Lecture 3: Host-Pathogen Interactions
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
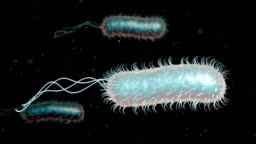
Identify the long and short perturbances from the bacilli
Long = Fimbriae/Flagella
Short = Pili
What is a “Facultative” intracellular pathogen
A bacteria that can exist intracellular/extracellular
T/F: Extracellular pathogens normally don’t invade cells but can occasionally
False, they don’t invade cells, they simply proliferate in the extracellular environment
T/F: Obligate intracellular pathogens cannot survive outside of their host cell, however, they can be grown on artificial media
False, they cannot be grown on artificial media, everything else is true
What is the difference between bacteremia and septicemia?
Bacteremia
Is the presence of bacteria in the blood
Septicemia
The presence and multiplication of bacteria in the blood
What is the difference between sepsis and septic shock?
Sepsis
A life threatening organ dysfunction caused by dysregulated host response to infection
SIRS (System inflammatory response syndrome)
Septic Shock
A severe complication of sepsis that can include low BP and multi-organ-failure
What is the difference between a primary pathogen and an obligate pathogen?
A primary pathogen can cause disease in healthy hosts and is more virulent than opportunistic pathogens
Obligate pathogens can cause disease, but the main difference is that they cannot survive outside the host for long
What are Koch’s Postulates?
The microorganism must be found in abundance in all organisms suffering from the disease
The microorganism must be isolated from a diseased organism and grown in a culture
The cultured microorganism should cause disease when introduced into a healthy organism
The microorganism must be able to be re-isolated from the newly infected organism
Are Koch’s Postulates 100% accurate every time? Why or why not
Nope, there will always be exceptions
Sometimes you cannot prove a causal relationship between a microbe and disease
What are the 3 factors that affect bacterial pathogenicity?
Characteristics of the bacterial pathogen
Genotype, virulence, tropism
Characteristics of the potential host
Species, breed, age, sex, etc.
Predisposing factors
Stress, nutrition, etc.
What are the 3 cells responsible for CMI?
T-cells
Macrophages
NK cells
What are PAMPs?
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns
They are specific things on bacteria that uniquely identify it as a threat
What are PRRs? Which cells are they found on?
Pathogen Recognition Receptors
They detect PAMPS
They are usually Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs)
PRRs are found on macrophages and dendritic cells
How do macrophages destroy bacteria?
They attach to them, engulf them, phagocytize via enzymes and then release the digested products out of the cell
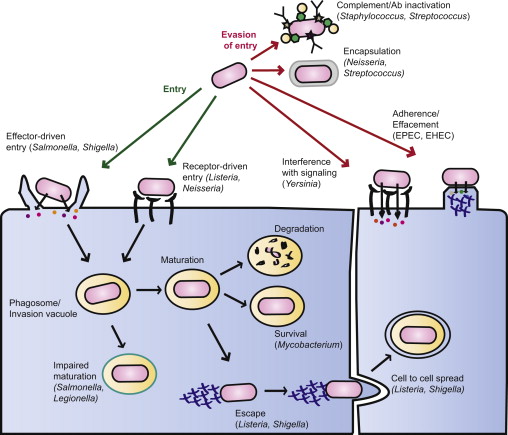
What is the main way that bacterial pathogens can evade the host immune system?
By disrupting TLR signaling
How do bacteria avoid intracellular destruction?
Prevent the lysozyme/phagosome from fusing
Escape into the cytoplasm of the cell
Gain resistance to lysozyme enzymes
Genes that control the expression of virulence in bacteria are called ______ ____
Virulence Genes
Virulence genes are tightly regulated and are ______ ____ in regards to environmental signals, ensuring their expression occurs at the appropriate stage of infection
Switched On/Off
Ex: Vibrio cholerae expresses its toxin genes only when inside the host intestine
What us Quorum sensing?
A process of cell-to-cell communication that allows bacteria to share information about cells so that they can adjust their gene expression accordingly
What are the 4 main ways that bacteria can cause disease?
By destroying tissues
Producing toxins
Stimulating overwhelming immune response
Combination of the 3 above
Bacteria have virulence factors both intra/extracellularly, what are some of the main ones from both?
Bacterial Intracellular Virulence Factors
Fimbriae/Pili, capsule, adhesions, LPS (Gram -)
Bacterial Extracellular Virulence Factors
Toxins, enzymes, iron binding proteins
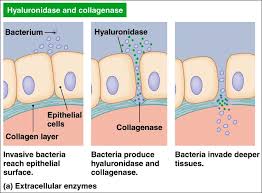
How do bacteria enter epithelial surfaces?
Invading bacteria reach the epithelial surface
The bacteria produce hyaluronidase and collagenase
Hyaluronidase
Breaks down/separates epithelial cells creating a gap (separates tight junctions)
Collagenase
Breaks down collagen
The bacterial then can invade deeper tissues
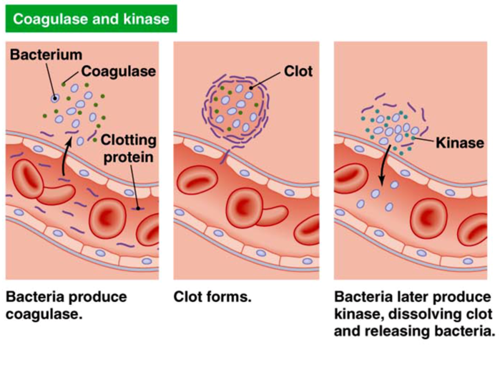
Once inside the organism, how do bacteria enter the vasculature?
Bacteria produce coagulase
Clot forms around the bacteria
Bacteria release kinase to break down the clot and then enter the vasculature
Bacterial toxins are some of the ____ powerful poisons in nature
Most
What are the 2 types of bacterial toxins? Describe each
Exotoxins (protein toxins)
Released from the cell
Cell-associated toxins (Part of the bacteria)
LPS
Lipoteichoic acids
Peptidoglycan
What is the difference between endotoxins and exotoxins?
Endotoxins are released from within the bacteria when it dies, Exotoxins are released from the bacteria while it is alive
Why is Sepsis such a huge issue?
It can cause a Sepsis Cascade (aka cytokine storm) which can result in the widespread inflammation/damage across the body (DIC, respiratory failure, etc.)
T/F: Gram - bacteria can cause a nasty sepsis/septic shock
True
What are bacterial Super-antigens?
Potent protein toxins, often produced by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes, that cause massive, non-specific activation of T cells
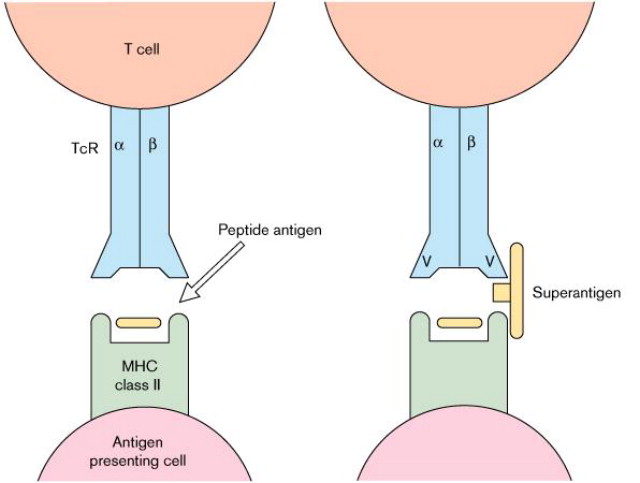
What is horizontal gene transfer? What type of genes are transferred?
It is the transfer of genetic material between two bacterial cells (not via replication)
Plasmids and jumping genes
What are the 3 methods of horizontal gene transfer?
Conjugation
Two bacteria connect (F+/F-)
The F+ shares some of it’s plasmid DNA with the F- cell
Transduction
A bacteriophage (a bacterial virus) accidentally transfers bacterial DNA from one bacterium (the donor) to another (the recipient)
Transformation
Bacteria taking up free/naked plasmid DNA from the environment (from other dead bacteria)
What are jumping genes? What carries them?
They are self-mobilizing genes that can perform transposition in the genome
Carried by Transposons and Integrons
T/F: Dual intracellular/extracellular pathogens use multiple virulence mechanisms to survive and grow inside/outside of the host cell
True
T/F: Attachment to and the colonization of host surface are key steps in bacterial infection
True
T/F: Host immune cells PRRs recognize bacterial PAMPs
True
T/F: Gram + cell LPS can cause endotoxemia with a massive cytokine release resulting in sepsis and septic shock
False, this describes Gram -
T/F: Bacteria are not able to share genes with different bacterial species
False
T/F: Plasmids, integrons, and transposons are mobile genetic elements
True
T/F: Horizontal gene transfer allows bacteria to evolve and adapt rapidly
True!