol
reduced vulnerability for LDL cholesterol to oxidate
reduced blood pressure
provides phytochems for antioxidants
consistency of Mediterranean diet
low red meat
high nut , fruit , fish , seafood
fufills American Dietary Guidelines
phospholipids
sim to triglyceride except one fatty acid is replaces with phosphate groups
phospholipid function
for the cell membrane and metabolic parts
hydrophobic tails to fatty acid
hydrophilic heads to water
Importance of fat
top energy storage as macronutrient
forms cell walls
hormone like compounds
organs involved with fat digestion
gallbladders - tell when fat eaten
pancreas - lipase digests fat
digestion of long chain fatty acids
triglycerides broken down into fatty acid , glycerol , chol , and PL
absorbed in intestinal cells
repacked as chylomicron
transported in lymph to blood
medium and short chains of fatty acids
water solubility lets it absorbed into blood
transported directly into liver
metabolism of fatty acid
energy
extra triglycerides and glycerol are stored
metabolism of adipose tissues
stored with glycerol and triglycerides
metabolism of chylomicron remnnrs
travel to liver
packed as lipoprotiens
circulates in blood
what happens from fat in adipose tissue to the time it is produced into atp
lipolysis - triglycerides broken into fatty acid and glycerol
beta oxidation - cells uptake fatty acid and breaks them down into acetyl-CoA, producing high energy molecules of NADH & FADH2
Krebs cycle and electron transport chain - krebs generates more NADH and FADH2 that move into electron transport chain and energy generates large amts of atp
ASK KEIRA IF THIS IS WHAT IS MEANT
what happens from fat in fatty acid to the time it is produced into atp
activation and transportation - fatty acid attatch to coenzyme A, forming fatty acyl-CoA and transported thru mitochondrial matrix
beta oxidation - cells uptake fatty acid and breaks them down into acetyl-CoA, producing high energy molecules of NADH & FADH2
Krebs cycle and electron transport chain - krebs generates more NADH and FADH2 that move into electron transport chain and energy generates large amts of atp
what happens from fat in chylomicron remnants to the time it is produced into atp
hydrolysis - chylomicron remnants circulate in blood stream and their triglycerides become broken down by lipoprotein lipase (LPL) in fatty acid and glycerol
beta oxidation - cells uptake fatty acid and breaks them down into acetyl-CoA, producing high energy molecules of NADH & FADH2
Krebs cycle and electron transport chain - krebs generates more NADH and FADH2 that move into electron transport chain and energy generates large amts of atp
rest of chylomicron eaten by lysomes in liver into more triglys and repeat
lipoproteins
water soluble form
classified based on density (lipid and protein content)
obesity related conditions
hypertension
heart disease
foot
weight assessment methods for kids
growth charts
weight assessment methods for adults
body mass index aka Quetelet Index
weight (kg) / height (meters)2
kg = lbs/2.2
meters = ( inches * 2.54 ) / 100
BMI obesity level
30
does not account for body comp tho
hamwi formula
male : 100lbs for first 5 ft + 6 lbs for each inch after
female : 100 for first 5 ft + 5lbs for each inch after
body comp 2 model assessment
fat
percentage
subcutaneous - under skin fat
visceral - fat for organs
lean
muscle tissue
organs
water
bone
healthy fat levels
men - 8-20%
essential 3-5%
women - 15-25%
essential 12%
dual energy absorptiometry (DEXA)
xrays beams through body to differ between lean mass and fat mass to create a generated image
skinfold thickness
use a pincher (calipers) measure thickness of a fat fold to estimate body fat
bioelectrical impedance
weak current through the body, mostly lean has a free current and mostly fat impedes the current
more impedance = more fat
less impedance = less fat
problems
fasted
hydrated
no excercise
hydrostatic weighting
person fully exhales and is submerged in water and weight determined by water displacement
person has to remain motionless tho
fat distribution
abdominal areas - high risk of obesity issues
lower body (legs/thighs) - low risk of obesity issues
android body shape
male often
square
gynoid pear shape
mostly women
pear
how to improve body weight and comp
diet - lower energy intake
exercise - burning more calories, has to be a consistent form like walking everywhere instead of potatoing
behavioral mods - writing down diet and activity, milestone rewards, positive behaviors > punishments
drugs - work but low nut
surgery - work but also like low nut
types of lipoproteins
VLDL - high levels are bad, can carry hazardous things like cholesterol and triglycerides
LDL - high levels are bad
HDL - high levels are good, it’s doing its job
protein sources
meat
dairy
fish
poultry
egg
nuts
soybeans
protein complementation
combo foods with incomplete proteins to provide adequate amts of all essential amino acids
protein requirements
(lbs 2.2) = kg * 0.8
adult RDA - .8 g/kg
AMDR - 10 to 35 % kcal
function of protein
enzymes - catalyst, reactions go faster
hormones - produced often in gland and used elsewhere
structures - for muscle contraction
transport - molecules across cell membranes and in circulatory systems
immunoproteins - fight off infection