Gr.10 Bio(Plant tissues, organs, organ systems)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Plant tissues
Tissues: group of cells that function together to perform specialized tasks.
Meristematic tissue, epidermal tissue, ground tissue, vascular tissue
Meristematic cells
Unspecialized plant cell that can form specialized cells.
“permanent embryos” because of their lifelong ability to produce the cells that can become new tissues/organs in their part of a plant.
Plants form new organs periodically throughout their lives.
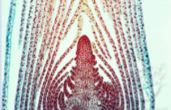
Meristematic tissue
Major functions: unspecialized tissue capable of dividing by mitosis, responsible for growing new parts of a plant.
Eg. stem tips, root tips, leaves.
Epidermal/dermal tissue
Major functions: forms a protective outer covering(barrier between plant’s internal and external environment), protects delicate inner tissues, allows the exchange of materials in and out
Eg. on top and underneath the leaf.
Specialized cells:
Guard cells: found on the lower leaf surface; forms a stomate(pore through which CO2 enters and oxygen + water vapour exit)! Plays a significant role in transpiration(the evaporation of water from leavers).
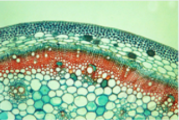
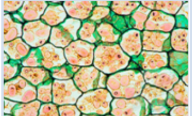
Ground tissue
Major functions:
In the stem: provides strength + support
In the roots: stores food + water
In the leaves: photosynthesis
Eg. stems, roots, leaves
Specialized cells:
Mesophyll cells: in the leaves where photosynthesis occurs
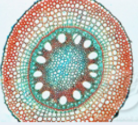
Vascular tissue
Major functions: transports water/nutrients/sugars throughout the plant, provides physical support to plant’s body
Eg. xylem and phloem
Specialized cells:
Sieve elements(in phloem): long cells that have pores at the end to allow easy flow of sugar.
Plant organs
Organ: structure in an organism made of cells and tissues which perform some specific function.
Roots, leaves, stem, flowers
Plant organ systems
System: a group of tissues and organs that perform a specific function.
Root system and shoot system
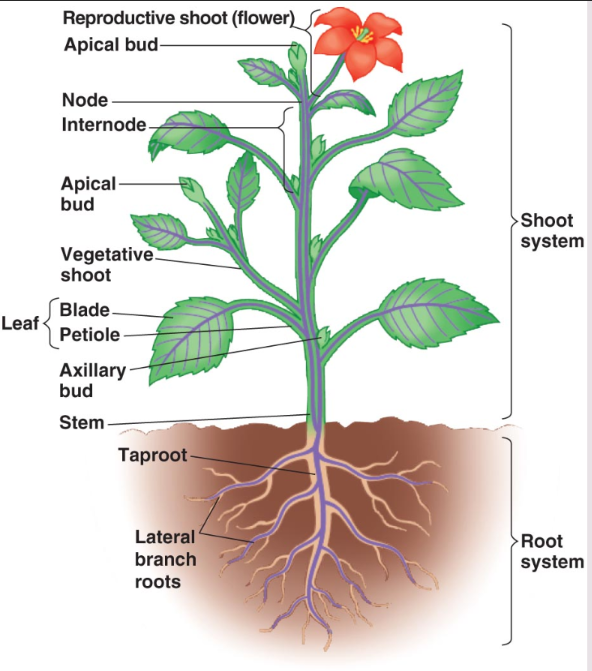
Root system
Consist of roots - the organ of the plant that lies underground to convey water/nutrients to the rest of the plant.
Functions of root system:
Absorbs and transports water/minerals from environment to stem(shoot system)
Anchors plant to ground
Stores food from photosynthesis in the leaves
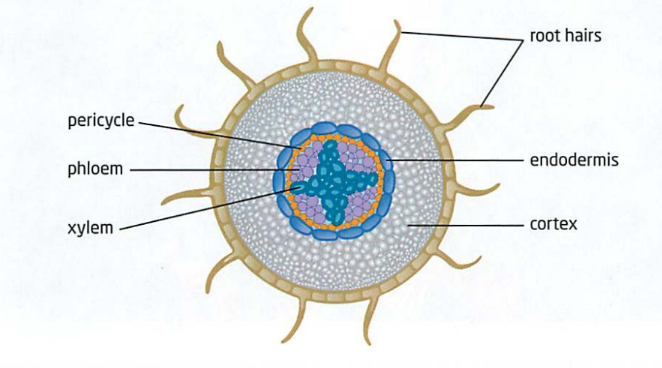
Roots
Anchors the plant to the ground so it can collect and transport water/nutrients from the soil
Plant’s storage area
Root hairs: site for water and mineral absorption.
Cortex cells: stores starch, no chlorophyll
Endodermis: controls transport between cortex and vascular tissues.
Pericycle: layer of tissue that surrounds xylem and phloem
Tissues: all 4
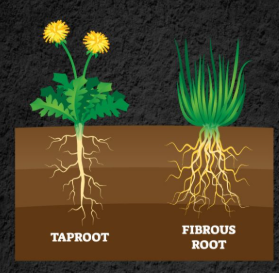
Types of root systems
Taproot system
Root system that comprises of one primary root and several secondary roots branching off the primary root.
Allows plant to reach far underground for water.
Eg. carrots, beets
Fibrous root system
Root system that has several primary and secondary roots of similar size.
Since roots spread out horizontally near surface —> allows plant to have large SA to take up water from surface of soil
Fibrous roots stabilize soil + prevent erosion/landslides.
Eg. grass, onion
Part of the root
Primary root: main/most important root in some plants.
Secondary root: roots that branch out from the primary root.
Apical meristem: found at the root tip where new cells develop.
Root cup: covers apical meristem and protects if from damage as it passes thru coarse soil particles.
Epidermis: skin cells that protect the surface of the root. Can grow root hairs: long hair-like projections which increase SA of root for more water uptake.
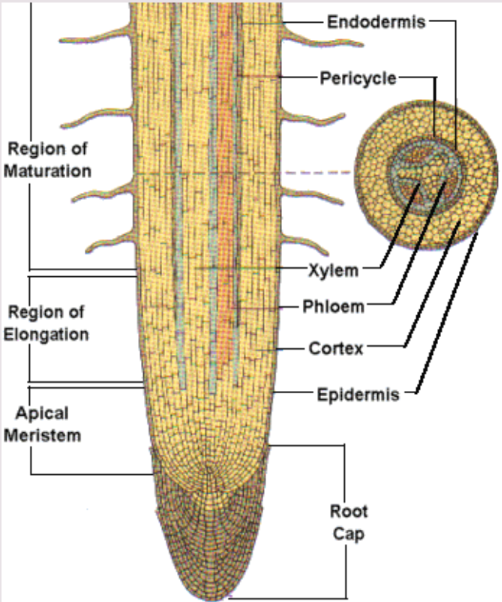
Vascular bundle
(Root System)
Found in the center of the root. Made of 2 transport tissues: xylem and phloem.
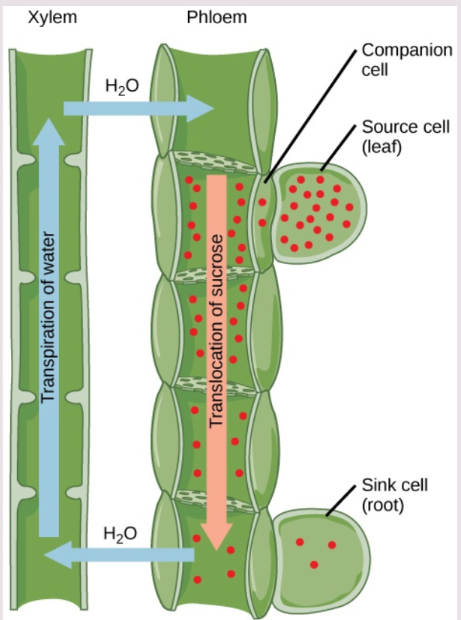
Xylem
Xylem cells grow and form long straw-like tubes. The cells die but their thick cell wall remains.
Xylem cells are dead, hollow, and connected to form a straw that water can pass through.
Root cells absorb minerals from the soil and pass them to the xylem.
Water diffuses into the xylem by osmosis.
Pressure in the xylem builds and forces water upward.
One-way transport to leaves
Ends at leaves
Phloem
Transports sugar created in photosynthesis(in leaves) to rest of plant.
2 way transportation(sugar down from leaves or upward from roots)
Phloem cells are alive and actively pump the sugar where it needs to go.

Shoot system
Supports the plant
Performs photosynthesis
Transports sap
Consists of: stem(w/branches), flowers, fruits, leaves
Stem
Function:
supports leaves
moves water, minerals, food through the whole plant
produces food through photosynthesis(not main job but occurs in plants with little to no leaves)
stores food that has been manufactured by plant
contains xylem
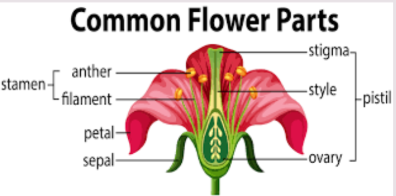
Flower
Function:
Reproductive structure of plant
Produces seeds
Male organs: stamens
Female organs: ovary(eggs), style, stigma which are contained in the pistil
Pollination: animals/wind transfer pollen from the male part of the flower to the female parts, allowing fertilization to occur.
Tissues: all 4
Fruit
Function:
protect seeds - prevents them from getting dried
fruits attract animals that feed on them allowing the seed to be dispersed
Leaf
Provides a large SA for photosynthesis
Transports sugar to other parts of plant
Upper/middle leaf: upper epidermis protects leaf and lets sunlight pass through to the mesophyll tissue where palisade cells perform most photosynthesis and spongy parenchyma cells allow gas exchange within the leaf. Vascular bundles ensure every cell in leaf is close to a supply of water + nutrients.
Lower leaf: lower epidermis contains guard cells and stomata, which play a significant role in transpiration.
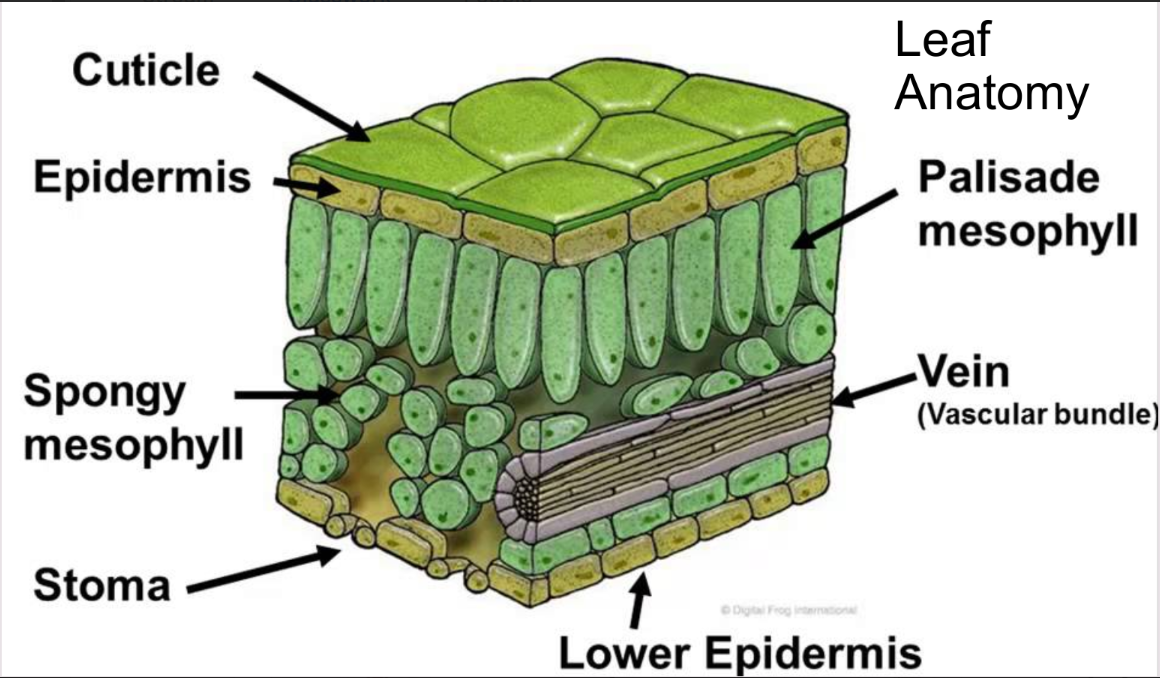
Epidermis
Top/bottom layer of tough cube-shaped epidermal cells
Function: protection
No chloroplasts —> no photosynthesis
Sunlight passes through epidermis to photosynthesis cells
Covered by cuticle(waxy coating)
Protect inner tissues from drying out by reducing water loss
LOWER EPIDERMIS:
critical for exchanges of gas between leaf and external environment.
contain guard cells/stomata
Mesophyll
Palisade layer:
Contain most of plants chloroplasts, site for photosynthesis.
Column-shaped mesophyll cells
Top of the cells are arranged to meet the Sun’s rays head on, so the rays pass through the length of the cell.
Very active —> lots of mitochondria
Spongy layer:
air spaces connect with stomata to allow gas exchange.
Stomata
Tiny poors that allow for gas exchange
Underside of leaf to prevent excessive water loss by closing
Vascular Bundle
(Shoot system)
Xylem + phloem
Sheath cells: surround bundles in leaf
Found in leaves - form veins
Transpiration
Water moves into roots from the soil by osmosis which replaces water moving up stem
Water moves up through stem and into leaves to replace water lost by evapouration
Water is lost from leaf by evaporation through open stomata
Stomata controls transpiration
Closed at night or when water is limited
Cohesion vs adhesion
Cohesion: ability of water molecules to cling together
Adhesion: ability of water molecules to cling to the wall of the xylem
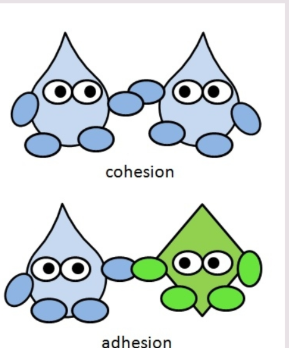
Adhesion
ability of water molecules to cling to the wall of the xylem
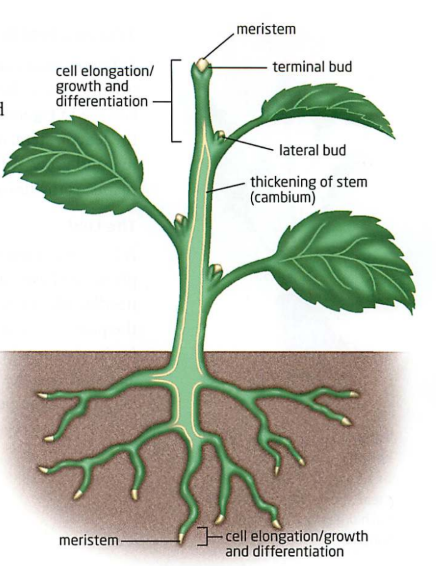
Bud
Swelling of the stem that contains meristem for new undeveloped tissues.
Terminal bud: most active growth
Lateral bud: dormant/inactive but have the potential to produce new branches/leaves/flowers.
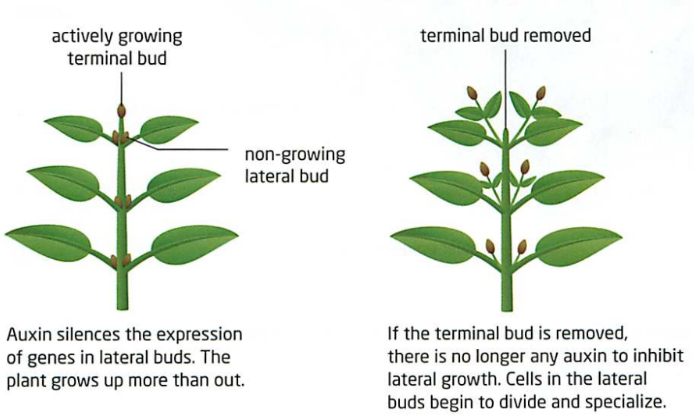
Auxin
Plant hormone created by cells in active growing areas.
This hormone holds back the development of the cells below and behind them.
Plant galls
Galls: An abnormal growth of plant tissue caused by insects/micro-organisms.
These insects/micro-organisms use the plant’s resources to support themselves/their offspring.
Gall growth is contained and doesn’t spread to other tissues.

Tobacco mosaic virus(TMV)
Virus that is highly destructive. Attacks leaves of plants and often lowers crop yields dramatically.
This was the first major plant virus whose structure was investigated because easy to work with, produced clear symptoms, had major scientific value, and was highly destructive.
Plants with too little vs too much water
Plants can’t survive without water because:
Minerals need to be dissolved in water to be absorbed and move up the xylem in the form of sap.
2. No water = no photosynthesis
Plants with too much water:
If the soil has too much water, there will be no room for oxygen —> root cells won’t have enough oxygen for cellular respiration.
Plants without soil
Hydroponics: type of agriculture that uses a nutrient solution instead of soil.