HRM - Lecture 6: Functions of the urinary system
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
- urea
- uric acid
- hormone metabolites
- toxins
- drugs
- ions
Name a 5 things excreted by the kidneys
- Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
- creatinine
- potassium
- phosphate
Name a few parameters that increase in renal failure
- renin (technically an enzyme, but important for angiotensinogen -> angiotensin I)
- 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol (Vit D3)
- erythropoeitin
Name 3 hormones produced by the kidneys
- control amount of water lost (lowers volume+pressure)
- erythropoietin (increase RBC)
- renin secretion (increas BP)
How do the kidneys control blood volume and pressure?
- Na+, K+, Cl- by controlling amount released
- Ca2+ via calcitriol synthesis
How do the kidneys regulate plasma ion concentration?
By controlling the amount of H+ and HCO3- excreted
How do the kidneys regulate pH?
- 25% of CO, highest perfusion/weight of any organ
- From renal artery - from abdominal aorta
- High rate of blood supply for high glomerular filtration
-
Describe the renal blood supply
Function as osmotic exchanger. It helps maintain a hypertonic interstitial fluid in the juxtamedullary nephrons
How do the vasa recta function in urine production?
glomerulus: 60mmHG - a lot of force, favours filtration (pushing fluid out)
peritubular: 20mmHg - less force, favours reabsorption
Compare the pressure of the glomerulus and the peritubular capillaries. What is the main effect of these pressures?
Via a single cilium, functioning as chemo- and mechano-receptor, protruding from the apical surface into the lumen
How do cells of the nephron sense fluid composition and flow rate?
85% cortical
15 % juxtamedullary
What proportion of nephrons is cortical and juxtamedullary respectively?
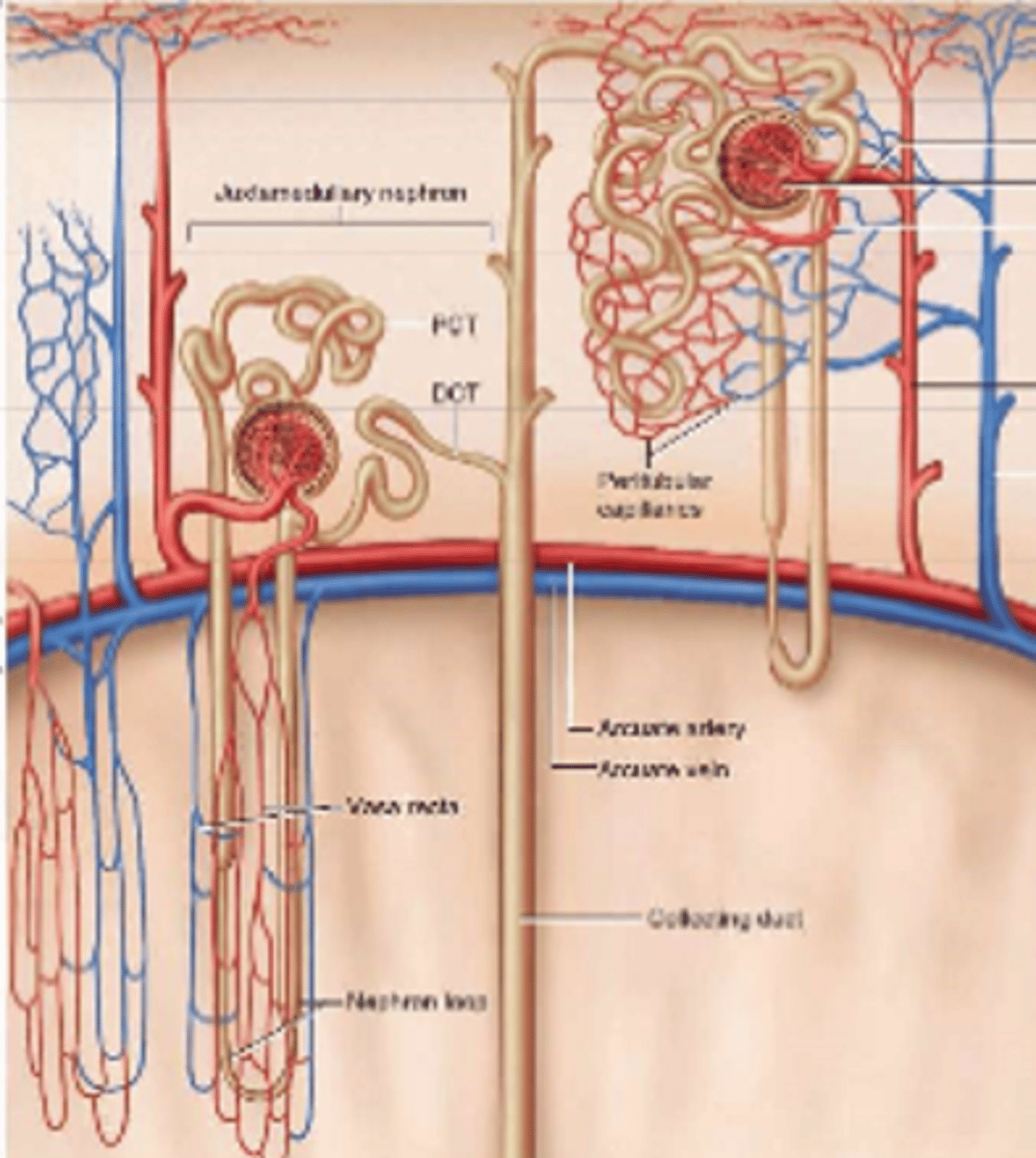
left: juxtamedullary: lower (closer to medulla), longer loop of henle, vasa recta present
right: cortical: higher (in cortex), shorter loop of henle, no vasa recta, only peritubular capillary network
What type of nephron is the left and the right? Give reasons for your answer.
Their contraction is coupled to basement membrane contraction which lowers surface area for filtration and decreases GFR
How do intraglomerular mesangial cells control GFR (glomerular filtration rate)?
- renin secreting cells
- granular cells
What are two other names for epitheloid cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus?
- in afferent arteriole close to glomerulus
- modified vascular smooth muscle resembling epithelium
Describe the structure and location of the granular cells
extraglomerular mesangial cells located between afferent and efferent arteriole
What are the Lacis cells?
- Salt detection in DCT
- cause constriction of afferent arteriole in response to high sodium chloride and decrease GFR
- signal renin release from juxtaglomerular cells when sodium is low
What is the function of the macula dense?
- fenestrated endothelium
- basement membrane
- filtration slits created by pedicels of podocytes
All have a negative charge and are selective in filtration
Briefly describe the filtration barrier of the glomerulus
8nm
What is the cutoff size for particles to pass through endothelial fenestrations?
- electrolytes
- water
- vitamins
- hormone metabolites
- amino acids
- fatty acids
- glucose
- urea
- uric acid
- creatinine
Name 5 things that can pass through fenestrations
- proteins
- large anions
- blood cells
- protein bound electrolytes or hormones
Name 4f things present in plasma that can't pass through fenestrations
This allows passage of neutral and positively charged particles and rejects negatively charged particles such as proteins
How does negative charge affect filtration?
The filtration slit diaphram is thin and made up of a number of proteins
Describe the filtration slit barrier
- Nephrin
- NEPH-1
- NEPH-2
- podocin
What are the proteins of the filtration membrane extracellularly?
- CD2-AP
- alpha-actinin 4
What are the proteins of the filtration membrane intracellularly?
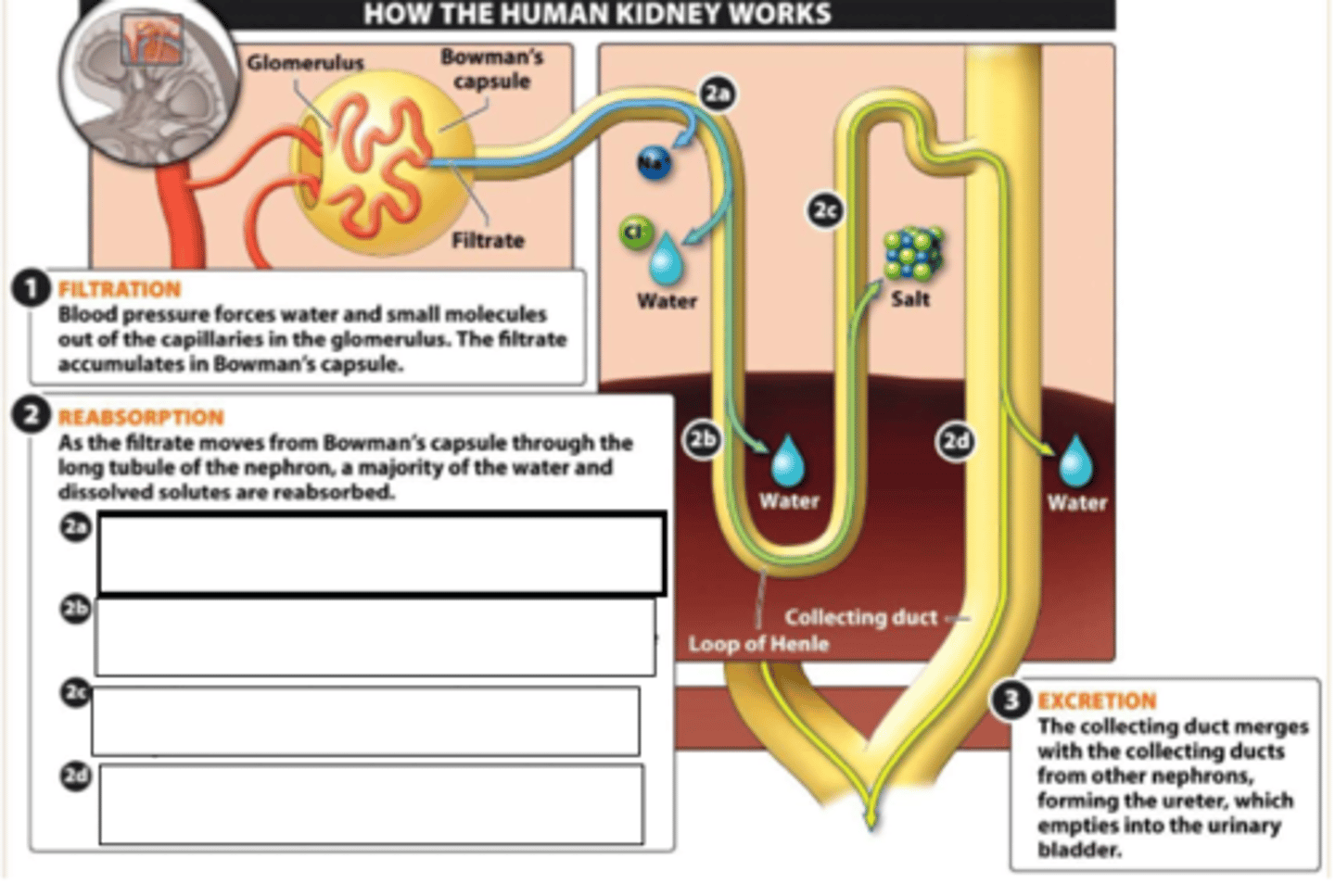
a: Na+ is actively transported out and water and Cl- follow
b: solute concentration in ISF very high causing further exosmosis from loop of henle
c: salt is drawn out actively and through diffusion in ascending loop as solute concentration in ISF drops
d: tubule exits into collecting duct which passes through high solute concentration levels in the kindey causing further exosmosis
Describe briefly what happens at points 2 a,b,c,d
Glomerular filtration rate is the sum of all filtrate production by all nephrons per unit time
Define GFR
Renal blood flow is the total amount of blood that flows through the kidneys
Define RBF
Renal plasma flow is the total amount of plasma that flows through the kidneys
Define RPF
GFR/RPF: usually about 20% of plasma is filtered
Define filtration fraction
The ultrafiltration coefficient: size of capillary bed x permeability of capillaries
What is Kf?
Kf x net filtration pressure
What are the factors of GFR?
Lower size of capillary bed (glomerular destruction)
In diseae states, which factor of GFR is most commonly affected?
Net filtration pressure = Glomerular HP - Glomerular OP - Bowman's capsule pressure
What are the factors of net filtration pressure?
Virtually no proteins in filtrate
Why is Bowman's colloidal osmotic pressure not a factor of net filtration rate?
increase GFR
How does dilation of the afferent arteriole affect GFR?
decrease GFR
How does dilation of the efferent arteriole affect GFR?
decrease GFR
How does constriction of the afferent arteriole affect GFR?
increase GFR
How does constriction of the efferent arteriole affect GFR?
- neural control
- hormonal control
- autoregulatory control
What are the 3 main mechanism types that regulate GFR?
This is intrinsic to the kidney. It is comprised of the arteriole myogenic mechanism and the tubuloglomerular feedback
Briefly describe autoregulatory control of GFR
Made up of the renin-angiotensin system
Briefly describe hormonal control of GFR
Mainly controlled by sympathetic input which constricts vessels and decrease GFR
Briefly describe neural control of GFR
The arterioles contain smooth muscle which contracts when stretched and relaxes when stretch dissipates. This reduces diameter variation
What is the myogenic mechanism?
This refers to the macula dense cells and Na+ level regulation.
Increased GFR -> increased NaCl in tubule fluid at macula densa level -> increased uptake of NaCl by MD cells -> increased adenosine and ATP in MD cells -> ATP binds to P2X receptor and adenosine binds to adenosine A1 receptors in smooth muscle of afferent arteriole -> increased intracellular Ca2+ -> contraction of smooth muscle vasoconstriction -> return of normal (lower) GFR
What is the tubuloglomerular feedback? Describe the steps
source: adrenal medulla and sympathetic nerves
site of action: beta receptors on afferent arterioles
action: reduced RBF and GFR
Name source, site of action and effect for Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Source: renal endothelium, mesangial cells and distal tubular cells
site of action: blood vessels
action: vasoconstriction and reduced GFR
Name source, site of action and effect for Endothelin
source: Converted in blood from ATI (mostly in lung by ACE)
site of action: afferent and efferent arterioles, particularly efferent (in kidney), brain, adrenal cortex
actions:
- powerful systemic vasoconstriction
- lower RBF but similar GFR
- Stimulate aldosterone and ADH (and ACTH) release -> increased sodium and water reabsorption -> increased blood pressure
- stimulate thirst and salt craving directly in the brain
Name source, site of action and effect for Angiotensin II
source: Macula densa in response to high Na+
site of action: afferent arteriole
action: reduced RBF and GFR
Name source, site of action and effect for Adenosine
source: widespread - mostly local release during renal ischaemia
site of action: renal vessels
action: vasodilation and increased RBF
Name source, site of action and effect for prostaglandins
source: myocardial cells
site of action: afferent and efferent arteriole
action: dilate afferent, constrict efferent. increase GFR, similar RBF, supression of Na+ reabsorption in PCT, inhibit ADH and aldosterone secretion -> natriuresis -> decrease BP
Name source, site of action and effect for ANP and BNP
Glomerular filtration - tubular reabsorption + tubular excretion
What are the factors of urinary excretion?
1. paracellular
2. transcellular
Name the two pathways
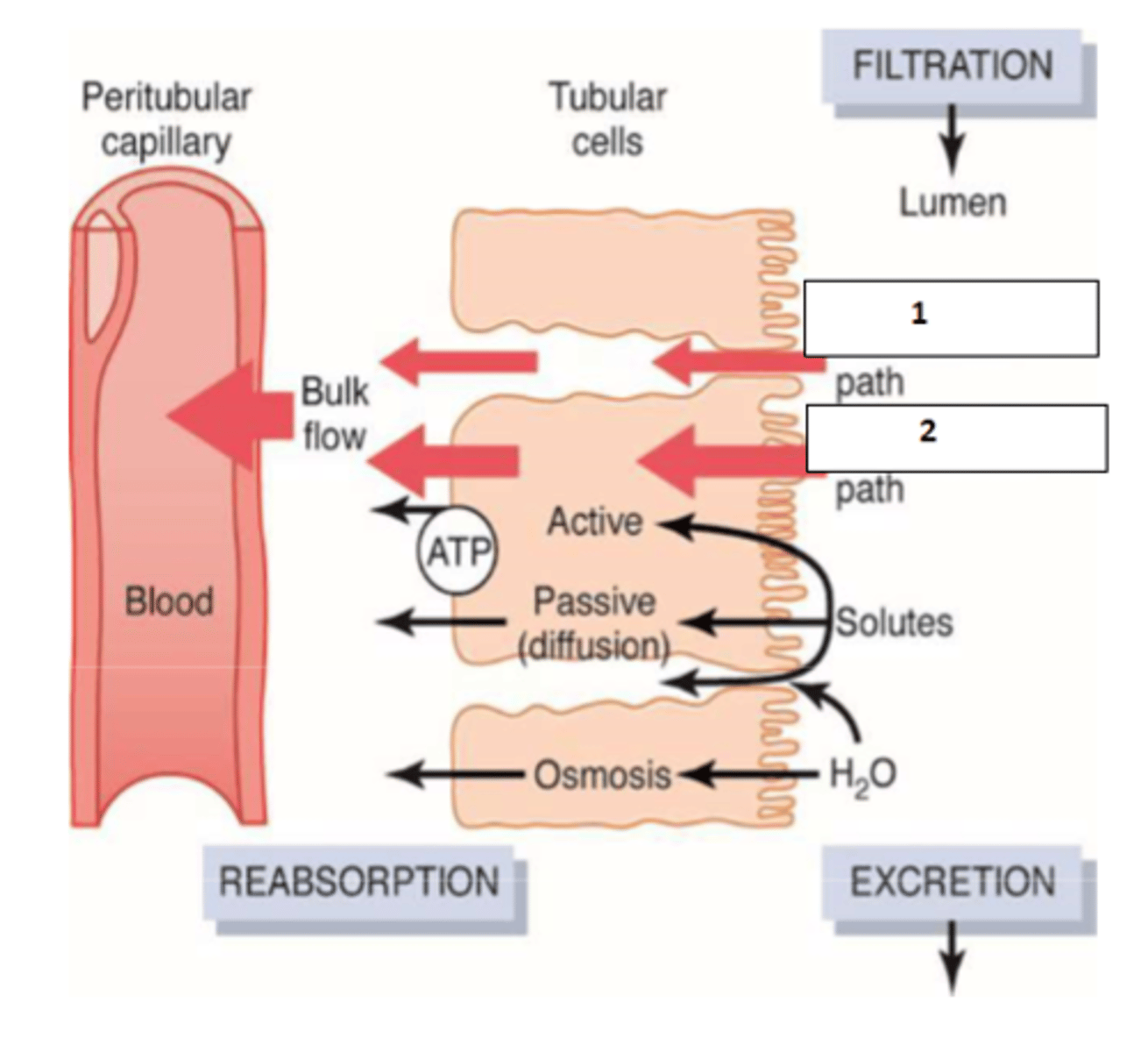
Bulk flow
What is the name of transfusion of water and solutes from ISF to blood?
- primary active transport
- secondary active transport
- pinocytosis
- passive diffusion
Name 4 types of cellular transport
- Na+/K+ ATPase pervasive in basolateral side of cells (side facing interstitium)
- Sodium actively transported into interstitium and from there enters capillaries.
- Cl- and water follow sodium
How is sodium reabsorbed in the tubules?
- Secondary active transport
- SGLT (sodium-glucose transport protein) transports Na+ down its gradient and pulls glucose together with it against its gradient
How does glucose move from the lumen into the epithelial cells of the tubule?
90% SGLT2
(10% SGLT1)
Which is the major subtype of SGLT?
H+/Na+ exchanger exports one H+ into lumen and brings in one Na+
How can H+ be concentrated in the lumen of the tubule?
Secondary active: Sodium cotransport
How are amino acids reabsorbed?
Pinocytosis via surface receptors
How are proteins reabsorbed in PCT?
Follows positive charge of Na+ (Passive reabsorption, not active)
How is urea reabsorbed?
65% - actively established sodium gradient is the main driver of reabsorption of other solutes and water
How much sodium chloride is typically reabsorbed under normal circumstances. What is the significance?
- thin descending
- thick descending
Which regions of the loop of henle are permeable to water?
- no significant reabsorption in thin ascending
- thick ascending reabsorbs sodium, chloride and potassium via NKCC2 symporter (1Na+,1K+, 2Cl-)
- ROMK channel allows K+ to be secreted after absorption through NK2C
- Ca2+, HCO3-, and Mg are also absorbed
- paracellular reabsorption of Na+, Mg2+, Ca2+, K+
Describe reabsorption in the ascending limb
ADH
Which hormone stimulates NKCC2?
H+ excreted, Cellular H+ exchanged for luminal K+, luminal K+ passively diffused into interstitium on basal surface,
Intracellular HCO3- exchanged for interstitial Cl-,
passive diffusion of Cl- into lumen
Which solutes are modulated by type A intercalated cells?
Intracellular HCO3- (from carbonic acid) excreted in exchange for luminal Cl-,
passive diffusion of Cl- in to interstitium,
H+ (from carbonic acid) reabsorbed at basal surface,
Intracellular H+ exchanged for interstitial K+ at basal surface,
passive diffusion of K+ out to lumen
Which solutes are modulated by type B intercalated cells?
In the collecting duct
Where are the intercalated cells?
- sites: principal cells, intercalated cells
- effect at principal cells: Na+ reabsorption, K+ secretion
-effect at intercalated cells: increased H+ secretion
How does aldosterone act on reabsorption (site and effect)?
- sites: PCT, TAL, DCT,
- effect for all: increased Na+ reabsorption, increased H+ secretion
How does angiotensin II act on reabsorption (site and effect)?
- site: DCT, collecting tubule, collecting duct
- effect: increased water reabsorption
How does ADH act on reabsorption (site and effect)?
- site: DCT, collecting tubule, collecting duct
- effect: decreased sodium reabsorption
How does ANP act on reabsorption (site and effect)?
- site: PCT, TAL, DCT
- effect: decreased phosphate increased Ca2+ reabsorption
How does PTH act on reabsorption (site and effect)?
enhances Na+ reabsorption in PCT, stimulates apical sodium-hydrogen exchanger and basal Na/K pump
How does the sympathetic nervous system act on reabsorption (site and effect)?
decreased sodium reabsorption
How does arterial pressure act on reabsorption (site and effect)?