Chapter 7 - How Cells Capture Light Energy via Photosynthesis
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Process of photosynthesis capture ? energy and uses this energy to synthesize ?
CO2 is ?
H2O is ?
Capture light energy, synthesize carbohydrates
CO2 is reduced
H20 is oxidized
General equation for photosynthesis is:
6CO2 + 6H2O + Light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
ΔG = +686 kcal/mol
Energy from light drives this ? reaction
endergonic
Biosphere refers to ? on the surface of the earth and ? where living organisms exist.
Regions, atmosphere
Autotrophs
make organic molecules from inorganic sources; plants
Photoautotrophs are most and use ? as a source of energy
Light as source of energy
Heterotrophs must?
consume food; acquire organic molecules from their envrionment
Life is primarily driven by the ? activity of ?, ? and ?
Driven by photosynthetic activity, of Plants, Algae, and Cyanobacteria
Which organelle carry out photosynthesis; containing the pigment chlorophyll.
Chloroplasts
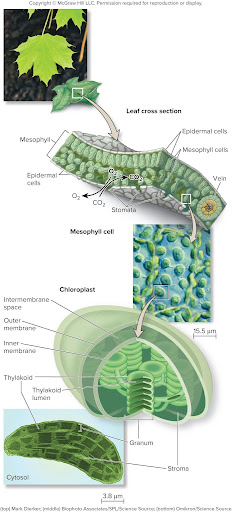
In most plants, photosynthesis occurs in the leaves, specifically within the ? cells
Mesophyll cells
Opening int he leaf surface, called?
allow the passage of ? and ?
Stomata
CO2 and O2
Chloroplast structures include:
the outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membranes (stacked to form grana), and the thylakoid lumen
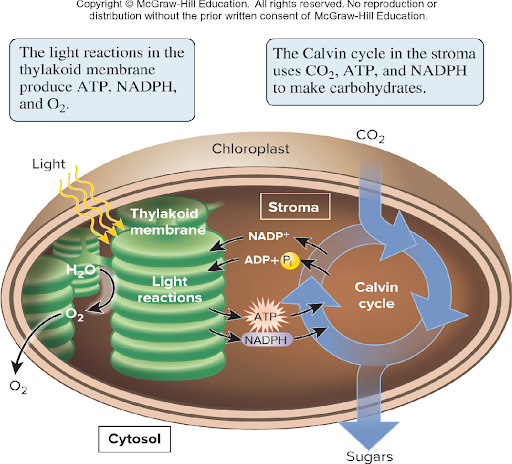
The light reactions involve a series of ? conversions, starting with ? energy and ending with ? energy stored in ? and ?
Energy conversions, starting with light energy, ending with chemical energy stored in NADPH and ATP
ATP and NADPH provide the ? and ? needed to make ? during the ? cycle.
Energy and electrons needed to make Carbs during the Calvin cycle
Light is a type of ? radiation; it consists of?
Electromagnetic radiation, consists of energy in the form of electric and magnetic fields.
Light travels as ?
waves
Light also behaves as particles called ?
Photons
When light encounters a molecule:
It may pass through the molecule
It may bounce off the molecule, changing its path toward a different direction
It may be absorbed by the molecule, pigments are molecules that can absorb light
Pigments absorb some ?
Light energy and reflect other; the wavelegnth of light that pigment absorbs depends on amount of energy needed to boost an electron to a higher orbital.
After an electron absorbs energy,
It is an excited state and usually unstable
The electron may release energy in different ways:
As heat
As light (fluorescence)
Excited electrons in pigments can be transferred to another molecule or “captured”
Two types of chlorophyll pigments:
Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b
Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are found in
Green plants and green algae.
Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b:
Contain porphyrin ring with a delocalized electron; delocalized electron can absorb light energy
Hydrocarbon tail anchors the pigment to proteins withn the thylakoid membrane
Carotenoids are another type of ?
Pigment
Having different pigments allows plants to
Absorb light at many diff wavelengths
An absorption spectrum is a graph that depicts the
Wavelengths that are absorbed by diff pigments
An action spectrum depicts the
Rate of photosynthesis by a whole plant at specific wavelengths
The thylakoid membranes contain 2 distinct complexes of proteins and pigment molecules called?
Photosystem I and Photosystem II
Light excited pigment molecules in both:
PS II and PS I
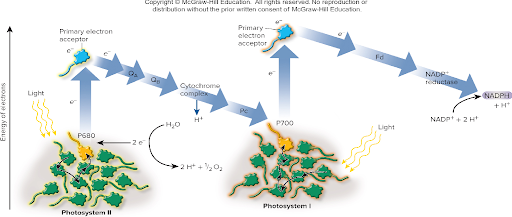
The combined action of PS II and PS I is termed ?
Linear electron flow; this process produces O2, ATP and NADPH.
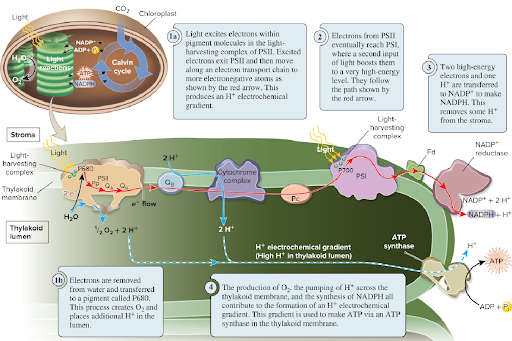
Role of photosystem II in linear electron flow:
The initial step in photosynthesis
Excited electrons travel from PS II to PS I
Oxidized water, generating O2 and H+
Releases energized electrons to electron transport chain (some energy used to make H+ electrochemical gradient.
Role of photosystem I in linear electron flow:
Primary role to make NADPH
Addition of H+ to NADPH+ contributes to H+ gradient that fuels ATO synthase activity
The process of ATP production in the chloroplast is called
Photophosphorylation
Linear electron flow produces ATP and NADPH is roughly
Equal amounts, however the Calvin cycle uses more ATP than NADPH
Another path of electron flow called?
Cyclic electron flow, produces additional ATP
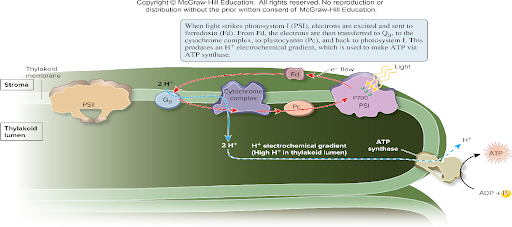
Cyclic electron flow produces
Only ATP
Cyclic flow is favored when the level of ? is low and ? is high; it is also favored when ? levels are low.
When the level of NADP+ is low and NADPH is high; it is also favored when ATP levels are low.
PS I and PS II have 2 main components:
Light harvesting complex, and a Reaction Center
Light-Harvesting (aka ?) is composed of dozens of
AKA antenna complex
Composed of dozens of pigment molecules anchored to transmembrane proteins.
Directly absorbs photons of light and transfers energy between pigments by a process of resonance energy transfer.
Light-Harvesting Complex directly absorbs..
Photons of light and transfers energy between pigments by a process of resonance energy transfer
Reaction Center is the site where
The redox reaction takes place; it contains P680, a special pigment molecule.
P680 is a:
It releases?…
Special pigment molecule
Releases its high energy electron and is oxidized
P680* → P690+ + e-
Water is ? to replace the electrons on P680+
Oxidized
PS II is the only known protein complex that can ?
Oxidize water, resulting in the release of O2
The Z scheme is a model developed in ? that proposed….
1960, Proposed that photosynthesis involved 2 events of light absorption.
Z scheme is consistent with linear flow:
PS II to PS I to NADPH
The ATP and NADPH generated during the light reactions are used during the
Calvin Cycle, to make Carbs
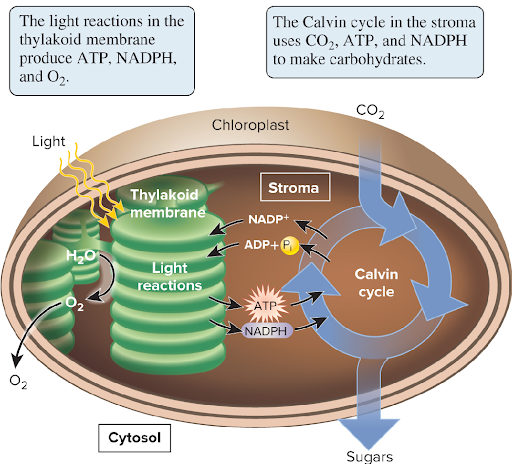
The reactions of the Calvin cycle require a ?
Massive input of energy
For every 6 CO2 incorporated, how many ATP and NADPH must be used?
18 ATP and 12 NADPH
The product of the Calvin cycle is ?
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P), a carb with 3 carbon atoms that can be used in the synthesis of glucose and other organic molecules.
The Calvin Cycle is divided into 3 phases:
Carbon Fixation
Reduction and Carbohydrate Production
Regeneration of RuBP
Carbon Fixation
CO2 is incorporated into RuBP, a 5-carbon sugar; the enzyme rubisco catalyzes this reaction and the 6-carbon intermediate splits into two 3-carbon molecules
Reduction and Carbohydrate Production
ATP is used as a source of energy and NADPH is used as a source of high-energy electrons; G3P is produced
Regeneration of RuBP
Most of the G3P is used to regenerate RuBP, allowing the cycle to continue
What conditions can alter the operation of the Calvin Cycle?
Environmental Conditions:
Temp, Water availability, and Light intensity
Most plants (~?%) are called ? plants because the…
~90%, C3 plants because the first molecule that CO2 is incorporated into (3PG) is a 3-carbon molecule
Photorespiration occurs when ?
Rubisco adds O2; as intermediates are processed, a molecule of CO2 is released.
Considered wasteful since loss of carbon can limit plant growth
If C3 plants are subjected to hot and dry environments, as much as ?-?% of their photosynthetic work is ? by photorespiration.
25-50%, Reversed by Photorespiration
What plants make oxaloacetate (4 carbon molecule) in the first step of carbon fixation?
C4 Plants
Leaves have two-cell layer organization:
Mesophyll cells
Bundle-sheath Cells
Mesophyll cells capture
CO2 into oxaloacetate (using enzyme that only binds CO2) that transport the captured carbon to the bundle-sheath cells.
Bundle-sheath cells
where the calvin cycle occurs
CAM plants open their?
What is captured and stored?
Stomata at night
CO2 captured and stored
Stomata close during the day to conserve?
During the day, stored ? is released and enters the Calvin cycle.
Water; CO2
You can tell whether the C3 or C4 plant is better because
Of the environment
In cooler climates, C3 used ? energy to fix CO2
Less energy
C4 and CAM plant adaptations evolved to help plants living in hot and dry environments to?
Conserve water and minimize photorespiration