Test 4 - Fiber, Hair Analysis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Crimes Involving Fiber Evidence
Homicide
Battery
Sexual battery
Hit and run
Burglary
Natural Fibers
Derived from animal (hair/fur) or plant
Classified according to their origin
Vegetable or cellulose-based
Cotton, jute, hemp
Animal or protein-based
Wool, mohair, silk
Mineral class
Asbestos
Cotton
Grow on thorny plants and have sticky seeds
Ribbon-like with twists
Hollow

Silk
Made from silkworm cocoons
Fibers are:
Smooth
Naturally transparent
Wool
Appears round
Cuticle pattern
Scale-like markings
Goat Hair Fibers
Mohair
Cashmere
Man-made Fibers
fibers derived from natural or man-made polymers
Polymer
A combination of many subunits
A substance composed of a large number of atoms (macromolecules) arranged in repeating units of monomers
Monomer - basic unit of a polymer
Regenerated Fibers
Man-made but from natural sources (cotton or wood pulp to get cellulose)
Rayon
First regenerated fiber
Fiber Analysis (Hard)
Single fibers
Microscopic Comparative Studies
Color comparison
Diameter comparisons
Examination for lengthwise striations
Examination for pitting
Look at cross-sectional shape
Striations
banding/grooves going lengthwise on fibers
Color Analysis of Fibers
Compare dyes of two different fibers
Use Thin-layer Chromatography
Thin-layer Chromatography
chemical analysis of dyes in a fiber
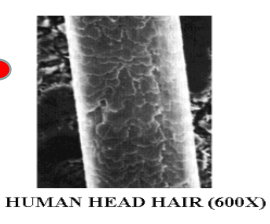
Layers of Shaft (moving inward)
Cuticle
Cortex
Medulla
Cuticle Layer
Tough and resistant outer layer
Formed by overlapping scales
Point toward the tip of the hair
Specialized keratinized cells (hardened)
Flattened in progressing from the follicle
Used for species identification
Coronal - mouse
Spinous - cat
Imbricate - human
very irregular pattern
Casting
Use clear nail polish to create an impression of the cuticle pattern on a microscope slide
Observe under a microscope
Cortex Region
Beneath the cuticle
Composed of spindle-shaped cells aligned parallel to the length of the hair
Embedded with pigment granules
Look at color, shape, and distribution of granules
Medulla Region
Center region of hair
Presence and pattern varies from person to person and from hair to hair on an individual
Fragmented - Short, discontinuous section
Intermittent - long, discontinuous sections
Continuous - one long section

Follicular Tissue
Skin cells from the hair follicle that are on the end of the hair when forcibly pulled
Anagen
actively growing
root is flame-shaped
Catagen
slowed growth
root elongated and shrunken
Telogen
hair growth ends
root is club-shaped
hair falls out of cuticle
Hair: Comparative Studies
Dyed hair (paint roller) vs. Natural
Bleached hair (yellowish tint)
Time of dyeing (hair grows 1cm/month)
Nits or fungal infections

Hair Growth Rate
1 cm/month
Types of Hair
Scalp = uniform diameter and pigment distribution
Pubic = short, curly and diameter variations
Facial = coarse, triangular, blunt tips
Baby Hair
Age cannot be determined by hair, unless it is the very distinct baby hair
Drug Use
drugs and poisons will remain in the hair
you can tell when a person used a drug, such as marijuana and cocaine, based on where it is on the hair