Kinesiology: Physiology - Metabolism and Energy
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
energy
ability to do work
1st law of thermodynamics
energy can’t be created or destroyed only converted from a form to another
all energy on earth ultimately comes from the sun
macronutrient - carbohydrate
all carbs come from plant sources
can be simple or complex
simple: sugar and startch
complex
fibre and whole grain
4.3 kcal/g
sources: legumes, grains, sugars, stems & roots
macronutrient - carbohydrate: sugar
glucose
fructose
sucrose
maltose
macronutrient - carbohydrate; startch
long chains of glucose formed for storage
macronutrient - carbohydrate; glocogen
animal form of startch
macronutrient - carbohydrate; fibre
undigestible part of plant
macronutrient - lipids
long chains attached to glycerol
mono, di, and triglycerides
insulates
protects
membrane - controls what enters and exists
9.3 kcal/g
processed in liver
sources: meat, diary, coconut, nuts, avocado, legumes, fish, olives, seeds
macronutrient - lipids; glycerol
fatty acid chains
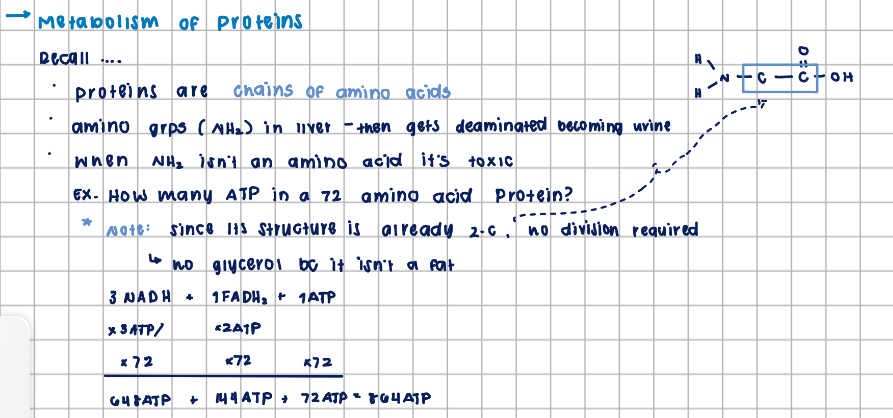
macronutrient - protein
key component made up of long chains of amino acids
20 diff amino acids
8 are essential
sources; meat, eggs, legumes
uses:
everything
muscle
11kcal/g
amino part of an amino acid is sent to the liver where it’s deaminated (urinated)
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
generated by cells through various processes most involving the metabolism of macronutrients
ATP → ADP + Pi + E
ADP
adenosine diphosphate
comes from ATP and when it turns to ADP, lots of energy is released
Cellular respiration
Biochemical process which cell breaks down GLUCOSE into its components & uses energy released to form ATP
Glycolysis
Occurs in the cytoplasm & is anarobic
series of biochemical reactions (10) that turn 1 molecule of glucose (6c) into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid
1st & 3rd steps involve the consumption of atp where it phosphorylates the glucose molecules
Following 7 steps, 4 new atp molecules are formed
Process is anaerobic but most times sufficient O2 is present
pyruvate proceeds to next stage → Kreb’s cycle where pryruvate becomes lactic acid
In short bursts (1-2mins) with rest between lactic acid is removed from muscle & brought into liver & safely metabolized but if anabolic activity persists, the lactic acid builds up in muscles stopping function
Kreb’s Cycle
Aerobic process that occurs in the mitochondrial matrix
pyruvate is decarboxylated forming acetyl-CoA (2-C molecule)
Acetyl-CoA joins with oxaloacetic acid (4C) to make citric acid (6C)
Oxaloacetic acid is reformed to start cycle again
Cycle happens twice since there is 2 pyruvate
2 NADH + 2ATP (glycolysis)
8NDH + 2 ATP + 2FADH2 (krebs)
10 NADH + 4ATP + 2FADH2
Electron Transport Chain
Aerobic process directly involving O2 that occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane
embedded in membrane are a series of biomolecules
NADH & FADH2 are passed along a sequence of membrane molecules & @ certain spots the H+ ions are passed through the membrane and form water
Protons fuel phosphorylation of ADP
For every NADH, 3 ATP forms
Every FADH2, 2 ATP forms
10NADH + 2 FAH2 + 4ATP
X3 atp. X2atp. 4atp
38 ATP
Metabolism of lipids - glycerol

Metabolism of lipids - fatty acid

Metabolism of Proteins
Energy systems during exercise - cellular respiration
Full aerobic breakdown of glucose to form max amount of ATP
main source of energy in endurance activities (3 mins+)
Energy systems during exercise - anaerobic glycolysis
Glycolysis as previously discussed but in a low O2 environment
causes lactic acid to build up ( 30s - 3 min activity)
Energy systems during exercise - ATP PC system
Anaerobic where phosphocreatin can phosphorylation small amounts of ADP into ATP
1-15 seconds
Alactic
No breakdown of glucose so no lactate is produced
Phosphocreatin
Chemical that’s readily available in muscle cells
Muscle fibres types and energy - slow twitch
Contract and relax slowly but can maintain low tension for long periods of time
dark red - high blood supply
Contains lower levels of enzymes that break down glycogen into glucose
Suited for long distance
Muscle fibre types & energy - fast twitch
Contracts and relaxes quickly & generates high tension for only short periods
pale - less blood supply
High enzyme muscles
Myoglobin
Protein that stores & delivers oxygen to working muscles
slow twitch muscles have a lot of myoglobin
Fast twitch muscles have less myoglobin