Later Mesopotamia and Assyrian Art
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Tell Brak
ancient city in Syria; Uruk expansion
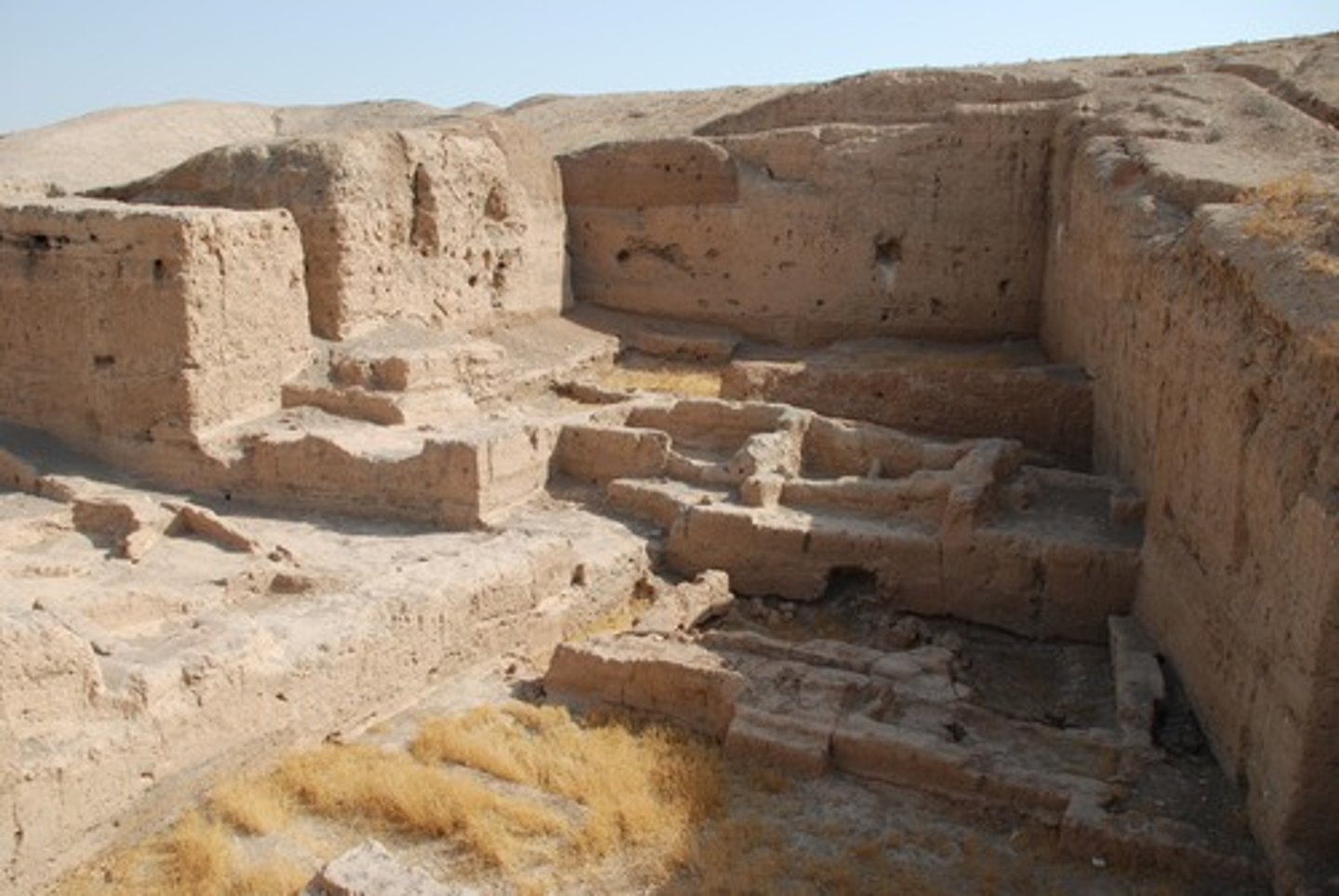

Assyria
a southwest Asian kingdom that controlled a large empire from about 850 to 612 B.C.
Ninevah
Capital of the ancient Assyrian empire
Khorsabad
built from about 720 BCE
The site of the Assyrian Palace of Sargon II, large rooms and courtyards with a circuitous path from entrance to thrown room

Persia
an empire in southern Asia; 6th century BC to the 4th century BC
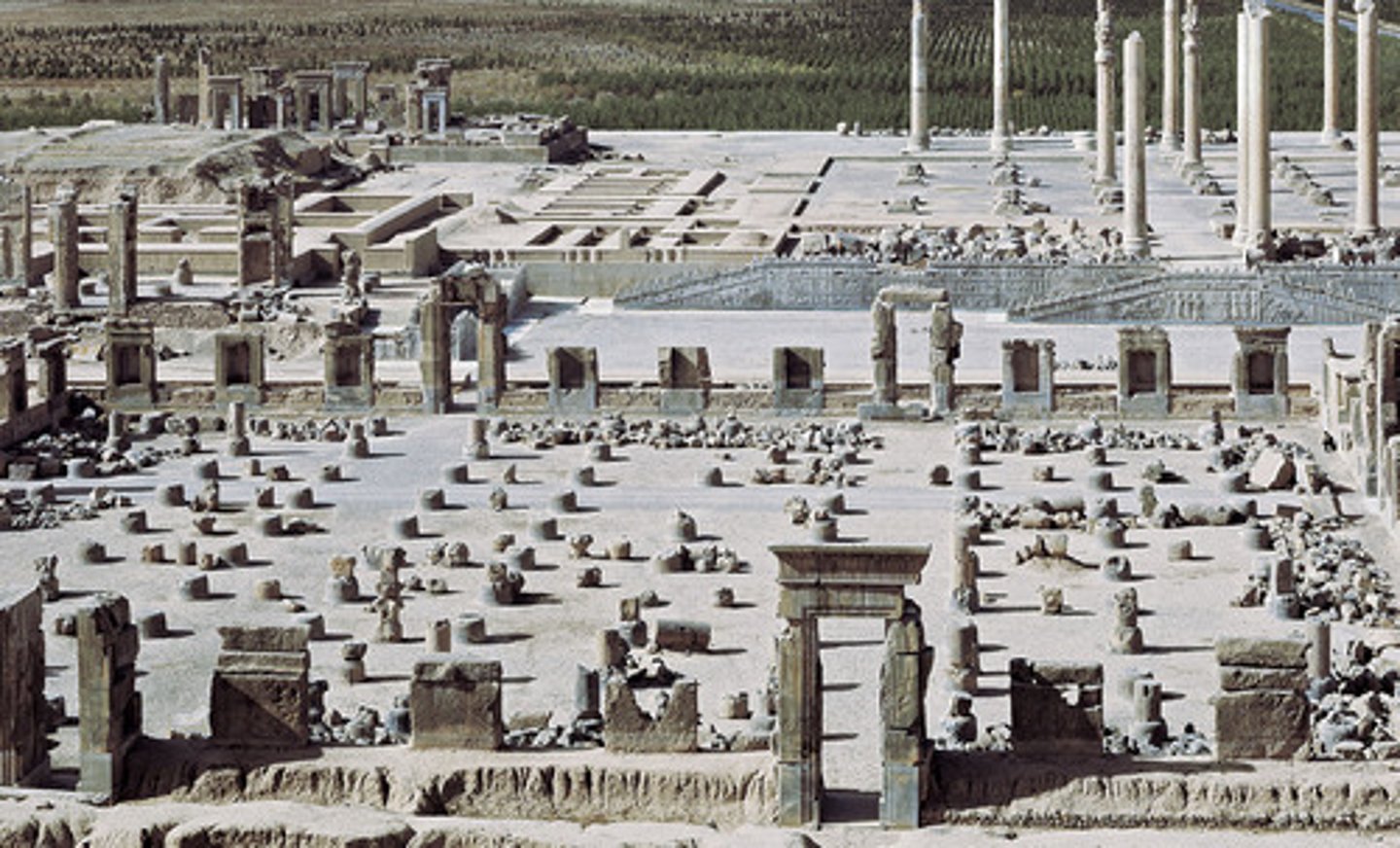
Persepolis
A complex of palaces, reception halls, and treasury buildings erected by the Persian kings Darius I (used columns rather than walls)
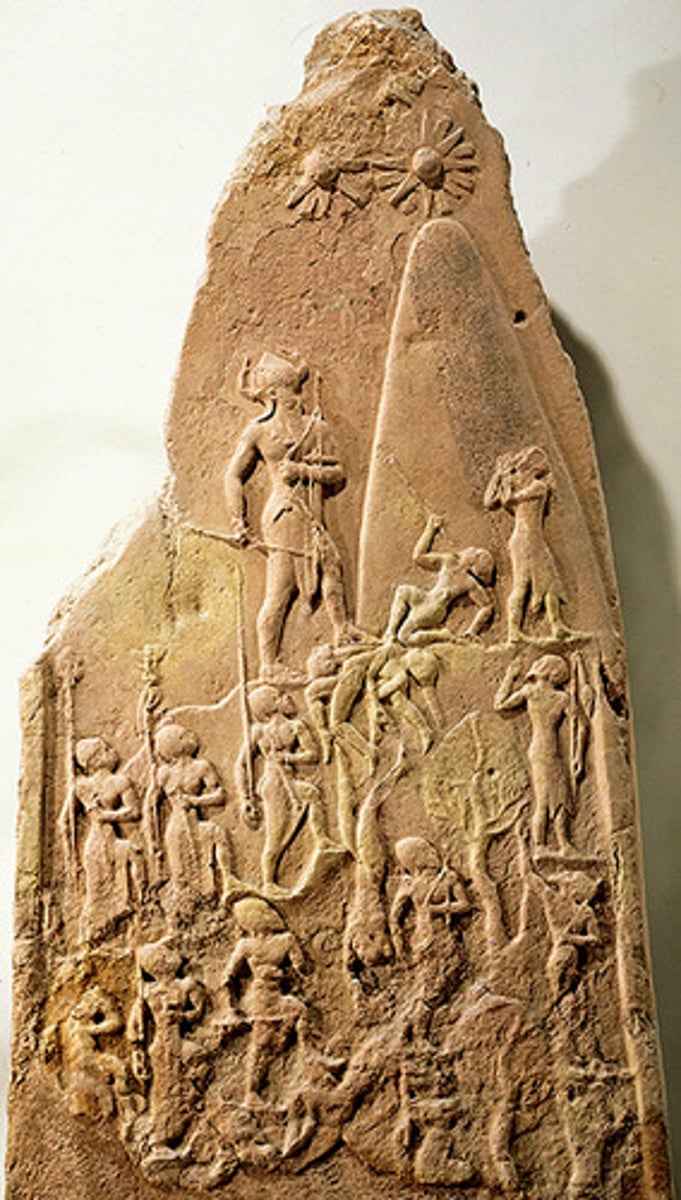
Akkadia
A people who ruled southern Mesopotamia from 2334-2180 BCE. The important trade center and first empire.
Naram-Sin
The Akkadian ruler who had a temple built for him

Mari
City in Akkadia
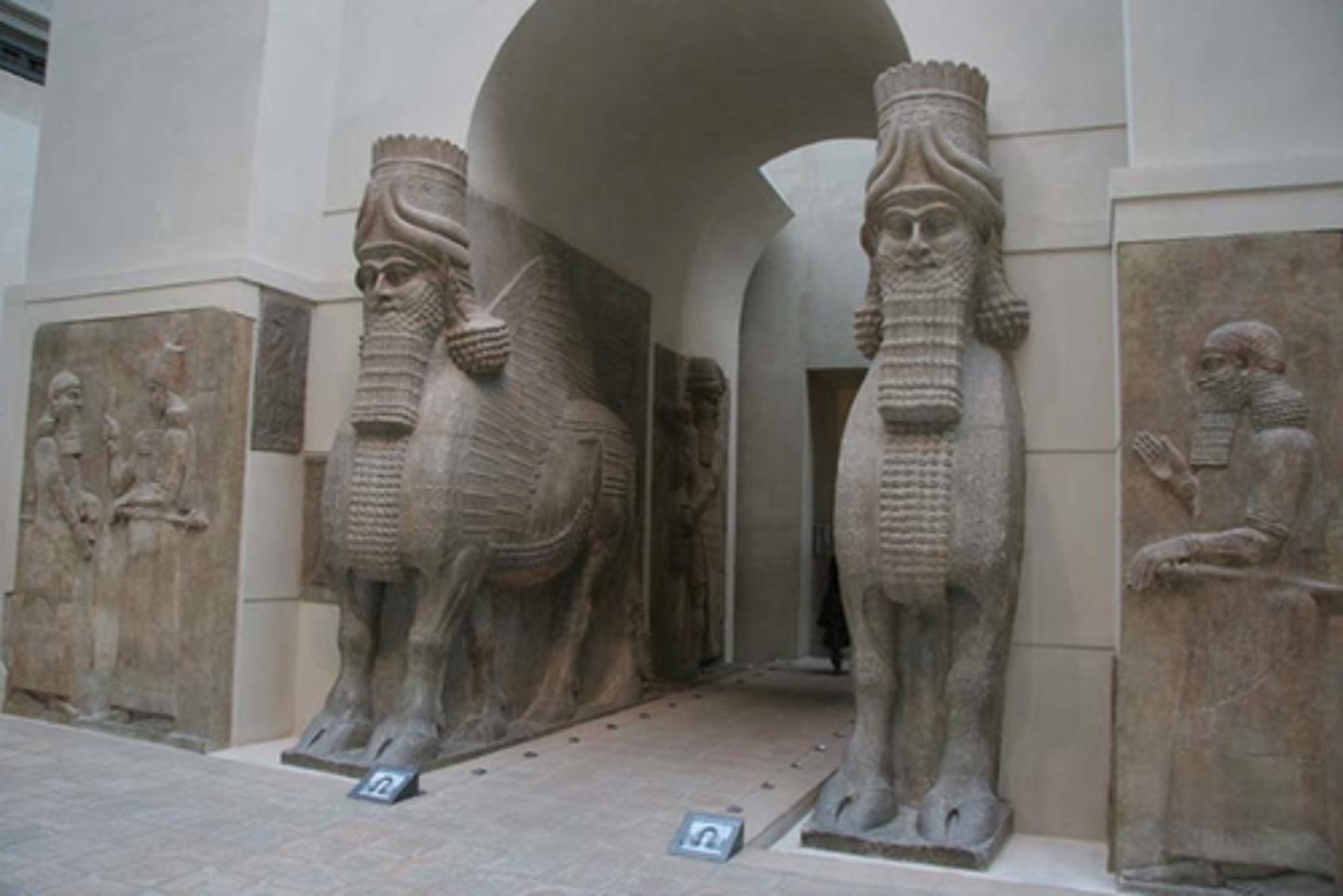
Ashurnasirpal II
Assyrian king who conquered lands stretching across north Mesopotamia during the Iron Age; his palace had a decorated throne room
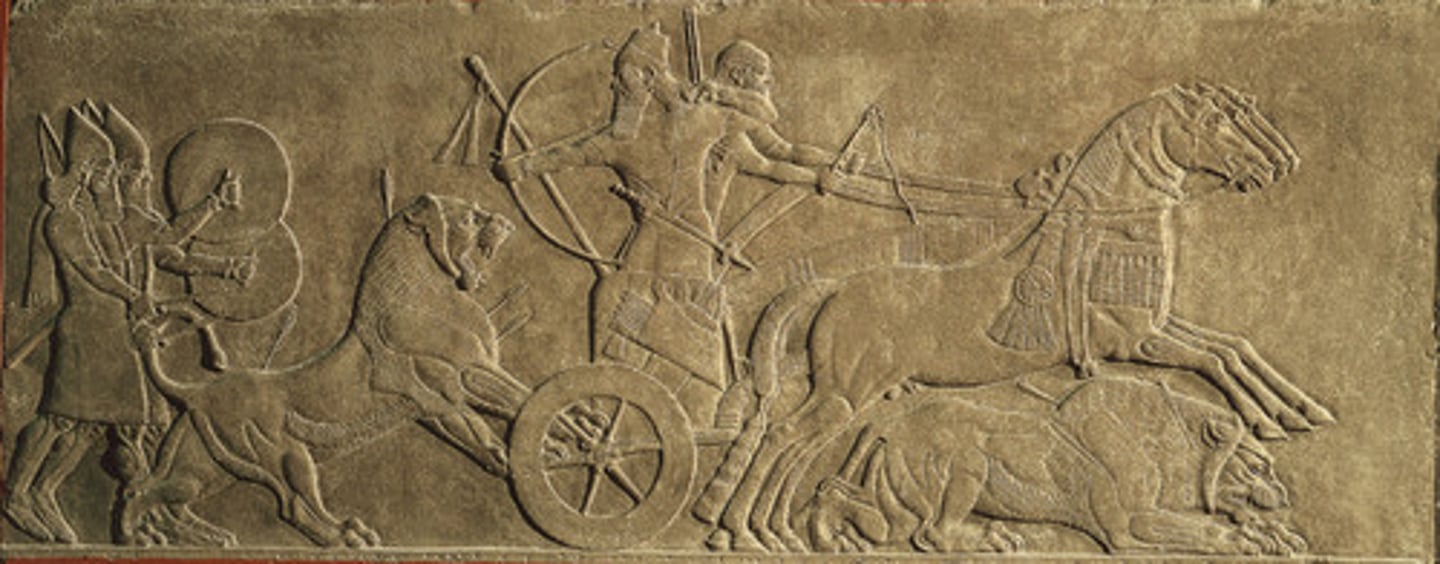

Nimrud
a city in Assyria
Babylon
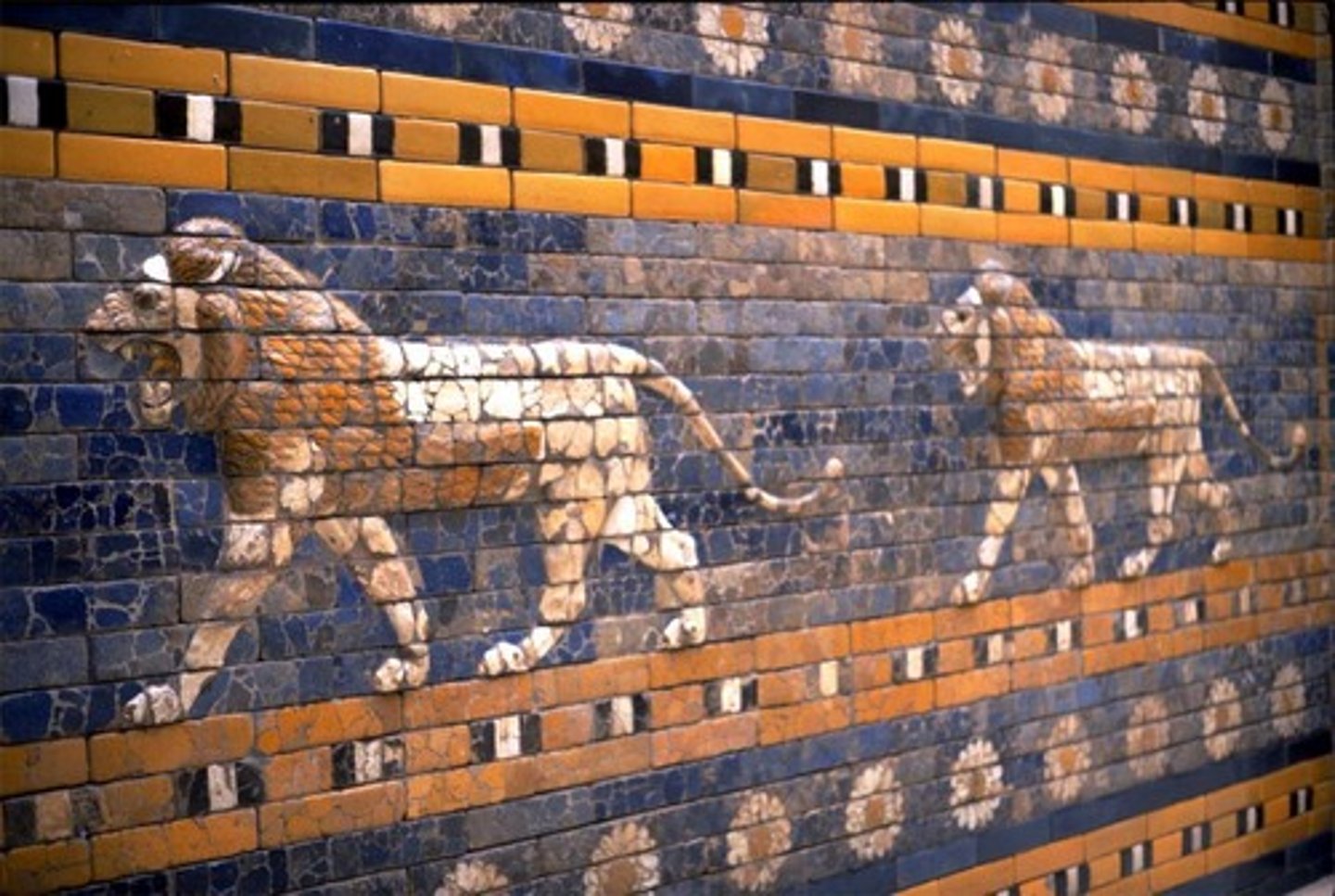
the chief city of ancient Mesopotamia and capitol of the ancient kingdom of Babylonia; it's entrance was decorated with glazed bricks
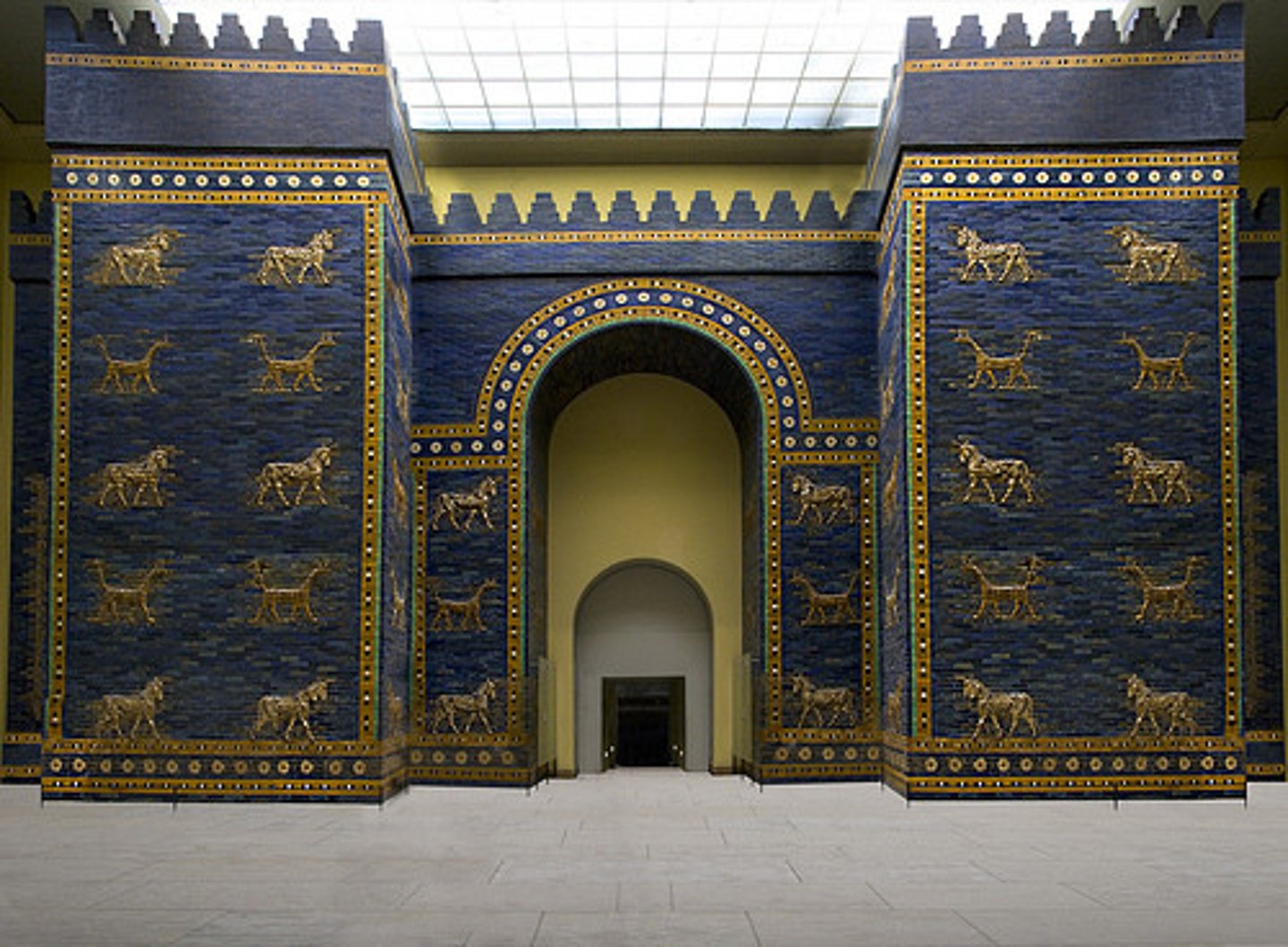

Nebuchadnezzar II
King of Babylon
Darius I
Persian king
Architecture
the art of designing and constructing buildings, for human inhabitance/use
royal architecture
the structure, patterns, methods used to build and design palaces
palace
places/structures where people or political power lived and conducted their policital
floor plan
This type of plan view shows the location of walls, windows, doors, fixtures and placement of various systems in a structure. It is drawn from an overhead or bird's eye view
courtyard
key to Mesopotamian palaces; central area between rooms that led people from one room to another

throne room
The official chamber in which the ruler would preside; Ashurnasirpal II had a highly decorated throne room
pictorial program
storytelling in pictures that presents a connected sequence of event, oftes used in ancient civilizations to tell of a King's accomplishments/ military victories
orthostat
an upright, standing stone slab, often protecting the lower part of a mud brick wall, can contain relief structures
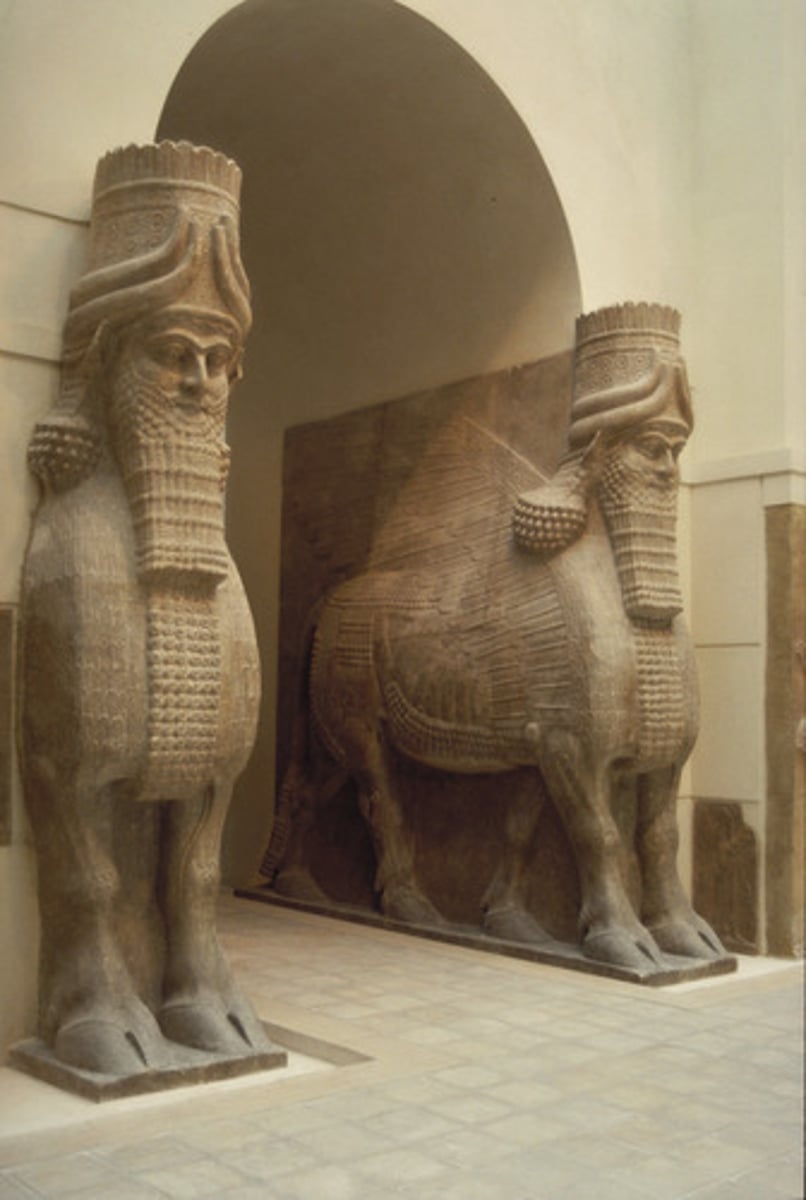
Lamassu
a colossal winged human-headed bull in Assyrian art, often a guard figure

glazed brick
Bricks painted and then kiln fired to fuse the color with the baked clay; used to construct the entrance to Babylon

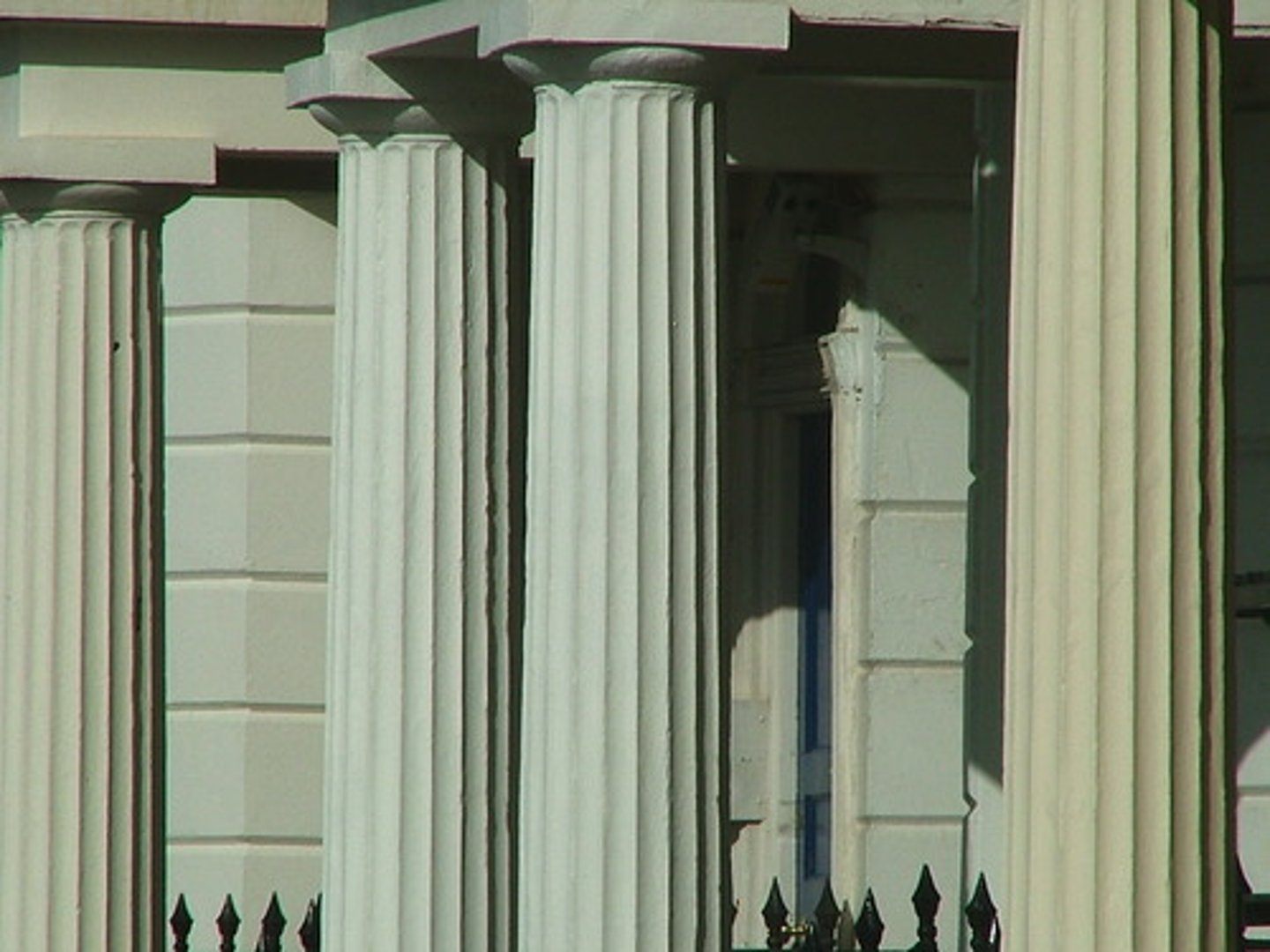
column
structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below (used in Persepolis)

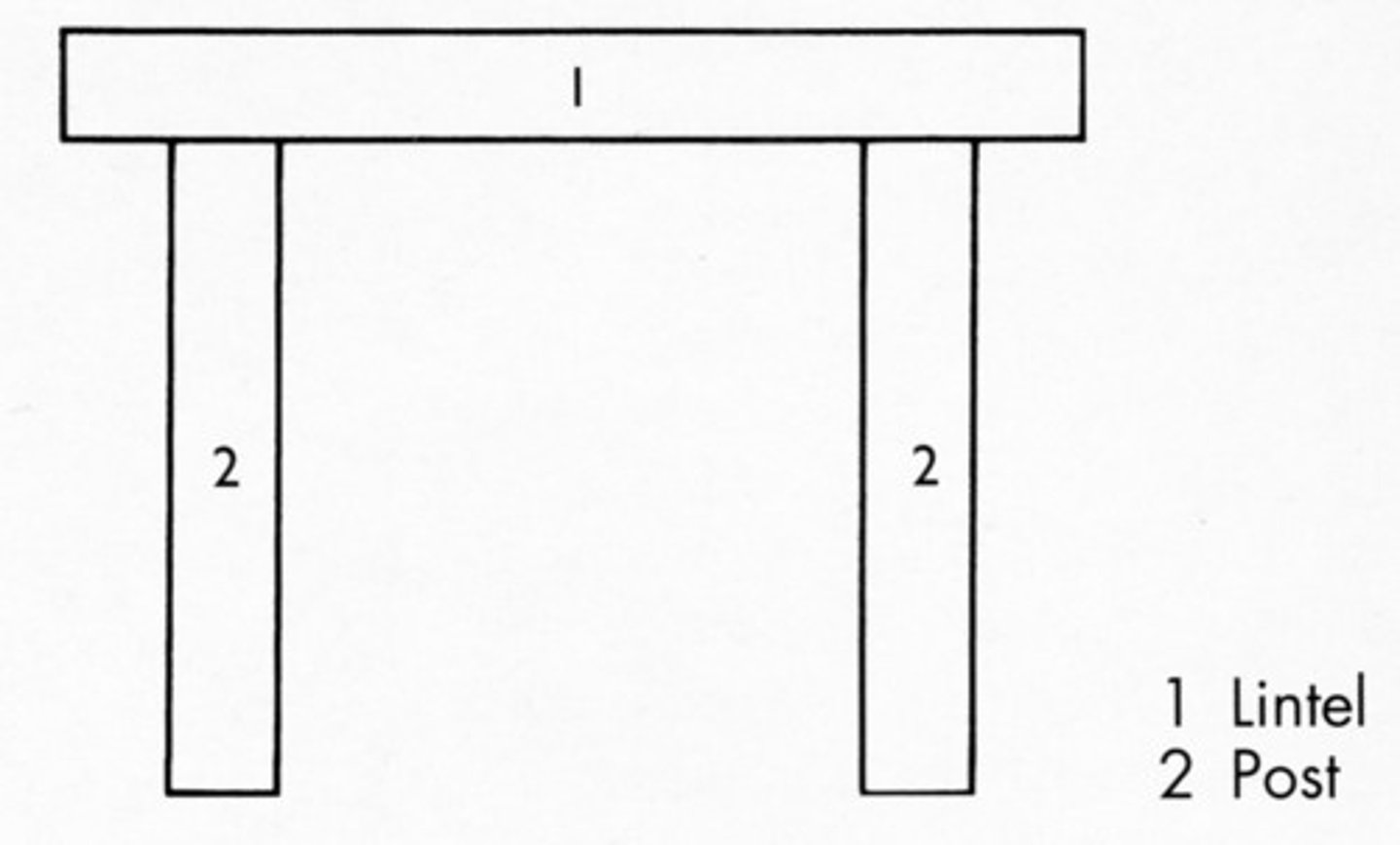
post and lintel
a structure consisting of vertical beams (posts) supporting a horizontal beam (lintel), used in the city of Persepolis to construct the palace of Darius I
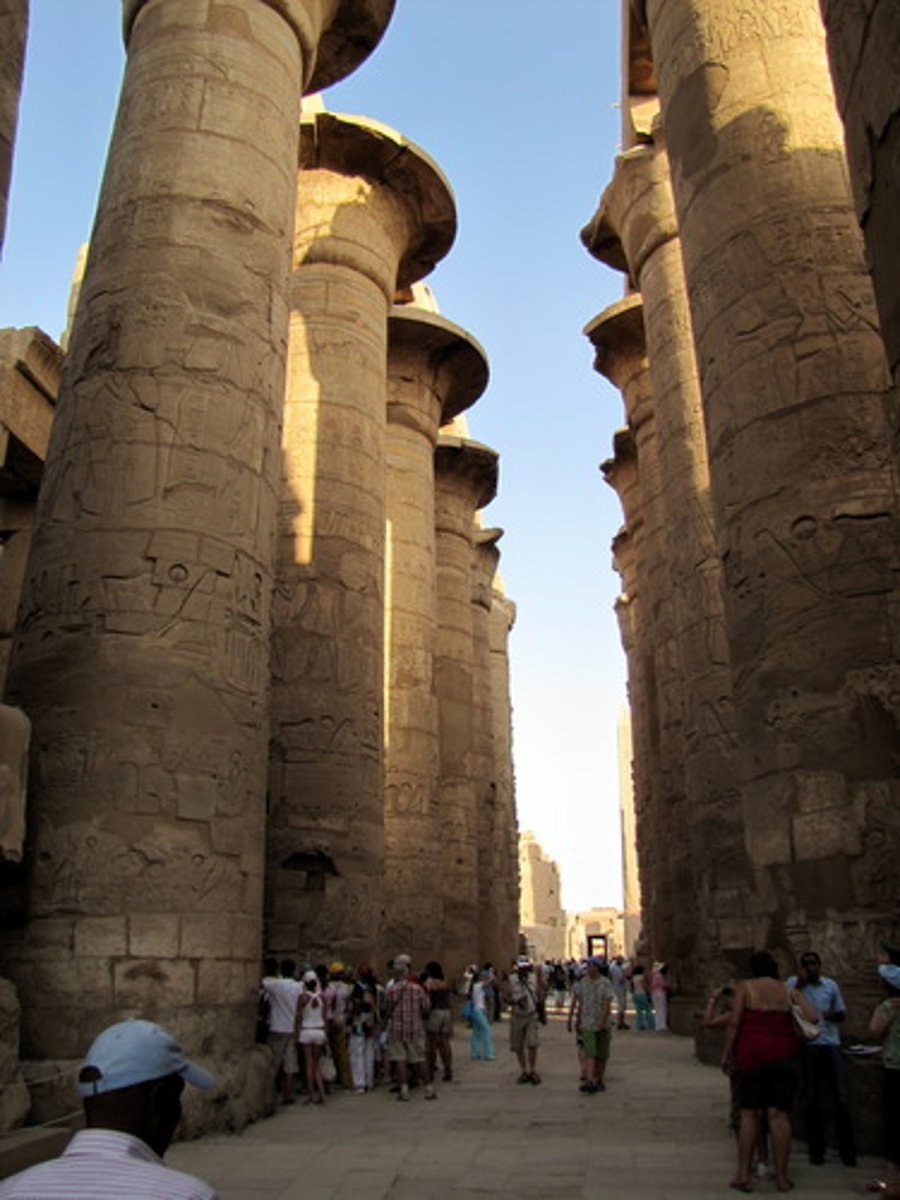
hypostyle hall
a large interior room characterized by many closely spaced columns that support its roof, used in Persepolis

site plan
a view of the building as seen from directly above. Shows roof of building, surrounding yards, and property immediately adjacent to the site