protein structure and function
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
what is one thing you need to make a functional protein
correctly folded protein
what goes hand in hand in bio
shape and function
what occurs with amino acids in protein synthesis
they are added together to form a polypeptide chain,this is the primary sequence (BEFORE FOLDING) and proteins are made up of 1 or more polypeptide chains.
what are the levels in protein structure
primary sequence (BEFORE FOLDING)
secondary sequence
tertiary sequence
quaternary structure
what do genes do when it comes to amino acids
genes (which are made of DNA) determine the order and number of these amino acids. (important for the structure and function of proteins)
what happens if an amino acid changes
it can affect the whole proteins function
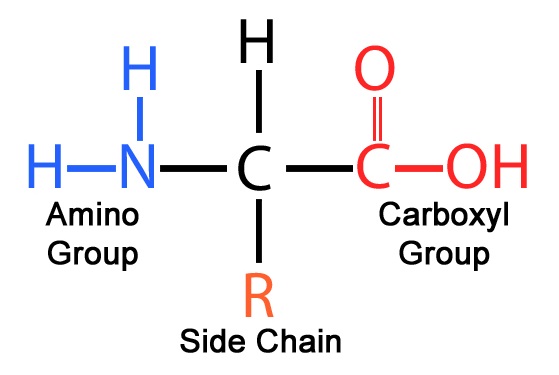
what is inside of each amino acid
a carboxyl group, a amino group, and a R group (which is the side chain)
WHAT HAPPENS IN SECONDARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS
protein folds in either, Alpha Helix (a-helix) swirllll, or Beta-Pleated sheet (B-pleated sheet) back n forth zigzag
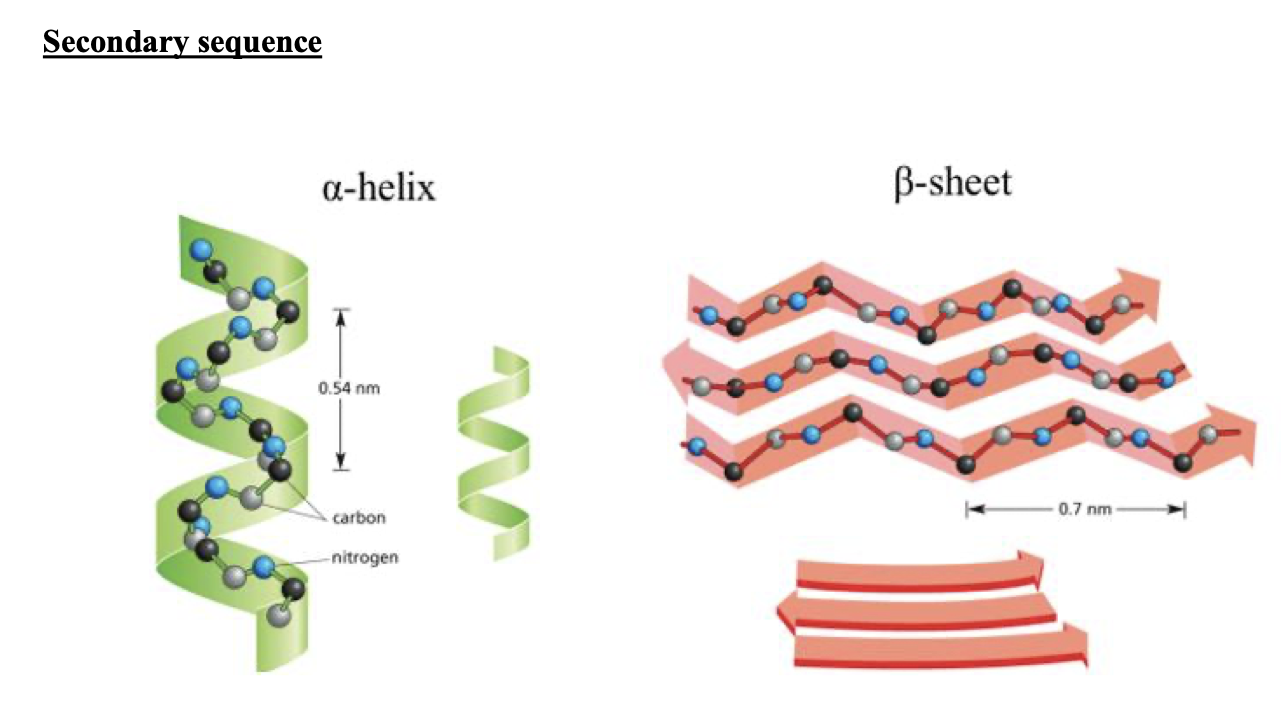
how is the type of fold the amino acid does in secondary structure determined by
it depends on the amino acid arrangement it has, and the hydrogen bonds on the backbone of the amino acid.
which hydrogen bond is specifically responsible for the two shapes amino acids form
these are the hydrogen bonds in the backbone of the amino acid structure
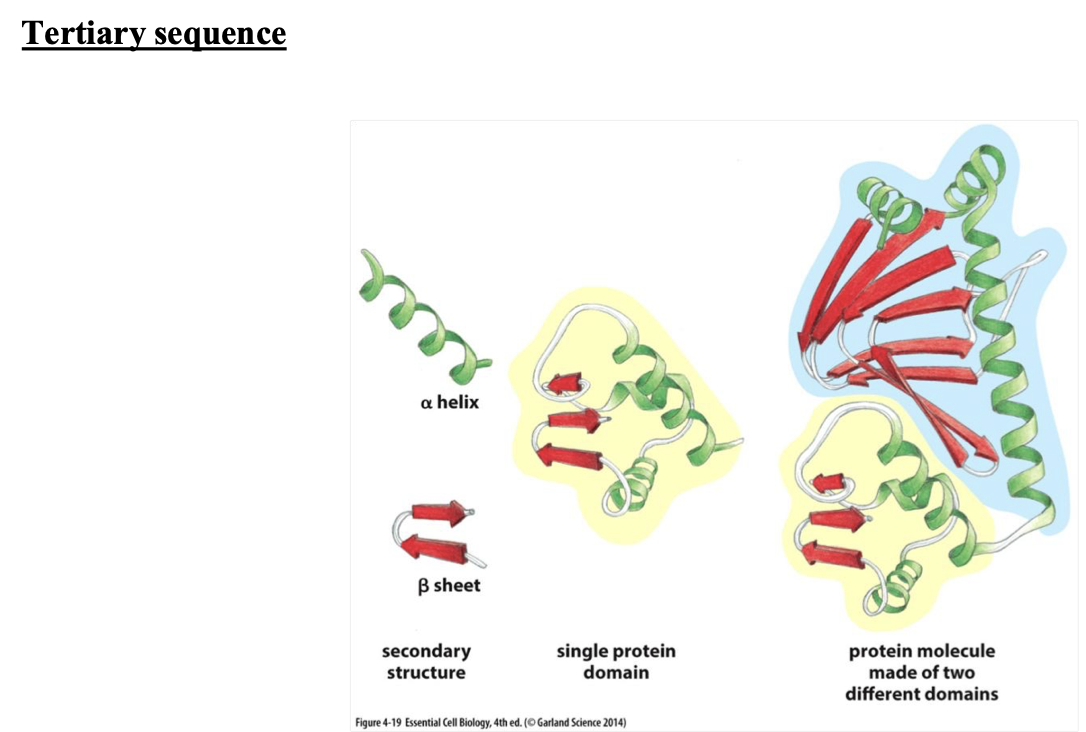
what occurs in tertiary structure
when you put together a bunch or a-helix's or b-pleated sheet (tertiary structure proteins aren’t always functional)
what is it called when you have one b-pleated sheet and a-helix structure, called in tertiary structure
a single protein domain
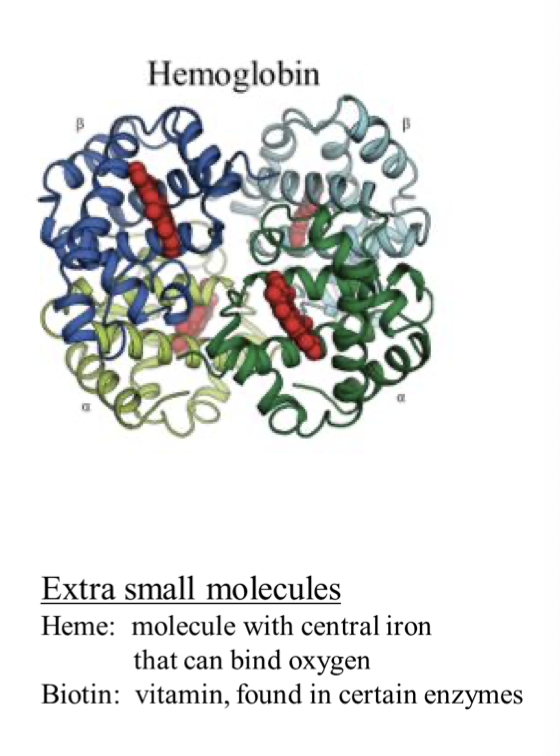
what occurs in a. quaternary structure
it is two proteins maybe along with other things to make a functional protein

what is. a hemoglobin
it is 4 different protein structures that bind
what do the R groups do in amino acids
they are different in each amino acid and make them act a certain way. EX. hydro-phobic
how does the different R groups affect the amino acid
when folding, it can make the hydrophobic aminos be more in the center of the fold while hydrophilic will be on the outside.
how many amino acids are there, and how many bonds can carbon form
20 different ones, and 4 covalent bonds
how many bonds can carbon form
4 covalent bonds
what is the backbone of the amino acid
it is the whole amino acid (amino group, carboxyl group etc.) except for the R group that hangs off.
what happens with carbohydrates in the cell
it circulerizes in water
what does it mean when an amino acid ionizes
a hydrogen ion (H+) is gained or lost. resulting in a charged species or ion.

why do amino acids ionize
Ph changes in the surrounding solution
ionization is essentially an acid based reaction
they ionize at ph of 7 (which is inside the cell)
what determines if an amino acid is polar or non polar
the R group,
what are the 4 types of bonds in proteins that hold everything together giving it its shape
1. disulfide bond
2. van der Waals attraction
3. hydrogen bond
4. electrostatic attraction
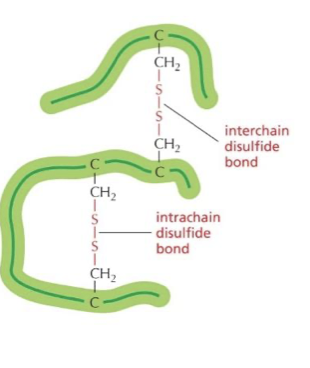
what is a disulfide bond
it occurs when two sulfurs bond together and it is a really tight bond
what consists in the van Der Waals attraction
they are interactions between things that are very hydrophobic. the molecules hide out in the center. it is a very weak interaction
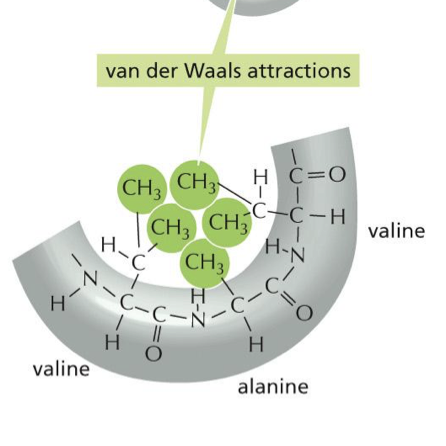
what are usually in van der Waals attraction
lots of carbons and hydrogens (CH)
what consists in a hydrogen bond
it is a hydrogen in between two things that have polarity that its bonded too. (which are usually nitrogens and oxygens.)
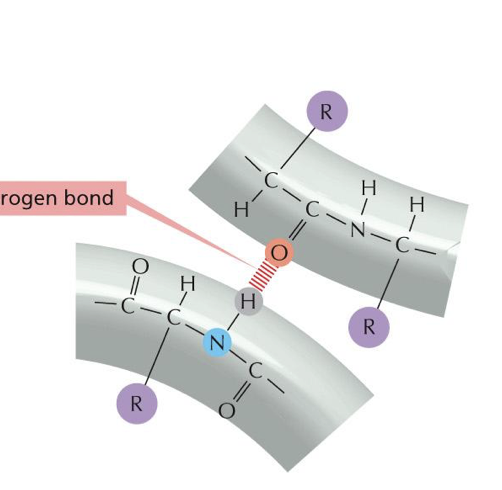
what does a hydrogen bond have to bond with
something with polarity which is something negative. with something positive
what do electro static attractions involve
they involve things that have charges that are gonna be interacted with eachother.

what is usually the case with electro static attraction
these charges are usually on the side chains of the amino acids. and they'll have a + and -
if you were to flip a protein would it still function the same
no, a protein must have a certain beginning and end with the amino group at the beginning and carboxyl at the end.
what is the beginning and end of a protein called
the N- terminus (because there's s nitrogen there) and C-terminus
what can form when a protein is mis-folded and not discarded
an amyloid structure forms where mid folded proteins mess up other proteins and can cause disease
what are enzymes regarding proteins
proteins are the big papa and enzymes are one of its babies. (enzymes are proteins)
enzymes carry out a chemical reaction, whats the process?
the enzyme binds to its specific molecule (the substrate) at the active site
it then breaks the bond in that molecule
3. and then releases it as 2 separate molecules
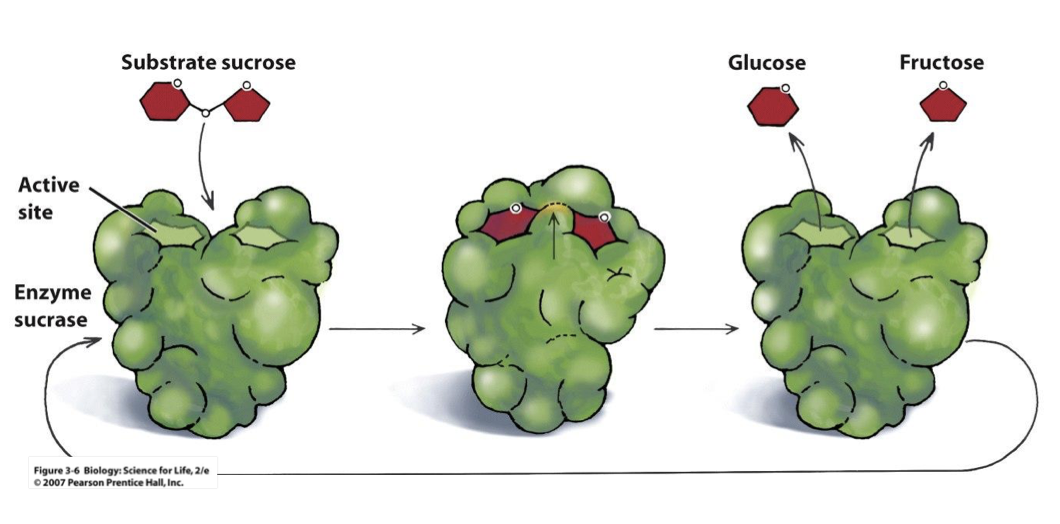
if you were to change a amino acid in the active site of an enzyme what would happen
it would ruin the protein because the active site has certain bonds for certain molecules. but if you changed an amino acid on the outside of the protein its not important
how do enzymes affect a chemical reaction
they speed things up by lowering the activation energy. making it easier for a reaction to occur
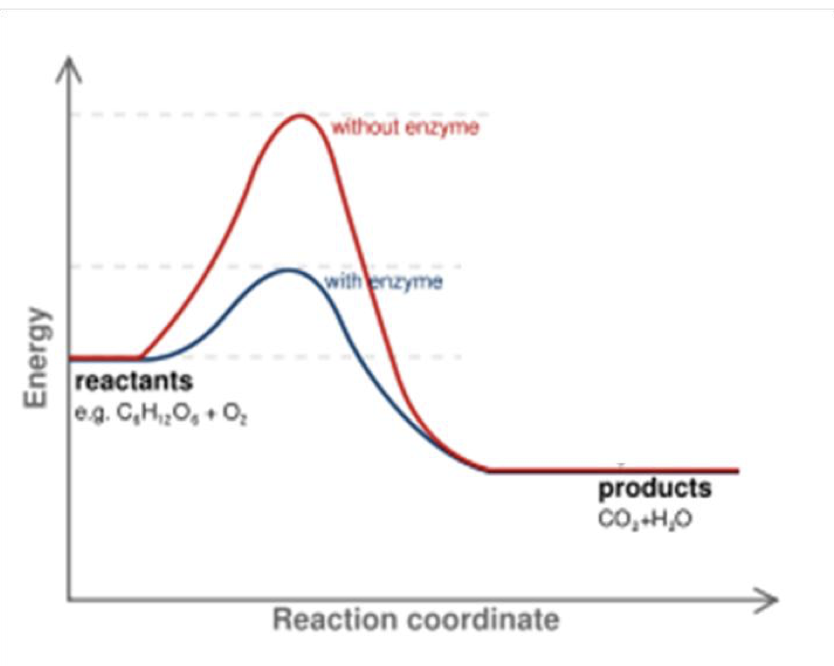
what happens in a reaction without an enzyme
you would have to use a lot more energy (ATP)
there is a maximum rate of reaction In enzymes, what is It called when it reaches that point
its called the Vmax, (when all active sites are occupied so its at its max use)
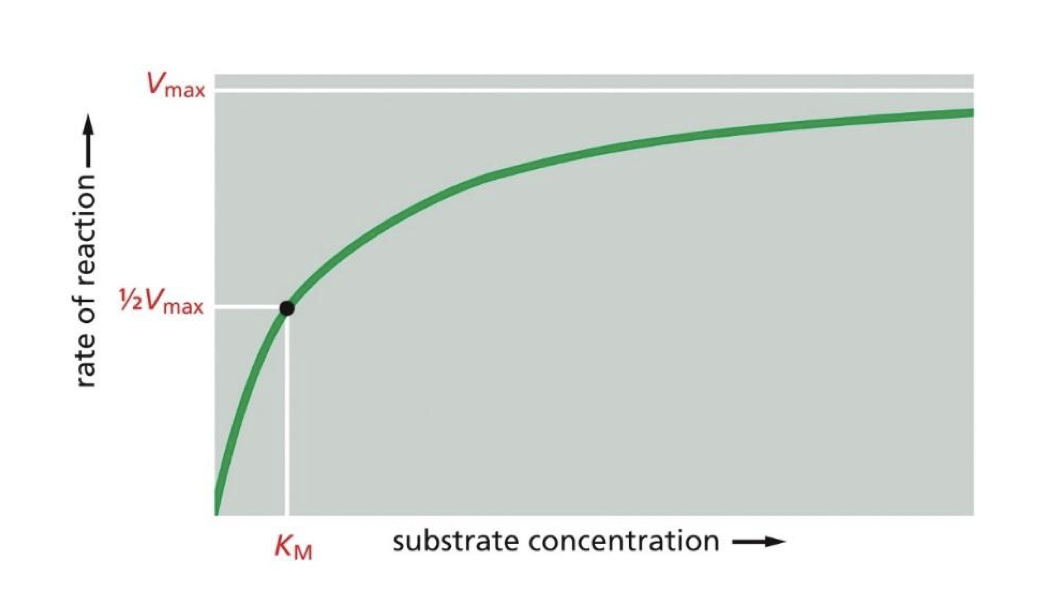
what's the term for the amount of substrate present when the enzyme is as 1/2 of Vmax
the Km
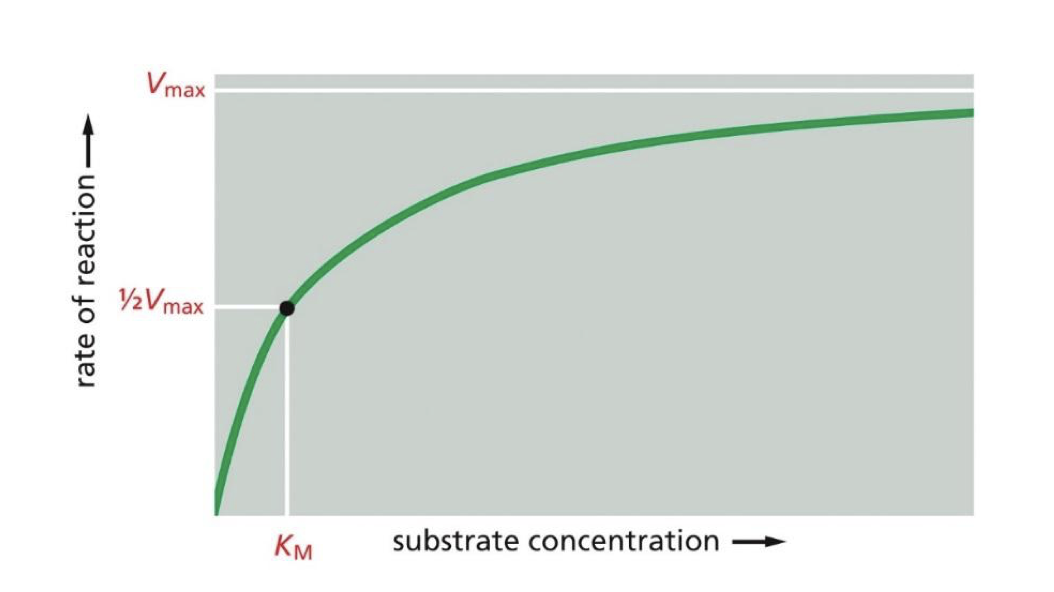
what does it mean when there's a low Km
there isn't as much needed by the enzyme to create a reaction. it has a tighter bind to the substrate
what does it mean when there's a high Km
the bind from the enzyme to the substrate is weak and it takes a lot of substrate for an enzyme to catalyze a reaction.