Chapter 12: Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
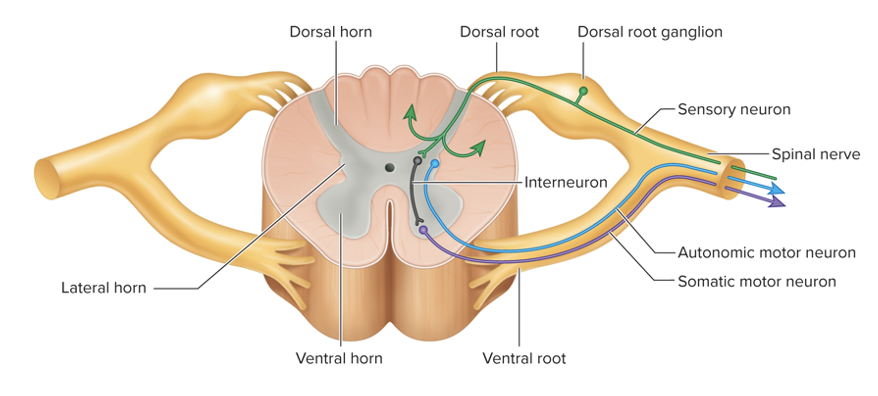
Dorsal root ganglion
collections of cell bodies of pseudo-unipolar sensory neurons forming dorsal roots
2
New cards
Where are motor neuron cell bodies located
anterior (multipolar/somatic) and lateral (autonomic) horns of the spinal cord gray matter
axons of motor neurons form ventral roots and pass into spinal nerves
axons of motor neurons form ventral roots and pass into spinal nerves
3
New cards
Reflex
automatic response to a stimulus that occurs without conscious thought; homeostatic
4
New cards
Reflex arc
neural pathway that controls a reflexcompe
5
New cards
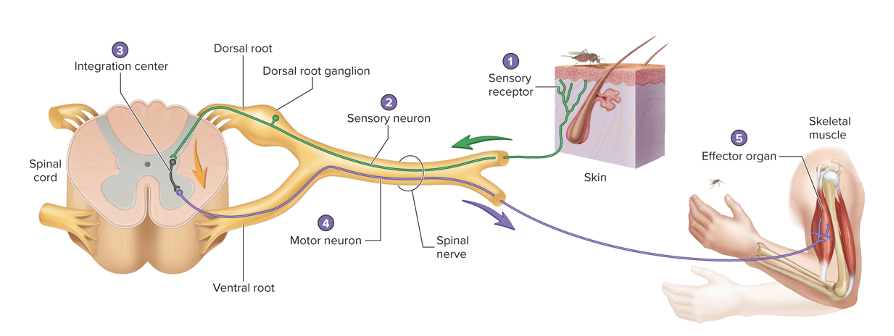
Components of a reflex arc
sensory receptor →sensory neuron → interneuron (not always) → motor neuron → effector organ
6
New cards
Different ways a reflex is classified
number of synapses, development, effector type, and location of integration centerMon
7
New cards
monosynaptic reflex
no interneurons
single synapse in excitatory arc
stretch reflex (patellar, achilles)
single synapse in excitatory arc
stretch reflex (patellar, achilles)
8
New cards
polysynaptic reflexes
multiple synapses with interneurons
more complex
more complex
9
New cards
innate reflexes
part of normal development
babinski reflex in babies, patellar
babinski reflex in babies, patellar
10
New cards
learned reflexes
develop as activities are repeated
skills required for a task (ride a bike)
skills required for a task (ride a bike)
11
New cards
somatic reflex
skeletal muscle
anterior horn of gray matter
anterior horn of gray matter
12
New cards
autonomic (visceral) reflexes
smooth muscle, cardiac, glands
13
New cards
cranial reflexes
integrate at the brain
14
New cards
spinal reflexes
integrate at the spinal cord
15
New cards
Steps in a reflex arc
1. sensory receptor detects a stimuli and generates an AP
2. sensory neuron sends AP through nerve → dorsal root → spinal cord
3. AP carried to integration center (may or may not involve a interneuron
4. interneuron synapses w motor neuron
5. motor axon conducts AP through ventral root and spinal nerve to an effector organ
16
New cards
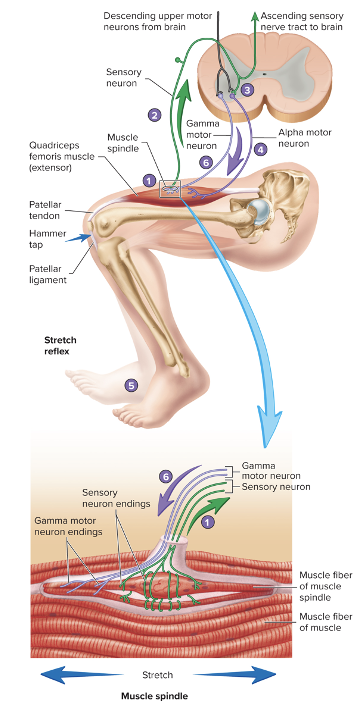
Stretch Reflex
muscles contract dues to stretching force detected by muscle spindle
no interneuron
sensory neurons synapse with alpha motor neurons with cause muscles to contract
no interneuron
sensory neurons synapse with alpha motor neurons with cause muscles to contract
17
New cards
muscle spindle
3-10 specialized muscle cells that respond to stretch
gamma motor neurons control the sensitivity (activate in response to alpha motor neuron signal)
gamma motor neurons control the sensitivity (activate in response to alpha motor neuron signal)
18
New cards
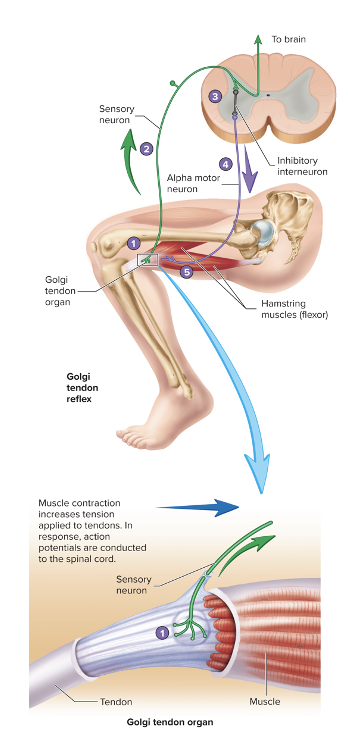
Golgi Tendon Reflex
prevents contracting muscles from applying excessive tension to tendons
prevents damage to tendons that could be caused by excessive tension
produces sudden relaxation of the muscles
example of neuromodulation
GTO → sensory neurons → inhibitory interneurons → inhibit alpha motor neurons → muscle relaxes
prevents damage to tendons that could be caused by excessive tension
produces sudden relaxation of the muscles
example of neuromodulation
GTO → sensory neurons → inhibitory interneurons → inhibit alpha motor neurons → muscle relaxes
19
New cards
Golgi tendon organ
encapsulated nerve endings that have their ends numerous terminal branches with small swellings associated with bundles of collagen fibers in tendon
located in tendon near muscle
located in tendon near muscle
20
New cards
Withdrawal Reflex
function: remove a body part from a painful stimulus
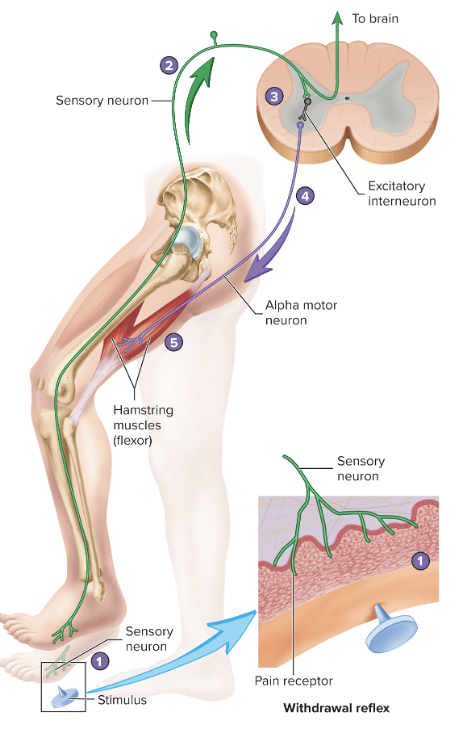
21
New cards
reciprocal innervation
causes relaxation of extensor muscle when flexor muscle contracts
also involved in stretch reflex
also involved in stretch reflex
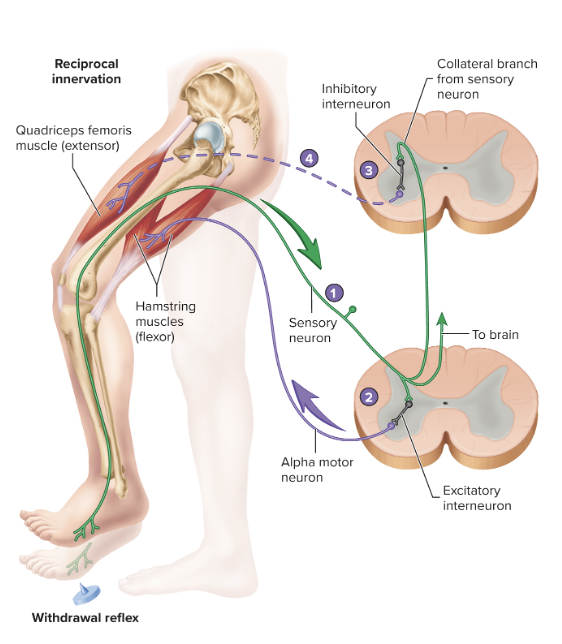
22
New cards
Crossed Extensor Reflex
when a withdrawal reflex is initiated in one lower limb, the crossed extensor reflex causes extension of opposite lower limb
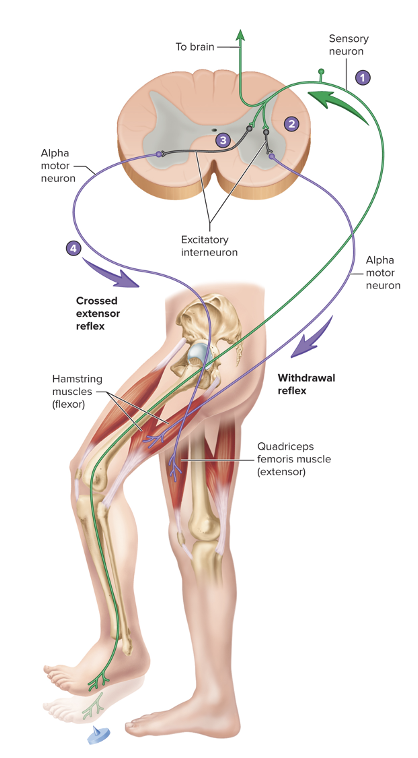
23
New cards
Interactions with spinal cord reflexes
sensory information goes to brain
descending tracts from brain carry information to reflexes
neurotransmitters produce IPSPs or EPSPs modifying the reflex
descending tracts from brain carry information to reflexes
neurotransmitters produce IPSPs or EPSPs modifying the reflex