MRAD 2218: Module 3 (Upper Ext Fractures)
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
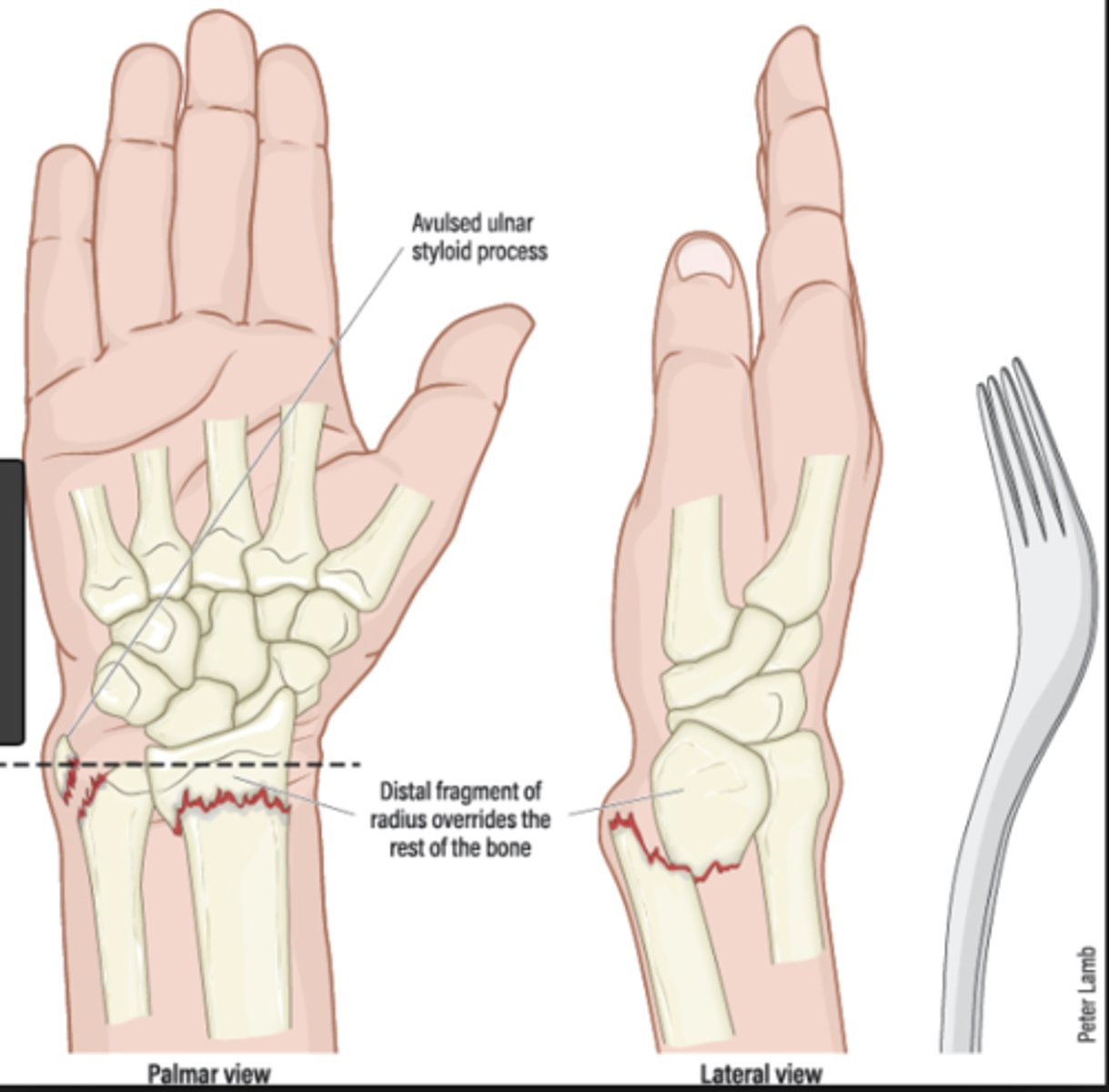
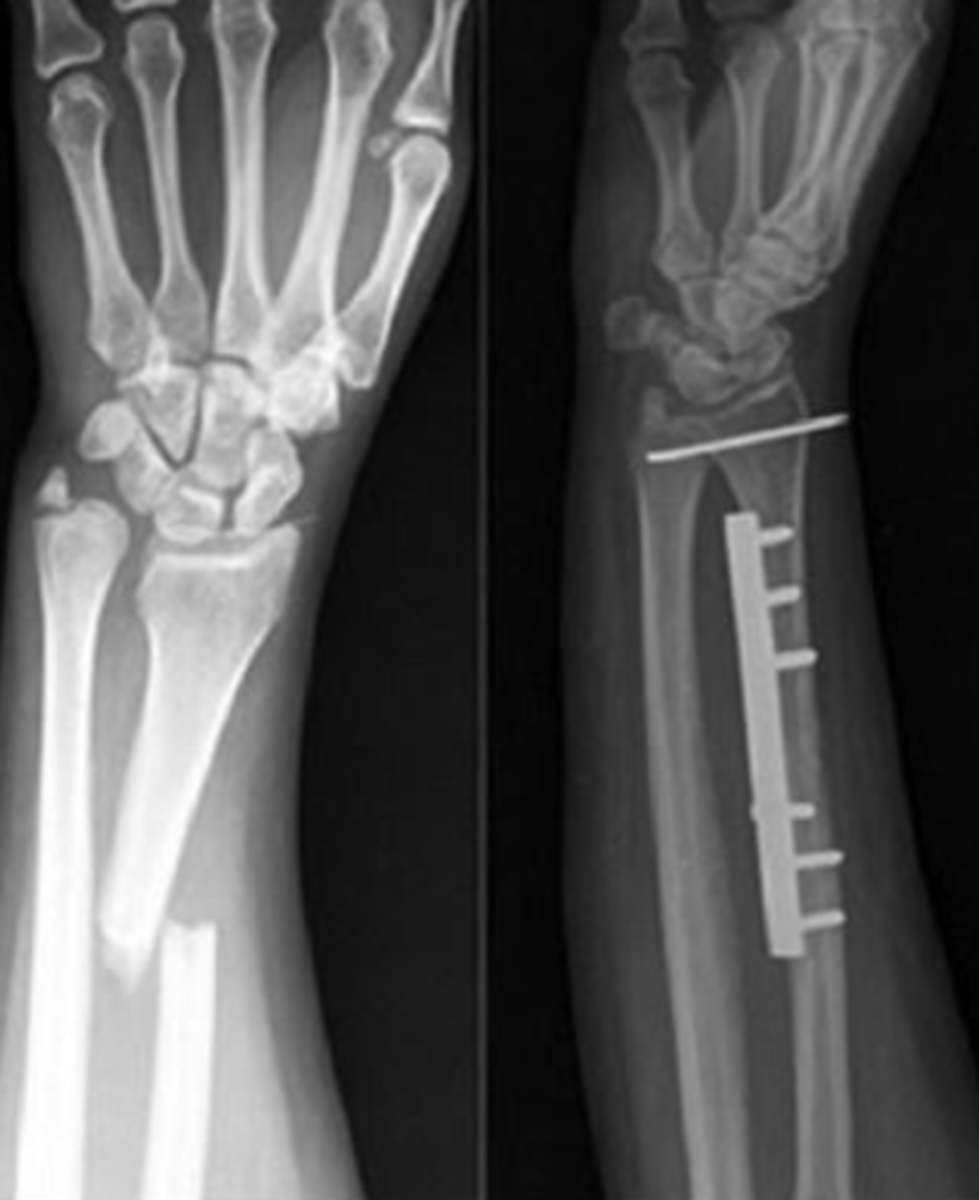
Colle's fracture
FOOSH
"Dinner fork" deformity
Features of the injury:
(1) Transverse fracture of the radius
(2) 1 inch proximal to the radio-carpal joint
(3) Dorsal displacement and angulation
Smith's fracture
A.k.a. reverse Colles' fracture
Falling with wrists flexed
Volar angulation of distal radius fragment
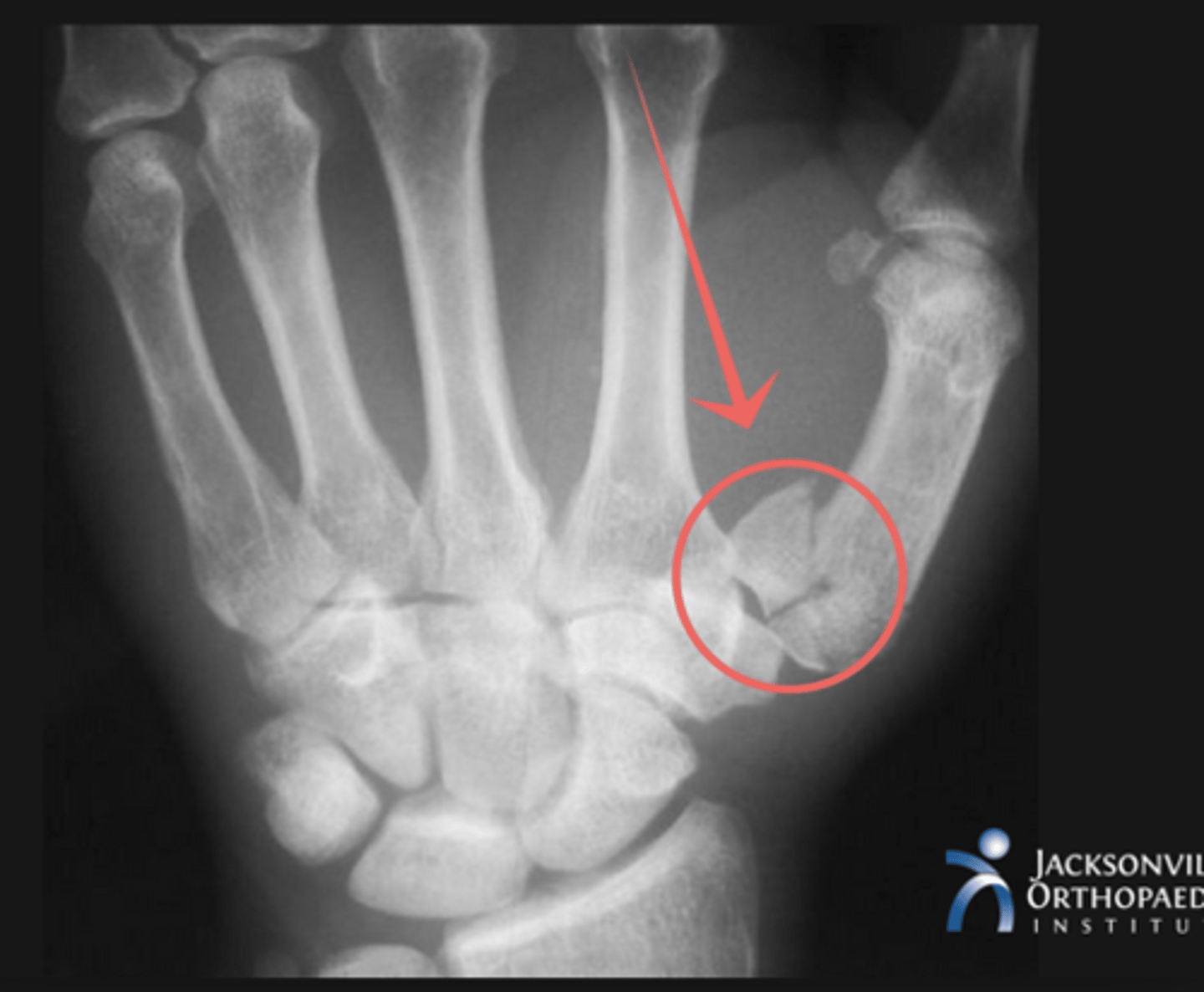
Bennett's fracture
First carpometacarpal joint
MOI: Impact on flexed metacarpal; Fist fights!!
X-ray: triangular fragment at ulnar base of metacarpal
Monteggia's fracture
Dislocation: proximal radio-ulnar Fracture: ulna
FOOSH with forced pronation
Needs prompt diagnosis to avoid disability
Monteggia's fracture: dislocation of radioulnar joint and ulna fracture
What fracture may occur with FOOSH and forced pronation?
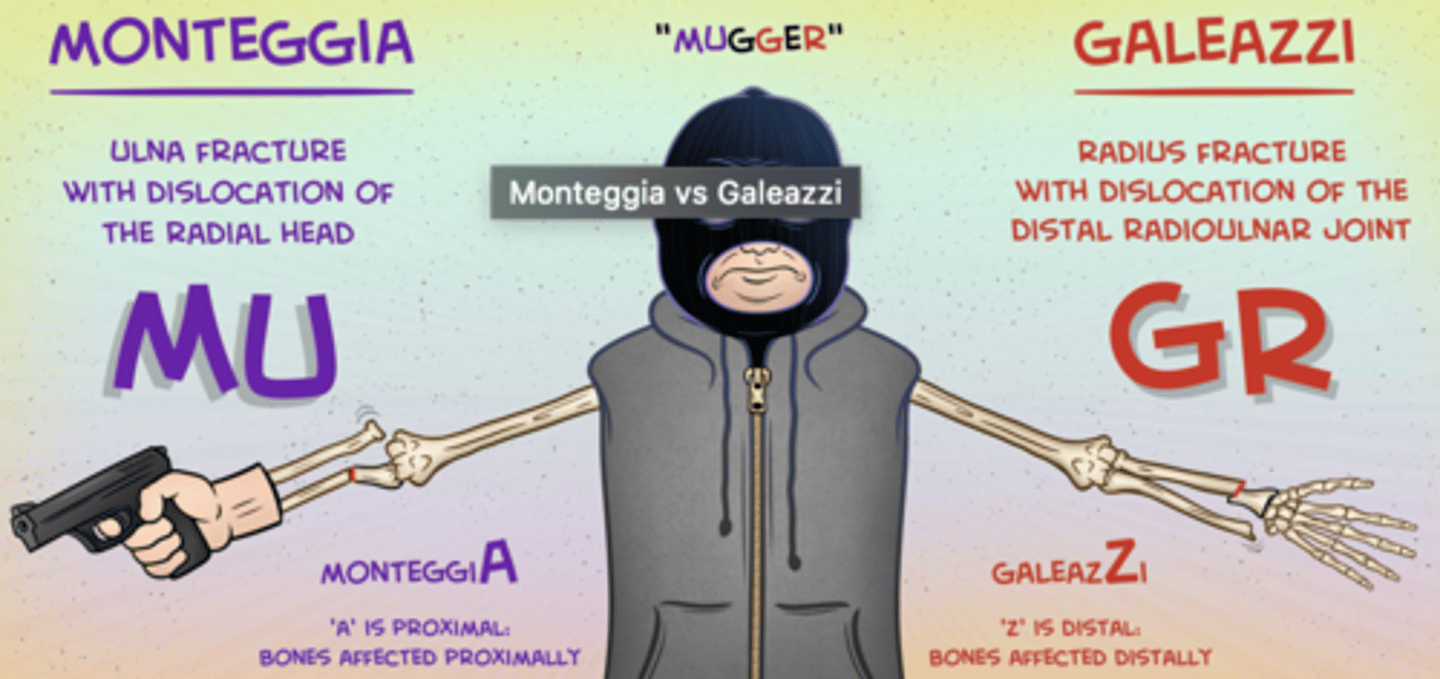
Galeazzi fracture
Dislocation: distal radio-ulnar
Fracture: radius
Fall on hand with rotational force
Ex: bruising, swelling and tenderness lower end of forearm
XR: displaced radius # with prominent ulnar head
(due to dislocation of the inferior radio-ulnar joint)
Barton's fracture
Distal radius fracture (Colles'/Smith's) with associated radiocarpal dislocation
Fall onto extended and pronated wrist
Scaphoid fractures
Common
Risk of vascular necrosis
FOOSH
Ex: swelling and tenderness in the anatomical snuff box, pain on wrist movements and thumb compression.
XR: Ulnar deviation AP needed for visualization of it
Immobilization of these fractures difficult
Treat anyway
-Fracture may take 10 days to show due to localized decalcification - return to clinic after 10 days
Management if clinical hx and ex of scaphoid fracture, but negative XR?
scaphoid fracture
what would you need a PA view with ulnar deviation for?
Radial head fracture
Common in young adults.
FOOSH
Ex: tender head of the radius, impaired elbow movements, sharp pain at the lateral side of the elbow at the extremes of rotation (pronation and supination).
Scaphoid fracture
Man with a painful swelling over the volar aspect of his hand after receiving a hard blow to his palm.
EX: pain on moving the wrist and on compression of the thumb.
- hard blow to palm or FOOSH
(1) swelling
(2) tender anatomical snuff box
(3) pain on wrist movements and compression of thumb
Fracture type?
radial head fracture
Man with swelling over his left elbow after a fall on an outstretched hand.
Ex: tenderness over proximal part of his forearm, and has severely restricted supination and pronation movements.
(radius rotates around ulna bone to allow supination/rotation)
Common in young adults
FOOSH
Ex: local tenderness radial head, impaired elbow movements, pain at during pronation and supination
Fracture type?
Galeazzi fracture
Lady presents with a painful swelling over the lower end of the forearm following a fall.
Imaging: distal radial fracture with disruption of the distal radio-ulnar joint.
FOOSH + rotational force
Ex: bruising, swelling and tenderness over the lower end of the forearm.
XR: displaced # radius and a prominent ulnar head due to dislocation of the inferior radio-ulnar joint.
Fracture type?
Buckle fracture
Child who fell on outstretched hand has XR showing incomplete fracture of the radial shaft with bulging of the cortex.
Incomplete #s of long bone shaft
Characterised by bulging cortex
Typically aged 5-10 years.
Mx: self-limiting
- splinting and immobilisation rather than a cast
Type of fracture?
Supracondylar fracture
A 14-year-old landed awkwardly on his arm . The fracture was reduced but the patient is still experiencing extreme pain, particularly on passive stretching. His arm appears swollen and he is complaining of tingling in his hand and forearm.
Compartment syndrome complications possible which include:
- disproportionate pain, esp. on passive stretching
- swelling and paraesthesia
- numbness and paralysis (late)
Tx: prompt fasciotomy
Which fracture is most commonly associated with the condition he is experiencing?
Galeazzi fracture
Woman presents with pain in her wrist after being struck on the back of her right wrist by a ball.
Right wrist: swollen, erythematous and disaffirmed. Skin intact. Extremely tender upon palpation of the distal radius. Difficulty pronating and supinating wrist. Unable to make the 'OK' sign. Sensation intact. Pulses present.
Ex: unremarkable
XR: fractured distal radius and associated dislocation of the distal radio-ulnar joint.
Fracture type?
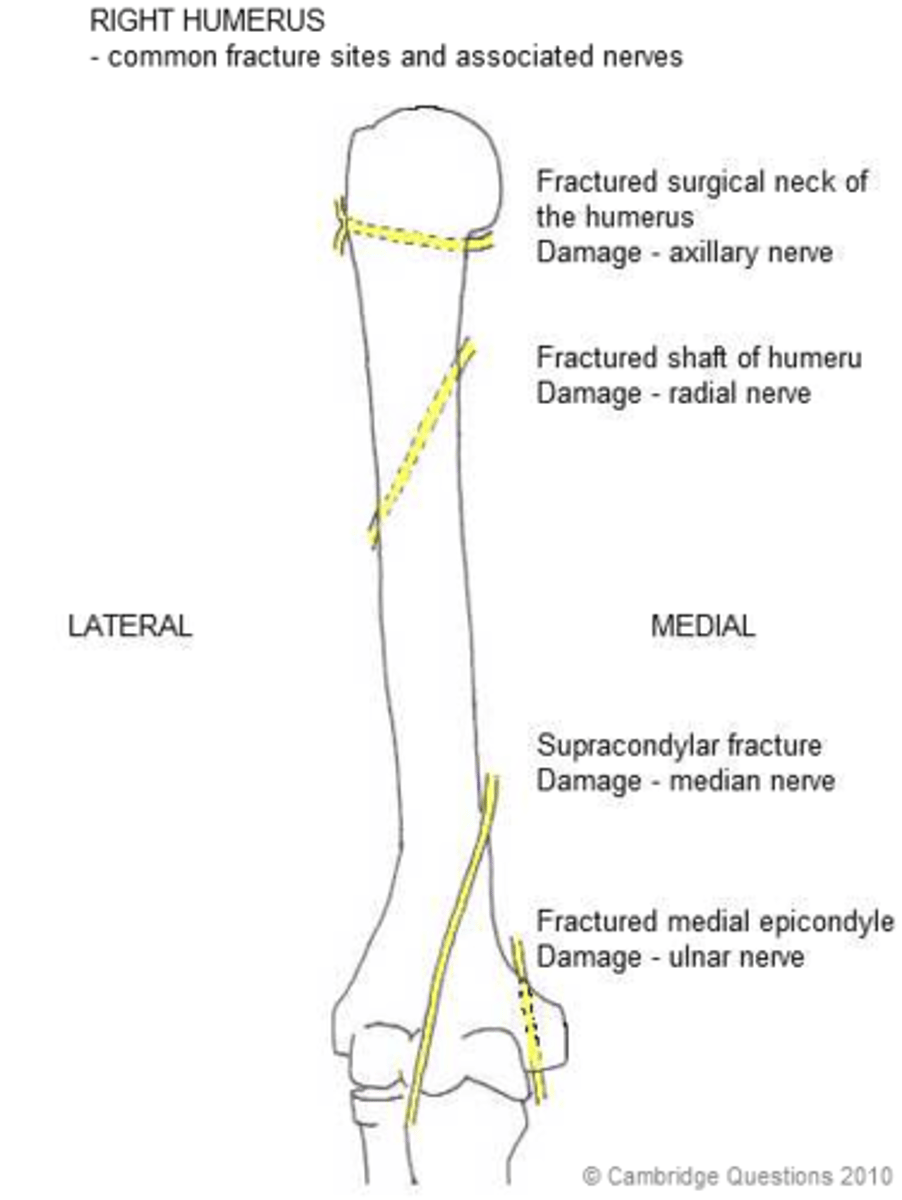
Humerus shaft
Which part of humerus fractured in patient with wrist drop?
Anterior shoulder dislocation
Man presents with pain after falling onto his backward stretching right hand.
Ex: right shoulder contour is flattened and a small bulge is felt below the right clavicle. There is a small patch of anaesthesia over the distal attachment of the deltoid muscle.
Axillary nerve palsy:
- weak deltoid muscle
- sensory loss over badge area
What injury would explain all the examination findings?
Clavicle fracture
Direct blow to it
Most common in middle third
Mx:
Non-displaced = broad arm sling
Displaced = ORIF
Complications:
- Brachial plexus
- Subclavian vessels
- Pneumothorax
baseball/mallet, boxer’s, bennett’s
list the 3 types of phalangeal fractures
tuft, shaft
what two locations of the phalanges do fractures usually occur at
baseball/mallet finger
a dorsal intra-articular avulsion fracture
base of the distal phalanx
where on the phalanx does a baseball/mallet fracture occur
baseball/mallet finger
forcible flexion of an extended finger
baseball finger
splint to immobilize
baseball finger
bone deformity if not treated, decreased ROM
boxer’s fractures
impacted bone at the neck of MC5
boxers fracture
impact with a closed fist
boxers fracture
surgery w k-wires, immobilization
boxers fracture
bone deformity = rotational deformity of the phalanx
bennetts fractures
oblique intra-articular fracture with dorsal dislocation
base of MC1
where do bennetts fractures occur on the bone
bennetts fractures
direct impact along the LA and hyperextension of the thumb, or axial force applied directly to the MC (ie fist fight, playing volleyball)
bennetts fractures
reduction + fixation with pins or k-wires
bennetts fractures
decreased ROM due to joint pain, loss of thumb function
zigzag
what pattern do the carpals form as they articulate with the MCs
true
T or F: the carpals are uniformly spaced
2mm
how wide are intercarpal joints
the arch; this is where most carpal fractures and dislocations occur
what is the vulnerable zone of the wrist
these are the most severe
the arch of the wrist is a vulnerable zone - injuries that occur at the ulnar aspect
these are the highest in number
the arch of the wrist is a vulnerable zone - injuries that occur at the radial aspect
dorsally (posteriorly)
which direction do the carpals tend to dislocate
true
T or F: when there is trauma, there is a loss of carpometacarpal spaces
properly positioned lateral wrist
MC3 + capitate + lunate + radius in a straight line (teacup)
lunate dislocation
on a lateral wrist view, what does a spilled teacup indicate
pain, loss of grip
what do ligamentous injuries of the wrist cause
lunate dislocation, scaphoid fracture, triquetral injury
list the 3 carpal injuries that occur
lunate dislocation
it loses the articulation with both the capitate and radius = spilled teacup
volar (anterior/palmar)
in lunate dislocations, which direction is the lunate displaced
moves proximally to fill the vacated space
in lunate dislocations, the lunate moves anteriorly. what happens to the capitate
lunate dislocation
forceful dorsiflexion of the wrist (FOOSH)
signs and symptoms of lunate dislocation
limited movement, swelling, tingling in fingers, pain
lunate dislocation
reduction, immobilization, surgery
lunate dislocation
arthritis, wrist instability
scaphoid fractures
occurs at the waist of it, snuffbox becomes swollen and tender
true
T or F: the scaphoid is the most common carpal bone to fracture
scaphoid fractures
FOOSH, direct blow
false negatives are common bc the fracture line doesn’t always show up on the initial image; image again in 7-10 days to look for evidence of healing
what imaging consideration must we keep in mind when imaging for scaphoid fractures
scaphoid fracture
immobilization with a cast, surgery
scaphoid fracture
can take up to 2 years to heal, identify early to avoid avascular necrosis
normal anatomy of the distal surface of the radius
angled 17 degrees towards the palm (anterior)
lateral
on which view do we see that the normal anatomy of the distal radius is angled 17 degrees towards the palm
radius
which extends further distally: radius or ulna
first row of carpals
what structure does the radial styloid line up with (normal anatomy)
colle’s, smith’s
list the 2 fracture types of the distal radius and ulna
colle’s fracture
looks like a fork in the lateral view, it’s within 3-5cm from the wrist joint, distal fragment is displaced dorsally, can be transverse or comminuted
etiology of colle’s fracture
dorsal space of the distal radius compresses the palmar surface, caused by FOOSH with the wrist hyperextended
colle’s fracture
reduction, immobilization, surgery
colles fracture
complex regional pain syndrome, bone deformity, loss of ROM, weak grip, nerve compression
smith’s fracture
reverse of colle’s fracture, garden spade appearance, distal fragment is displaced anteriorly
smith’s fracture
force applied to the posterior aspect of the wrist that causes anterior displacement of the distal fragment (ie falling backward with the wrist in flexion)
smith’s fracture
reduction, immobilization, surgery
smith’s fracture
weak grip, ongoing pain, bone deformity = reduced ROM
compression force along the LA of the bones (via FOOSH)
what is the most common MOI for radius and ulna shaft fractures
Galaezzi, Monteggia, radial head fractures, olecranon fractures, elbow dislocation, elbow joint fracture
list the 6 radius/ulna shaft fractures
Galeazzi fractures
type of fracture dislocation, middle third of the radius fractures, the radioulnar joint is dislocated
signs and symptoms of Galeazzi fractures
pain, swelling, forearm deformity
Galeazzi fractures
blunt force trauma; FOOSH with the forearm in pronation
Galeazzi fractures
surgical fixation with reduction of the fracture and stabilization of the radioulnar joint
Galeazzi
increased risk of compartment syndrome when the fractures are severe, non or mal union
Monteggia fractures
fracture of the ulnar shaft with anterior dislocation of the radial head
Monteggia fracture symptoms
pain, swelling at the elbow joint, decreased ROM
Monteggia
FOOSH with the forearm in pronation
Monteggia
closed reduction, immobilization with a cast, surgery maybe
Monteggia fracture
deformity, bone angulation, non union of the ulnar shaft, radioulnar synostosis, compartment syndrome
radial head fracture
what is the most common type of elbow fracture in adults
radial neck fractures
what is the most common type of elbow fracture in children
signs and symptoms of radial head fractures
pain, swelling
radial head fracture
FOOSH
radiographic appearance of radial head fracture
oblique view needed to show the head clear, or a 45 degree cephalad angle
radial head fracture
splints or casts, surgery
radial head fracture
stiffness, loss of mobility
olecranon fractures
they cause the triceps muscle to separate a bone fragment from the ulna
olecranon fracture
fall onto a moderately flexed elbow
olecranon fracture
surgery
olecranon fracture
ongoing pain, loss of full elbow extension, non-union, scar tissue can fill the gap = decreased mobility
elbow dislocations
Description: usually posterior, the capsule and ligaments surrounding the it can rupture, can cause associated fractures
elbow dislocations
Associated fractures that are caused due to ________ include: coronoid process can fracture as it moves proximal and posterior to the humeral condyles
elbow dislocations
fall onto an extended elbow