Physics Class 4 - Electrostatics, Capacitors, Batteries, Resistors
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What is electric charge? Symbol, units.
Q or q
Units: [q] = C (coulombs)
Positive or negative
What is elementary charge?
e = 1.6 × 10-19 C
Smallest possible unit of charge; exists in multiples of this
Ex: 1 electron, 1 proton
What is coulomb’s law?
FE = k|Q||q|/r²
Q and q are each charges that interact
k = 9 × 109 N*m²/c²
r is distance between charges
FE can be attractive (opposites attract) or repulsive (like repels like)
Inverse square law
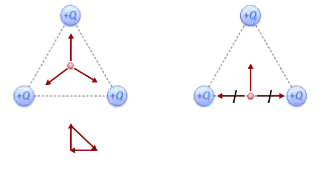
What is superposition of forces?
Allows determination of FE when >2 charges in the system
Net effect is the vector sum of the force from each individual charge
Multiple instances of the same force
What are electric fields?
FE = qE
E is a vector
FE is positive in the same direction as E, negative in the opposite direction
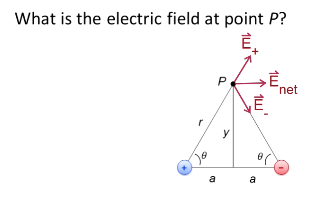
What is the electric field at a point a distance away from the source charge?
E = k|Q|/r²
E is positive going away from the source, negative towards (figure out superposition first)
Units = N/C = V/m
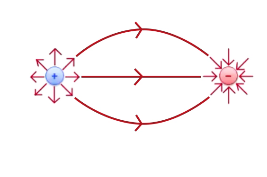
What are electric field lines?
Summary of all electric field vectors in space
Direction of electric field is tangent to the field line
Strength corresponds to density of field lines
Electric field is in the same direction as acceleration
This applies to the dipole of water molecules that connect
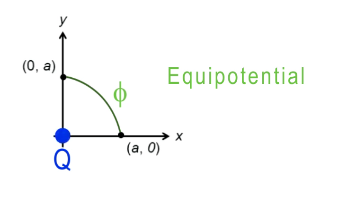
What is electric potential?
Electric potential = kQ/r
Units: J/C = V (+, -, or 0)
Use for scalar problems (work, energy, speed)
What is electric potential energy? Work by electric potential energy? Kinetic energy?
change in PE = qV
Wby E = -change in PEE
change in KE = - change in PE in absence of non-conservative forces
Spontaneous: change in PE < 0
What is change in PEE for positive charges for spontaneous action?
change in PEE = q change in electric potential
(-) = (+)(-)
Positive charges want to accelerate to regions of lower electric potential
What is change in PEE for negative charges for spontaneous action?
change in PEE = q change in electric potential
(-) = (-)(+)
Negative charges want to accelerate to regions of higher electric potential
What is a capacitor?
Two conducting surfaces separated by insulator (dielectric)
C = k(epsilon0) A/d in F(farads)
k = dielectric number (1 for vacuum and air, >1 for other insulators)
Epsilon0 constant (no need to know)
A = area of conducting surface
d = distance between two conducting surfaces
What is a batterie?
Source of voltage (potential difference) → not source of charge or current
Positive terminal (longer line): higher potential
Negative terminal (shorter line): lower potential
Voltage of batterie: V = change in voltage between + and - terminals
Symbol for potential is phi (circle w/vertical line)
What charge is stored by a capacitor when connected to batterie in closed circuit?
Q = CV
Q = charge
C = capacitance
V = voltage difference between plates of the capacitor
What is the electric field in a capacitor?
From positive to negative
E = V/d
V = voltage of plates
d = separation of plates (a constant)
What is the point charge equation of electric field?
E = k|Q|/r²
What is the energy stored by a capacitor (potential energy)?
PEcap = ½ QV = ½ CV² = Q²/2C
Area under a QV graph
What is a dielectric?
Insulating materials that polarize in an electric field
Induced dielectric field opposing the external electric field → Enet drops, and so does V
Battery has greater voltage than capacitor and can move charge into it
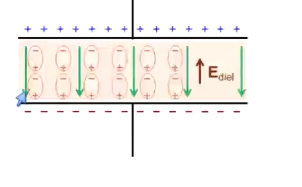
What is dielectric breakdown?
Insulator is ionized by too large of an external electric field, allowing charge to move through it
Results in a spark
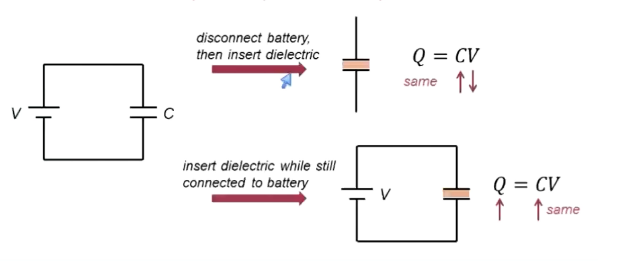
What is capacitance of a capacitor when a dielectric is inserted into it?
If you disconnect battery, then insert dielectric? If you insert while still connected?
C = kC0
k = dielectric number
What is a conductor?
Material in which charges move freely
No net movement of charge → current = 0
How do you get a current through conductors?
Impose a potential energy difference → induces a net movement of charge
delta PEE = q delta phi
(-) = (-)(+)
What is the flow rate of a charge through a conductor (current in a conductor)?
I = Q/t
Charge per second
Units A = C/s
What is resistance?
How much an object opposes the flow of charges through it
V = IR
R is constant
Units: omega
What is resistivity (rho)?
How much a material opposes flow of charges through it
Units: omega * m
What are resistors?
Segments of a circuit with known resistance
Use up energy in a circuit as heat/light
Represent via jagged lines
With one resistor and one battery, how do you find total current?
Voltage of battery determines voltage across the resistor
Use Ohm’s law (V = IR)
What is a series?
One path through resistors
Same current through each
Requivalent = sum of (R1 + R2 +… Rn)
What does it mean for resistors to be in parallel?
Multiple paths through resistors (not necessarily geometrically parallel)
Same voltage across each
1/Req = sum of (1/R1 + 1/R2 +…1/Rn)
How do you find Req for two resistors?
Req = (R1*R2)/(R1 + R2)