SEX DETERMINATION & SEX LINKAGE
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Sex determination systems
genotypic sex termination
environmental sex determination
Genotypic sex determination
due to specific DNA sequences
genic balance
chromosome determination
mating-type determination
Genic balance
amount of gene products
Chromosome determination
presence or absence of gene products
Mating-type determination
which alleles are present and are therefore expressed
Environmental sex determination
signals from environment
ex: day length, temperature, social clues
XX
wild-type (normal) female
causes gonads to develop into ovaries and produce eggs
XY
wild-type (normal) male
causes gonads to develop into testes and produce sperm
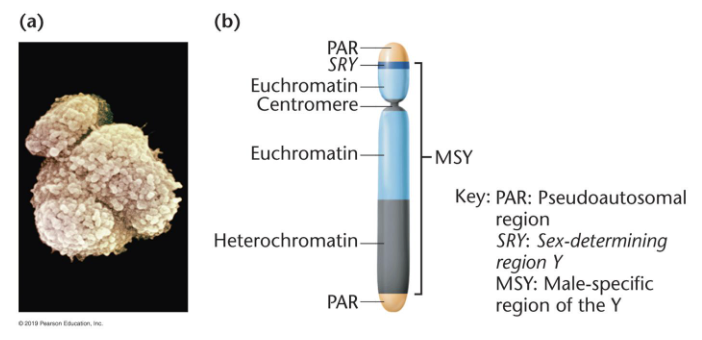
Y chromosome
pseudoautosomal region (PAR)
synapses with X chromosome during meiosis
male-specific region of the Y (MSY)
euchromatin containing SRY locus
Sex-linked genes
genes present on X & Y chromosomes
many linked genes don’t influence sex development
most sex-linked genes are X-linked because Y doesn’t contain many genes
X-linked recessive inheritance
traits more frequently observed in males
males are hemizygous for genes on the X chromosome
no second allele to compensate for recessive allele
females express the trait when they are homozygous for the allele
female heterozygotes are carriers
Barr bodies
inactive X chromosomes
blastocyst stage → X is deactivated in XX mammals
barr body is made of heterochromatin
form of imprinting
monoalleleic expression allows for gene dosage compensation
equal amounts of X-linked gene expression between males and females
number of barr bodies in somatic cells = all X chromosomes except one are deactivated
Lyonization
how barr bodies are formed
XIST gene on X chromosome
weakly expressed
one XISt gene copy is silened
becomes the active X chromosome
other X continues to express XIST and becomes the barr body
XIST encodes a long non-coding functional RNA (lncRNA)
coats chromosome and recruits epigenetic machinery (DNA methyltransferases and HDAC) to pack up the chromosome
Mosaicism
mixed phenotype resulting from different genotypes or gene expression levels in the cells of a multicellular organism
in this case, due to monoallelic expression resulting from random barr body lyonization
diff monoallellic expression in diff cells of the body
some cells have paternally derived X chromosome silenced and only express maternally dervied X chromosome genes and vice versa
all mitotic descendants of a cell inherit the parent cell’s inactivation pattern