Diagnostics - Exam 2
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
216 Terms
Anti-nuclear antibody (ANA)
SLE, connective tissue disease
autoimmune conditions: rheumatoid arthritis and thyroid disease
sensitive but not specific
ANA is measured through
indirect immunofluorescence as a titer
ANA is clinically significant when
greater than or equal to 1:160
1:40 seen in some healthy people
ANA patterns
nuclear fluorescence under microscopy
certain patterns are associated with specific diseases
Anti-Dsdna & anti-Sm antibodies
ordered when ANA is positive and concern for lupus
Dsdna - positive in 70-80% of lupus; high levels are associated with lupus nephritis and predictive of lupus flare
Smith - 30% associated with lupus
Serum complement levels (C3 + C4)
low levels in increased activity of disease with SLE, systemic vasculitis, cryoglobulinemia
increased consumption due to complement activation
Sjrogrens antibodies
Anti-SSA(Ro) and anti-SSB(La)
SSA positive in 75% of Sjrogrens and 40% of SLE
SSB positive in 40-50% of Sjrogrens and 15% of SLE
Anti-scleroderma antibodies
anti-centromere ab and anti-topoisomerase ab
anti-centromere - seen in limited scleroderma (CREST syndrome)
anti-topoisomerase ab (Scl-70) - seen in systemic sclerosis/scleroderma / higher risk of severe lung disease
ESR
indirect measurement of alterations in acute-phase reactants and quantitative immunoglobulins
non-specific
high levels caused by rheumatologic (connective tissue disease, giant cell arteritis, polymyalgia rheumatic, inflammatory arthritis) or malignancy
CRP
pentameric protein present in trace concentrations in everyone
more specific than ESR - measures specific acute phase reactant
high levels suggest underlying bacterial infection
Rheumatoid factor
50-80% sensitive for RA
positive from chronic immune stimulation
can be caused by chronic disease (hepatitis and pulmonary disease), lupus, systemic sclerosis, Sjrogrens, polymyositis, sarcoidosis, neoplasms, infections, cryoglobulinemia
can also be seen in normal individuals at lower titer
HLA-B27
seen in seronegative spondyloarthropathies (ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis, enteropathic arthritis), IBD, or reactive arthritis
if positive, increased risk of ankylosing spondylitis
helpful in patients with inflammatory back pain
Uric acid
end product of degradation of purines
target in gout is less than 6
may be falsely low in flare
could be asymptomatic hyperuricemia
Synovial fluid
ultrafiltrate of plasma found in joints to allow for friction-free movement
excess can accumulate as result of noninflammatory, inflammatory or septic processes
Joint aspirations are assessed for
synovial fluid cell count, Gram stain, & culture - infections
presence of crystals - crystalline arthropathy
Arthrocentesis indications
removal from fluid from a swollen, inflamed joint
suspicion for septic arthritis
excessive joint fluid removal to improve ROM and patient comfort
Arthrocentesis contraindications
active cellulitis or abscess overlying the joint
caution if INR is greater than 3
Major determinant of clarity and color of arthrocentesis is the
cell count
Noninflammatory fluid
low cell count and clear
ex. OA
Inflammatory arthritis fluid
higher cell count and translucent-yellow
Rice bodies in fluid
free-floating aggregates of tissue --> RA, SLE, septic arthritis
Milky white fluid
large quantities of urate crystals in acute gout
Normal synovial fluid has less than ____ WBC
200
WBC in non-inflammatory vs inflammatory
< 2000 in noninflammatory
> 2000 in inflammatory
> 50,000 in septic arthritis or gout if crystalline
Crystal analysis of synovial fluid
performed on a wet mount under polarized light
yellow or blue - birefringent material
Crystals that are yellow when oriented parallel and blue when perpendicular
negatively birefringent - gout
Crystals that are blue when oriented parallel and yellow when perpendicular
positively birefringent - pseudogout or inflammatory joint disease, hemarthrosis, trauma, pancreatitis
MC bacteria in septic arthritis
staph aureus
strep pyogenes
strep pneumonia
Classes of synovial fluid
1 - noninflammatory
2 - inflammatory
3 - septic
4 - hemorrhagic
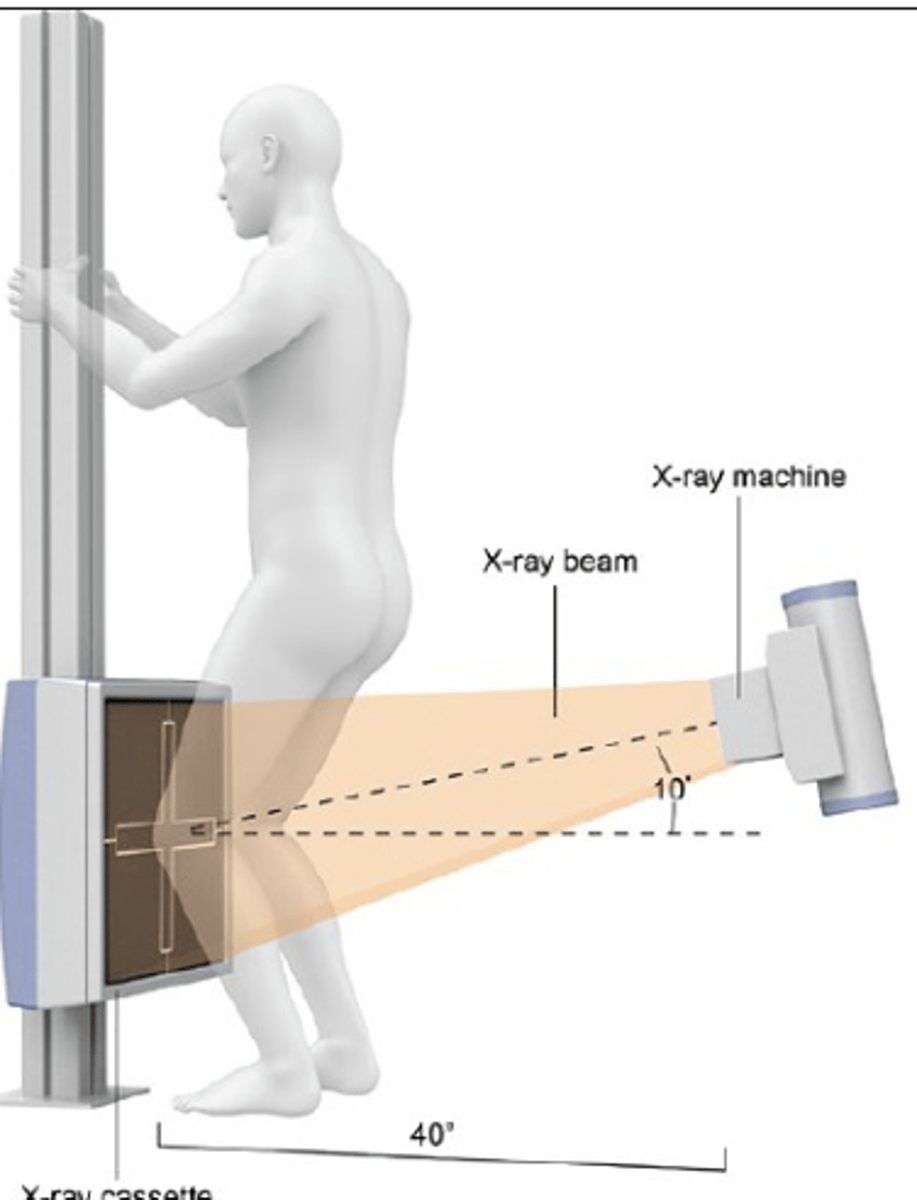
Fluoroscopy
continuous XR
Desired structure in imaging should be closer to plate or source of XR?
plate - so spinal imaging is best with AP
MRI time
20-30 minutes - not used typically in emergent settings except something like cauda equina
Dual energy XR (DEXA)
low dose XR with 2 different energies that attenuate differently in bone and soft tissue
allows for calculation of bone mass density
typically looks at lumbar spine and proximal femur
Positron emission tomography (PET)
uses radioactive tracer to evaluate metabolic activity
evaluates cancer mets earlier than CT/MRI
Osteoporosis imaging
DEXA
Osteoarthritis imaging
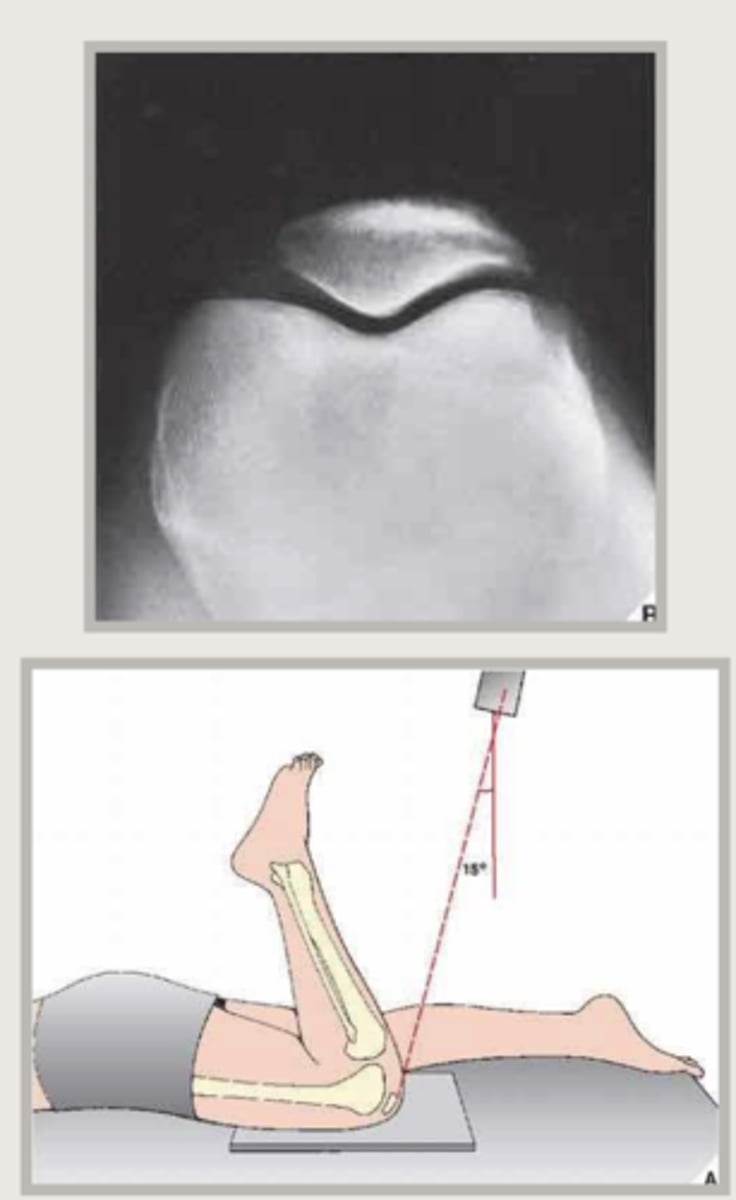
XR with Rosenberg view or sunrise view
Sunrise view
Osteoarthritis radiographic findings
joint space narrowing - medial compartment MC
osteophyte formation
subchondral sclerosis
cyst formation
bone attrition (flattening)
Pseudogout on imaging
calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate deposition (CPDD) - may mimic OA - differentiated bc isolated or disproportionate patellofemoral OA with chondrocalcinosis
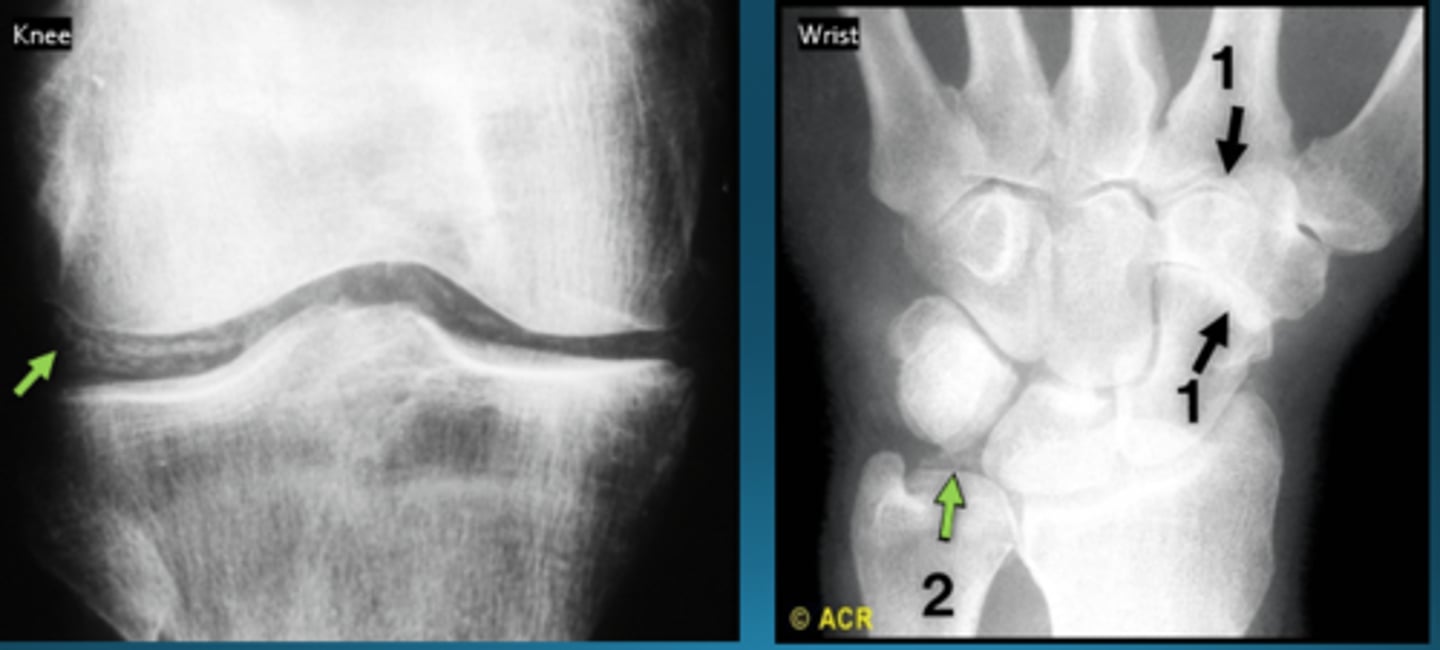
Early RA on imaging
MRI or US with synovial proliferation or bony erosions in both MRI and US
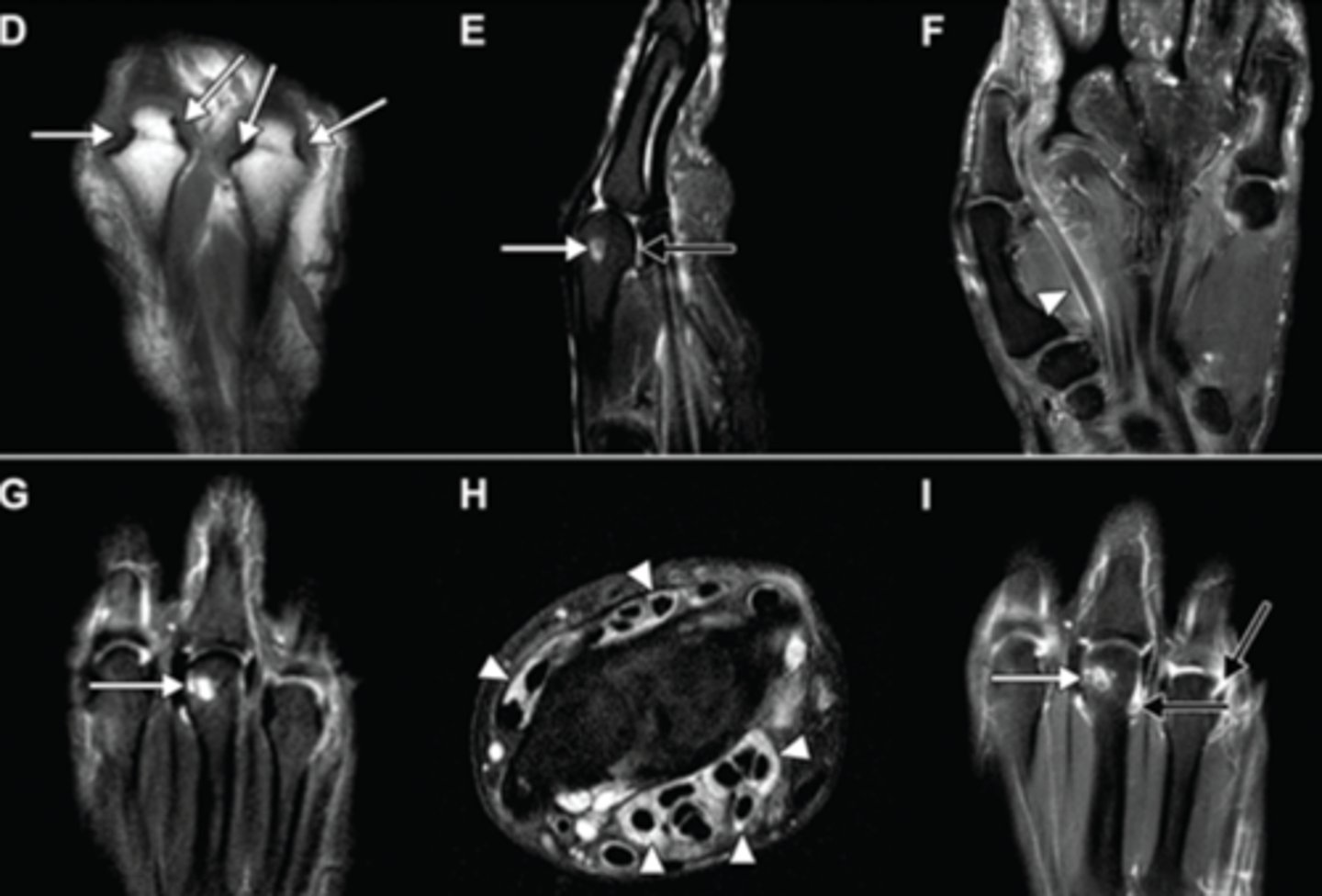
Late RA on imaging
symmetric polyarthropathy with joint space narrowing
involves distal radioulnar, radiocarpal, intercarpal, carpometacarpal, and metacarpophalangeal articulations
distal IP joints are spared
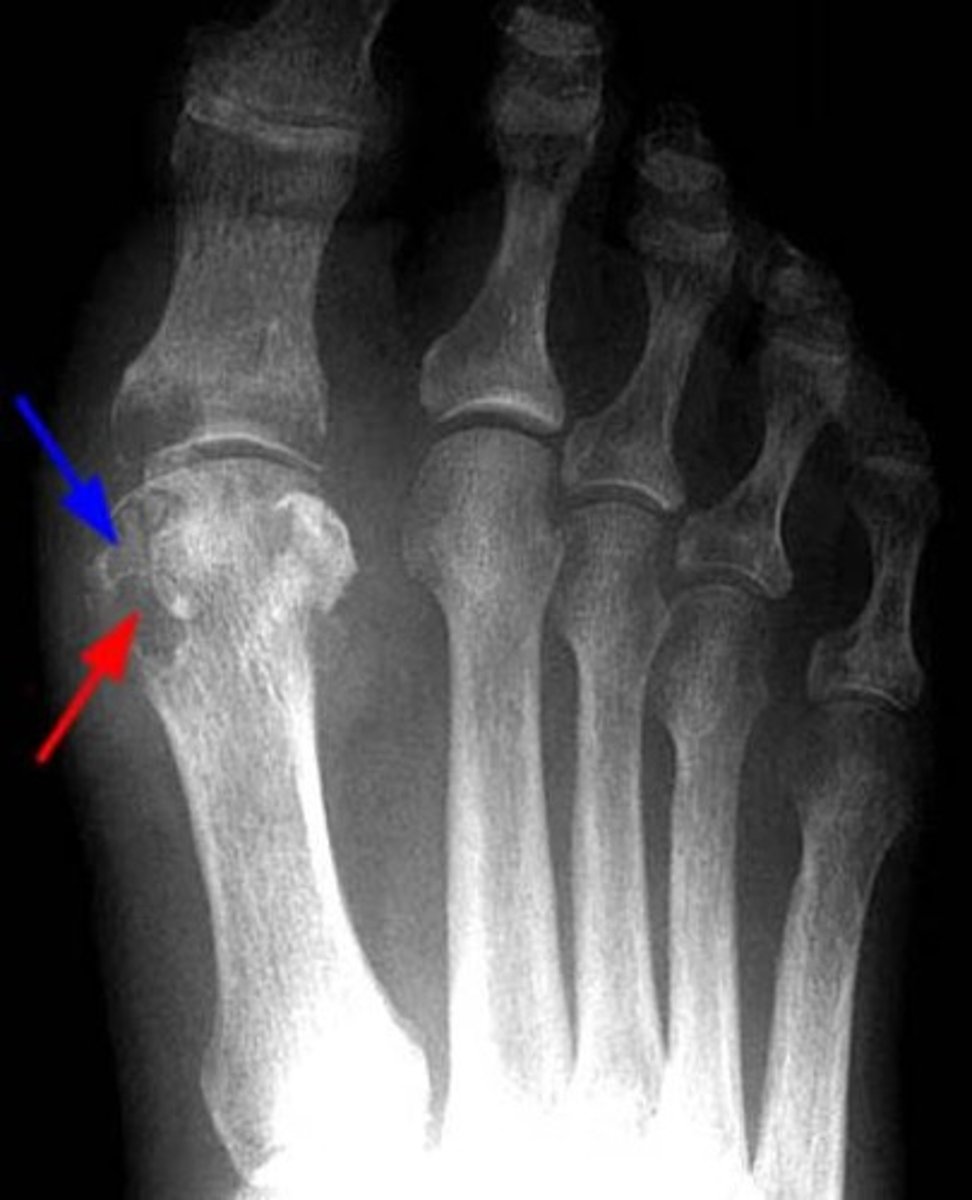
Gout on imaging
soft tissue swelling
XR with soft tissue calcification, tophi, cortical erosions and irregularity, juxta-articular erosions with sclerotic rims and overhanging margins, preservation of mineralization and joint space
MRI can detect smaller tophi and earlier disease
CT not preferred but can be used
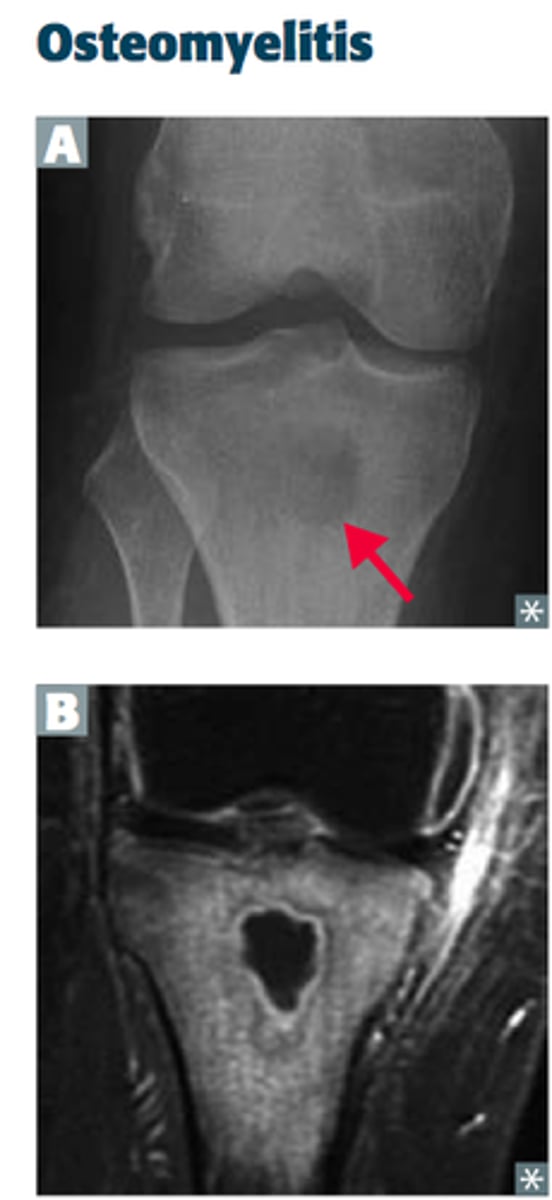
Osteomyelitis on imaging
infection of bone
radiographs + MRI w/ contrast
bone marrow edema with decreased bone marrow signal (same or lower signal than muscle --> diagnostic)
soft tissue swelling
ulcers, sinus tracts, abscesses, and necrosis
Pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVS)
inflammatory vs neoplastic process of knee
painful joint swelling and decreased ROM
radiograph with large joint effusion or intra-articular soft tissue mass
well defined erosions with preservation of joint space
Systematic review of images in trauma
Adequate and Aligned
Bones
Cartilage and joints
Soft tissues and spacing
Open vs closed fracture
open = break in the skin
closed = skin intact
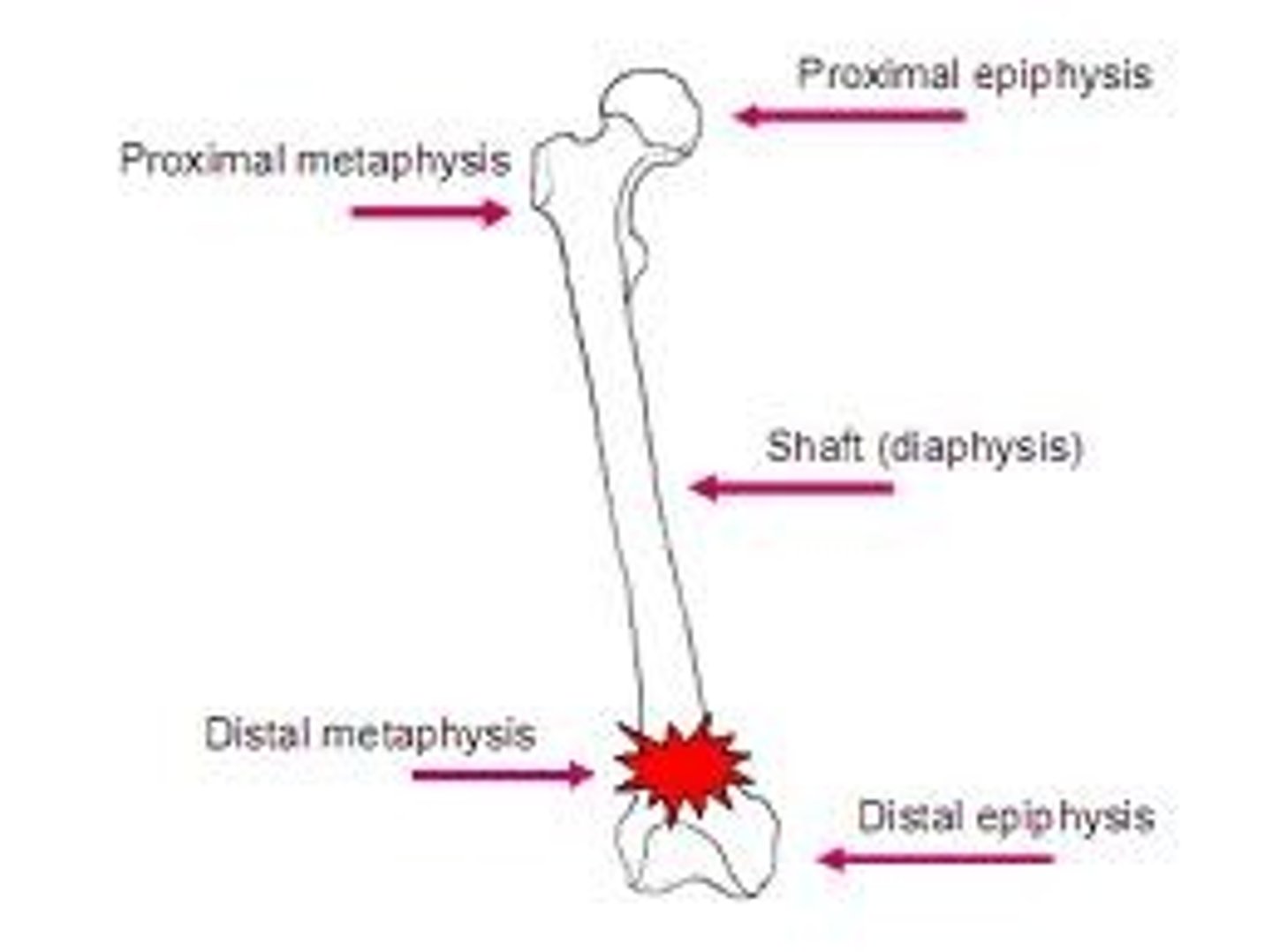
Midshaft of the bone
diaphysis
Distal end of bone
metaphysis and epiphysis with physis (growth plate) between in kids
How to note joint involvement in fracture imaging
intra vs extra-articular +/- displaced
Type 1 intra-articular fracture
nondisplaced
Type 2 intra-articular fracture
single displaced fracture plane
Type 3 intra-articular fracture
2 displaced fracture planes
Type 4 intra-articular fracture
highly comminuted
Types of fractures
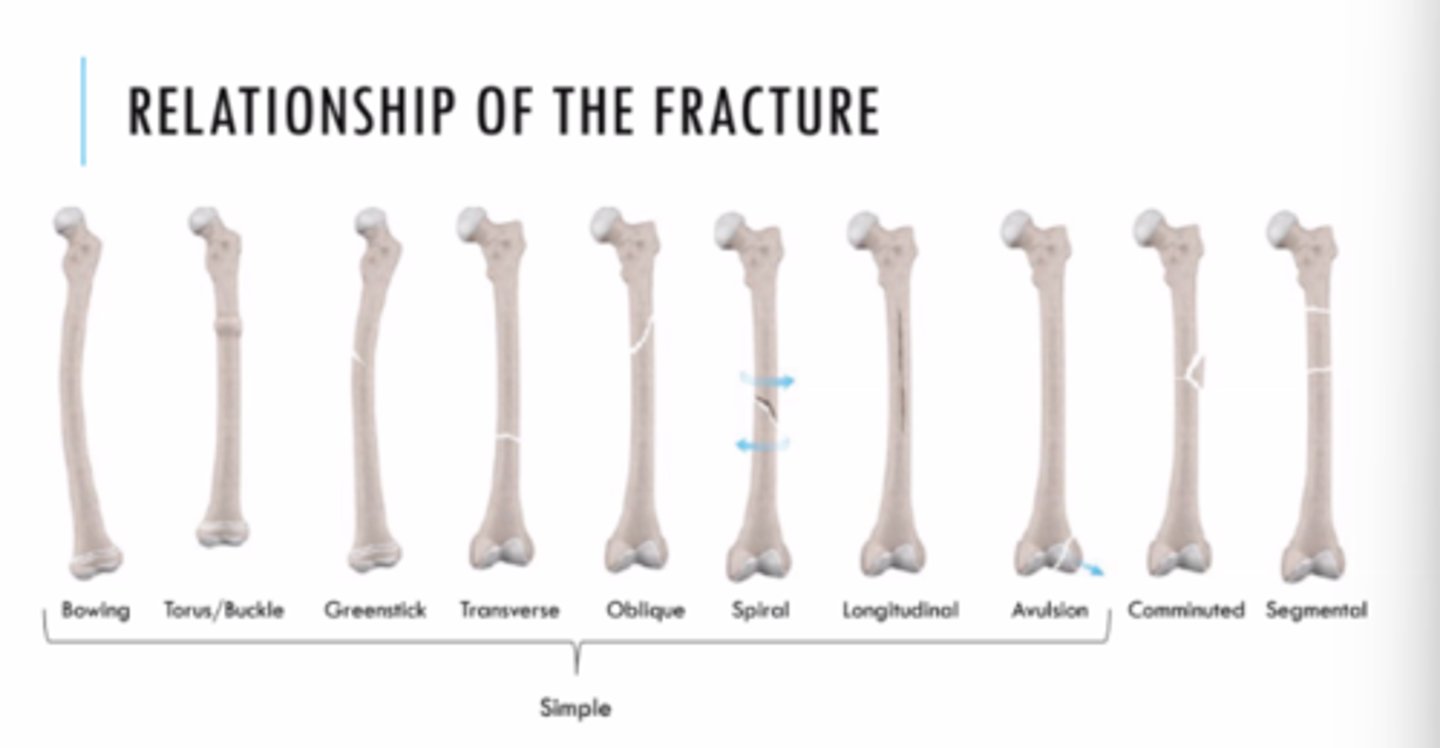
Orientation of fracture
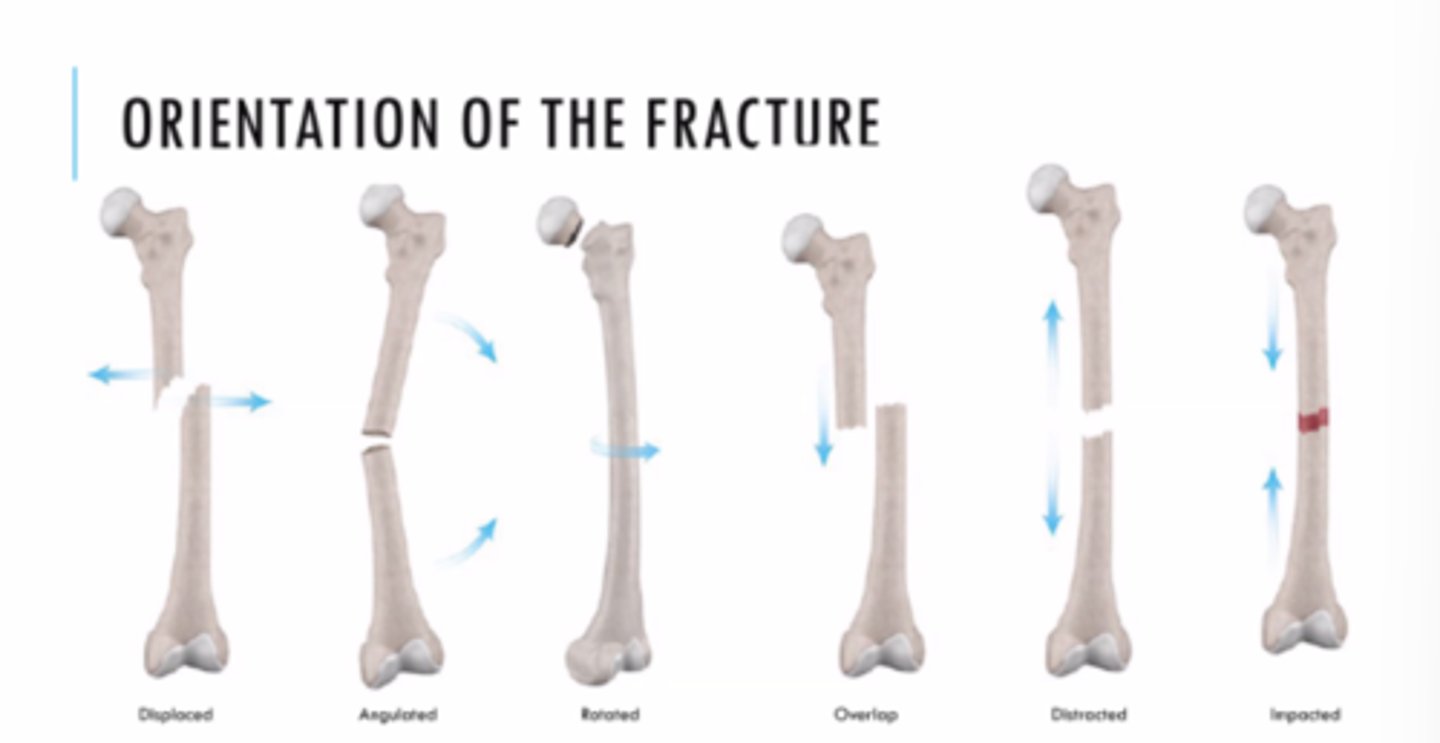
In displacement, describe the displacement of the proximal or distal fragment?
distal (medially or laterally)
Soft tissue and joint spaces
effusion or soft tissue swelling or gas
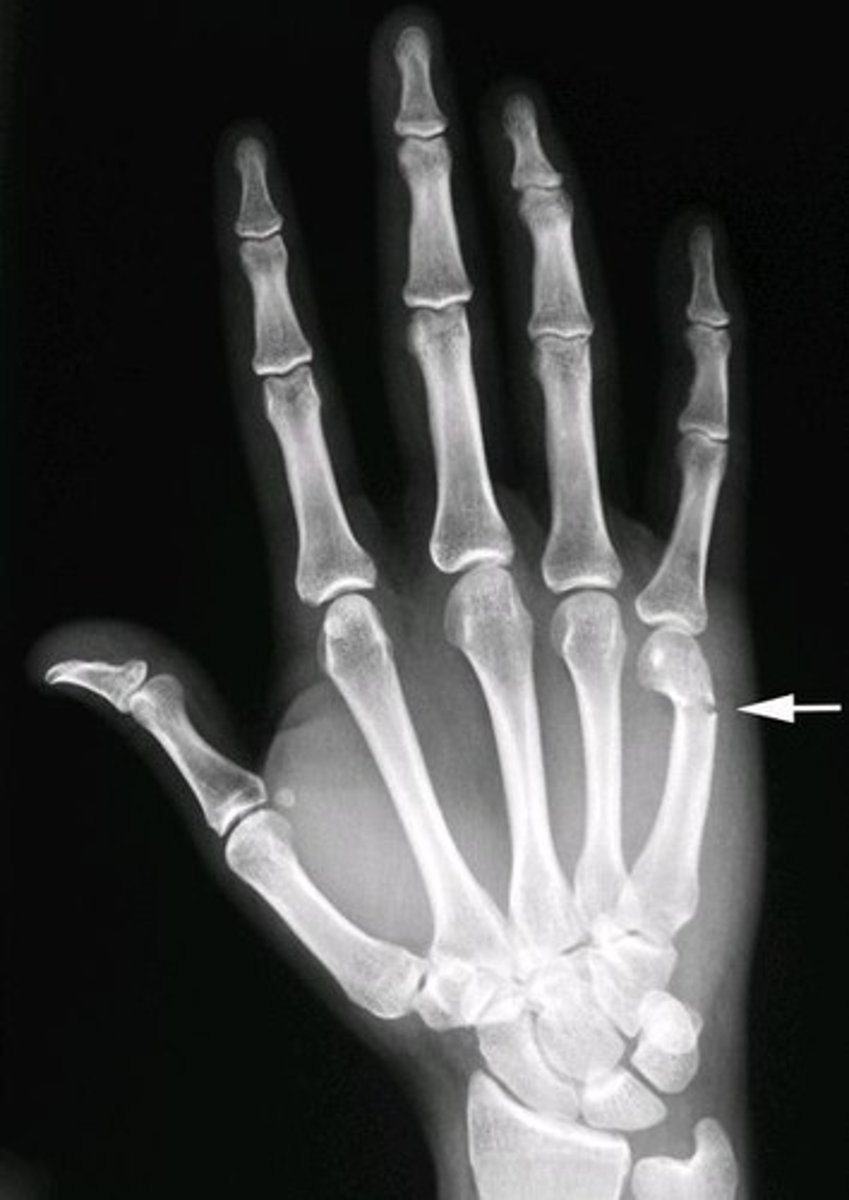
Boxer's fracture
punching wall or other object
seen on XR
fracture of mid-diaphysis of 4th and/or 5th metacarpal
Stress injury/fractures
focal pain in athlete with repetitive stress/loading of bone
commonly proximal tibia
diagnosed with XR and then MRI for prognosis
Classification of stress fractures
fatigue fracture - abnormal activity on normal bone (excessive running)
insufficiency fracture - normal activity on abnormal bone (walking but osteoporotic)
Insufficiency fracture of knee on imaging
subtle impression along medial femoral condyle
if delayed - subchondral lucency that process to flattening and collapse of articular surface
late findings - degenerative changes
MRI - extensive bone marrow edema (usually in medial femoral condyle)
Soft tissue foreign body imaging
US - limited to visualization of radiopaque foreign bodies
posterior acoustic shadowing on radiograph with surrounding area of hypoechoic granulation tissue, edema, or hemorrhage
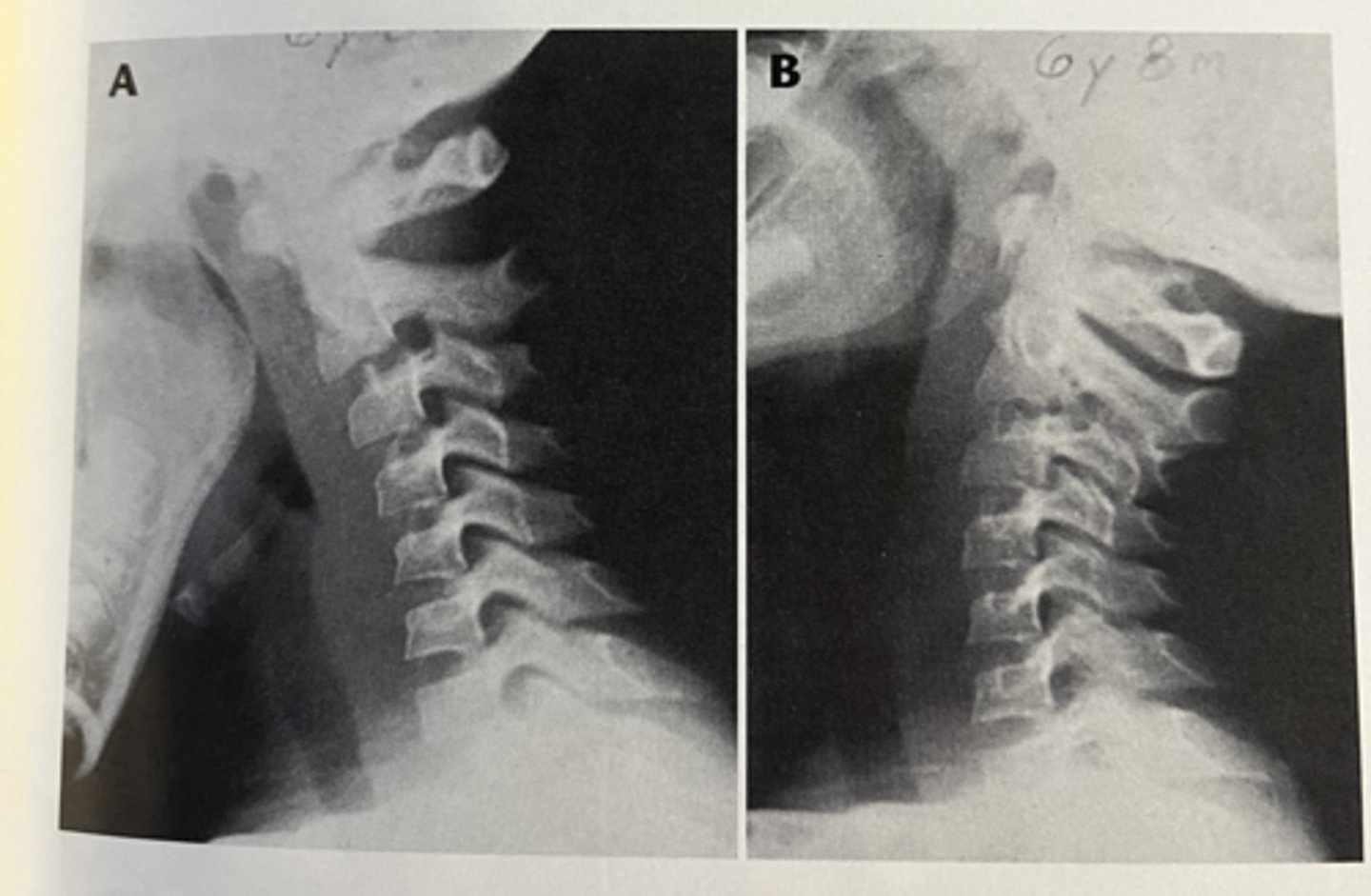
Pseudo subluxation of spine
neck pain often s/p MVA
may be anatomic variant in adolescents due to ligamentous laxity
seen on XR with subluxation of vertebral body that would be accentuated with flexion
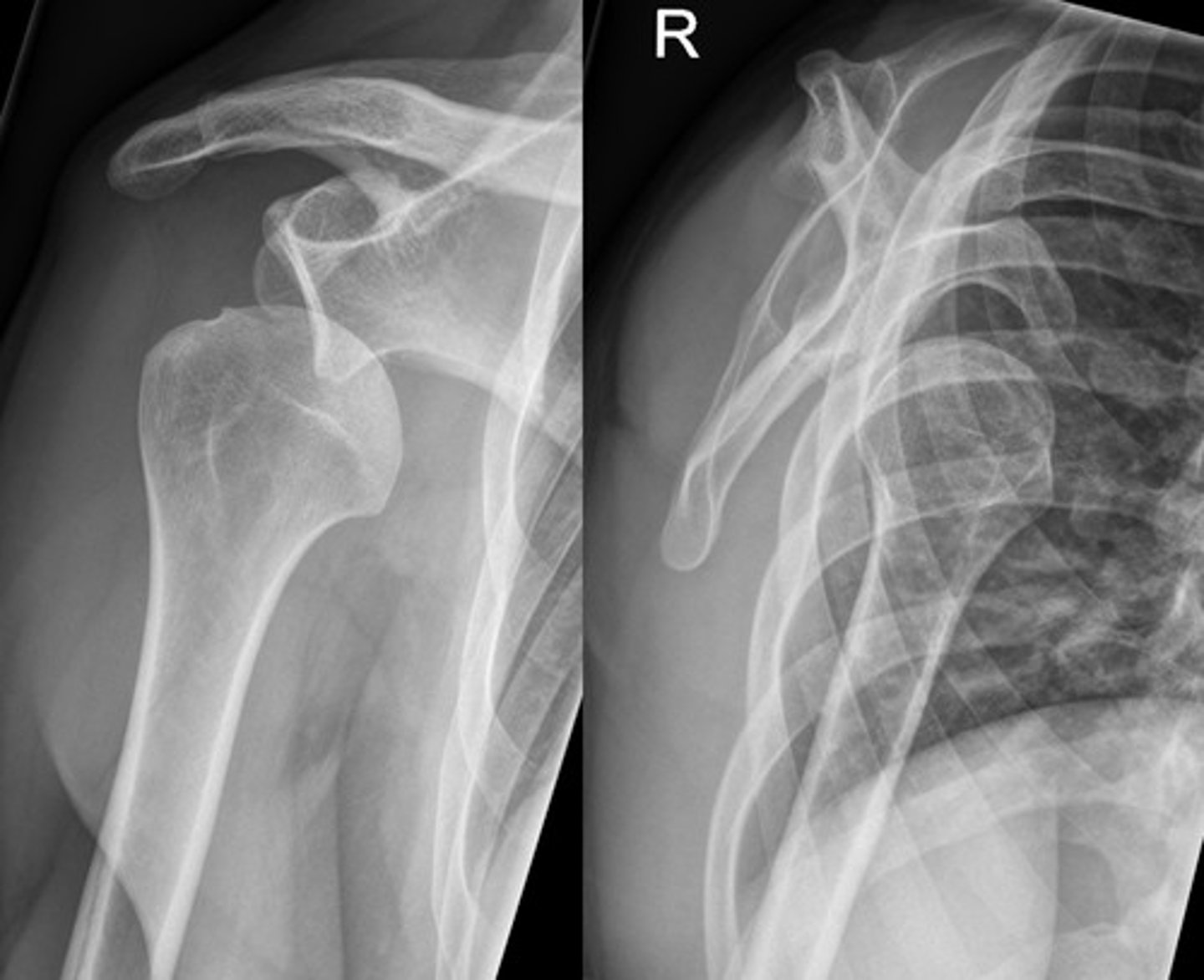
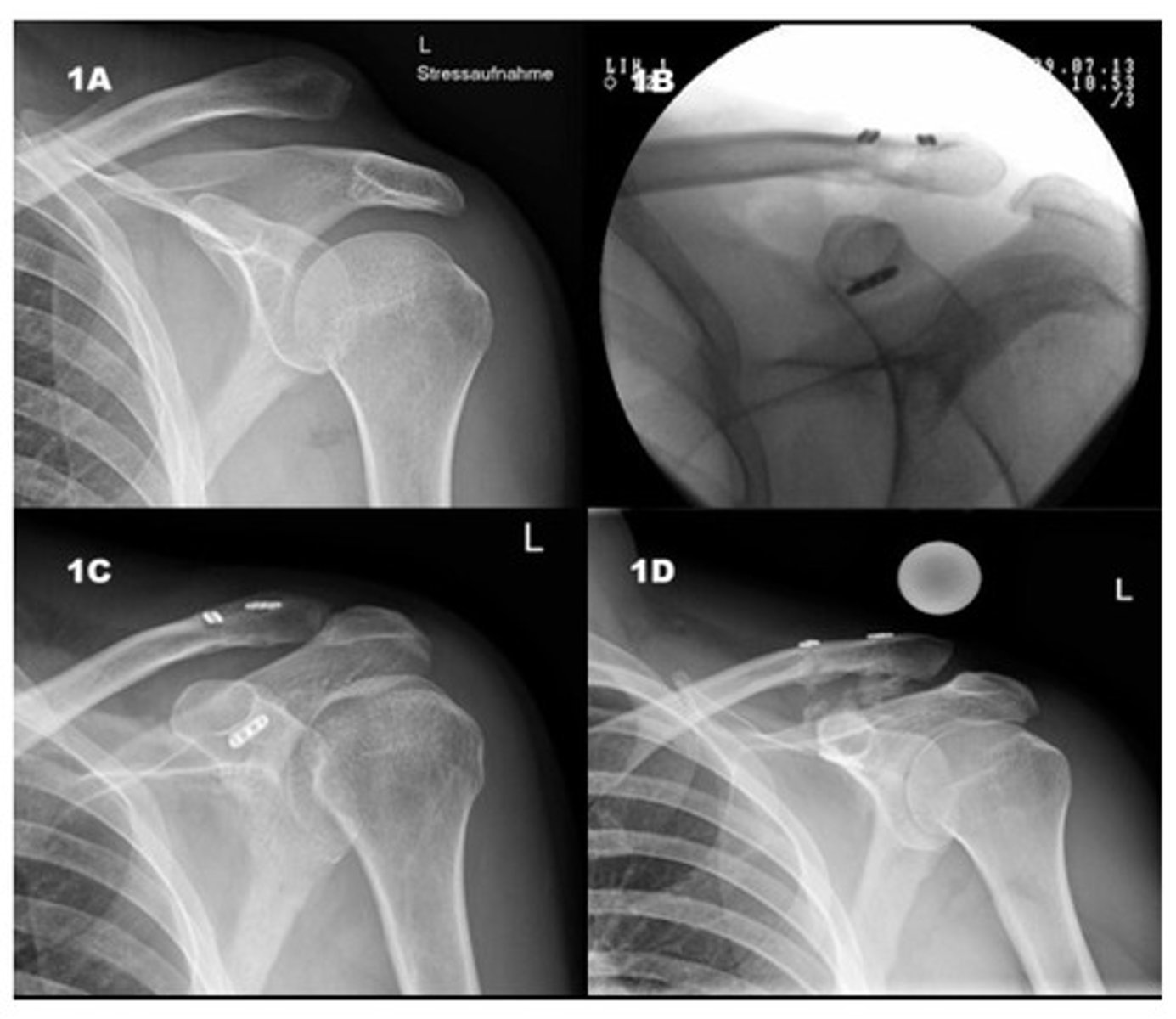
Glenohumeral dislocation
shoulder deformity after FOOSH
arm abducted and held in ER
seen on XR with axillary or scapular "Y" view
Glenohumeral dislocation on imaging
humeral head displaced medially and inferiorly in relation to glenoid fossa
inferior to coracoid process
Bankart lesion - fx of anteroinferior glenoid rim seen on CT or MRI
Acute rotator cuff tear
persistent shoulder pain that's worse with overhead activity
seen on XR, MRI, or US with inferior osteophytes at AC joint and cephalad migration of humeral head
US findings that may mimic rotator cuff tear
tendinosis
calcific tendonitis
adhesive capsulitis
subacromial/subdeltoid bursitis
greater tuberosity fracture
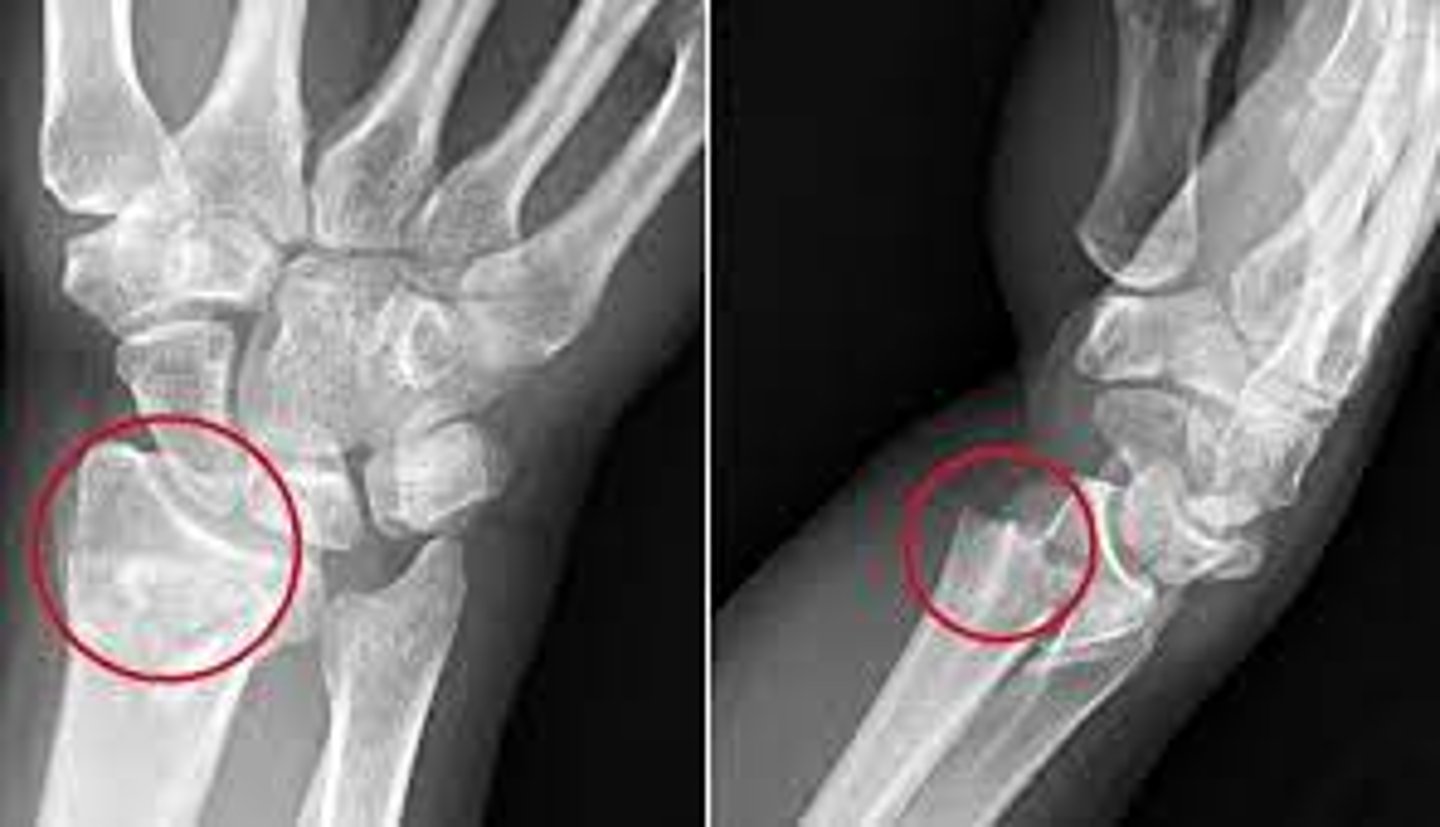
Colles fracture
FOOSH with extended wrist
pain of distal radius/wrist
radiographic findings - volar fracture angulation with dorsal proximal displacement or "dinner fork" deformity
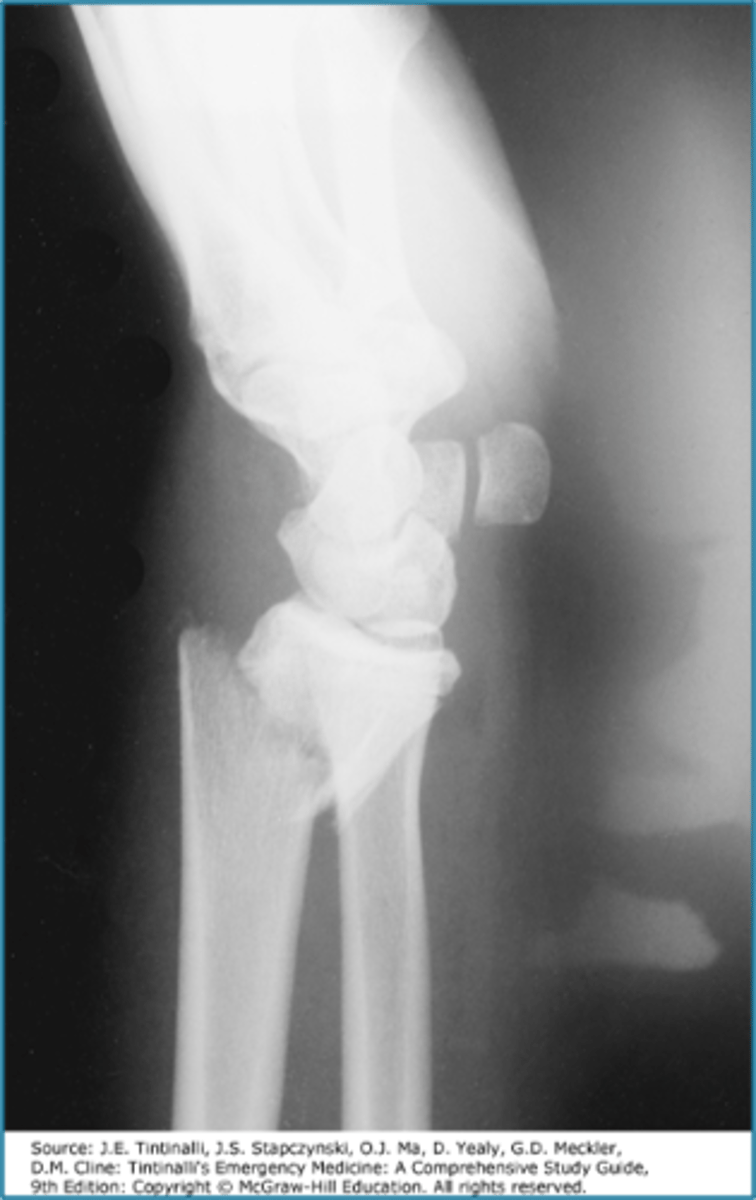
Smith fracture (reverse Colles)
FOOSH with flexed wrist
pain of distal radius/wrist
may be extra-articular, intraarticular or part of fracture-dislocation of wrist
radiographic findings: dorsal fracture of distal radius with hand and wrist displaced volarly
Galeazzi fracture
pain and tenderness along shaft of radius that typically requires ORIF
radiographic findings: isolated fracture along the length of radius with or without associated ulnar fracture
Monteggia fracture
FOOSH
required ORIF
radiographic findings: fracture at proximal 1/3 of ulnar with anterior dislocation of radial head
Scaphoid fracture
FOOSH and tenderness over anatomical snuff box
vascular supply of scaphoid bone is distal to proximal
1/3 of fractures of middle scaphoid develop avascular necrosis
Scaphoid fracture radiographic findings
subtle!
splint anyone with suspected scaphoid fx
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
atraumatic fracture with posterior and medial displacement of proximal femoral epiphysis (in relation to metaphysis)
adolescent with limping gait +/- growth spurt, overweight, or increased activity
XR with frog leg view
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE) on imaging
widening of physis
medial displacement of epiphysis on lateral view
Lines of Klein - superior edge of femoral neck
Patellar fracture
knee pain following blunt trauma
XR with merchant/sunrise view
Tibial plateau fracture
severe knee pain, inability to bear weight, large knee joint effusion
seen on XR with oblique view
CT or MRI for further eval
Tibial plateau fracture on imaging
lipohemoarthrosis with intraarticular fractures
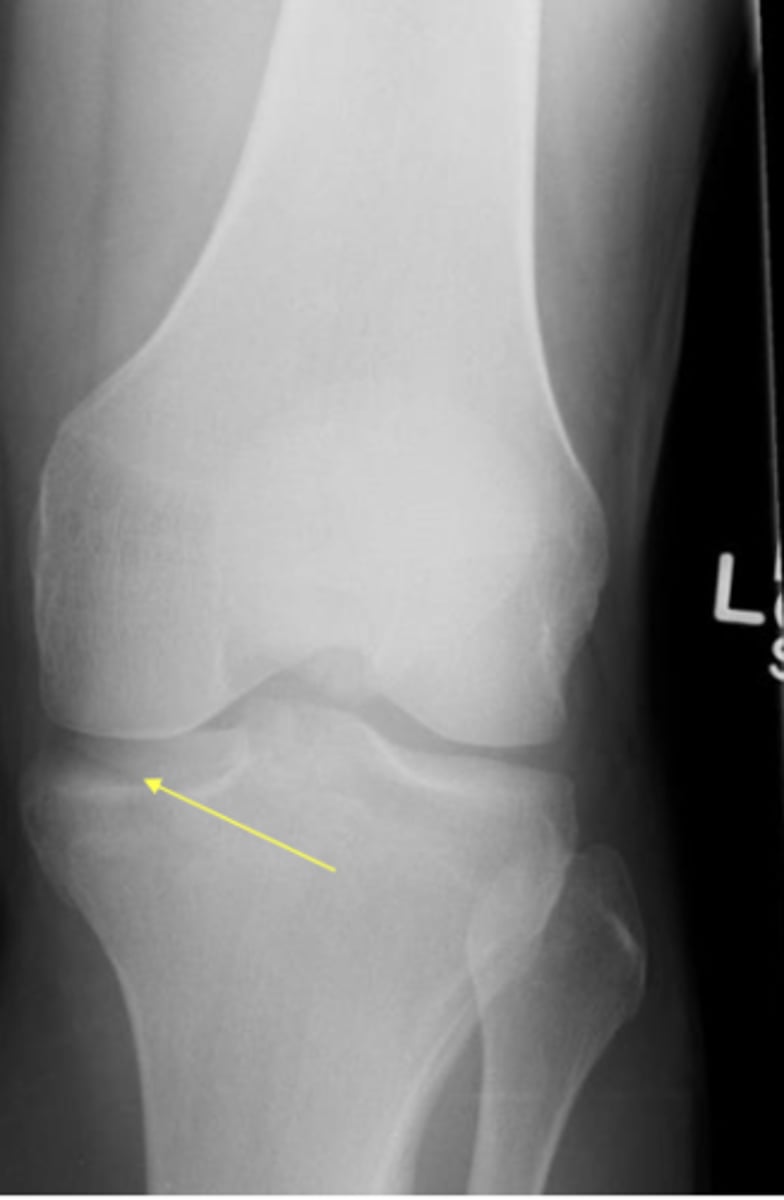
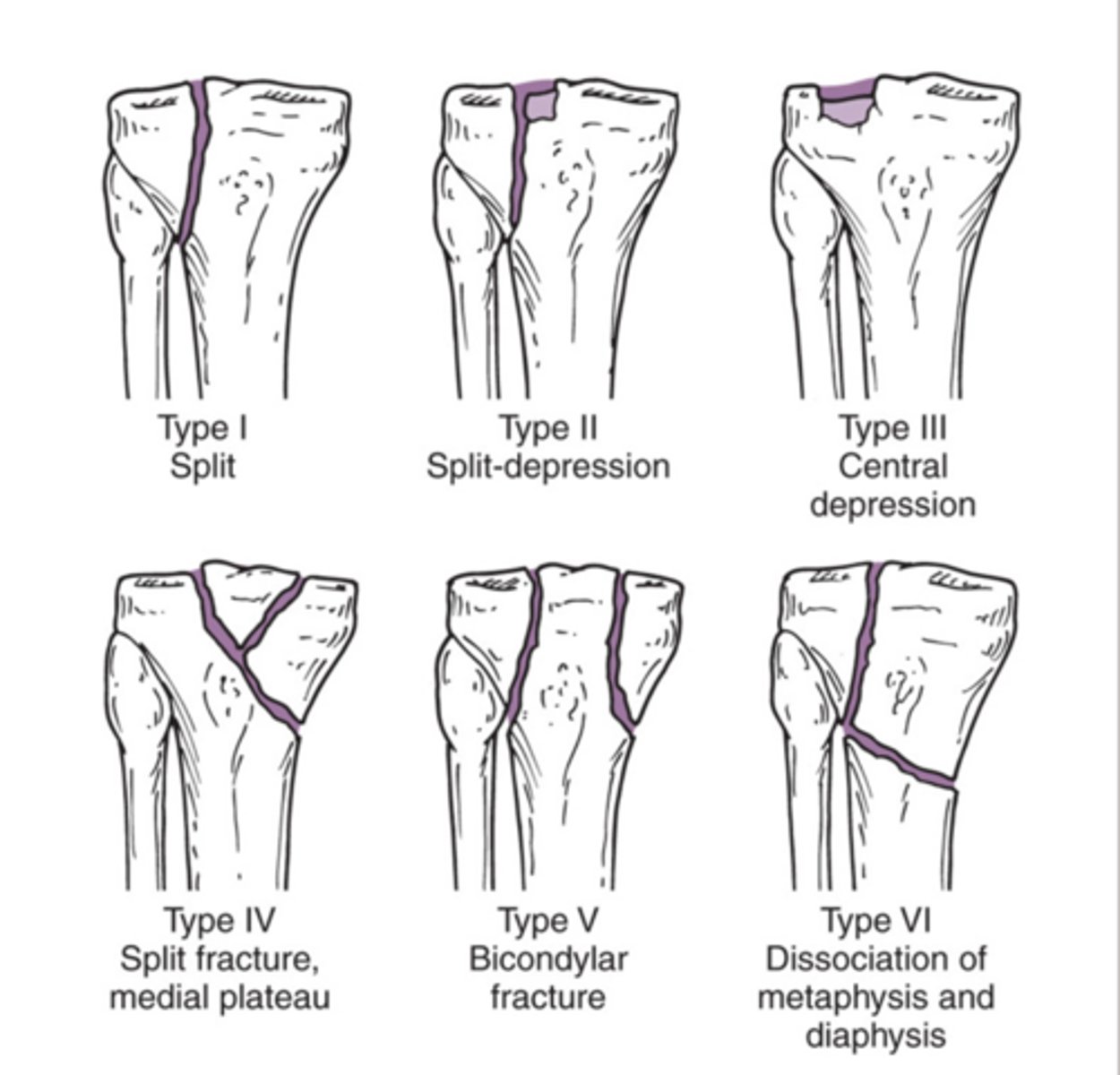
Tibial plateau fracture - Schatzker classification
ACL tear
injury with deceleration, twisting, or jumping
XR to r/o fx and MRI for fx
joint effusion, Segond fracture (avulsion fx secondary to ACL tear) and deep lateral femoral notch sign
Calcaneus fracture
axial loading after jumping or falling
XR with Harris view: lucent line, loss of height of central calcaneus, increase in Bohler's angle, and/or decrease in critical angle of Gissane
Plantar fasciitis
heel pain with first steps of day and after sitting for extended periods
sharp pain with palpation of medial plantar calcaneal region
discomfort in proximal plantar heel on passive ankle dorsiflexion
commonly co-occur with calcaneal spurs
Bone sarcoma - solid
intact cortex with solid, continuous overlying bone formation
Bone sarcoma - unilamellated
slow growing lesion contained by bone
Bone sarcoma - multilamellated
waxing and waning, bone continually tries to contain lesion "onionskin"
Bone sarcoma - spiculated
most aggressive - highly suggestive of malignancy "hair on end" or "sunburst"
Bone sarcoma - Condman triangle
elevation of periosteum away from cortex
Bone sarcoma - buttress
beaklike new bone formation
Bone sarcoma - cortex or patterns of bone destruction
IA - well defined with sclerosis
IB - well defined without sclerosis
IC - ill defined
moth-eaten
permeative
Giant cell tumor of bone
XR: geographic bone destruction with well-defined margins, often IB or IC patterns
located in metaphysis with extension into diaphysis
Enchodroma
may be found incidentally on imaging
imaging of choice: MRI
found in long bones with mineralization in form of dots, rings, or arcs
may be radiolucent in short tubular bones of hands and feet
Incidental cystic bone lesion
atraumatic pain
seen on XR: well defined borders of lesion and adjacent bone, evaluate for pathologic fracture
Osteoid sarcoma
benign, bone producing sarcoma
nocturnal pain relieved with aspirin
imaging of choice CT: small cortical lucency surrounded by sclerosis involving one side of diaphysis
subtypes classified by location in bone: cortical, medullary, and subperiosteal
Multiple myeloma
bone pain, pathologic fracture
abnormal labs with anemia, hypercalcemia, renal insufficiency
radiograph: multiple lytic foci with round, punched out areas of bone destruction uniform in size
Padget disease
chronic skeletal disorder characterized by focal resorption of bone followed by disorderly bone formation and abnormal bone remodeling
Padget disease - lytic stage
osteolysis in epiphysis extending to metaphysis and then diaphysis
Padget disease - mixed stage
advanced osteolysis with thickening of bone trabeculae and cortex
Padget disease - blastic stage
osteosclerosis with high concern for insufficiency fractures
Myositis ossificans
benign, self-limiting, nonneoplastic response to injury
mature bone develops within the injury in about 2 months
Osteochrondroma
palpable hard mass in extremity
XR: bony protrusion with contiguous marrow and cortex to underlying normal bone