AP Biology Unit 3 - Cellular Energetics Diagram | Quizlet
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Enzyme
A protein that acts as a catalyst - a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
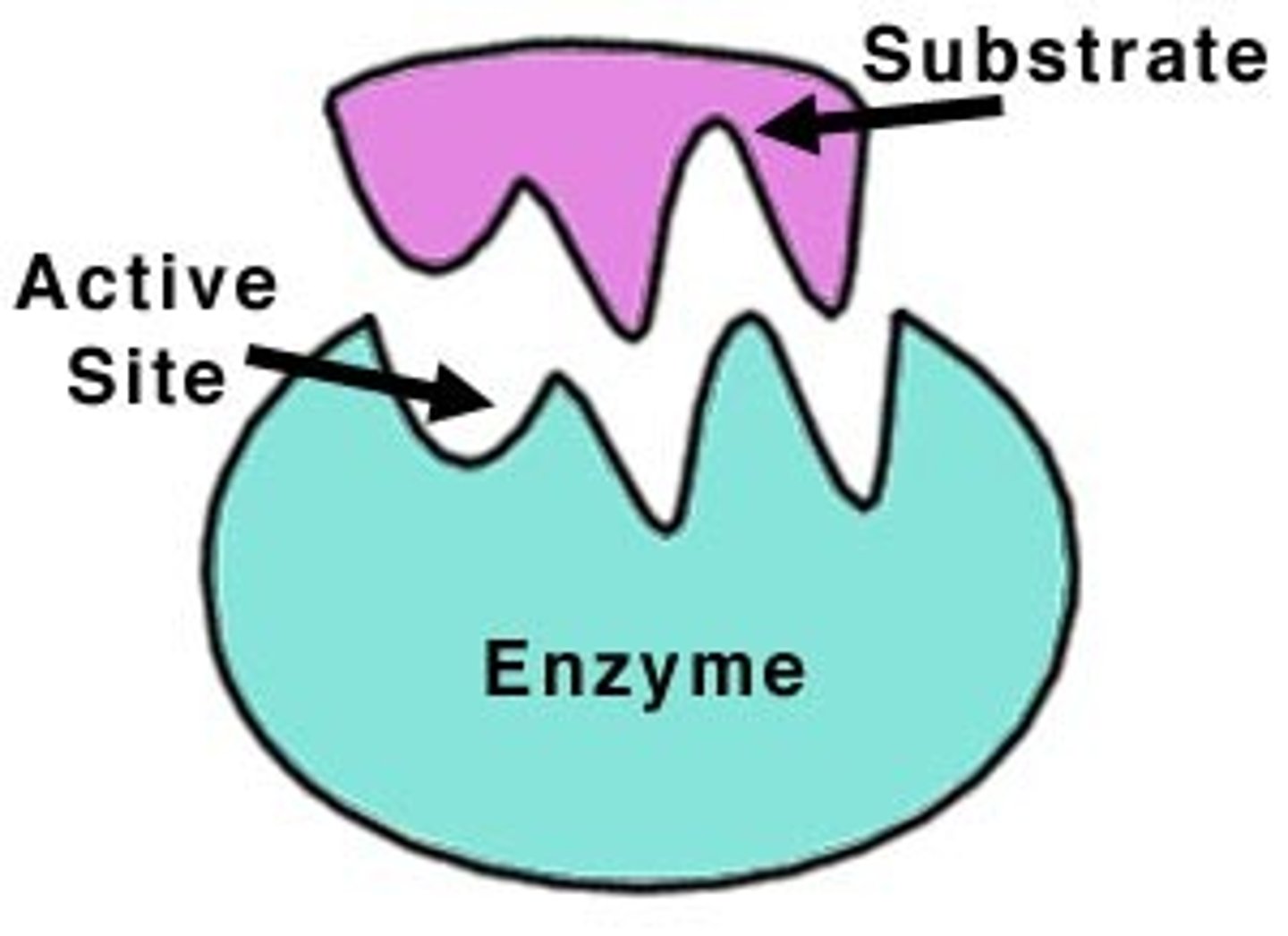
Substrate
A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme
Activation Energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
enzyme mediated reactions
with these type of reactions the rate of product formation is greatly influenced by the concentrations of the reactants
Active Site
a region on an enzyme that binds to a protein or other substance during a reaction.
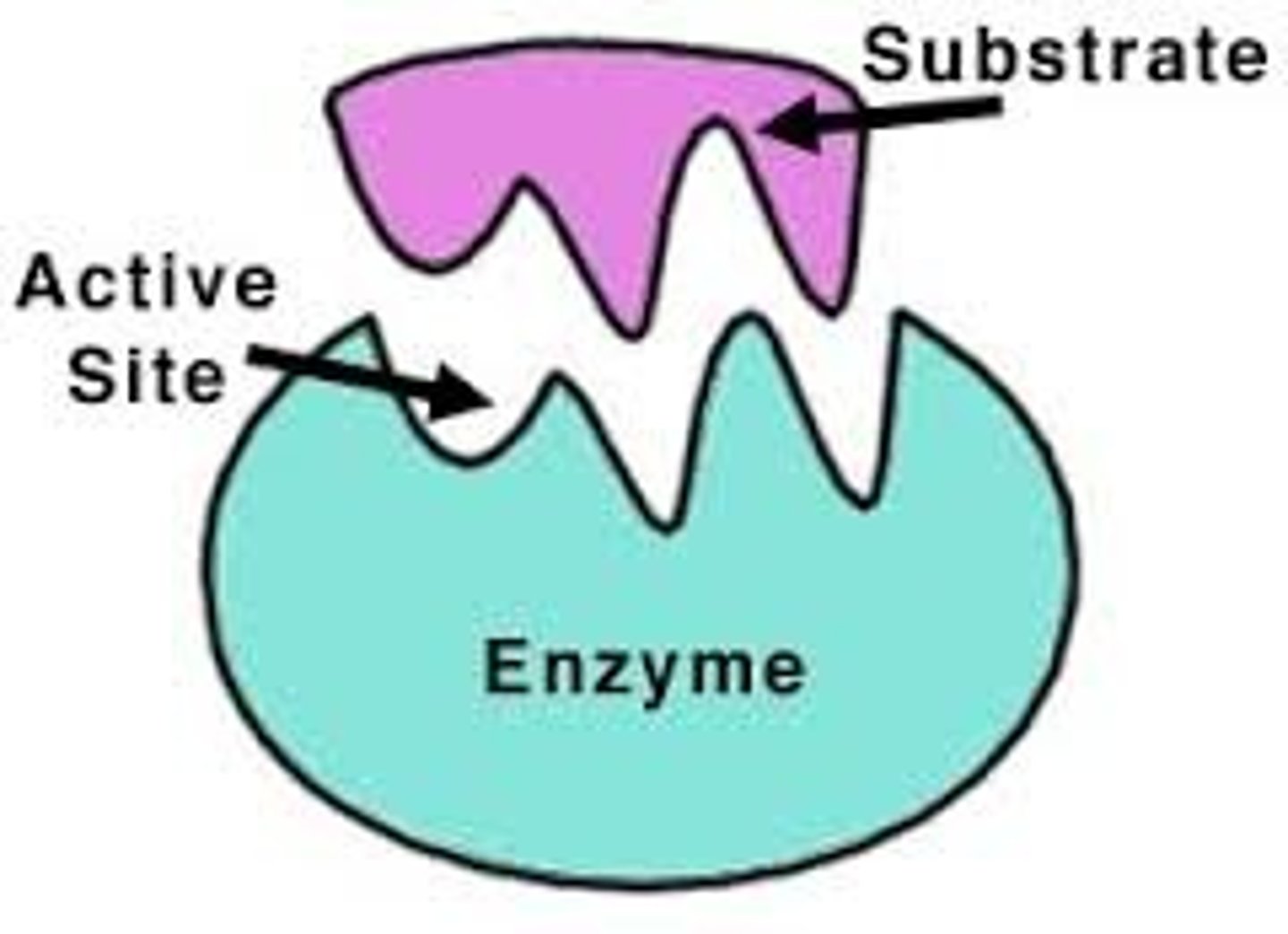
Induced Fit
The change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate, induced by entry of the substrate.
Denaturation
In proteins, a process in which a protein unravels and loses 3D structure, thereby becoming biologically inactive.
pH
hydrogen ion concentration
Inhibitor
A substance that slows down or stops a chemical reaction
Competitive Inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics.
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
A substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by binding to a location remote from the active site, changing its conformation so that it no longer binds to the substrate.
TERM
Enzyme
DEFINITION
A protein that acts as a catalyst - a chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
TERM
Substrate
DEFINITION
A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme
Energy
The ability to rearrange a collection of matter
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
System
The matter under study
Surroundings
everything outside the system
Thermodynamics
The study of energy transformations that occur in a collection of matter.
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
Entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness.
Spontaneous Process
A process that occurs without an overall input of energy; a process that is energetically favorable.
Exergonic Reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy.
Endergonic Reaction
A non-spontaneous chemical reaction in which free energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
Equilibrium
A state of balance - equilibrium = dead
Energy Coupling
The use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one.
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
phosphorylated intermediate
A molecule (often a reactant) with a phosphate group covalently bound to it, making it more reactive (less stable) than the unphosphorylated molecule.
the energy stored in bonds
The potential energy that can be released when new bonds are formed after the original bonds break, as long as the products are of lower free energy than the reactants
Metabolic pathway
series of chemical reactions in which the product of one reaction is the substrate for the next reaction
Anabolic Pathway
A metabolic pathway that consumes energy to synthesize a complex molecule from simpler compounds.
Catabolic Pathway
A metabolic pathway that releases energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds.
photosynthesis
process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches
cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic, oxygen-producing bacteria (formerly known as blue-green algae).
autotroph
an organism that is able to form nutritional organic substances from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide.
photoautotroph
organism that uses energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water to carbon compounds
Light independent reactions
set of reactions in photosynthesis that do not require light; energy from ATP and NADPH is used to build high-energy compounds such as sugar; also called the Calvin cycle
Light dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
granum
stack of thylakoids
stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
NADPH
An electron carrier involved in photosynthesis. Light drives electrons from chlorophyll to NADP+, forming NADPH, which provides the high-energy electrons for the reduction of carbon dioxide to sugar in the Calvin cycle.
Excited state
when an atom absorbs energy, its electrons move to a higher energy level
chlorophyll
Green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
photosystem
cluster of chlorophyll and proteins found in thylakoids
photosystem I
One of two light-harvesting units of a chloroplast's thylakoid membrane - uses electrons from photosystem II to create NADPH
photosystem II
One of two light-harvesting units of a chloroplast's thylakoid membrane - uses electrons from splitting water to supply electrons to photosystem I
photophosphorylation
The process of generating ATP from ADP and phosphate by means of a proton-motive force generated by the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast during the light reactions of photosynthesis.
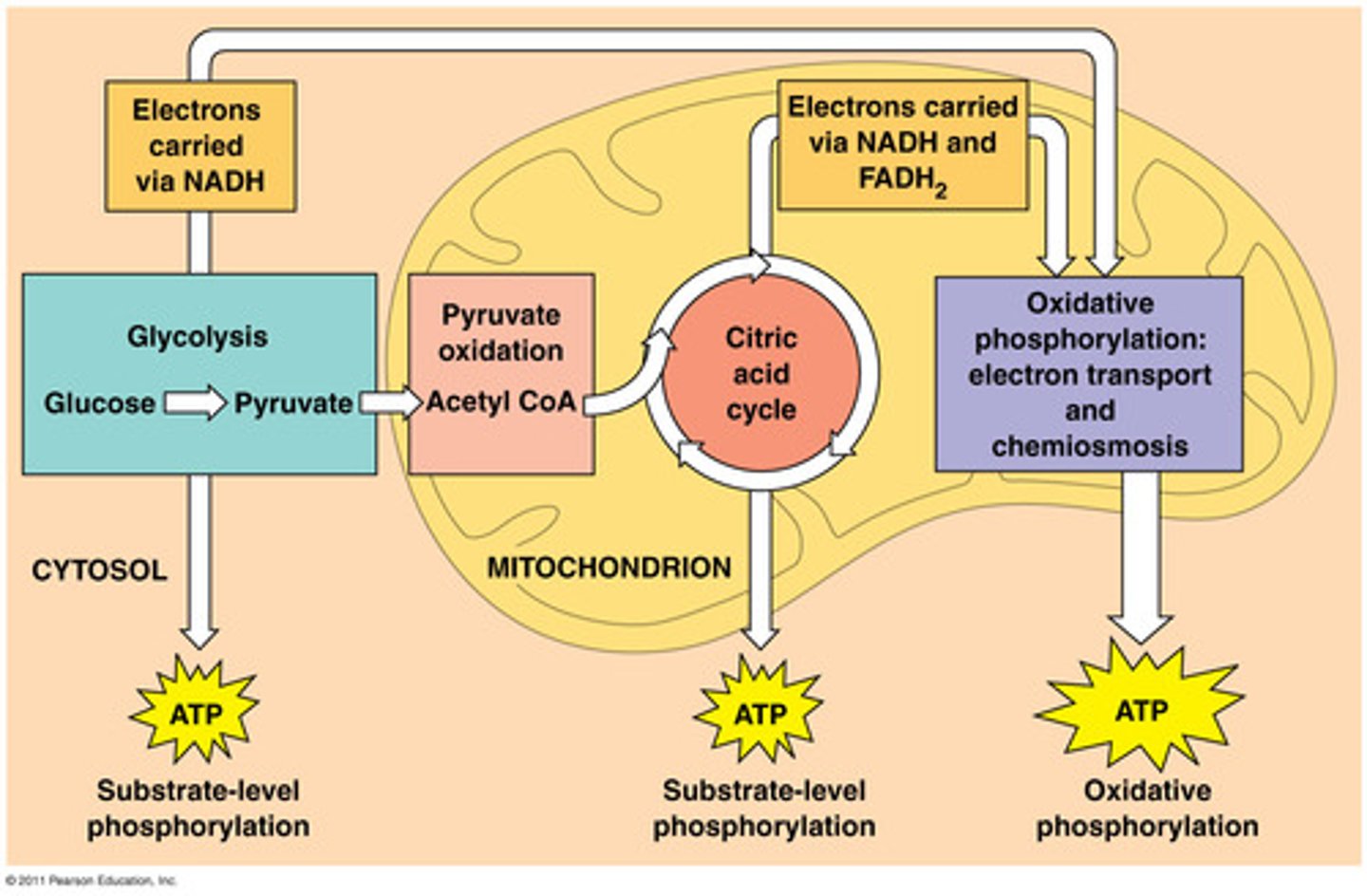
Cellular Respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
Fermentation
Process by which cells release energy in the absence of oxygen
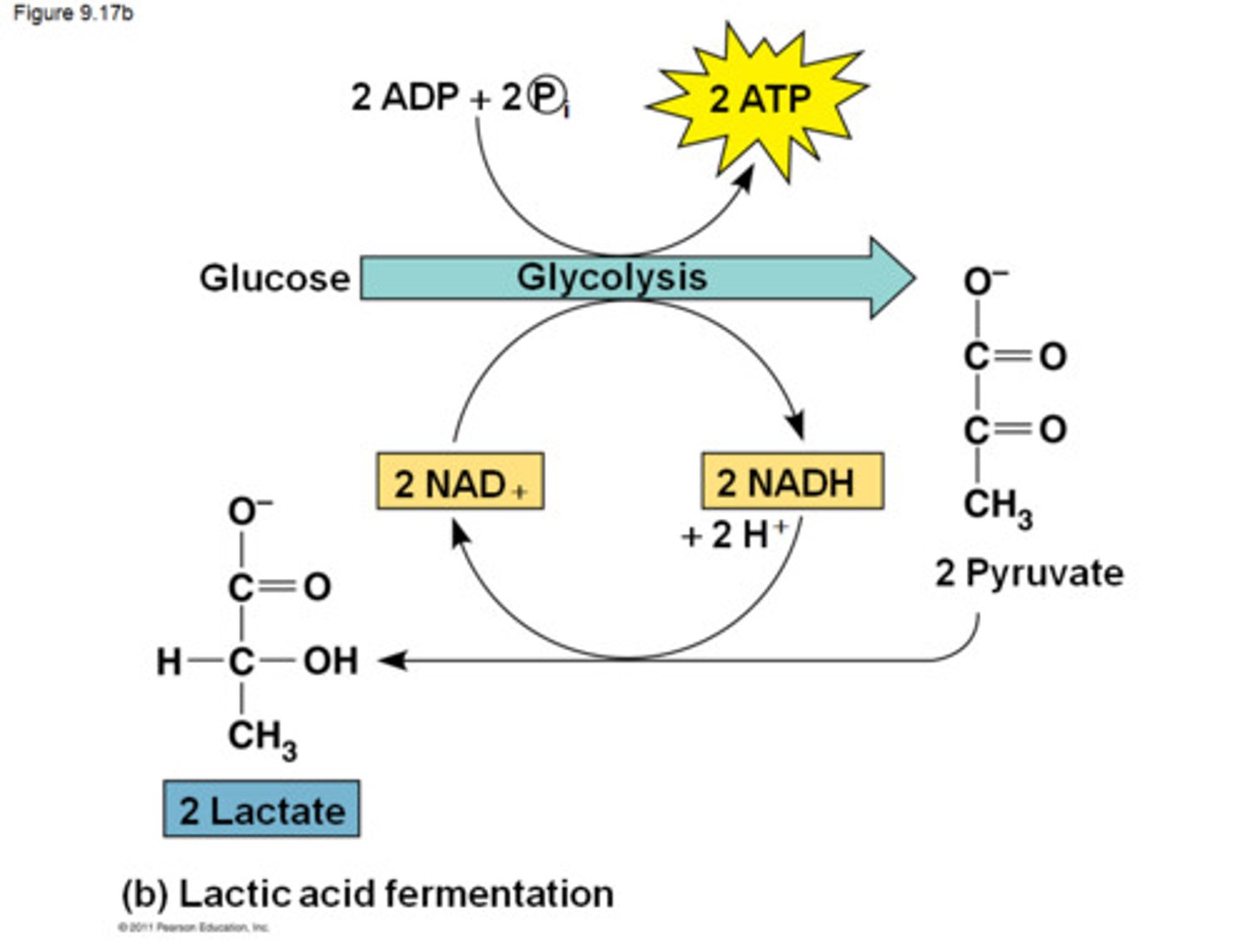
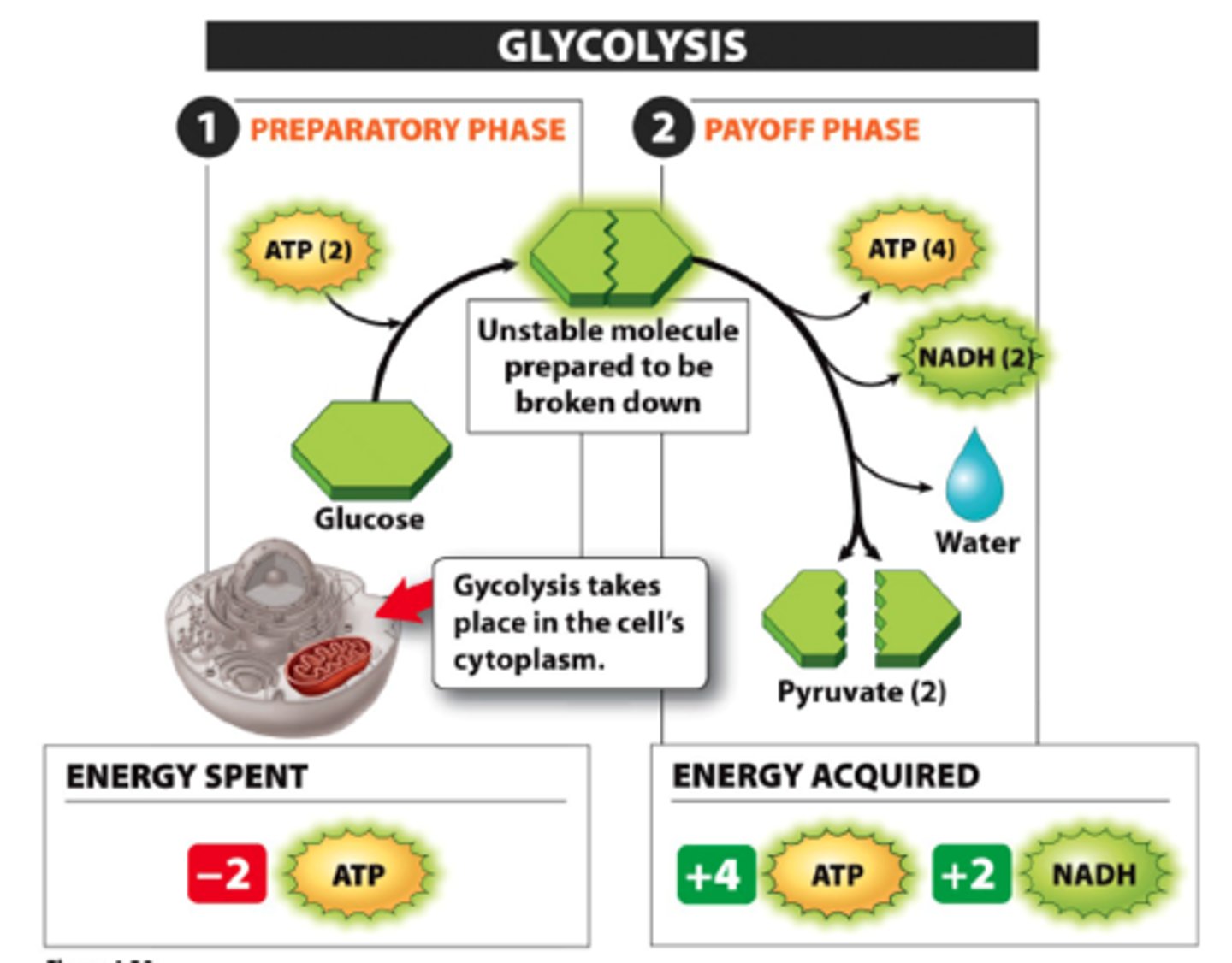
Glycolysis
first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid
substrate-level phosphorylation
The enzyme-catalyzed formation of ATP by direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate in catabolism.
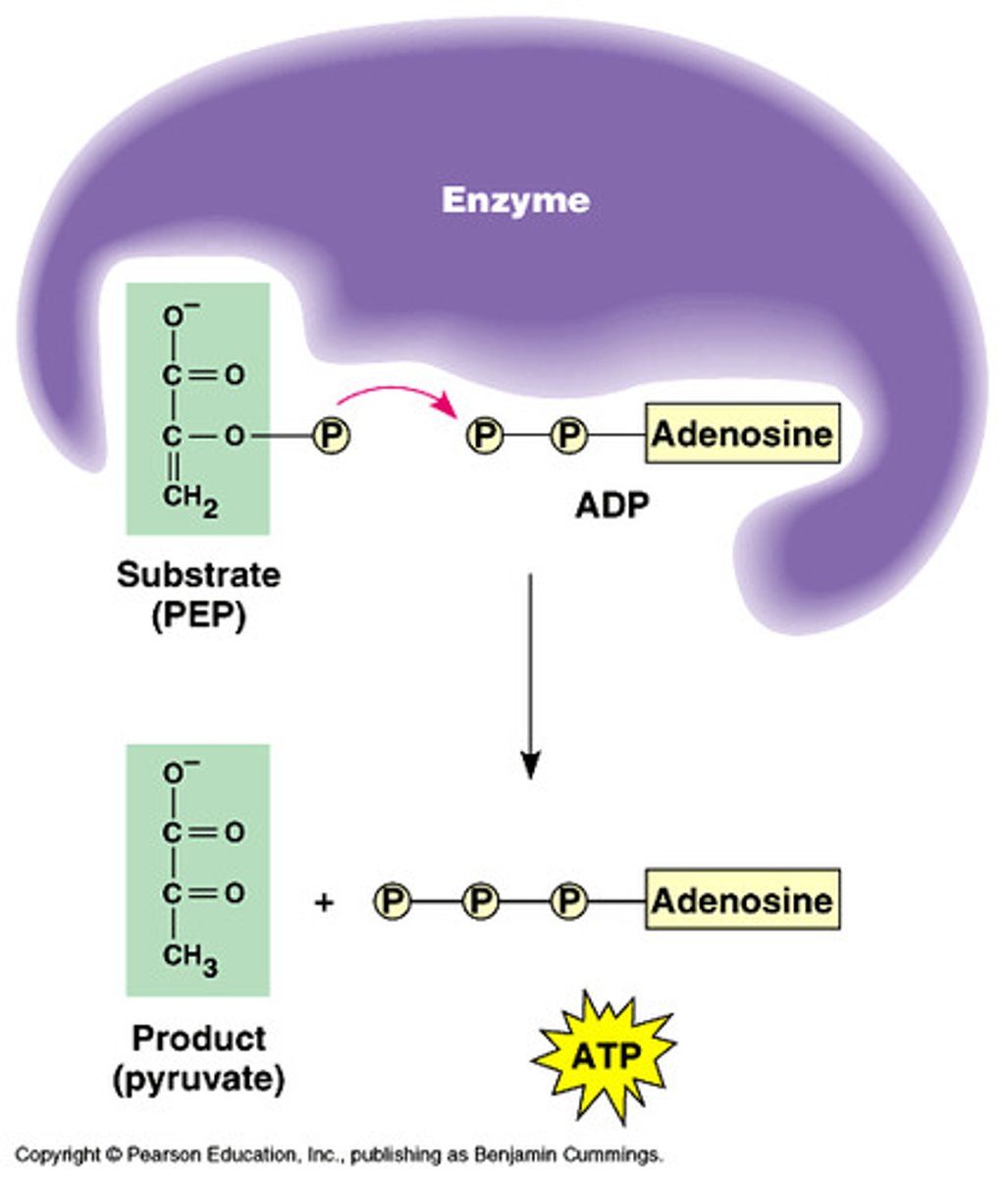
Pyruvate
Organic compound with a backbone of three carbon atoms. Two molecules form as end products of glycolysis
Link reaction
a decarboxylation reaction that occurs in the mitochondrion between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle.
Acetyl CoA
the entry compound for the citric acid cycle in cellular respiration, formed from a fragment of pyruvate attached to a coenzyme
Kreb's Cycle
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
FADH2
A molecule that stores energy for harvest by the electron transport chain.
NADH
An energy-carrying coenzyme produced by glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. NADH carries energy to the electron transport chain, where it is stored in ATP.
Electron Transport Chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP.
Mitochondrial Matrix
The compartment of the mitochondrion enclosed by the inner membrane and containing enzymes and substrates for the Krebs cycle.
inner mitochondrial membrane
The inner mitochondrial membrane is the innermost membrane of the mitochondria. Oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis take place at the inner mitochondrial membrane, which produces ATP via the flow of protons across the membrane.
intermembrane space
the fluid filled space between the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes
Chemiosmosis
A process for synthesizing ATP using the energy of an electrochemical gradient and the ATP synthase enzyme.
oxidative phosphorylation
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain; the third major stage of cellular respiration.
alcoholic fermentation
anaerobic process in which cells convert pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide and ethyl alcohol; carried out by many bacteria and fungi such as yeasts
lactic acid fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate to lactate (lactic acid) with no release of carbon dioxide.