APES UNIT 6
1/54
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
⚡ Energy
The capacity to do work or cause physical change in a system.
☀ Sun: The Primary Energy Source
Provides energy for most life on Earth.
Energy is produced through nuclear fusion in the Sun’s core.
🔋 Forms of Energy
1⃣ Chemical Energy – Stored in bonds between atoms.
2⃣ Electrical Energy – Results from moving electrons.
3⃣ Electromagnetic Energy – Travels in waves (e.g., light, radio).
4⃣ Mechanical Energy – Includes:
Potential Energy – Stored energy (e.g., a stretched rubber band).
Kinetic Energy – Energy in motion (e.g., a rolling ball).
5⃣ Nuclear Energy – Stored in atomic nuclei, released by fission (splitting) or fusion (joining).
6⃣ Thermal Energy – Due to movement of molecules; related to heat.
⚖ Units of Energy & Power
British Thermal Unit (Btu) – Heat needed to raise 1 lb of water by 1°F.
Btu/hr – Used in air conditioning.
Horsepower (HP) – Used in cars; 1 HP = 746 watts.
Kilowatt-hour (kWh) – Measures energy usage (used in electricity bills).
📜 Laws of Thermodynamics
1⃣ First Law (Conservation of Energy) – Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
2⃣ Second Law – Energy conversions are never 100% efficient; some energy is always lost as heat.
3⃣ Zeroth Law – If A = B and A = C, then B = C (basis for temperature measurement).
🌍 Renewable Energy
Energy from naturally replenished resources on a human time scale.
Found in wide geographical areas, unlike fossil fuels, which are concentrated in a few countries.
⛽ Nonrenewable Energy
Not sustainable because formation takes billions of years (e.g., fossil fuels).
⚖ Arguments for Continued Use of Fossil Fuels
1⃣ Abundant supply → Leads to low prices for consumers.
2⃣ High net-energy yield → Concentrated and efficient fuel.
3⃣ Existing infrastructure → Already in place for extraction, processing, and delivery.
4⃣ Political factors → Fossil fuel industries hold economic and political influence.
5⃣ Established technology → Technology for fossil fuel use is already widespread.
🔥 Fossil Fuels
Formed from past geological remains of living organisms.
🌲 Burning Wood Fuel
Produces CO₂, heat, steam, water vapor, and wood ash.
🌱 Peat
Partially decayed vegetation from wetlands (e.g., mosses, sedges, shrubs).
Forms in acidic and anaerobic conditions.
⛏ Coal Formation
Dead plant matter decays into peat, then heat & pressure over millions of years convert it into coal.
🛢 Types of Coal
1⃣ Lignite → "Brown coal," most harmful to health, mainly used for electric power generation.
2⃣ Bituminous → Primarily used as fuel in steam-electric power generation.
3⃣ Anthracite → Used for residential & commercial space heating.
🌿 Clean Coal Technology
Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS) → Pumps & stores CO₂ underground.
🔥 Natural Gas
Formed from buried plants & gases exposed to intense heat & pressure.
🛢 Oil
Fossil fuel from decomposed organic material under high temperature & pressure for millions of years.
⚡ Cogeneration (CHP - Combined Heat & Power)
Generates electricity & heat simultaneously, improving efficiency.
🛠 Pollutant Removal Technologies
1⃣ Baghouse Filters → Fabric filters reduce particulates.
2⃣ Burning Pulverized Coal → Fine coal powder reduces emissions.
3⃣ Coal Gasification → Converts coal into "syngas" with lower emissions.
4⃣ Cyclone Separator → Uses spinning effects & gravity to remove particulates.
5⃣ Electrostatic Precipitator → Uses electric charge to remove dust & smoke.
6⃣ Fluidized-Bed Combustion → More air than normal combustion, reducing NOx, SOx & particulates.
7⃣ Scrubbers → Inject chemicals to "wash out" acidic gases.
8⃣ Sorbents → Charcoal, calcium compounds, or silicates trap gaseous pollutants.
📈 Law of Supply
As price increases, quantity supplied increases.
Suppliers maximize profits by increasing production.
📉 Law of Demand
Higher price = Lower demand (Inverse relationship).
🔥 Fossil Fuels Formation
Coal → Formed from land vegetation over millions of years.
Natural Gas → Formed from marine organisms, relatively cleaner than coal & oil.
Oil → Liquid fossil fuel, formed from marine organisms, trapped in rock & sediment, extracted by drilling.
⛽ Other Nonrenewable Fossil Fuel Resources
1⃣ Methane Hydrates (Clathrates)
Found in permafrost, ocean floor, & continental shelves.
2⃣ Oil Shale
Fine-grained rock containing kerogen, which can be converted into shale oil.
3⃣ Synfuels
Fuels derived from coal, natural gas, or biomass via chemical conversion.
4⃣ Tar Sands
Contain bitumen (semi-solid oil), extracted via strip mining or in situ methods (steam injection).
🔥 Combustion Reaction of Fossil Fuels
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is released, contributing to global warming due to the greenhouse gas effect.
⚡ Steps from Fuel to Electricity
1⃣ Extract thermal energy from fuel to raise steam.
2⃣ Convert thermal energy into kinetic energy in the turbine.
3⃣ Use a rotary generator to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
💧 Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking)
Injects water, sand, and chemicals at high pressure to create & expand rock fractures.
Used in low-permeability rocks (e.g., sandstone, shale, coal beds).
Increases oil/gas flow from petroleum-bearing rocks.
⚛ Nuclear Fission
Atom splits into smaller nuclei + by-product particles.
Releases heat, which can be controlled for electricity.
Uncontrolled reaction → Meltdown (severe reactor accident).
🔥 Nuclear Meltdown
Overheating in a nuclear reactor → core damage.
🔋 Nuclear Fuels
1⃣ U-235
Less than 1% of natural uranium.
Critical Mass: Minimum amount needed for a chain reaction.
2⃣ U-238
Most common uranium isotope.
Half-life: 4.5 billion years.
Decays into Pu-239 when hit by a neutron.
3⃣ Pu-239
Half-life: 24,000 years.
Produced in breeder reactors from U-238.
Provides 1/3 of total energy in nuclear power plants.
🔧 Nuclear Reactor Components
1⃣ Core
Holds up to 50,000 fuel rods (each packed with fuel pellets).
2⃣ Fuel
Enriched U-235 (concentrated uranium).
1 uranium atom fission = 10 million times the energy of a coal atom combustion.
3⃣ Control Rods
Absorb neutrons to slow down reaction.
4⃣ Moderator
Slows neutrons for a sustainable chain reaction.
5⃣ Coolant
Removes heat → Produces steam → Generates electricity.
🌱 Biomass
Biological material from living or recently living organisms.
Burned to create steam → generates electricity.
Can be grown on marginal land (not suitable for agriculture)
🦠 Anaerobic Digestion
Microorganisms break down biodegradable material without oxygen.
Produces methane gas → burned for energy.
Benefits:
✅ Reduces reliance on coal & oil.
✅ Lowers land disturbances from coal mining.
✅ Reduces methane emissions from landfills (helps fight global warming).
⛽ Biofuel
Liquid fuel from living organisms.
Biodegradable & can be converted into:
🚗 Biodiesel
🚜 Bioethanol (powers vehicles).Renewable & can be produced anywhere (unlike fossil fuels).
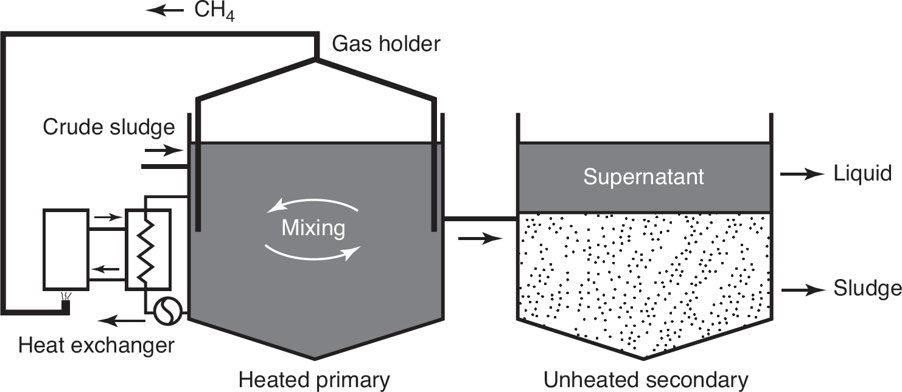
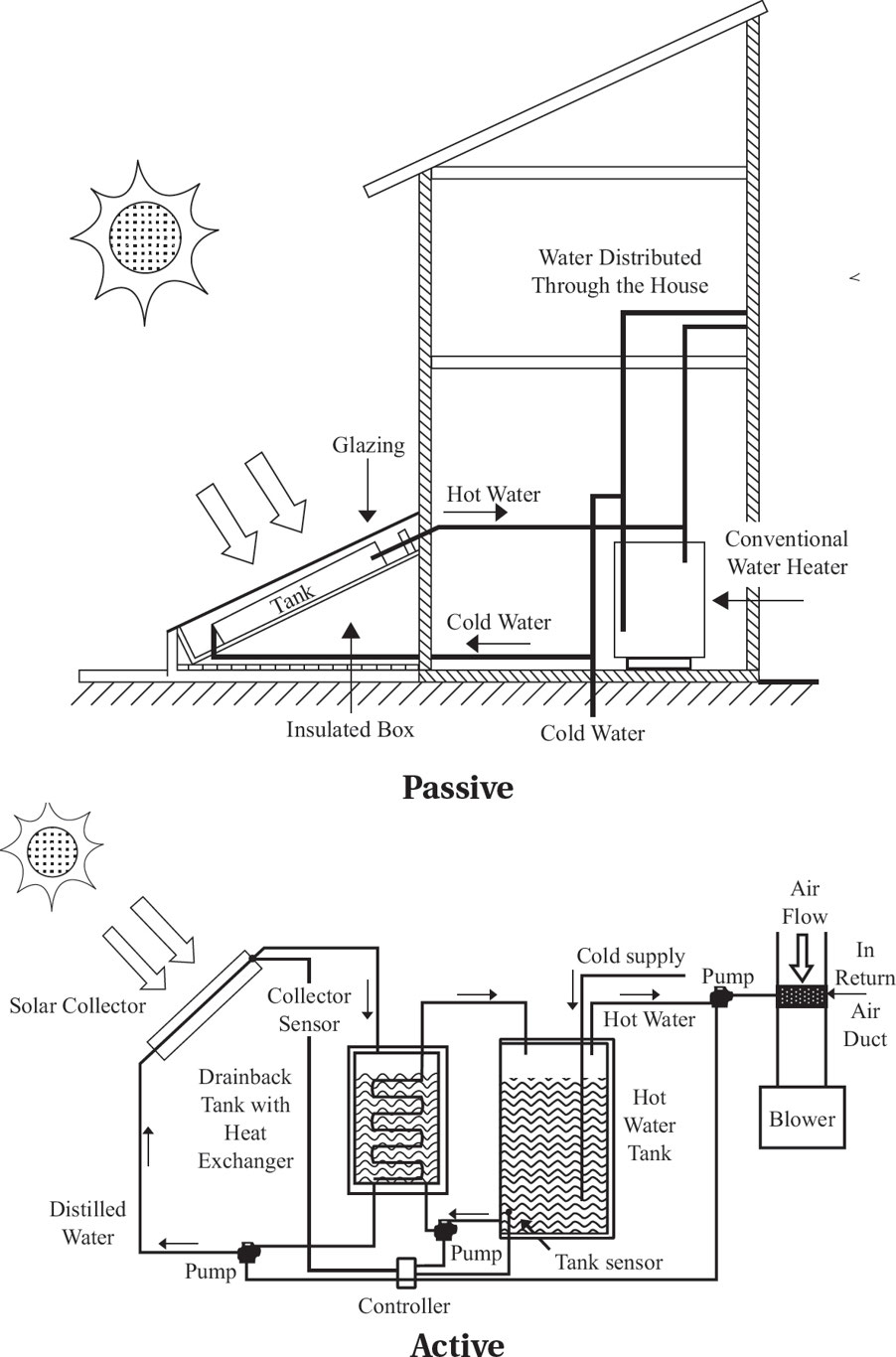
☀ Solar Energy
Collects & harnesses radiant energy from the sun.
Generates heat & electricity using:
🔋 Photovoltaic (PV) cells
🌡 Solar collectors
🔥 Central solar-thermal plants
🏡 Passive Solar Heating
No mechanical devices.
Uses building features to absorb & release heat slowly.
Helps maintain temperature naturally.
⚡ Active Solar Heating
Generates more heat than passive systems.
Requires three components:
1⃣ Solar collector (absorbs energy)
2⃣ Storage system (stores heat)
3⃣ Heat transfer system (moves heat where needed)
🔋 Residential Photovoltaic System
Converts sunlight → electricity using:
📌 Solar panels (absorb sunlight)
🔄 Solar inverter (DC → AC conversion)
🔋 Battery storage & backup system
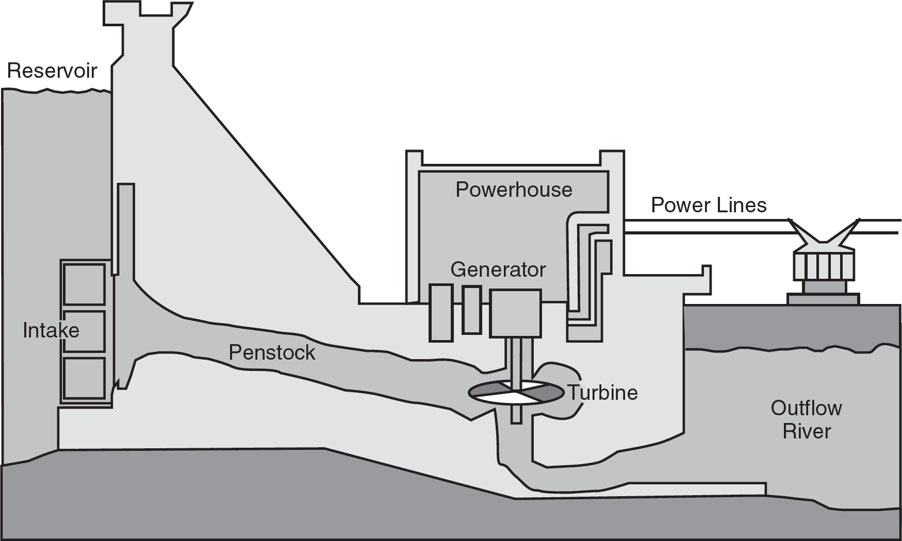
🌊 Hydroelectric Power
Dams trap water, which is released through turbines to generate electricity.
Hydroelectric generation accounts for:
🔋 44% of U.S. renewable electricity
⚡ 6.5% of total electricity in the U.S.
🏗 Dams in the U.S.
~75,000 dams.
Block ~600,000 miles (~1 million km) of once free-flowing rivers.
✅ Advantages of Dams
✔ Control flooding
✔ Long life span
✔ Low maintenance & operating costs → affordable electricity
✔ Moderate to high net-useful energy
✔ No polluting waste
✔ Water storage for cities & farms
❌ Disadvantages of Dams
❗ Expensive to build
❗ Displace people by flooding large areas
❗ Destroy wild rivers & wildlife habitats
❗ Prevent fish migration
❗ Reduce agricultural land
❗ Sedimentation buildup requires dredging
🌊 Causes of Floods
🌧 Heavy rainfall & fast snowmelt
🏗 Dams, levees, or pump failures
🔥 Wildfires (reduce vegetation that absorbs rain)
🏙 Impervious surfaces (asphalt/concrete) increase runoff
🌪 Severe winds over water
🌊 Tsunamis, storm surges, & high tides
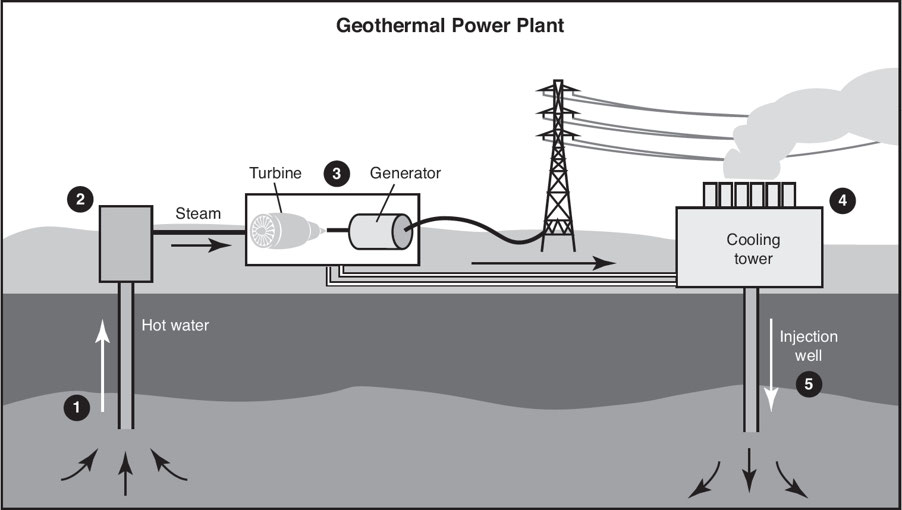
🔥 Geothermal Energy
Heat stored in underground rock and fluids.
Comes from magma, hot dry-rock zones, and warm-rock reservoirs.
Produces steam and hot water pockets underground.
Used to drive turbines → generate electricity.
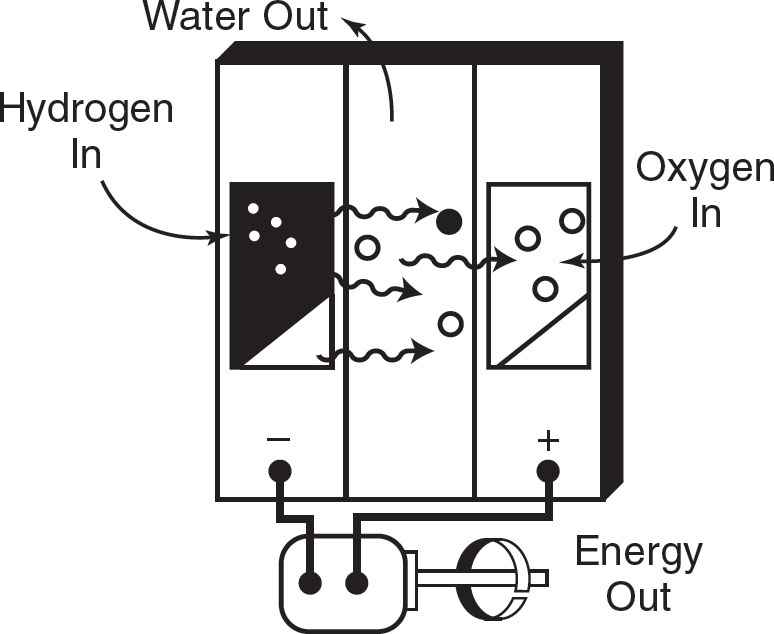
⚡ Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Operates like a battery with two electrodes.
Oxygen passes over one electrode, hydrogen over the other.
🔬 Reaction Process
Hydrogen reacts with a catalyst → forms electrons (-) and hydrogen ions (H⁺).
Electrons flow out → used as electrical energy.
Hydrogen ions move through a membrane.
H⁺ combines with oxygen and electrons → produces water (H₂O).
Unlike batteries, fuel cells never run out!
🌬 Wind Turbines
Convert wind into electricity (opposite of a fan).
Wind turns blades → powers generators to produce electricity.
⚡ Wind Farms
Clusters of wind turbines generating large amounts of power.
🌱 Efficiency & Impact
Most efficient method of producing electricity.
1 megawatt of wind energy offsets ~2,600 tons of CO₂.
🏡 Wind Energy in the U.S.
6% of electricity demand comes from wind energy.
Current wind capacity powers ~20 million homes.
🌊 Offshore Wind Energy
Major opportunity to power coastal cities.
🌍 Global Wind Energy
Largest turbines can power 600 U.S. homes.
China has the largest installed wind energy capacity, followed by the U.S..
25% increase in wind turbine use in the last decade, yet wind still provides only a small percentage of global energy.
🏠 Home Insulation & Sealing
Add insulation & seal air leaks to reduce energy waste.
Improving attic insulation can save 10%+ on annual energy bills.
🌡 Programmable Thermostats
Adjusts heating & cooling automatically for efficiency.
Can save up to 15% on heating & cooling costs.
💡 Efficient LED Lighting
Consumes less energy than incandescent bulbs.
Contains no mercury → safe for household disposal.
🔌 Phantom Loads
Energy consumed by electronics when turned off.
75% of home electronics' energy use comes from phantom loads.
Unplug devices or use smart power strips to reduce waste.
⚙ Energy-Efficient Appliances
Use less electricity, reducing energy consumption & costs.