Interpersonal and Group processes
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Intro to Psych
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
what is social psychology?
the scientific attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings and behaviours of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined or implied presence of others
what are intrapersonal topics?
(those that apply to the individual) emotions and attitudes, the self and social cognition
what are interpersonal topics?
(those that apply to dyads and groups) helping behaviour, aggression, prejudice and discrimination, attraction and close relationships
what is social influence?
any change in an individual’s thoughts, feelings or behaviours caused by other people, who may be actually present or whose presence is imagined, expected or only implied
what are the 3 types of social influence?
conformity: a change in behaviour caused by the perception of others
compliance: a change in behaviour that is requested by another
obedience: a change in behaviour that is ordered by another
conformity?
the tendency for individuals to change their behaviour/ beliefs to align with the majority even when they personally disagree
Asch (1950): 76% conformed to group pressure at least once by indicating the incorrect line
why do people conform?
normative influence: public conformity to gain social approval
informational influence: believing the group know better
compliance?
a change in a person’s behaviour in response to a direct request
going along with a request/ demand even if you do not agree with the request
why do people comply?
reciprocity
liking
scarcity
social proof/ consensus
authority
consistency and commitment
consistency and commitment?
we are motivated to appear consistent in our words and actions
foot-in-the-door technique: get someone to agree to a small request, then they will agree to a larger one
Freedman and Fraser (1966): 112 California residents asked to display a drive carefully sign in their front garden, simply ask- 16% agreed, small sign first then ask- 55% agreed
liking?
we are more likely to comply when requesters are dressed similarly to us or physically attractive
Burger et al (2004): random similarity increases compliance, students who believed they shared a birthday/ first name/ fingerprint similarities were more likely to comply
heuristic processing
authority?
people comply more with requests made by individuals in a position of authority such as people who have power or expertise
clothes, titles etc give authority
Martin and Bull (2008): thematic analysis of midwives responses, junior wives completed a questionnaire on best practices and beliefs then later asked by senior midwife to perform actions they had previously opposed: 65% reflected obedience, 35% reflected conformity
obedience?
the change of an individual’s behaviour to comply with a demand by an authority figure
a tendency to follow orders from a person with a higher status within a defined hierarchical social system or chain of command
Milgram (1960s)- obedience?
40 male volunteers
Pps told to administer a shock whenever the learner got an answer wrong
shocks increased in 15 volt increments up to 450V
when experimenter instructed to continue, 65% shocked to the max voltage
location reduced obedience- 40% in run down office block
proximity reduced obedience- 40% same room, 30% placing hand on shock plate, 23% orders over phone
obedience reduced when victims humanity was made more clear and authority of experimenter was diminished
Hofling et al Hospital Study (1996)
nurses received a phone call from someone claiming to be a doctor asking them to administer 20mg of Astroten
a non approved drug, dosage was twice the label, instructions supposed to be given in person, doctor was unfamiliar
21/22 nurses who took the calls were ready to give the injection
no questions asked, just obeyed
group performance- social loafing?
exertion of less effort by a person working in aa group because individual performance cannot be evaluated separately from the group, thus causes performance to decline on easy tasks
Latane et al (1979): sat blindfolded pps in group of 6, had them put headphones on, pps asked to clap/cheer. 1/3 less noise when they thought others were also making noise
group performance- the bystander effect?
the tendency for individuals who witness someone in need to refrain from helping, instead remaining passive observers
feeling less personal responsibility to act
shaped by surrounding social context rather than personal traits
the case of Kitty Genovese
Latane and Darley (1968)- the bystander effect?
pps told they would discuss ‘problems faced by students in a high pressure urban environment’
discussion over intercoms: alone, with one or with four people
experimenter left the room
shortly after discussion began, one of the other “pps” on the intercom began to choke and appear to be having an epileptic seizure

what are the principles that can prevent helping?
evaluation apprehension: bystanders fear being negatively judged by others if they misinterpret the situation and there is no need for help
pluralistic ignorance: relying on others’ reactions to recognise the need for help in an ambiguous situation
diffusion of responsibility: the tendency to refrain from helping when others are present due to a reduced feeling of responsibility
encouraging intervention- Coker et al (2011)?
teaches to recognise red dots and to take action using green dpts
46% had attended a green dot talk on campus
14% had taken part in active bystander training in the past two years
trained students showed lower acceptance of rape myths, reported more active bystander behaviours and also observed more active bystander behaviours than untrained peers
what is social facilitation- Zajonc (1969)?
being in the presence of other improves individual task performance
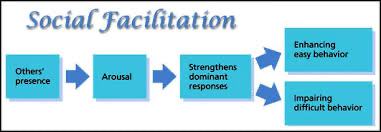
what is social inhibition?
decreased performance in the presence of others
what is the dominant response?
the reaction elicited most quickly and easily by a given stimulus