Planning for Implant Treatment
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
What are some factors influencing wound healing?
Blood thinner medication
Ongoing chemotherapy
Ongoing corticosteroid medication
Ongoing/ recent bisphosphonate treatment (IV)
Uncontrolled Diabetes
Smoking (5 cig/day)
Why is ongoing blood thinner use important in implant patient selection?
Stopping blood thinners puts the patient at high risk of stroke or cardiac arrest
How is blood thinner medication typically managed before surgery?
It may be stopped 24 hours to 1 week prior, depending on medical guidance
What must always be done when a patient is on blood thinners?
Contact the patient’s physician
How do chemotherapy drugs affect cells?
They alter cell activity in both normal and malignant cells
How does chemotherapy affect wound healing?
It can impair healing by preventing cell division and protein synthesis
What is the effect of chemotherapy and radiation on healing?
They slow wound healing
Why is healing compromised in cancer patients?
Cancer treatments impact normal processes like:
Cellular replication
Inflammatory reactions
Tissue repair
How does acute corticosteroid use affect wound healing?
If high-dose steroids are used for less than 10 days, there is no effect on wound healing
What is considered chronic corticosteroid use?
Doses >10 mg/kg for more than 1 week
What happens to patients on chronic corticosteroids before surgery?
They have:
2× increased risk of wound infection
2–3× higher risk of wound dehiscence
How long of steroid use increases surgical risk?
About 30 days prior to wounding or surgery
What is osteoporosis?
A systemic disorder with a generalized decrease in bone mineral density
Where is osseointegration more likely to fail in osteoporotic patients?
The maxilla (higher risk than the mandible due to lower bone density)
Does osteoporosis clearly impair bone healing?
No—there is no strong evidence that it has detrimental effects on bone healing
What loading protocol should be avoided in osteoporosis?
Immediate loading (3 mo of loading covered to heal)
What is recommended for implant healing in osteoporotic patients?
Extended healing time before loading
What is the concern with patients on bisphosphonates?
Elevated risk of osteonecrosis
What are some considerations with patients who are on psychoparacological medication?
Difficult to manage
Problems with communication
Frequently need sedation
Challenging to work on
Elevated risk of conflicts due to unrealistic expectations
High risk patients
What are some considerations for patients who are undergoing/previous exposure to radiation?
It leads to increased wound-healing complications
How does radiation affect saliva production?
It reduces saliva - It increases the risk of peri-implant infection
What happens to irradiated tissue over time?
It becomes hypoxic (low oxygen) and fibroblasts become dysfunctional
When is wound healing most affected after head/neck radiation?
When surgery is performed 6 months or more after radiation therapy
How does radiation therapy affect bone remodeling?
It damages osteoclasts and decreases proliferation of bone marrow, collagen, and blood vessels
What is the effect of radiation on bone vasculature?
Vascular injury leads to decreased microcirculation
What changes occur in irradiated bone marrow?
It becomes hypocellular, hypovascular, and shows fibrosis and fatty degeneration
Why do dental implants fail more often in irradiated bone?
The tissue becomes hypocellular, hypovascular, and hypoxic, impairing osseointegration
What information must you collect during treatment planning visit?
Patients chief complaints
Current radiographs- Peri-apical/ panoramic
Thorough clinical examination
Jaw opening range- must be sufficient for surgery
Evaluation of existing prostheses if any
Documentation of treatment needs
Impression diagnostic casts- mount on articulator
What is the criteria for ideal successful implant placement?
Good oral health!
No ongoing periodontal disease/fungal infections
Need for restorative treatment- composite restorations and crowns
No ongoing periapical infections
Extractions/removal of non-restorable teeth/residual roots /cysts/infections
Evaluation of occlusion
Super-erupted teeth; occlusal adjustment/crown therapy
Sufficient bone volume/height in the area
What dental conditions must be controlled before implant therapy?
Ongoing periodontal disease/fungal infections
What must a patient complete before starting implant treatment?
A full periodontal evaluation and treatment
What should be done with hopeless or compromised teeth?
They should be extracted and replaced with good-quality provisional restorations or prostheses
When should post-treatment results be evaluated?
At a 6-week evaluation
Why is patient compliance important?
Successful implant outcomes depend on hygiene and follow-up care
How are mild to moderate fungal infections treated?
Nystatin
Meticulous oral and denture hygiene (for removable prostheses)
How are severe fungal infections treated?
Fluconazole or another antifungal
Given orally or IV if not responsive to fluconazole
What is required if a periapical lesion is detected?
The patient must undergo endodontic treatment.
How should active caries be managed before implants?
Remove caries
Place restorations and crowns as needed
Why must these conditions be treated first?
To eliminate infection and create a healthy oral environment for implant success
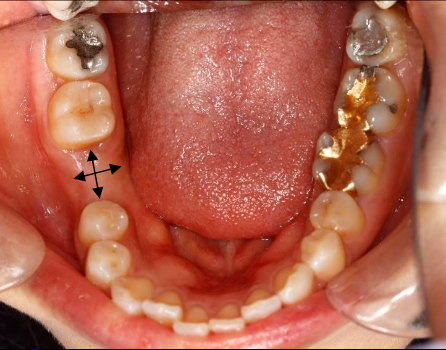
What are components of a site specific clinical evaluation?
Mesial-Distal space
Buccal-lingual alveolar ridge width
Condition/anatomy of teeth adjacent to the site
Health of mucosa
Site specific occlusion-super eruption/ vertical clearance
A dental implant requires about 1- 2mm of bone around the entire implant body
How much horizontal space is needed?
Minimum space between tooth and implant: 1.5 mm
Avoid damaging PDL, preserve proper blood supply
Minimum space between implant and implant: 3 mm
Adequate space to allow for soft tissue “cuff”/papilla formation
Buccal/lingual bone layer at least 1 mm thick
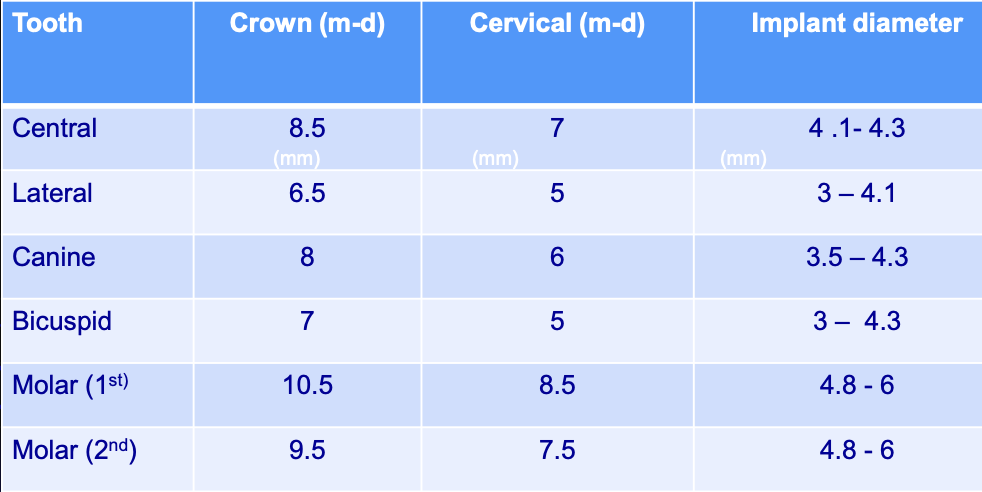
Tooth dimensions and recommended implant diameter
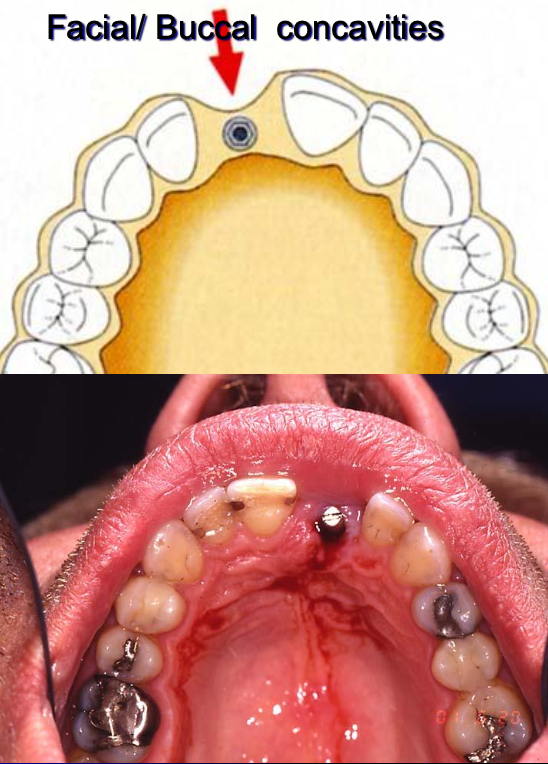
What are some considerations regarding the width of ridge?
Careful extractions
Socket preservation- bone augmentation
Buccal bone plate plays a major role
Always do Cone Beam CT/ surgical exploration if indicated
What position should the implant be placed?
Ideally in the same position where the missing tooth was
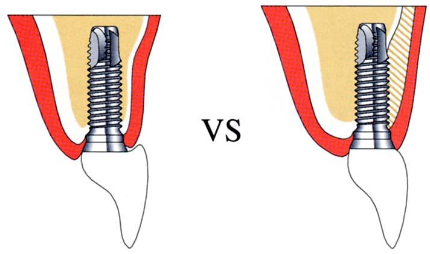
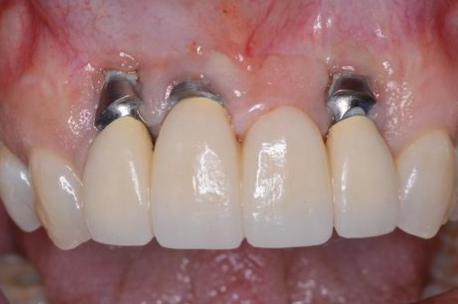
What are the consequences of having an incorrect buccal/lingual implant position?
Cosmetic problems
Hygiene problems
Oral comfort problems
Increased risk of failing implant
What are the consequences of having inadequate mesial/distal space?
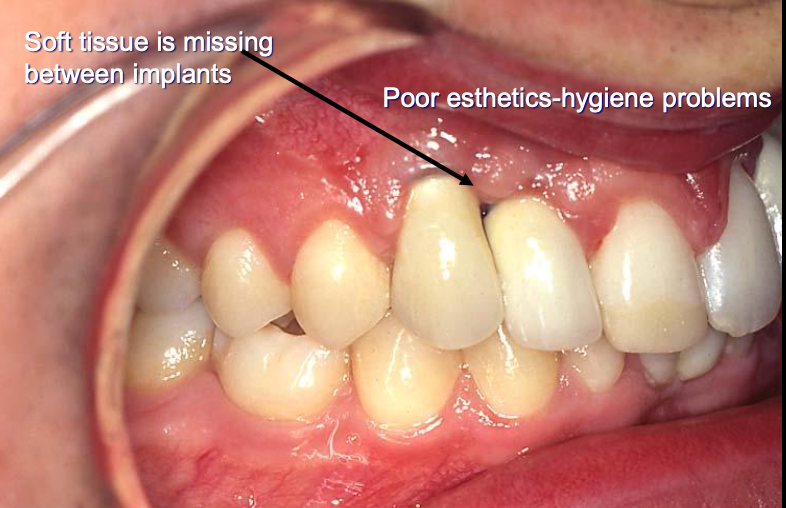
After extraction, when does major remodeling of the bone happen?
8 weeks
After extraction, when does major resorption of the bone happen?
6 mo- 2 years
Where in the mouth would you see more severe bone resorption?
Buccal bone plate where the bone is thinner
What does resorption affect?
Both vertical and horizontal bone height
After extraction in the molar/bicuspid area, what can you see 12 months later?
Reduction of the alveolar ridge width up to 50%
When should bone graft be recommended after extraction?
If the site is planned for an implant
What is the exception for grafting following extraction?
Immediately EXCEPT if there is an ongoing infection (wait 4-6 weeks before re-entering and grafting)
What type of extraction is recommended in esthetic zones?
Gentle extraction (peritome) to preserve buccal bone
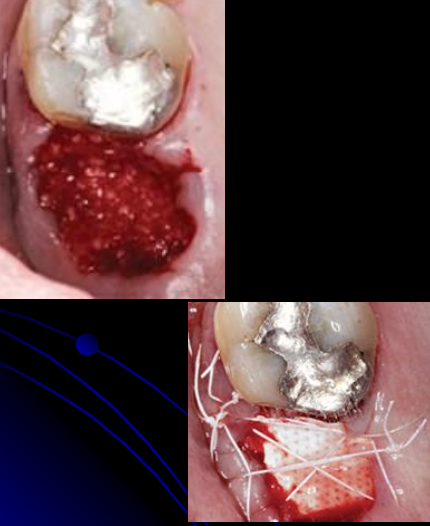
What are the steps for ridge preservation?
Rinse and clean socket properly
Pack the graft material leveled with the surrounding bone
Place non-resorbable membrane (Cytoplast) or collagen plug/membrane to protect the graft
Never touch the graft materials or membrane with gloves or non- sterile instrument!!
Two week follow-up visit
Remove sutures and membrane
Complete soft tissue covering the socket
6-9 month healing before surgical implant placement.
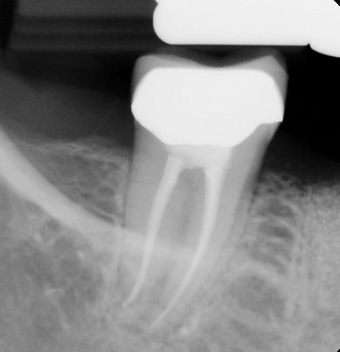
What are the steps for ridge preservation follow-up?
Take PA 3 mo after EXT to evaluate bone healing / degree of mineralization
Graft materials look “grainy” on PA
Dark areas indicate failing graft
Osteoinductive
Process why which osteogenesis is induced
Osteoconductive
Ability of bone-forming cells in grafting area to move across a scaffold and slowly replace it with new bone overtime
What are some osteoinductive graft materials?
Autografts (autogenous graft)
Demineralized Allograft Bone Matrix
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs)
What are some osteoconductive graft materials?
Hydroxyapatite
Xenograft (bone from cow)
Coralline-derived hydroxyapatite
Tricalcium phosphate
Calcium sulphates
Glass ceramics (tissue graft from a donor of same species but not genetically identical)
What do you have to check for in interocclusal clearance?
Opposing teeth for supereruption, occlusal adjustment may be necessary