Drugs for pain, fever, & inflammation
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Antiprostaglandin
can be good or bad and is formed when theres a cellular injury
Antipyretic
works to get rid of fever(100.4); lowers body temp
pyrogen
fever causing
Hyperuricemia
too much uric acid in the blood…gout
NSAIDs
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
steroids are ___-_______….what does that mean?
anti-inflammatory; they tell your immune system to chill out
Prostagladin
chemical mediator and participates in the inflammatory response = PAIN
Cyclooxygenase
basically produces prostoglandens
what is inflammation?
its a normal body response to an invader or injury
what does histamine do during injury?
a vasodilator that improves blood flow aka swelling
what are the cardinal s/s of inflammation
pain, swelling, redness, heat
why do we experience malaise during inflammation process?
your tired because your metabolic demands increase. You fight off something better when you have a fever
whats a fever?
an increase in pyrogens (naturally found in the body)… body temp greater than 100.4
other assoc s/s: dehydration, inflammation, infectious processes, drug use, etc
what drug class do (NSAIDS) ibruprofen, Advil/Motrin fall under?
Propionic acid derivatives
what drug class does ketorolac, Toradol fall under?
acetic acid derivative
what drug class does meloxicam, Mobic fall under?
Oxicam derivative
what drug class does acetaminophen, Tylenol fall under?
Nonnarcotic analgesic antipyretic
what drug class does allopurinol, Zyloprim fall under?
uricosuric
drug therapy for osteoarthritis?
produces inflammation and degeneration of joints; begins around age 30 and peak age 50-60
acetaminophen (pain) and NSAIDS (anti-inflammatory)
ibuprofen
NSAID, rapidly absorbed in the GI tract and is metabolized in the liver but excreted in kidneys(nephrotoxic)
relieves mild to moderate pain, treats inflammation and reduces fever
why cant you take NSAIDs if your are pregnant? What about older pop.?
they cross the placenta and into breastmilk; older adults kidneys don’t function as fast or as well as they used to so you have to be careful
What is the black box meaning/label for NSAIDs?
increase risk of CV events and GI bleeding
anticoagulants, alcohol, and glucocorticoids increase risk of bleeding
NSAIDs block COX-1 and COX-2
Do not take ibuprofen with ___? why?
aspirin because it decreases antiplatlet effects
patient edu NSAIDS
Take with food or liquid to decrease gastric irritation
Avoid alcohol
Report signs of bleeding, severe stomach upset or weight gain & decreased urine output
what is one other drug found in the NSAID class?
naproxen, Aleve
Used to treat mild to moderate pain, arthritis, and dysmenorrhea
Longer acting (two a day); More likely to have GI side effects
be more conservative with older pop.
oxicam derivates: meloxicam, Mobic function?
Treatment of OA and RA(autoimmune);Inflammation, fever and pain
metabolized by liver, excreted in feces/urine…Cox-1 and Cox-2 inhibitor
nursing assessment/implications: meloxicam, Mobic
Caution in renal impairment
AEs: respiratory, hematologic, GI
Black Box: CV events and GI bleeding
Patient with aspirin allergy contraindicated
patient teaching: meloxicam, Mobic
Take with food—why??
Report sore throat, dyspnea, edema, tarry stools
which NDAID affects the kidneys the most?
Acetic Acid Derivatives: Ketorolac (Toradol) **Potent Drug
purpose and assessment of Acetic Acid Derivatives: Ketorolac (Toradol) **Potent Drug
treats moderate to severe pain (only for short term use 5 days or less!)
metabolized by liver (hepatic impairment), cant use if patient has advanced renal disease (renal impairment)
avoid giving to older adults
patient teaching ..Acetic Acid Derivatives: Ketorolac (Toradol) **Potent Drug
Take with food to decrease GI irritation
Report AEs such as chest pain, weakness, disorientation, jaundice-liver, edema-kidneys
Report sore throat, fever, rash, weight gain, tarry stools(GI bleeding)
Non-Narcotic Analgesic Antipyretic: Acetaminophen (Tylenol)- strong antipyretic
Reduce fever and decrease minor pain
Aspirin & NSAID substitute (safe drug)
Found in many combination products *
where is acetaminophen metabolized? interactions?
liver; interactions include warfin and alcohol
nursing assessment/implications for acetminophen
Review History and LFTs– assess for allergy
AEs: HA, rash, renal dysfunction, hepatotoxicity
4 gram max per 24 hours—less for alcohol use or someone with hepatic injury—leads to toxicity!
how do we treat acteminophen overdose
acetylcysteine (Antidote) or gastric lavage with oral activated charcoal
patient teaching for acetaminophen
Children: Can alternate with ibuprofen for fever control, weight-based dosing
Older adults use first for msk pain
Can be used in pregnancy
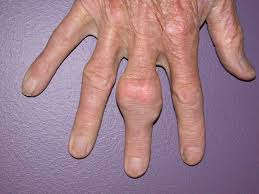
gout
Arthritic condition characterized by an overproduction of uric acid or inability to excrete uric acid, resulting in hyperuricemia and urate crystal deposits in kidneys and joints.
s/s: enlarged joints (typically 1), pain and swelling 10 days, tophi(little knobs)
what are the short term and long term antigout medication?
Colchicine (Short term) & Allopurinol (Long term)
patient teach emphasis need to take long term drugs; diet alterations
what should I consider when altering a gout patients diet?
low purine diet to reduce uric acid; avoid red meat, seafood, and alcohol
uricosiuric agent? purpose?
allopurinol, management of gout—long term therapy
pharmacokinetics/MOA of allopurinol
absorbed in GI tract, slow excretion through kidneys
inhibits conversion of purines to uric acid
nursing assessment/implications of allopurinol … adverse effects?
Dosage adjusted by CrCl (creatine clearnace)
AEs: hypersensitivity reaction, hematologic and GI, renal and hepatic toxic
patient teaching: allopurinol
Take after meals- prevents GI upset
Increase fluid intake
Report any rashes-allergy--hypersensitivity
Report decreased urine output---why??? can be renal toxic