Plant Anatomy: Eudicots vs Monocots
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Eudicot
A group of angiosperms with 2 embryonic seed leaves.

Monocot
A group of angiosperms with 1 embryonic seed leaf.
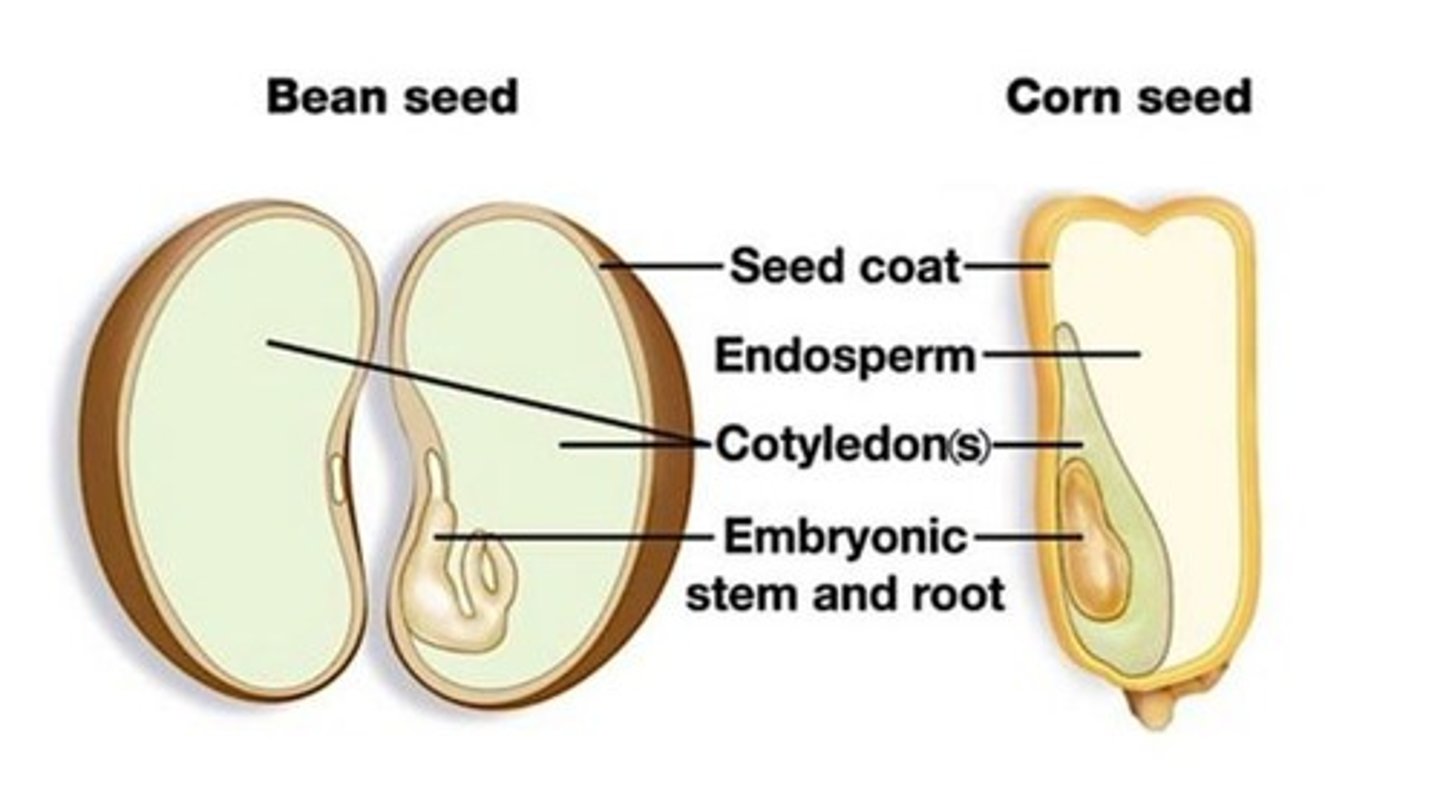
Cotyledon
Embryonic seed leaf.
Primary Growth
Growth in length and the elongation of the plant, producing primary tissues.
Secondary Growth
Growth in girth, expanding roots or stems and producing secondary tissues.
Root System
Absorbs water and minerals, anchors the plant, and stores food, primarily underground.
Storage Roots
Modified underground organs that store nutrients for long periods.
Taproot System
A root system with one main root and many branching roots, typical of eudicots.
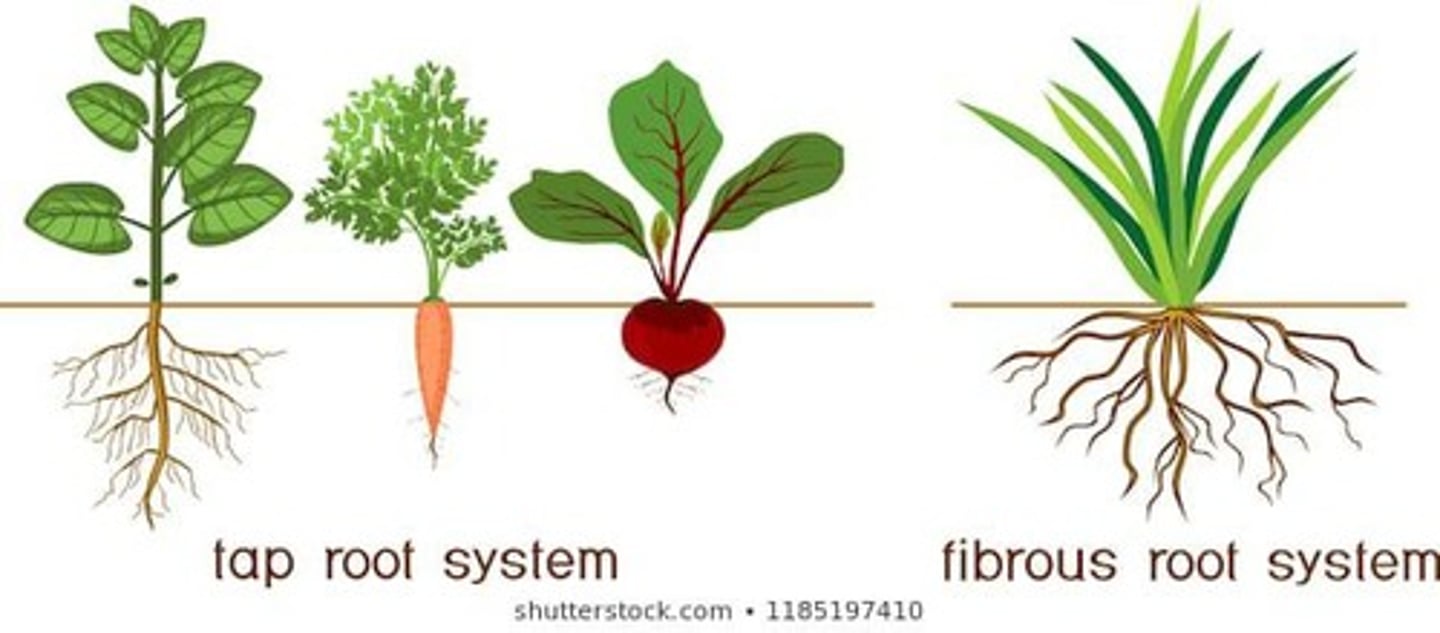
Fibrous Root System
A root system that lacks a main root and has many branching roots, typical of monocots.
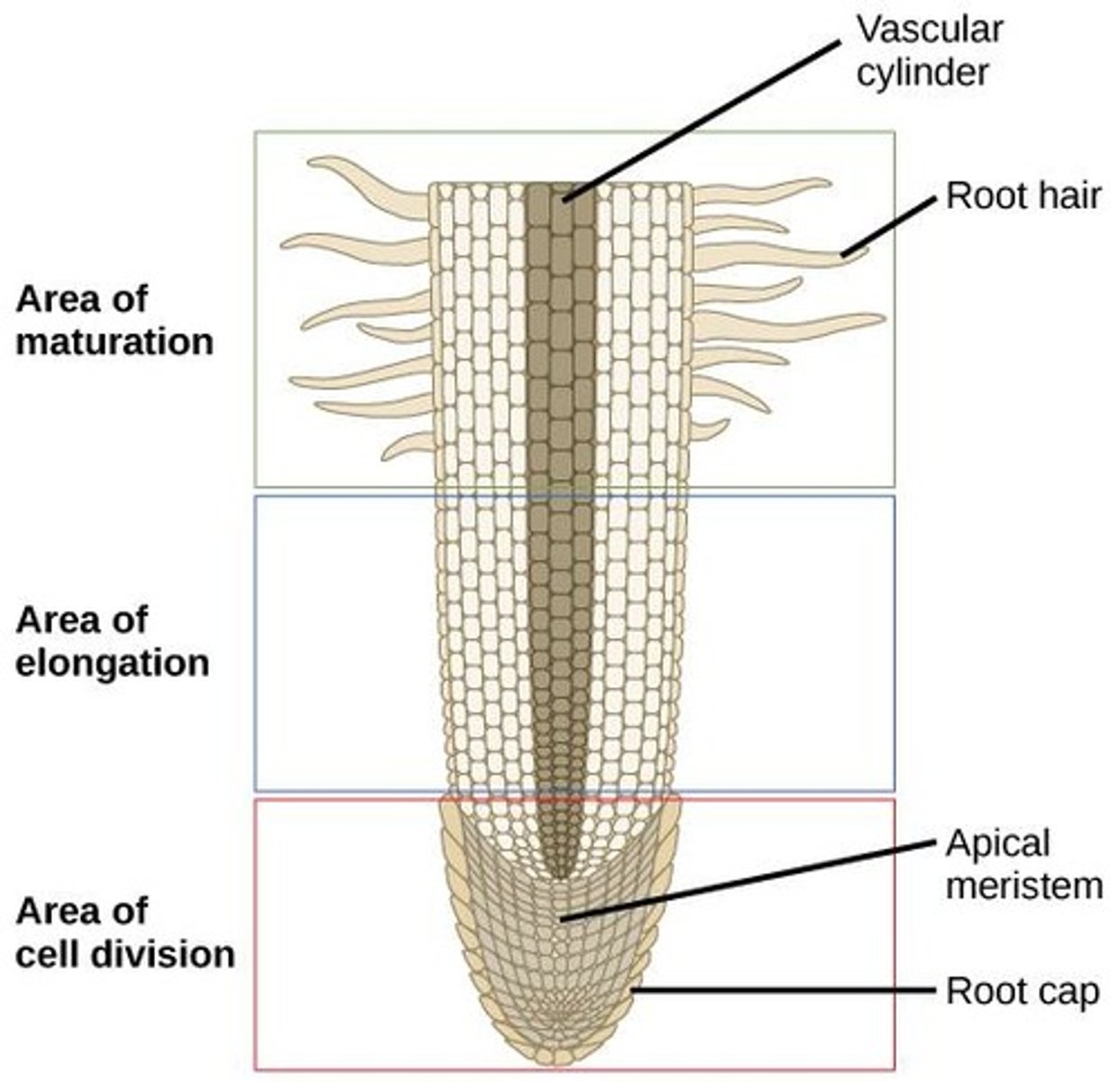
Apical Meristem
Region of cell division in the root tip where actively dividing cells are found.
Eudicot Root
Has xylem and phloem forming an 'X' or '+' in the center with no pith.
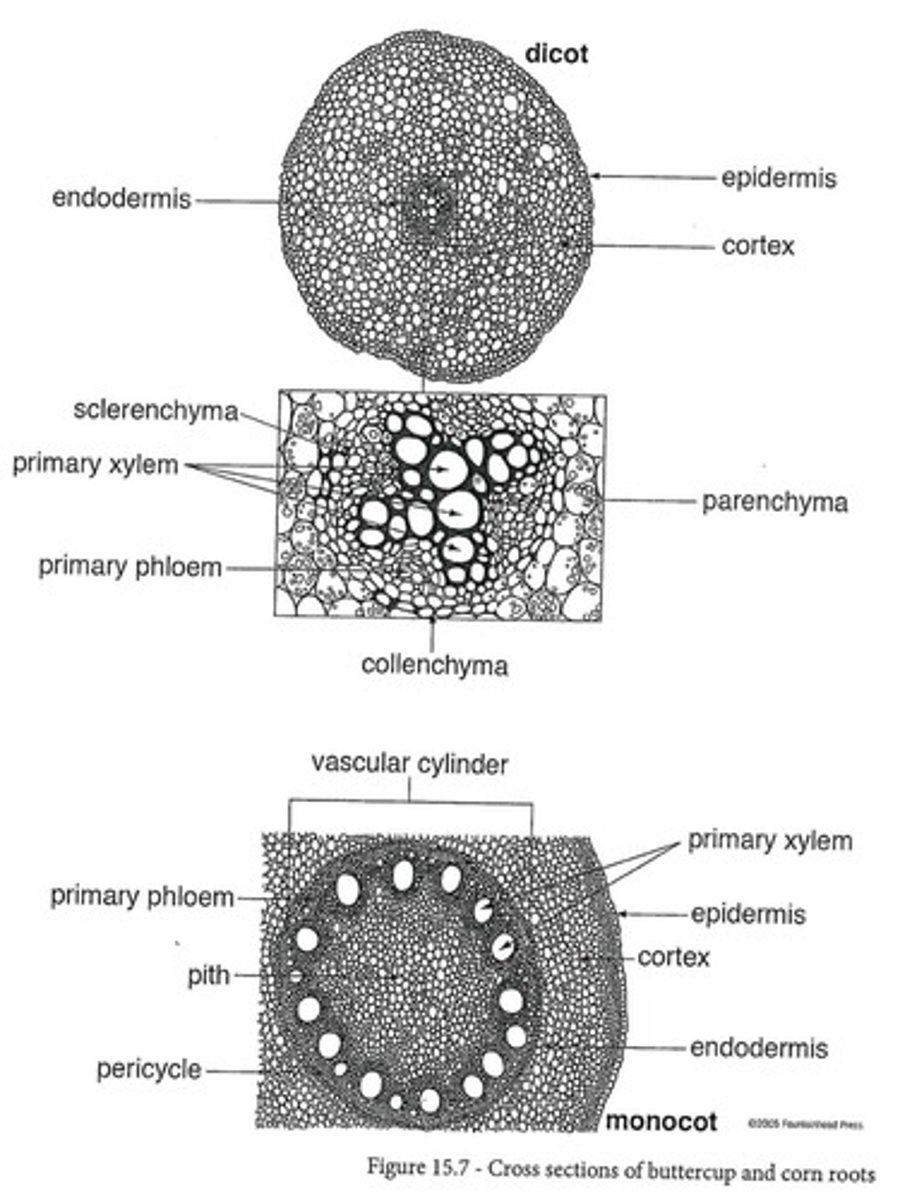
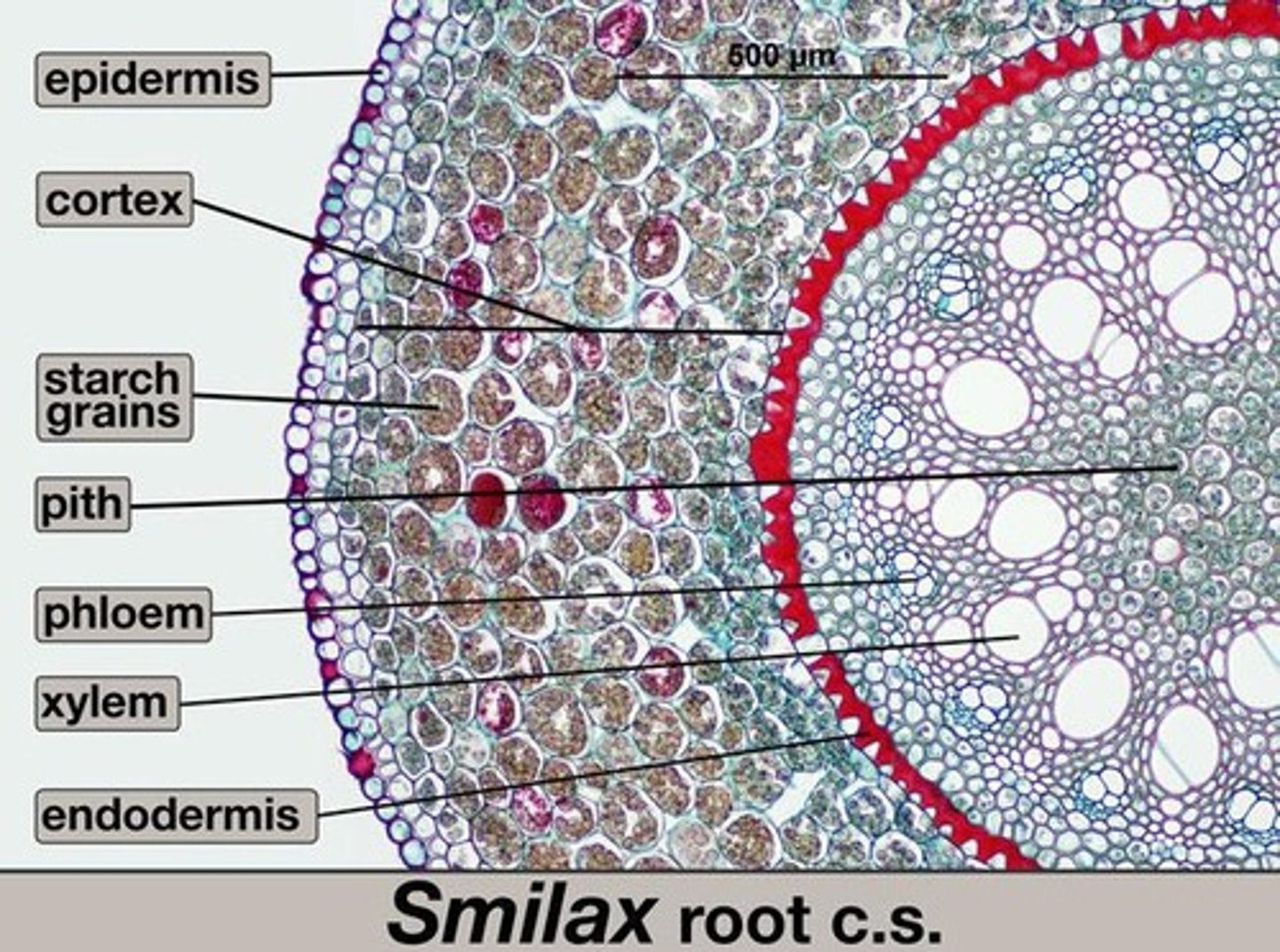
Monocot Root
Has pith in the center with xylem and phloem forming a ring around it.
Shoot System
Includes stems and leaves, primarily above ground organs.
Leaf Primordium
The early developmental stage of a leaf.
Node
The part of the stem where leaves are attached.
Vascular Bundles
Structures in plants that transport water, minerals, and nutrients.
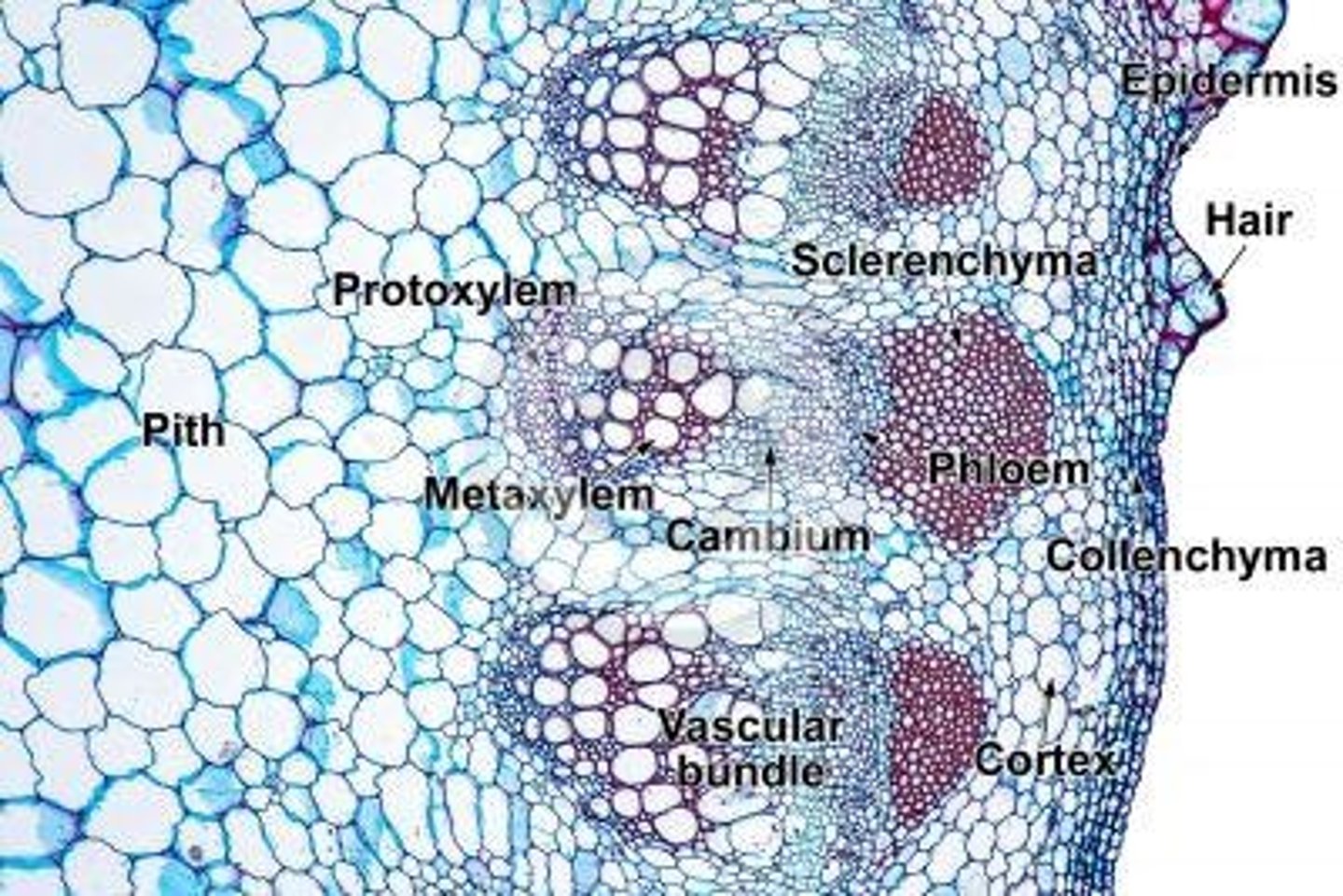
Eudicot Stems
Characterized by vascular bundles arranged in a ring.
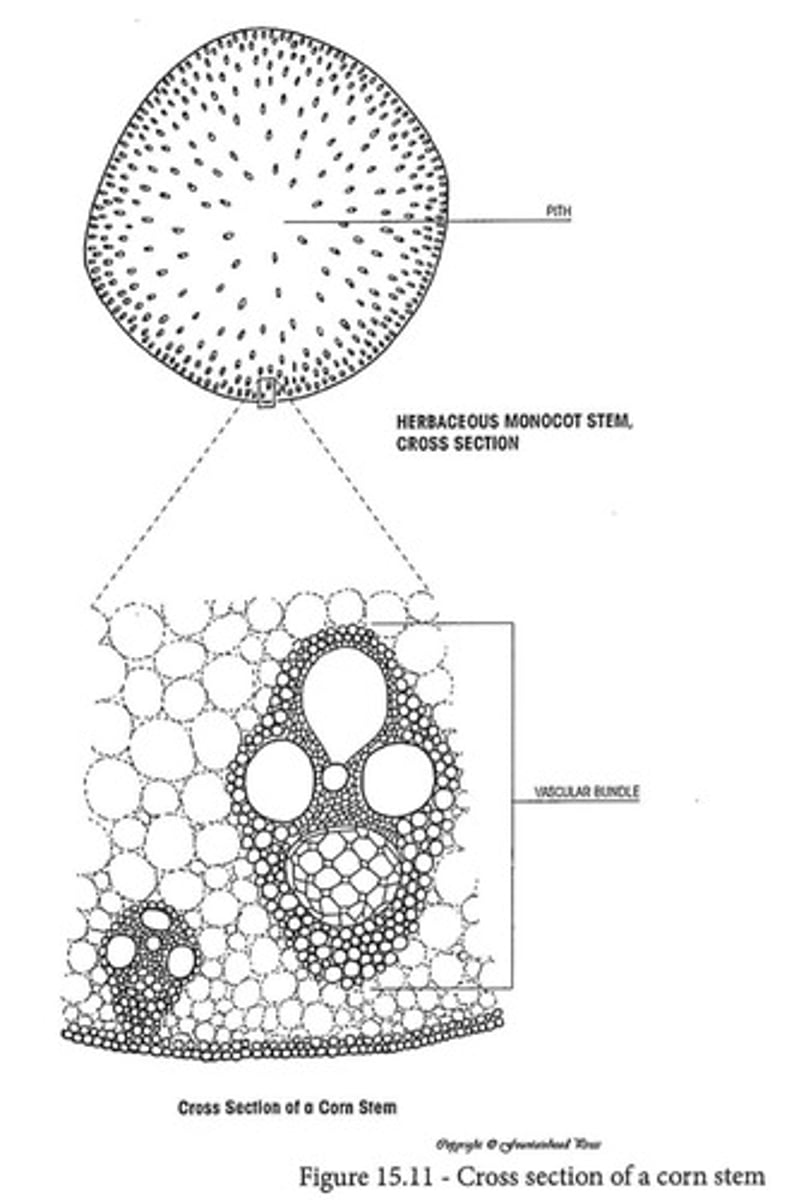
Monocot Stems
Characterized by scattered vascular bundles.
Mesophyll
The tissue in leaves where photosynthesis occurs.
Eudicot Leaf
Has differentiated mesophyll and large vascular bundles.
Monocot Leaf
Mesophyll is not differentiated and has both large and small vascular bundles.
What shape do the xylem and phloem make in eudicot roots?
X or +
What shape do the xylem and phloem make in eudicot stems?
ring
What shape do the xylem and phloem make in monocot roots?
forms a ring around the pith
What shape do the xylem and phloem make in monocot stems?
no ring
Do eudicots have piths in their roots?
no
What type is this: pollen grains have 3 pores or furrows
dicot
What type is this: seeds have two cotyledons
dicot
What type is this: flowers have 4 or 5 floral parts
dicot
What type is this: leaves are oval or palmate with net like veins
dicot
What type is this: vascular bundles arranged in a ring around stem
dicot
What type is this: tap roots
dicot
What type is this: pollen grains have one pore or furrow
monocot
What type is this: seeds have one cotyledon
monocot
What type is this: flowers have 3 floral parts
monocot
What type is this: leaves are narrow, with parallel veins
monocot
What type is this: vascular bundles are small and spread throughout the stem
monocot
What type is this: fibrous roots
monocot
Monocots exhibit what type of growth?
parallel vascular growth
Primary growth =
growing upward
Secondary growth =
growth in girth (formation of woody tissue)
Secondary growth can refer to:
stems, sometimes roots, but never leaves
Primary tissues in primary growth?
epidermis, parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, primary xylem, and primary phloem
Primary tissues in secondary growth?
periderm (outer bark), secondary xylem (wood), secondary phloem (inner bark)
Radicle =
primary root when seed germinates
Shoot system =
stems and leaves
Difference in stems of eudicots and monocots?
eudicots from a ring of xylem and phloem, but monocots don’t have specific organization
What causes secondary growth?
cell division activities of lateral meristems (vascular cambium and cork cambium)