Nuclear medicine
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Nuclear medicine
Uses radioactive atoms called radionuclides. Introduced via injection. They emit radiation which machines detect to help how to treat diseases. Specifically emits gamma radiation. Goal is to understand functions of organs.
Nuclear reactor
Uranium-235 fission undergoes fission to give neutrons rich radionuclides which undergo beta-minus decay.
Cyclotron
Charged particles to make proton rich radionuclides. Flourine-18.
CP accelertaed via electric field.
Radiopharmacy
Well shielded room and ventilation system. Laminar airflow cabinet for radio-pharmiceutiacls.
NM 2
Delivers radipharmectical to patient. To assess real time body function and monitor behaviour of treatment. Whole body scanning and dynamic studies.
Colimator
A device used in nuclear medicine to focus and direct gamma rays emitted from a radiopharmaceutical, enhancing image quality during diagnostic imaging.
Photomultiplier tube
Convert photon to electric signal. Ejects photoelectron when photon of sufficient energy strikes photocathode.
Thyroid pathologies
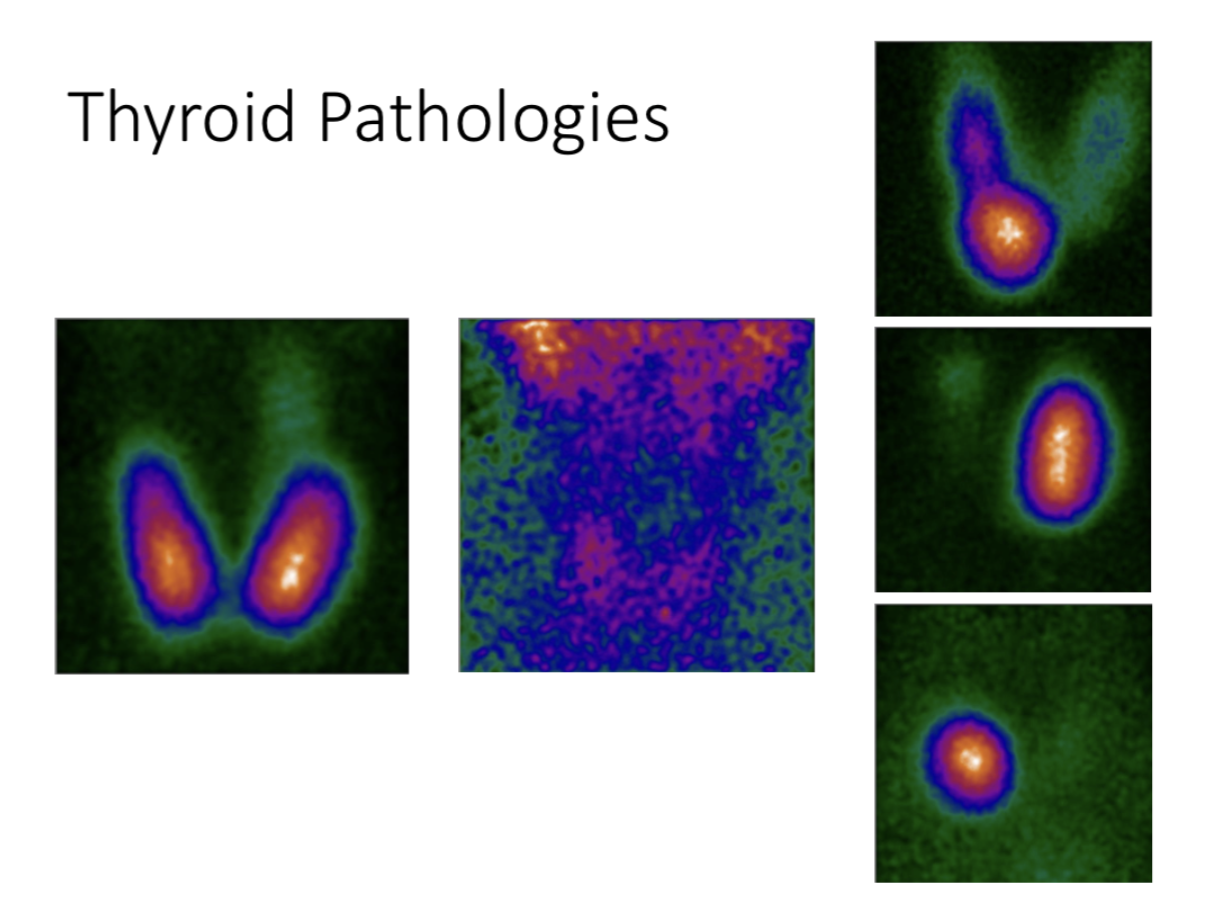
Radioguided surgery
Interstitial administration of an appropriate radiopharmaceutical (typically a
radiocolloid) that mimics the pattern of lymphatic drainage from a solid tumor to
identify the sentinel node(s) to which the primary tumor drains.
Systemic administration
of a tumor-seeking radiopharmaceutical that accumulates
preferentially in the target lesion.
Direct intralesional administration
of a radiopharmaceutical that, due to its large
size, is retained indefinitely at the injection site in a procedure called ROLL
(Radioguided Occult Lesion Localization).
Sentinal node
Fist lymph node that directly drains lymph from tumour site. 99mTc-nanocolloid used.
Radioembolization
Ytrium-90