Brain structures (week 1)
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
Behavioural Neuroscience
Study of the neural basis of behaviour in humans and animals.
Neuroscience
scoentific study of the nervous system
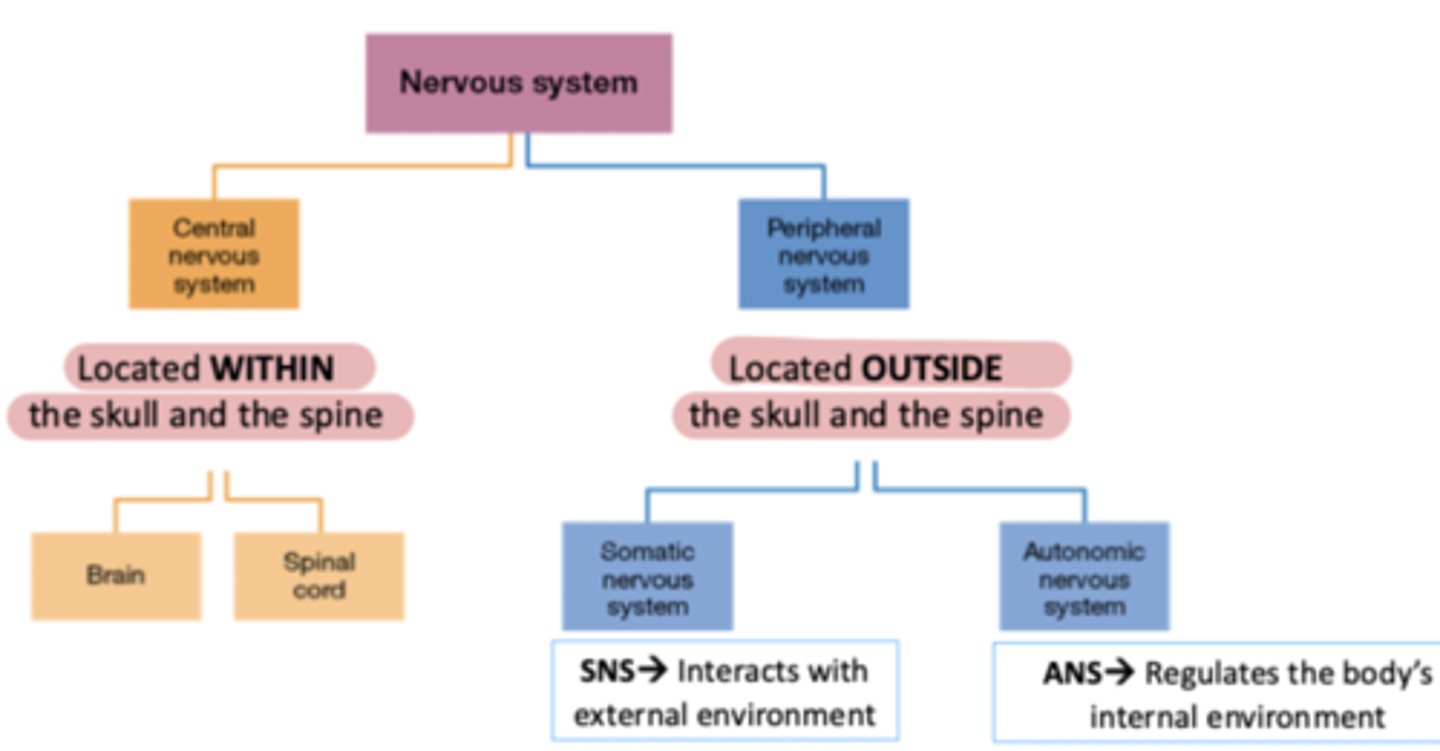
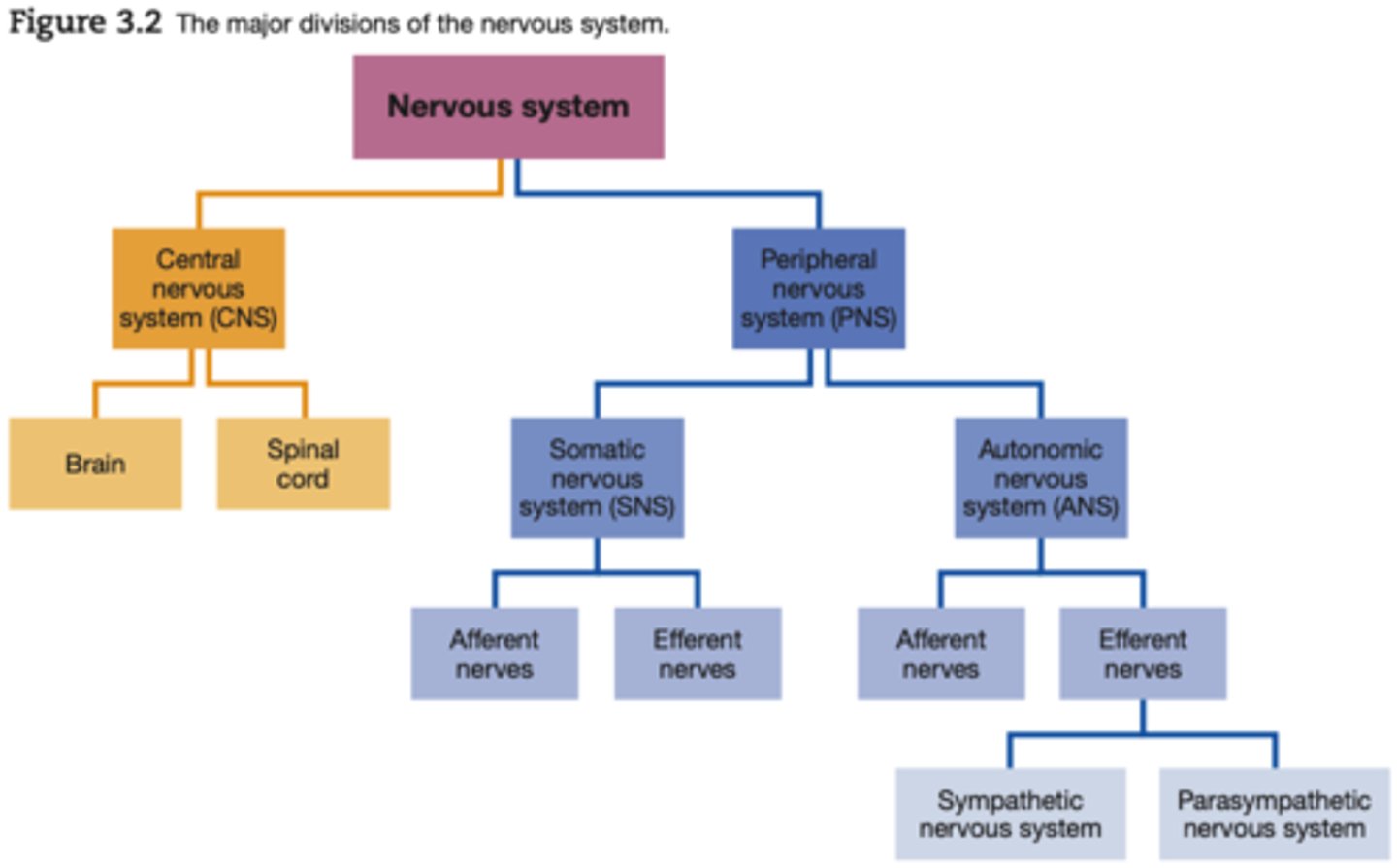
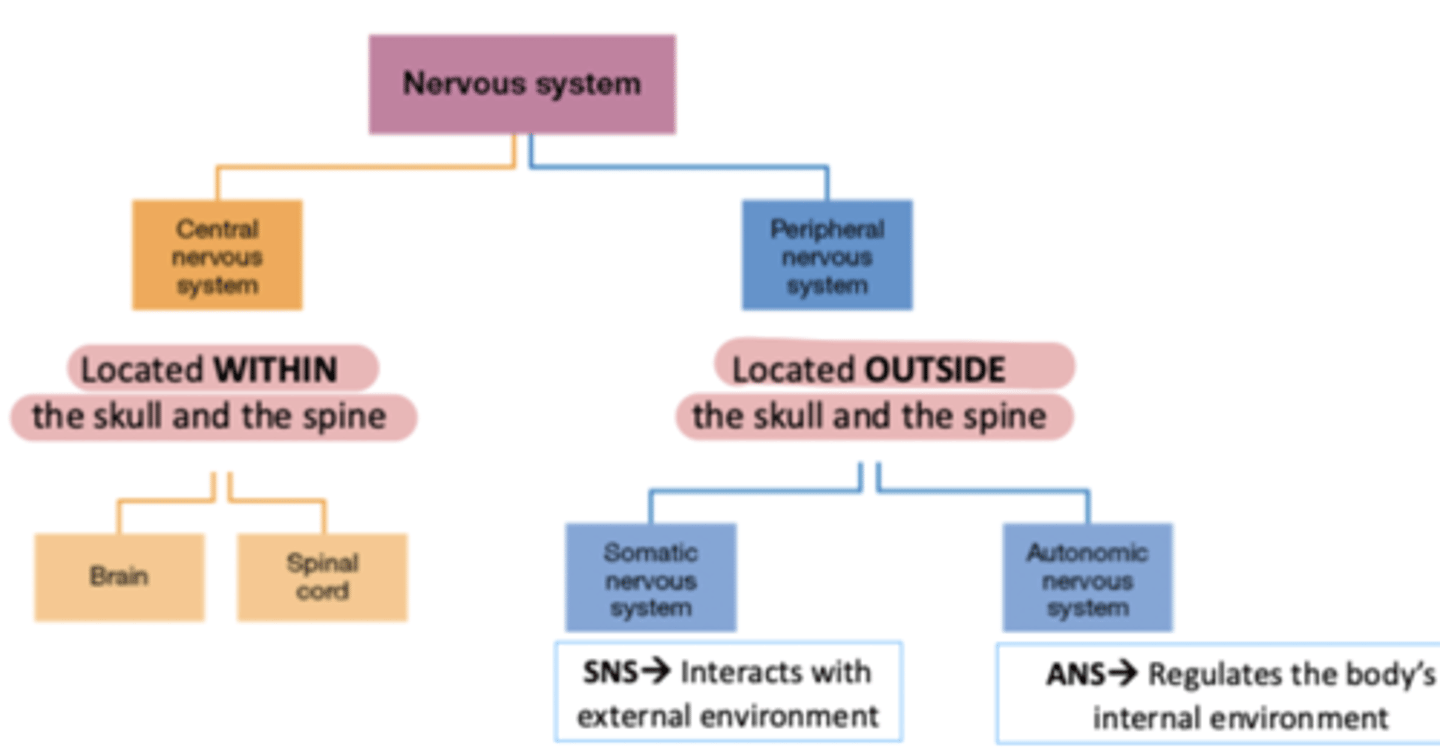
The Central Nervous System (CNS) is located where?
Located WITHIN the skull and the spine
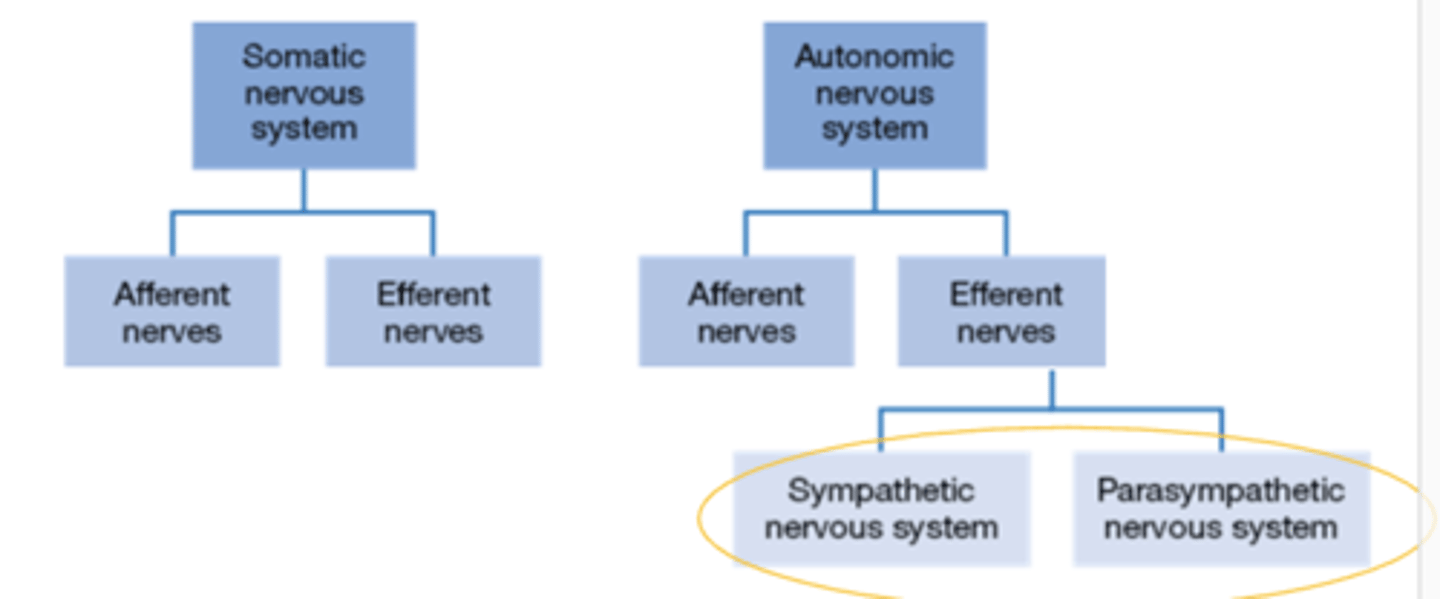
sympathetic nerves
are autonomic motor nerves that project from the CNS in the lumbar (small of the back) and thoracic (chest area) regions of the spinal cord.
parasympathetic nerves
are those autonomic motor nerves that project from the brain and sacral (lower back) region of the spinal cord.
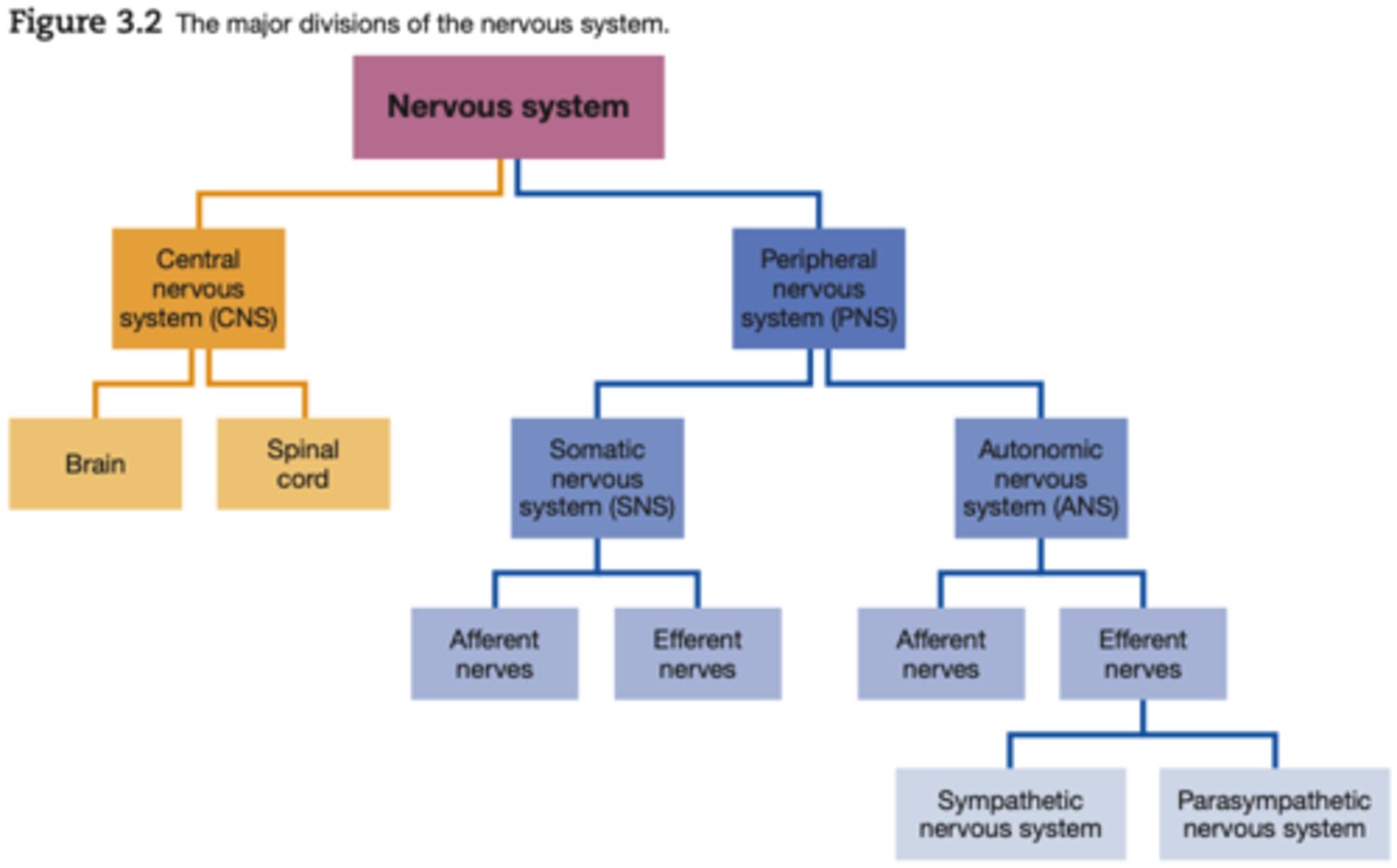
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is located where?
Located OUTSIDE the skull and the spine
Neurons
cells that receive and transmit electrochemical signals
Somatic Nervous System (SNS) interacts with?
Interacts with external environment
composed of afferent nerves to send signals from skin, skeletal muscles, eyes, etc to the CNS; and efferent nerves to send motor signals from the CNS to the skeletal muscles
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) interacts with?
Regulates the body's internal environment
composed of afferent nerves to carry sensory signals from internal organs to CNS; and of efferent nerves to send motor ignals from CNS to internal organs.
Afferent nerves
towards the CNS (approach)
Efferent nerves
from the CNS (Exit)
Anatomical Directions
are described in relation to the orientation of the spinal cord
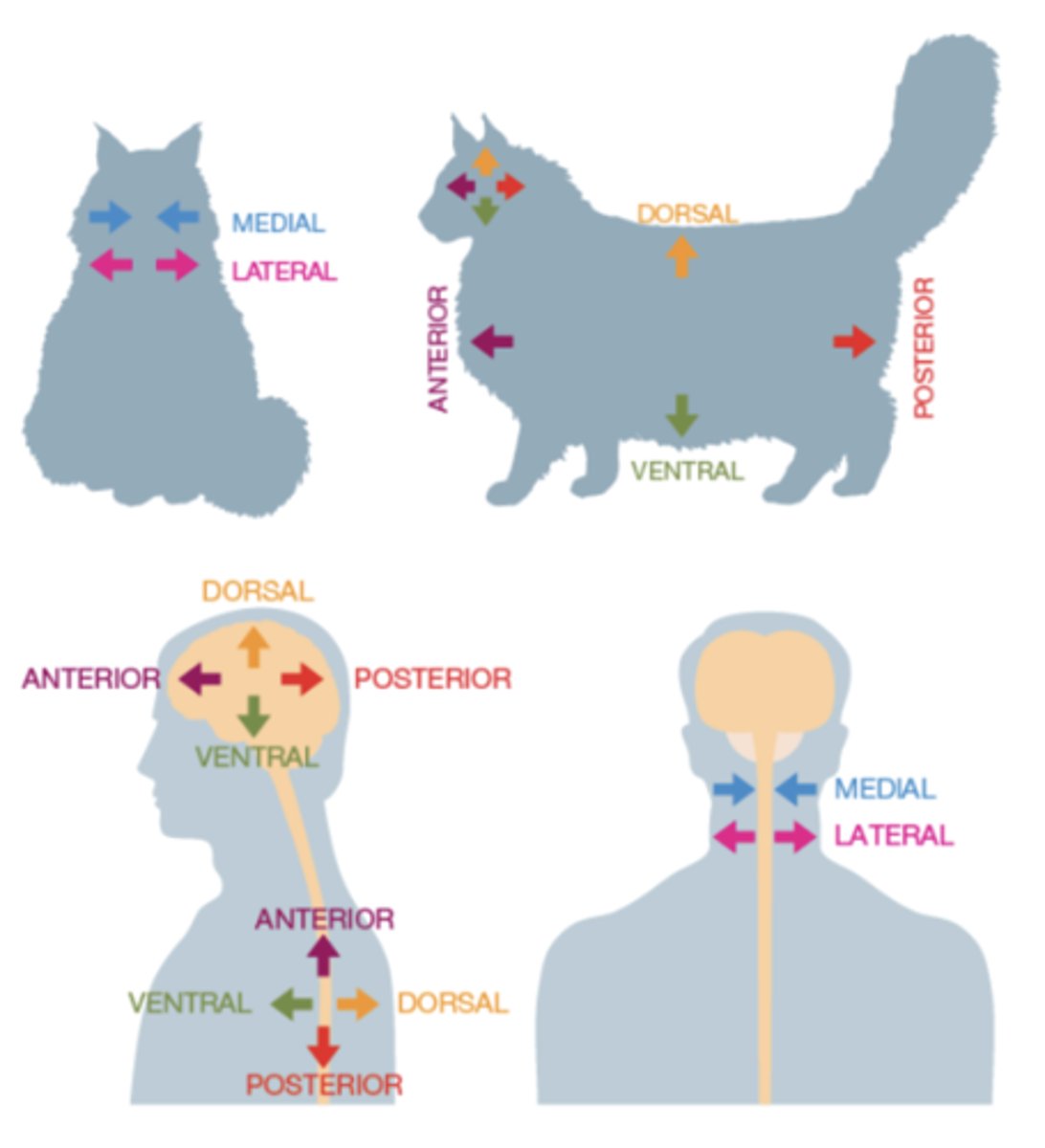
Anterior
front
Posterior
back
Dorsal
toward top/ at back
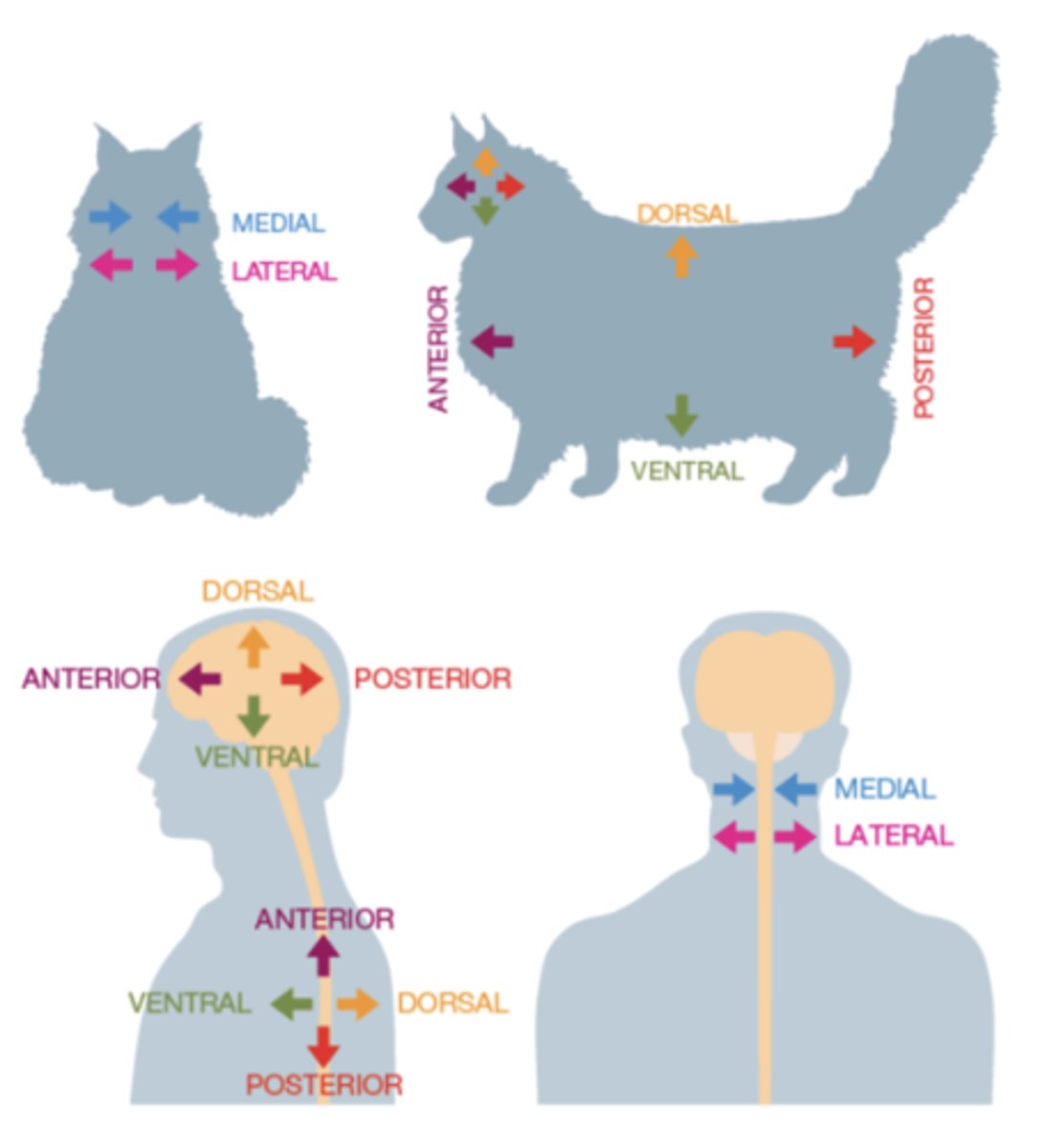
Ventral
under/ belly/ front
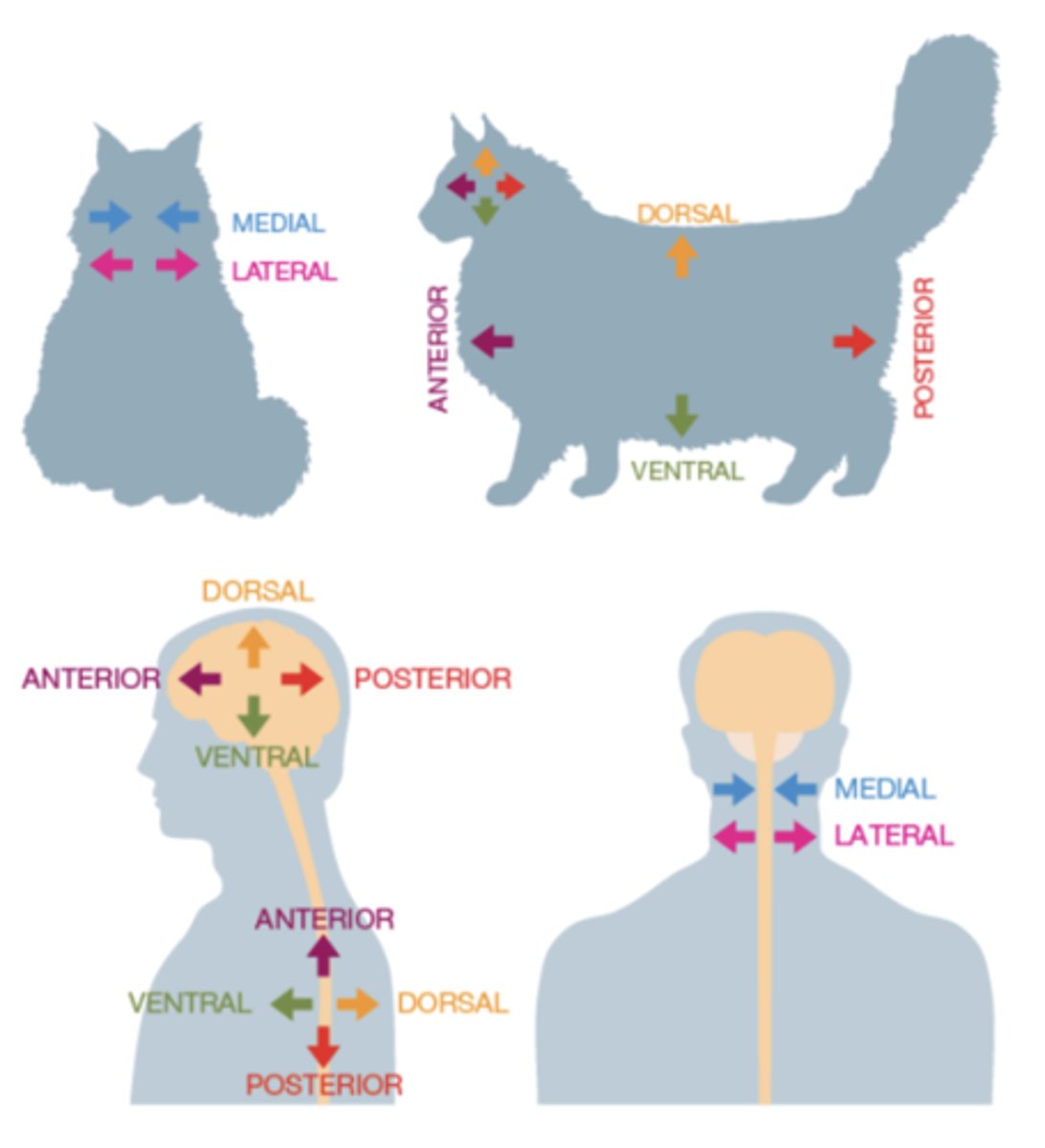
Medial
towards the midline
Lateral
away from the midline
Proximal and distal are two other common directional
terms - what do they mean?
closel; far
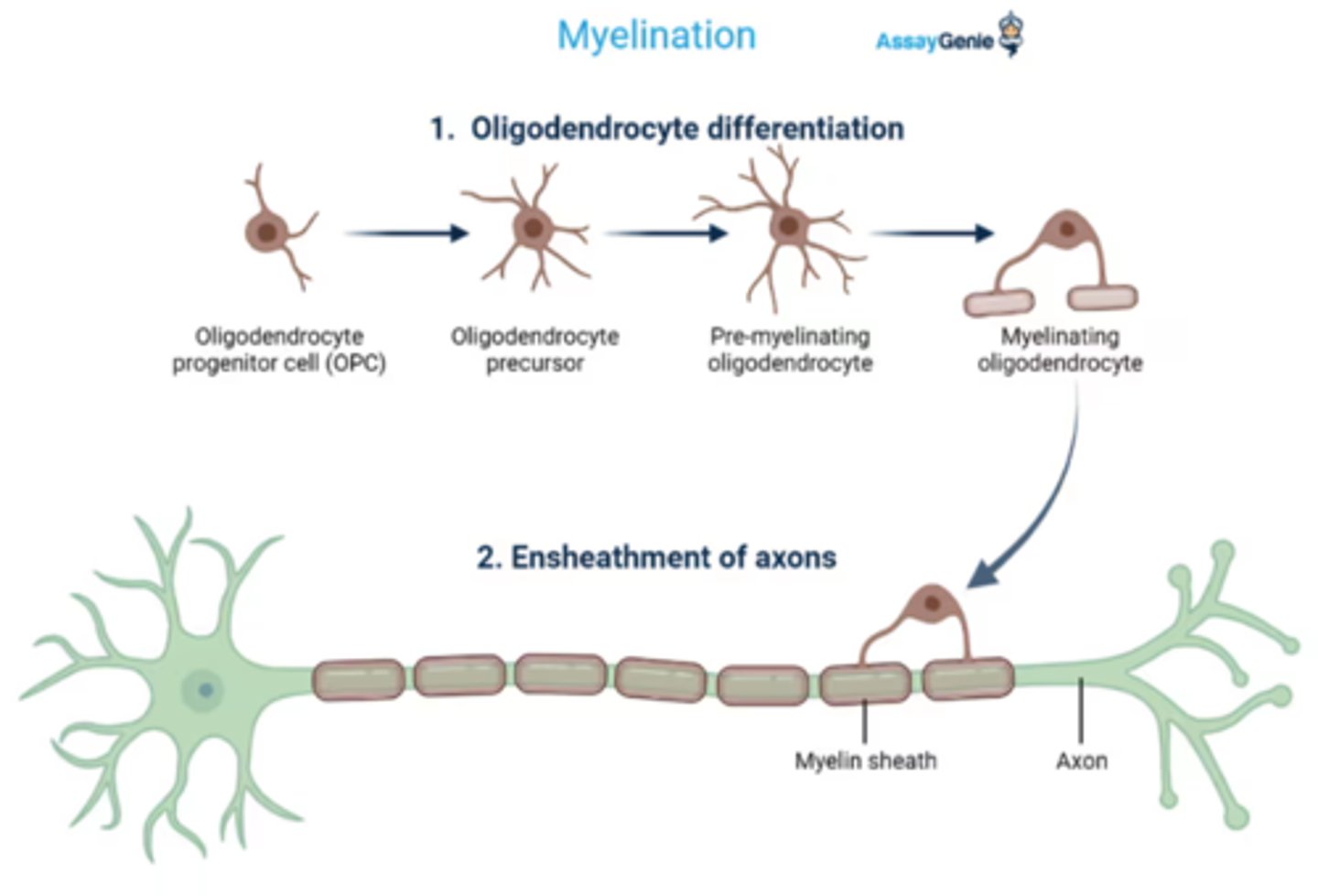
Myelin
fatty substance
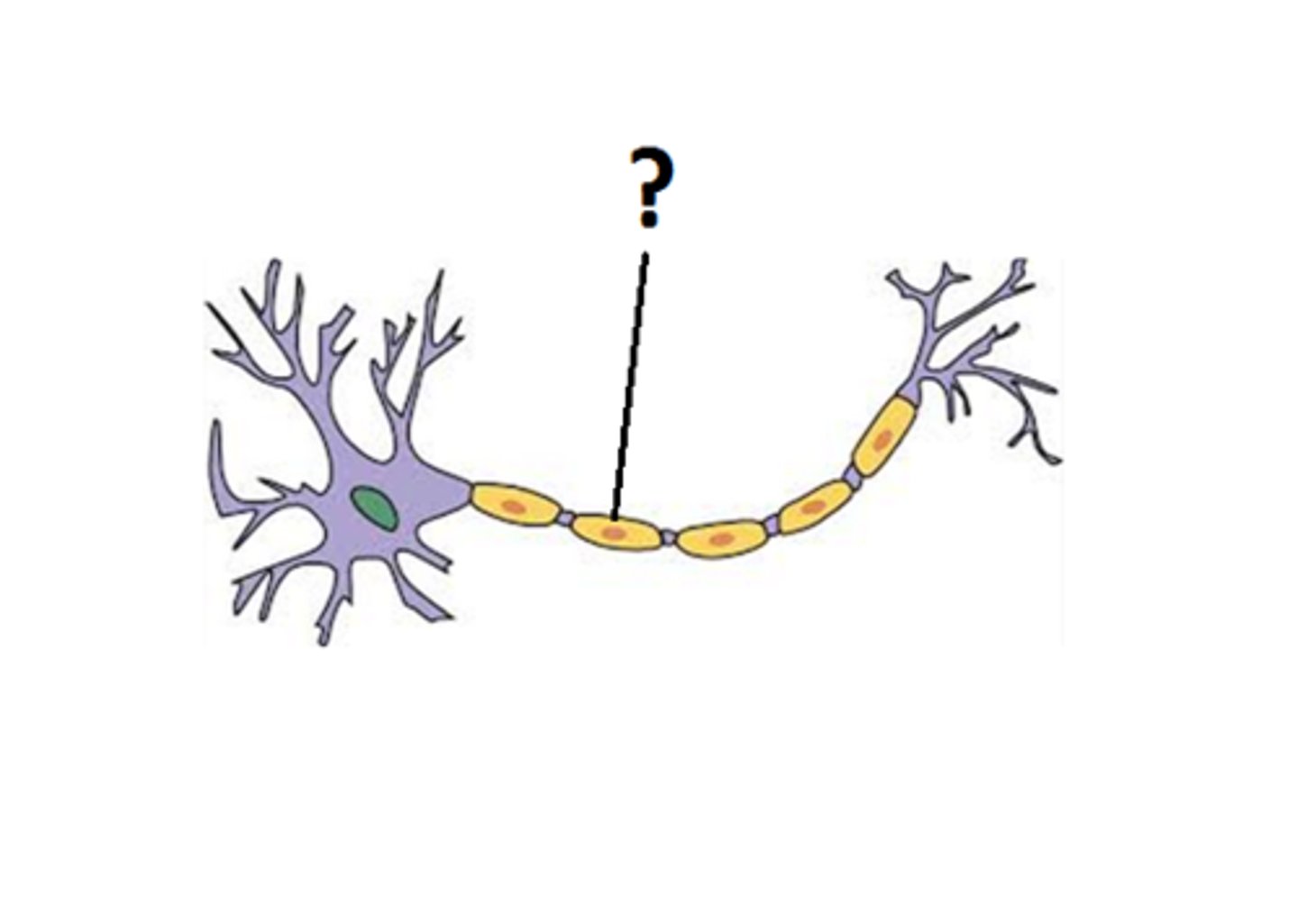
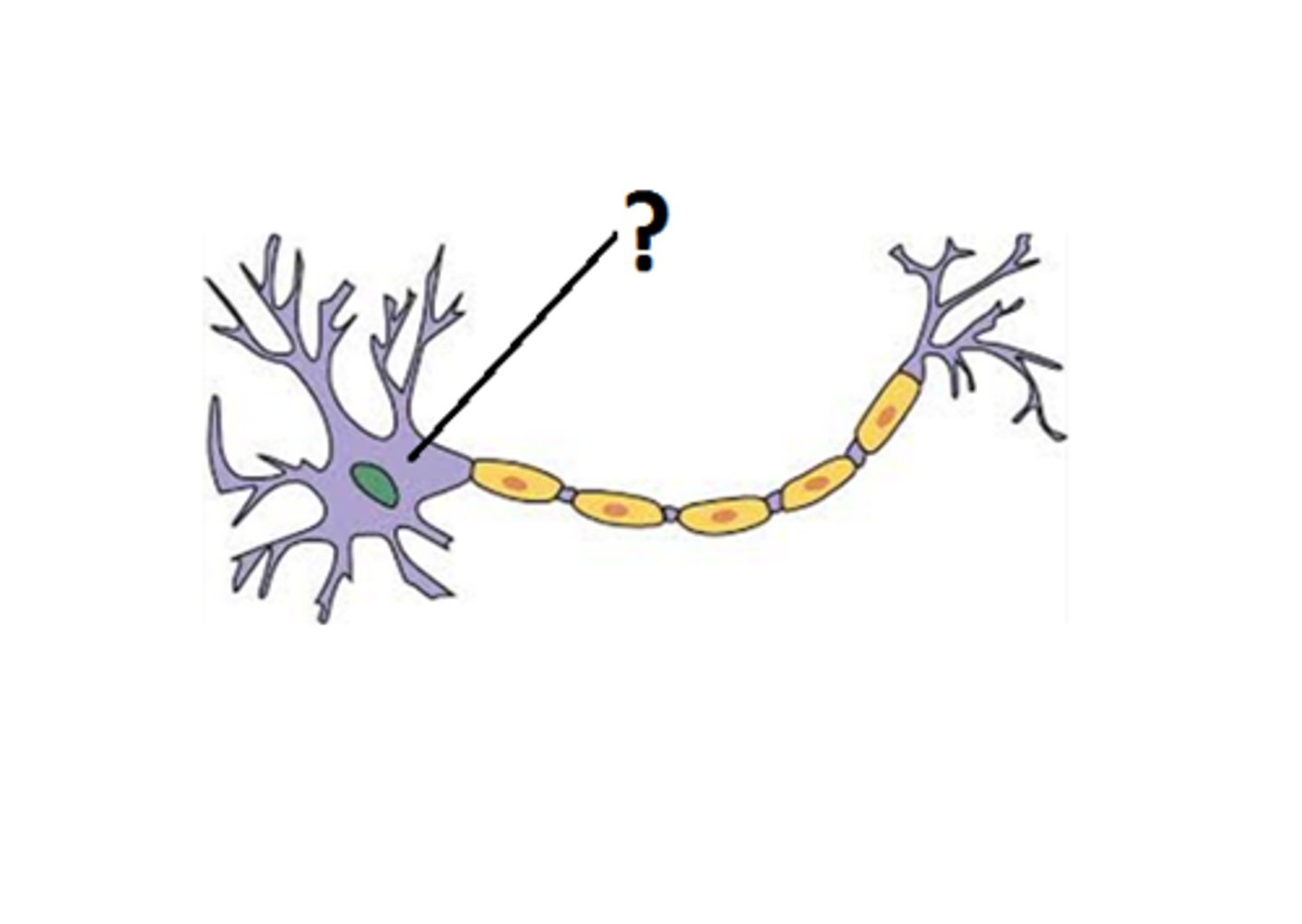
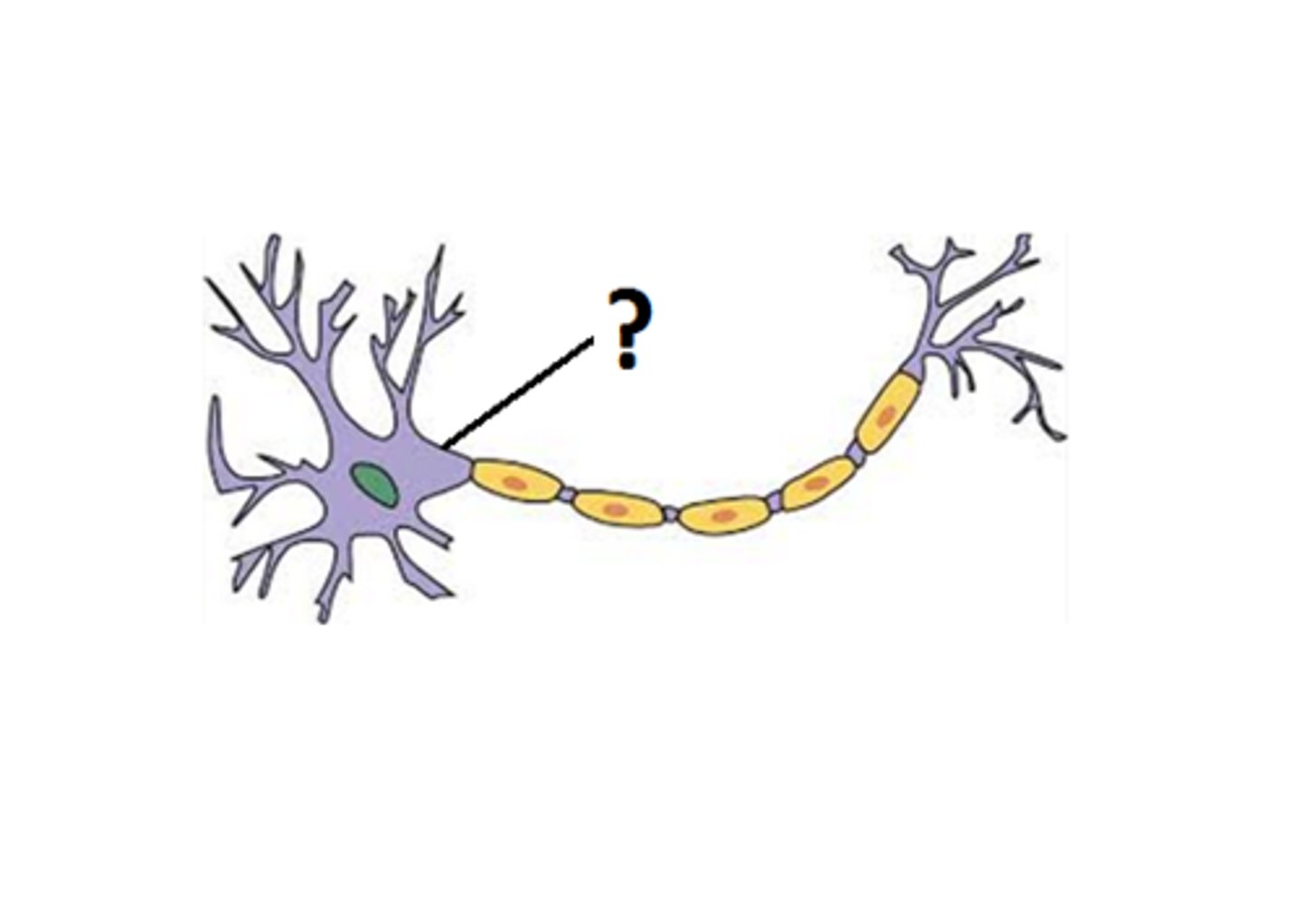
Soma
cell body
Axon
cone-shaped region
Encephalon
within the head
Golgi complex
packaging membranes
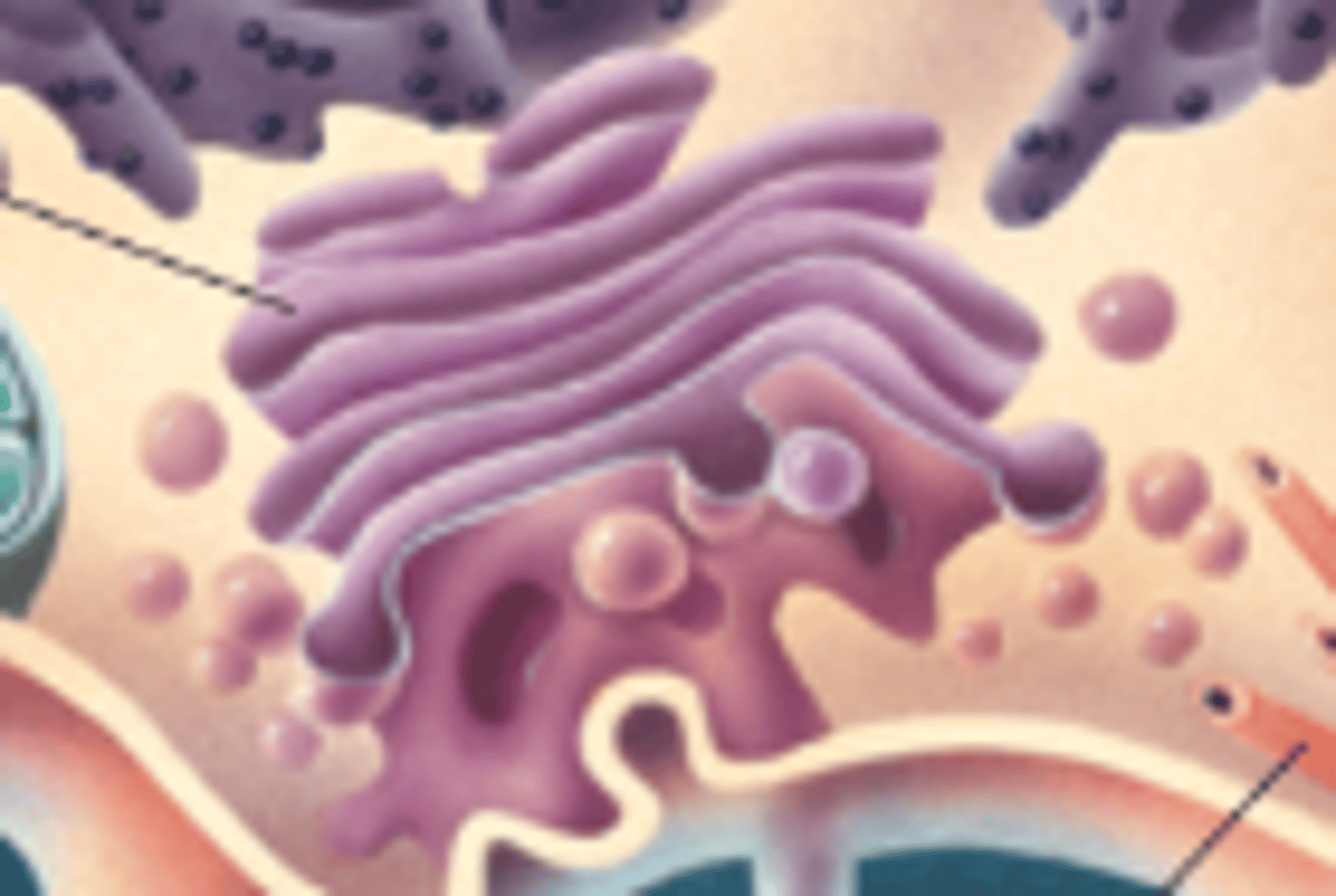
ribosomes
protein synthesis

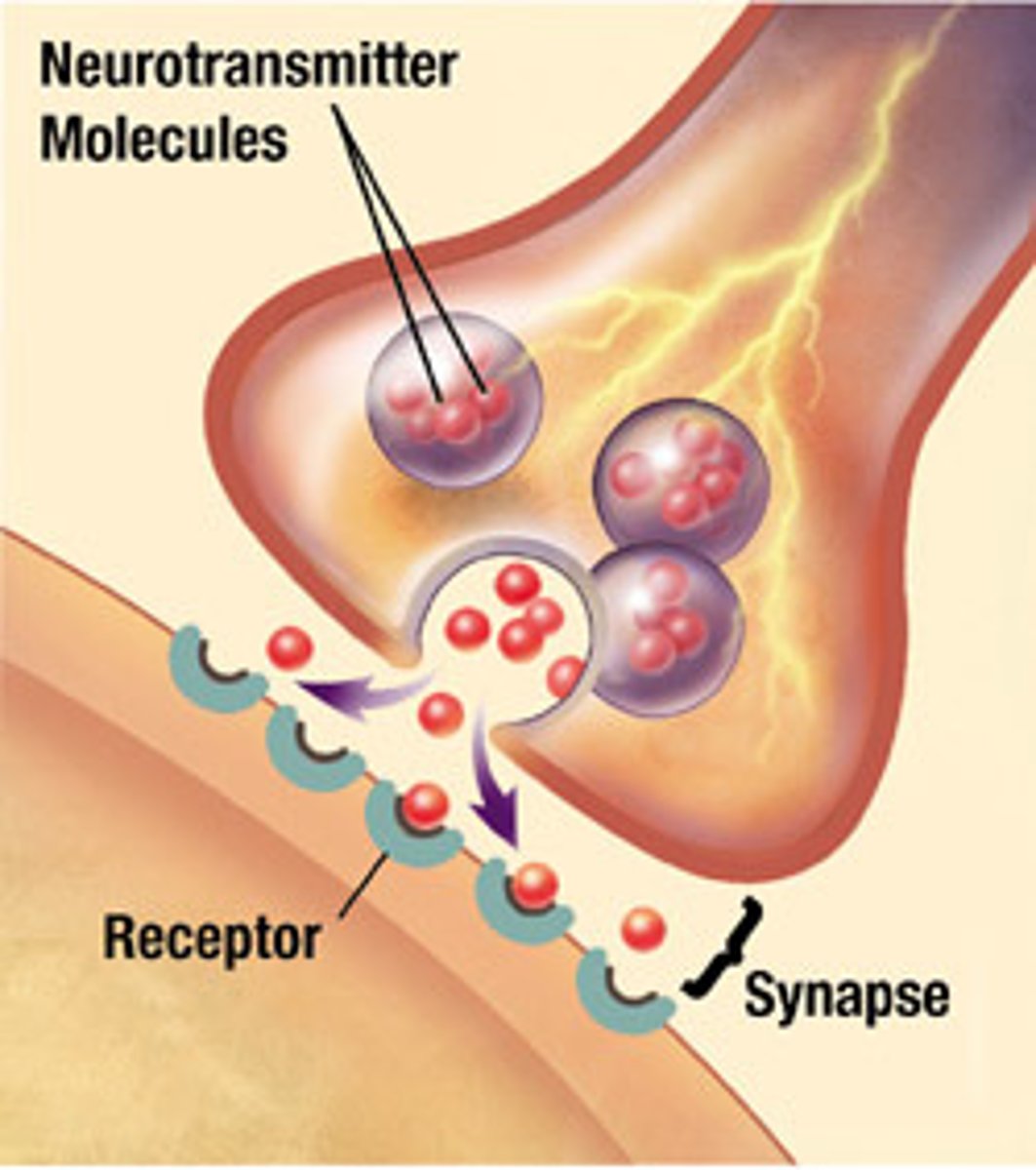
synapses
gaps
glial cells
the forgotten cells
synaptic vesicles
neurotransmitter storage
astrocytes
largest glial cells
ganglia
In the peripheral nervous system (PNS), a cluster of neuron cell bodies
oligodendrocytes
CNS myelinators
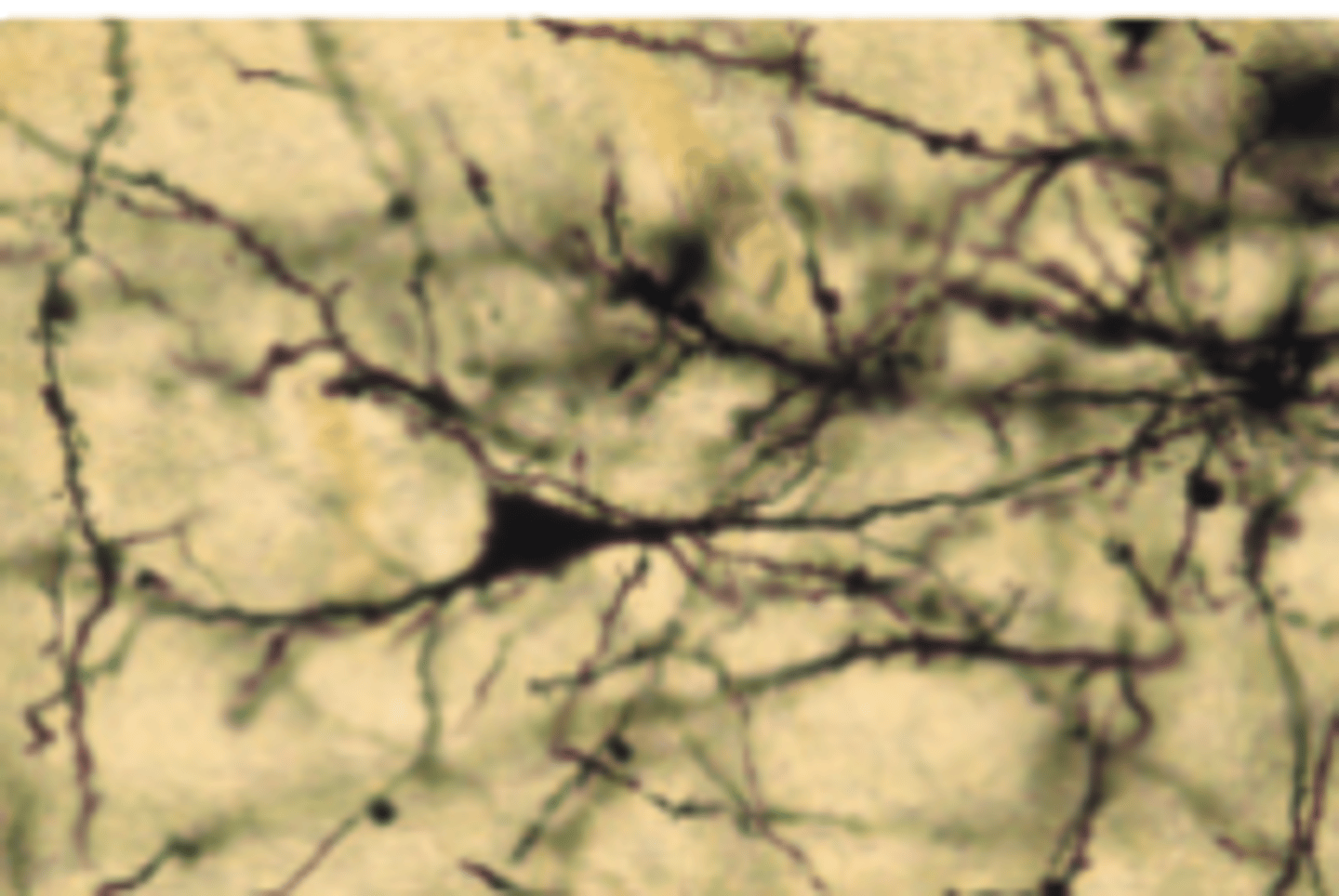
Golgi stain colour
black
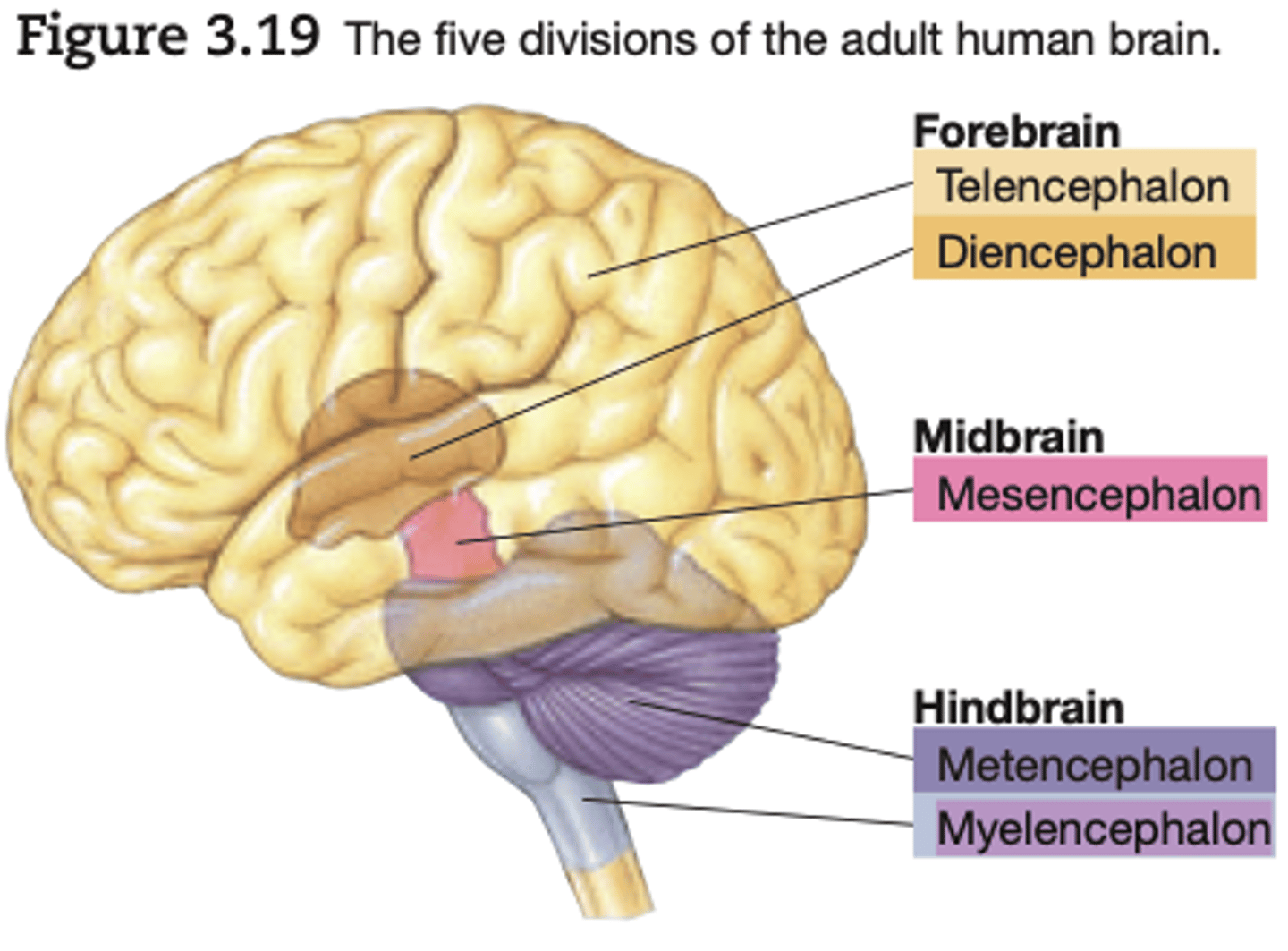
Forebrain Division
Telencephalon
Diencephalon
Midbrain Division
Mesencephalon
Hindbrain Division
Metencephalon
Mylencephalon
gray matter of spinal cord
is composed largely of cell bodies and unmyelinated interneurons
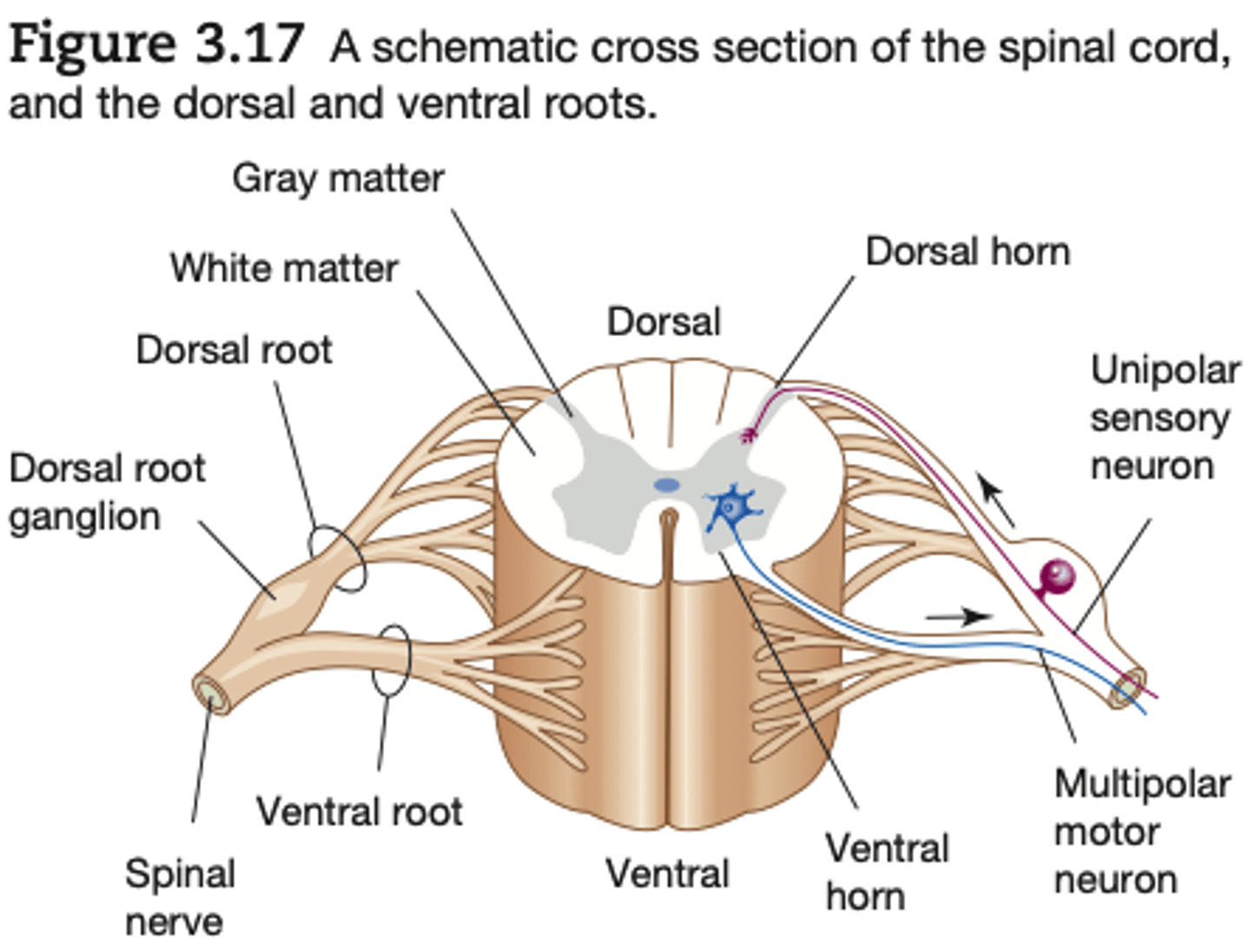
white matter of spinal cored
composed largely of myelinated axons. (It is the
myelin that gives the white matter its glossy white sheen.)
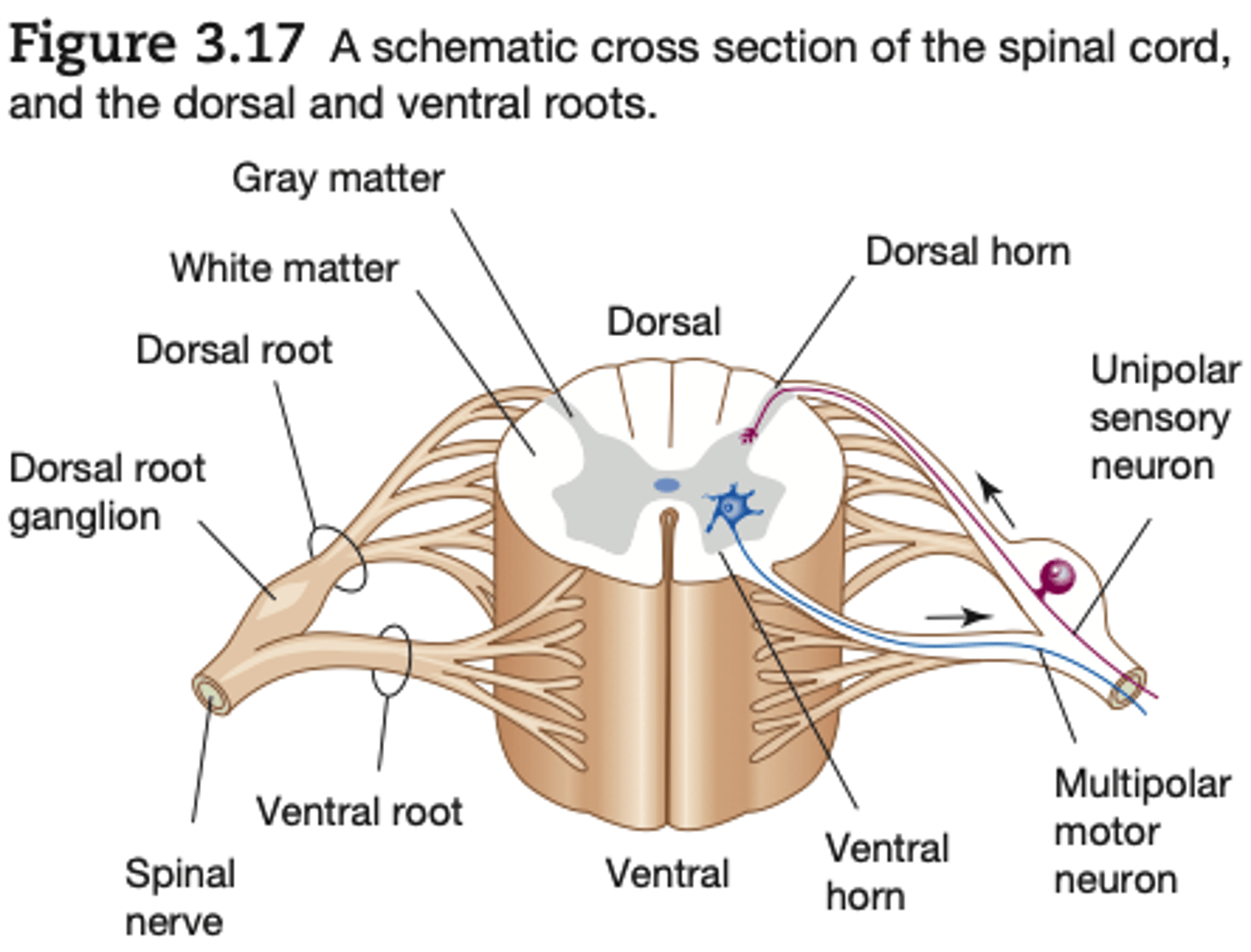
The two dorsal arms of the spinal gray matter are called the
dorsal horns
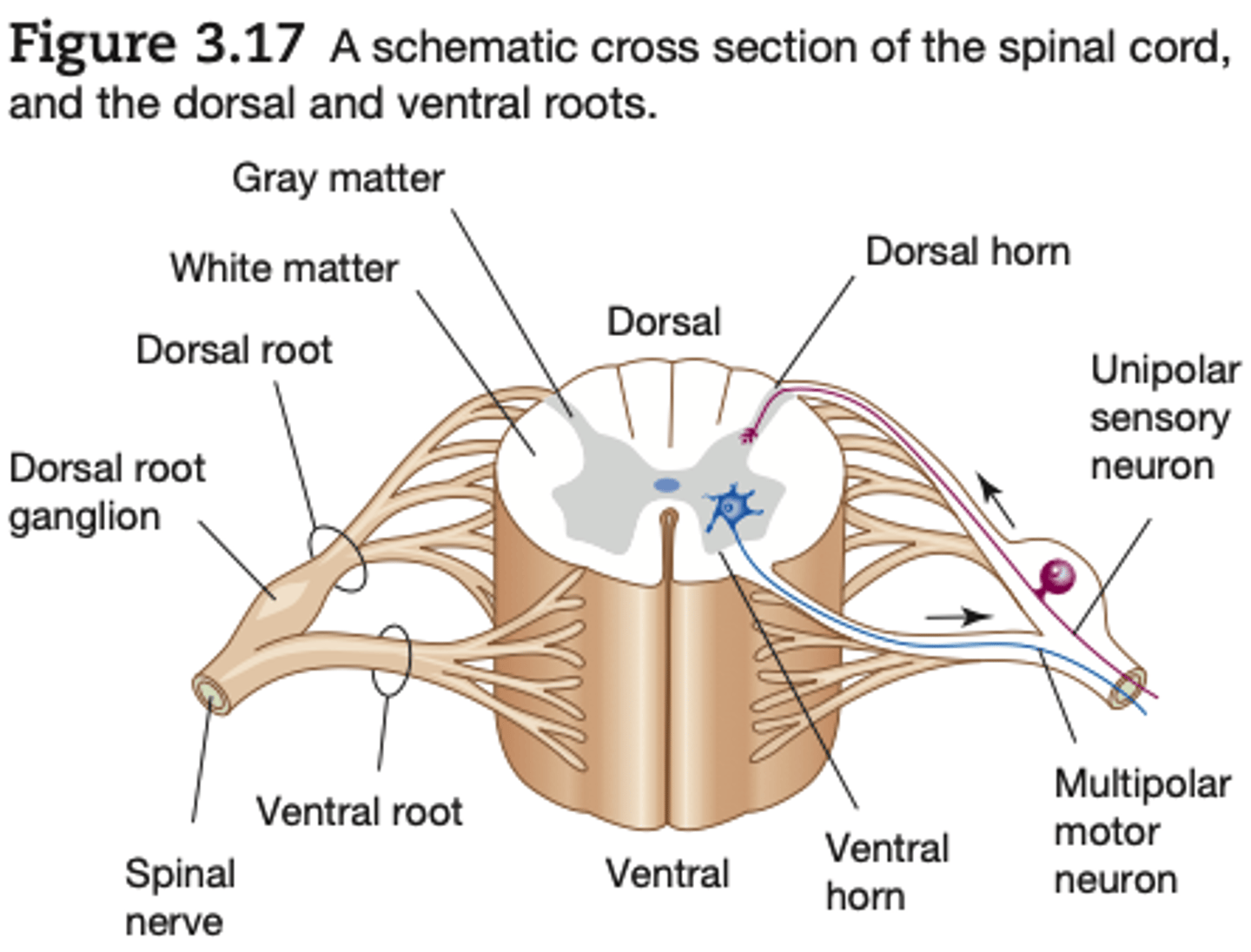
the two ventral arms are called the
ventral horns.
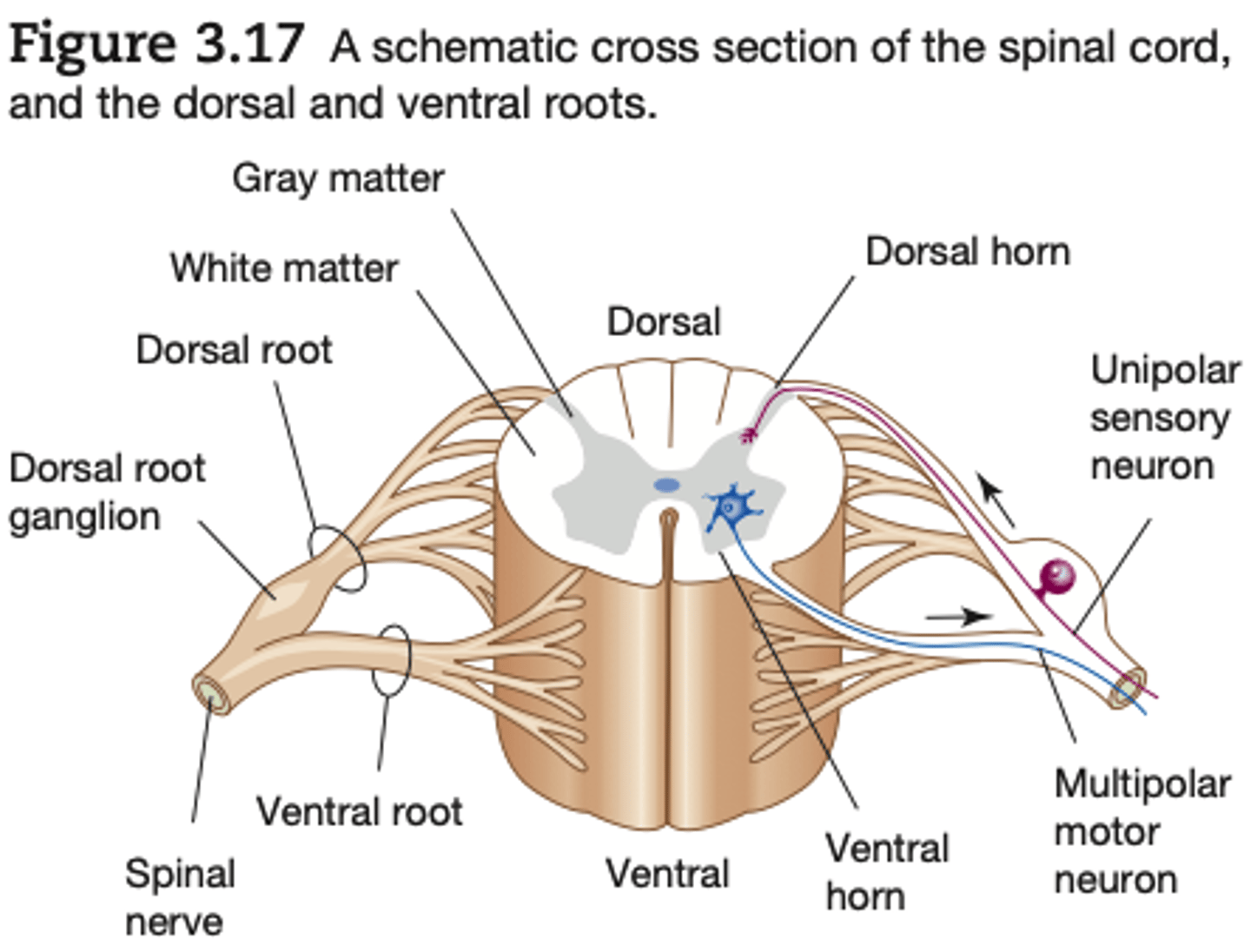
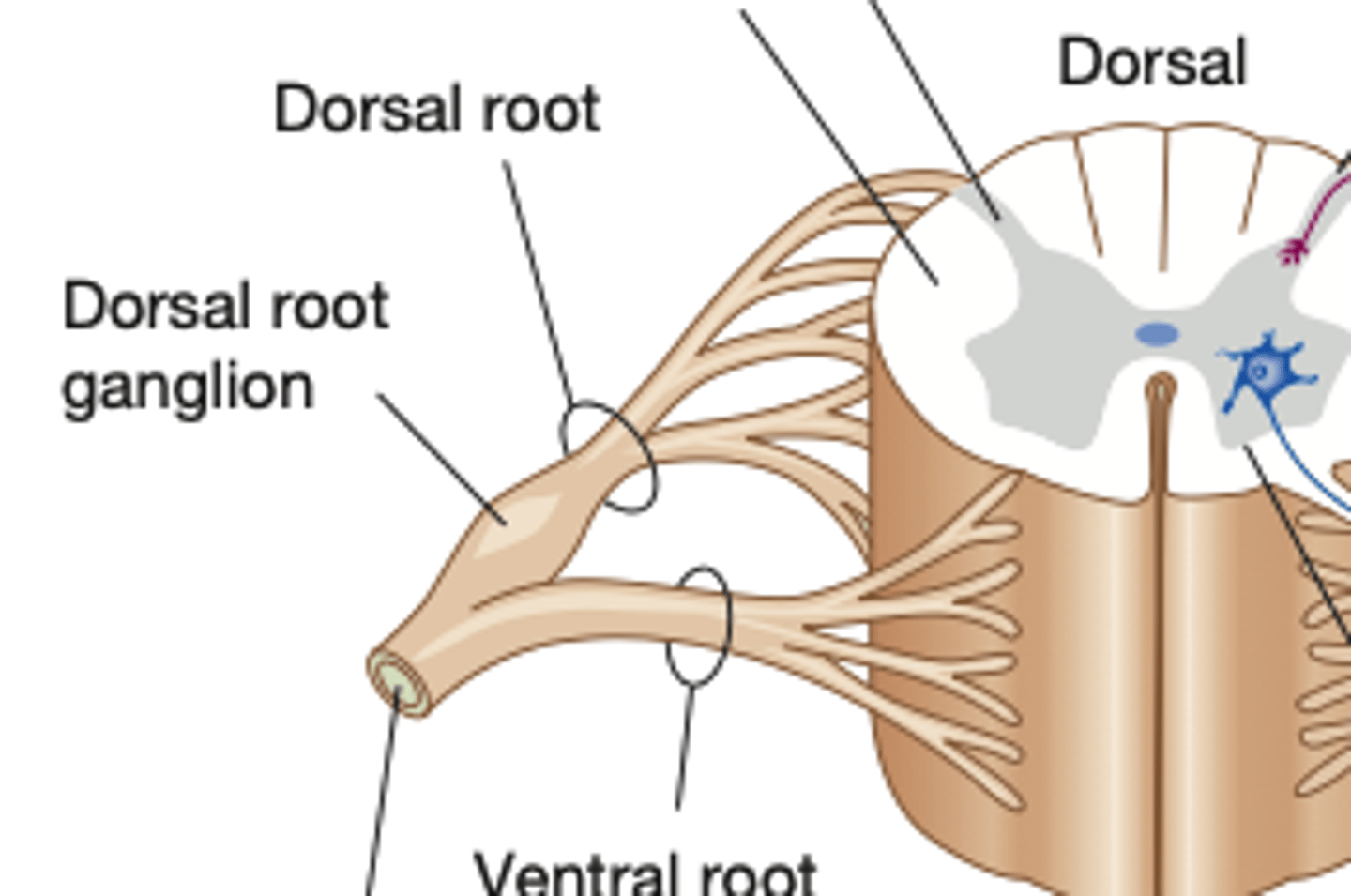
All dorsal root axons, whether somatic or autonomic, are sensory (afferent) unipolar neurons with their cell bodies grouped together just outside the cord to form the
dorsal root ganglia
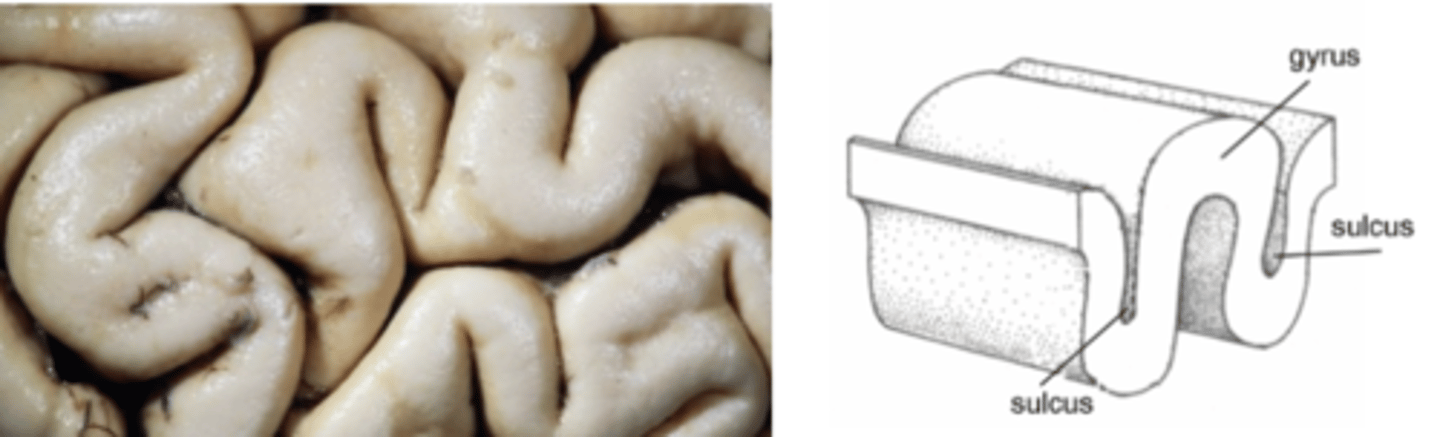
Gyrus
Bump or ridge
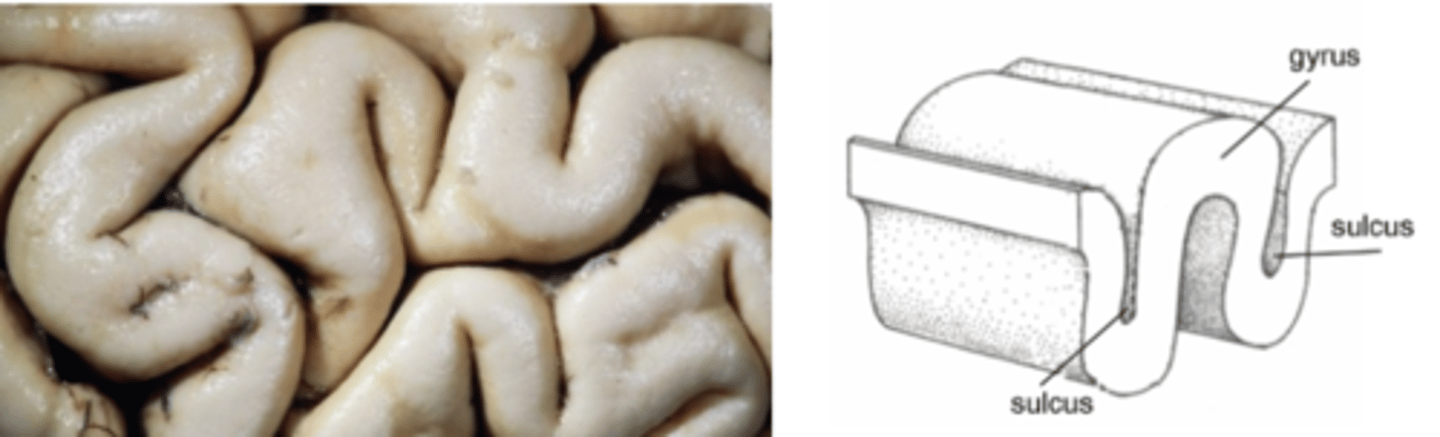
Sulcus
small furrow
Fissure
large furrow; the largest of which the "longitudinal fissure" - almost seperates the 2 hemispheres → groove
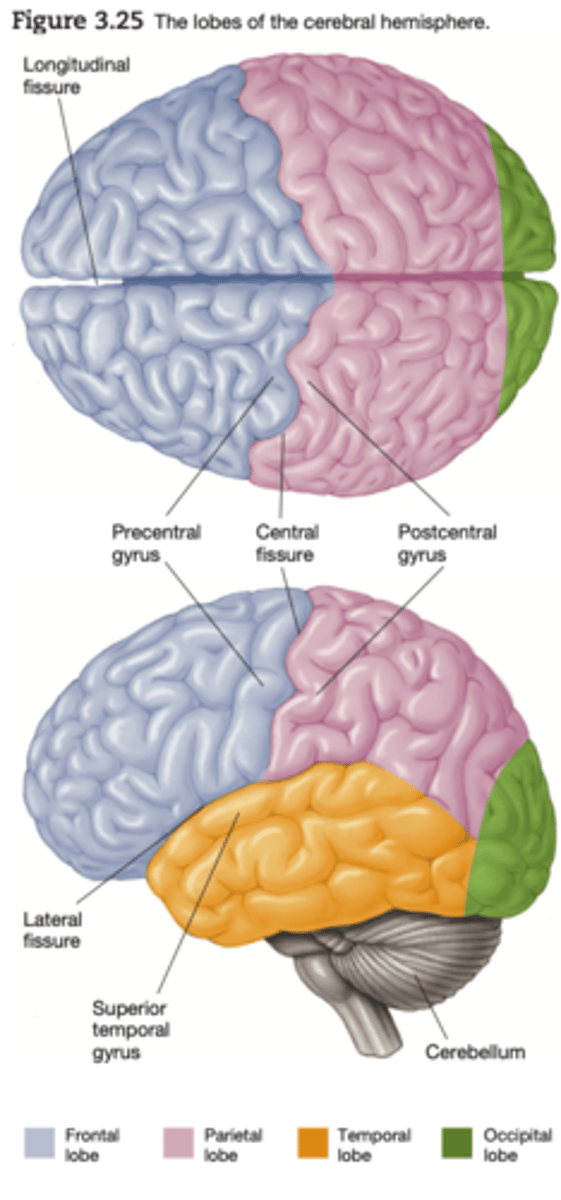
Major Divisions of the Cerebral Cortex: Frontal Lobe
executive functions, thinking, planning, organising and problem solving, emotions and behavioural control, personality.
What are the 5 divisions of the adult human brain
forebrain - Telencephalon & Diencephalon
midbrain - Mesencephalon
hindbrain - Metencephalon & Myelencephalon
Myelencephalon
the myelencephalon (or medulla), the most posterior division of the brain, is composed largely of tracts carrying signals between the rest of the brain and the body.
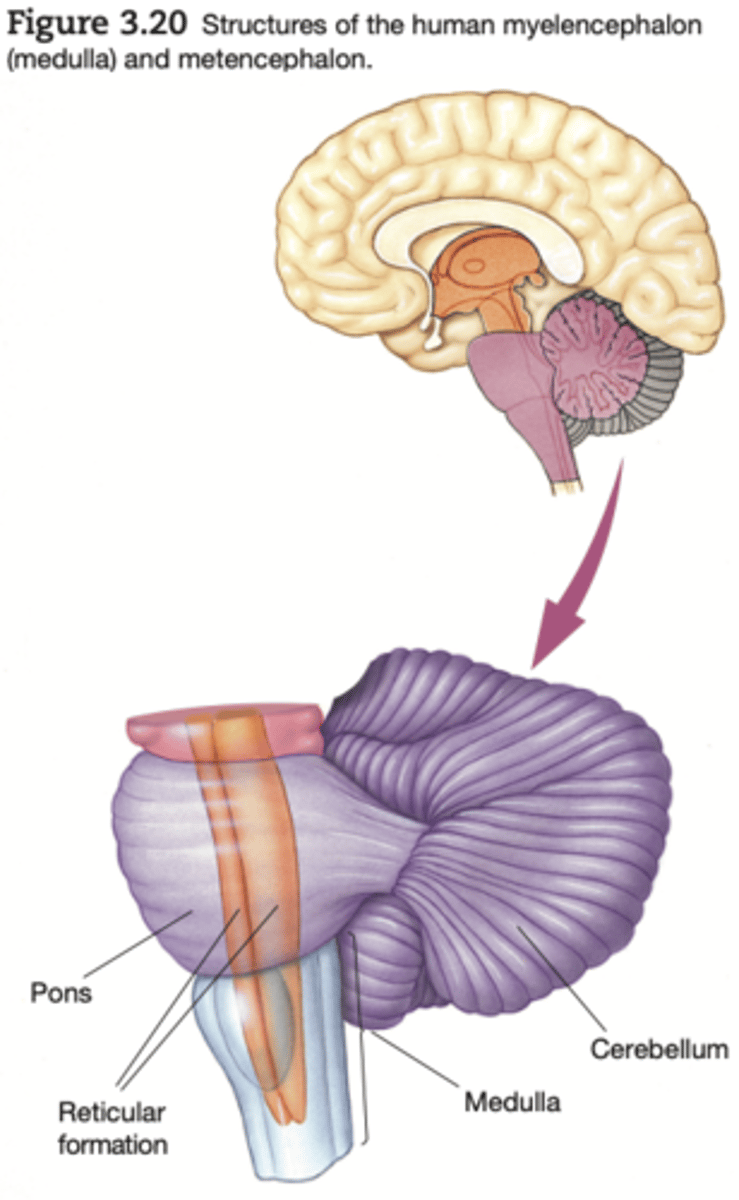
reticular activating system (reticular formation)
the part of the brain that is involved in attention, sleep, and arousal
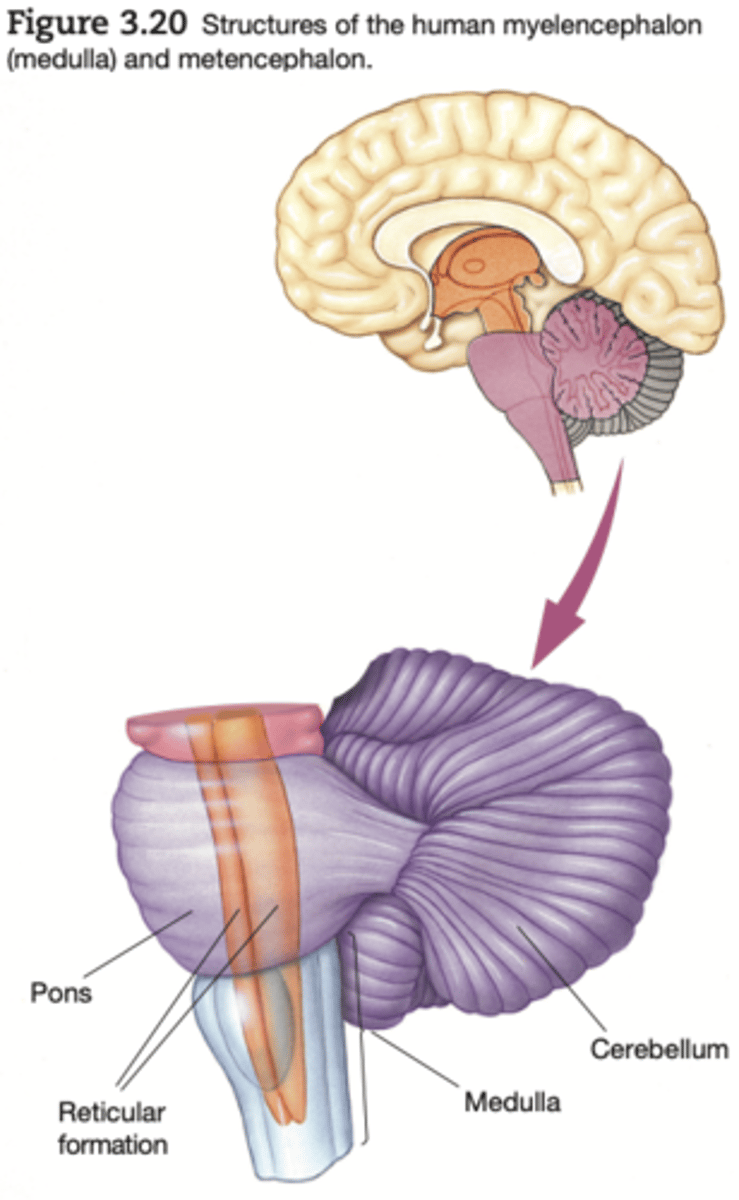
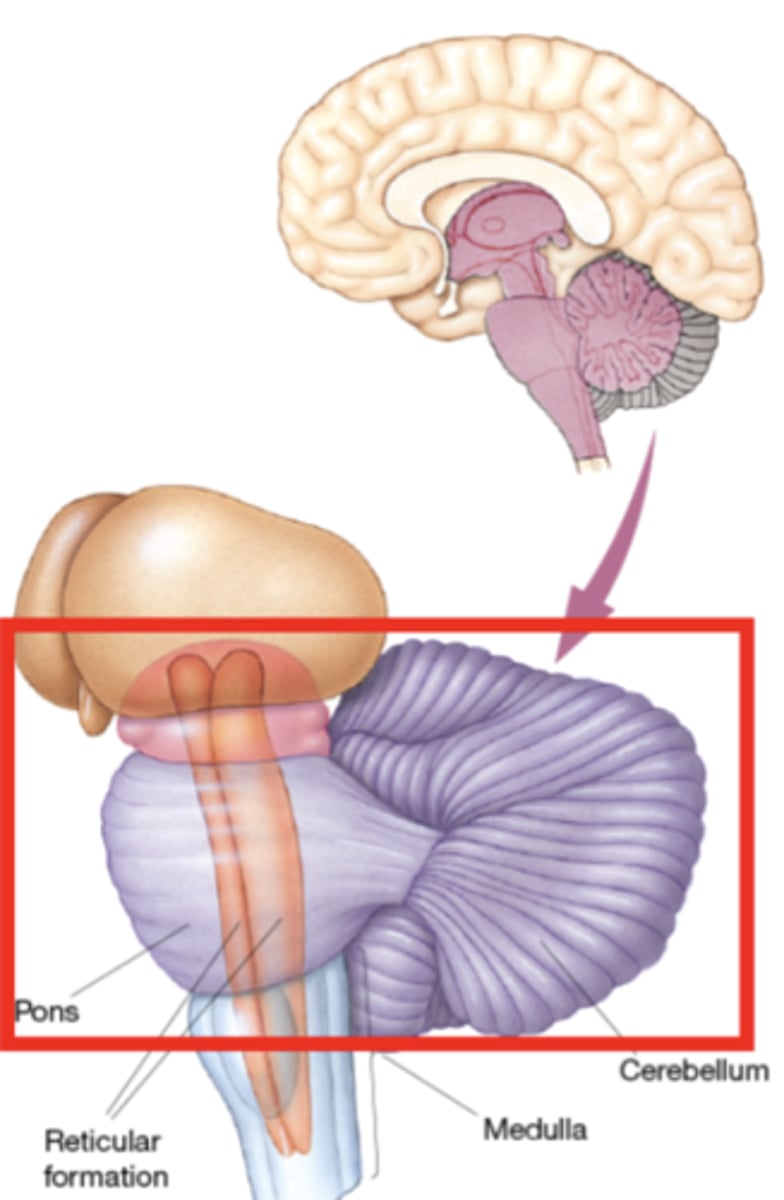
Metencephalon
like the myelencephalon, houses many ascending and descending tracts and part of the reticular formation. These structures create a bulge, called the pons, on the brain stem's ventral surface. The pons is one major division of the metencephalon; the other is the cerebellum (little brain)
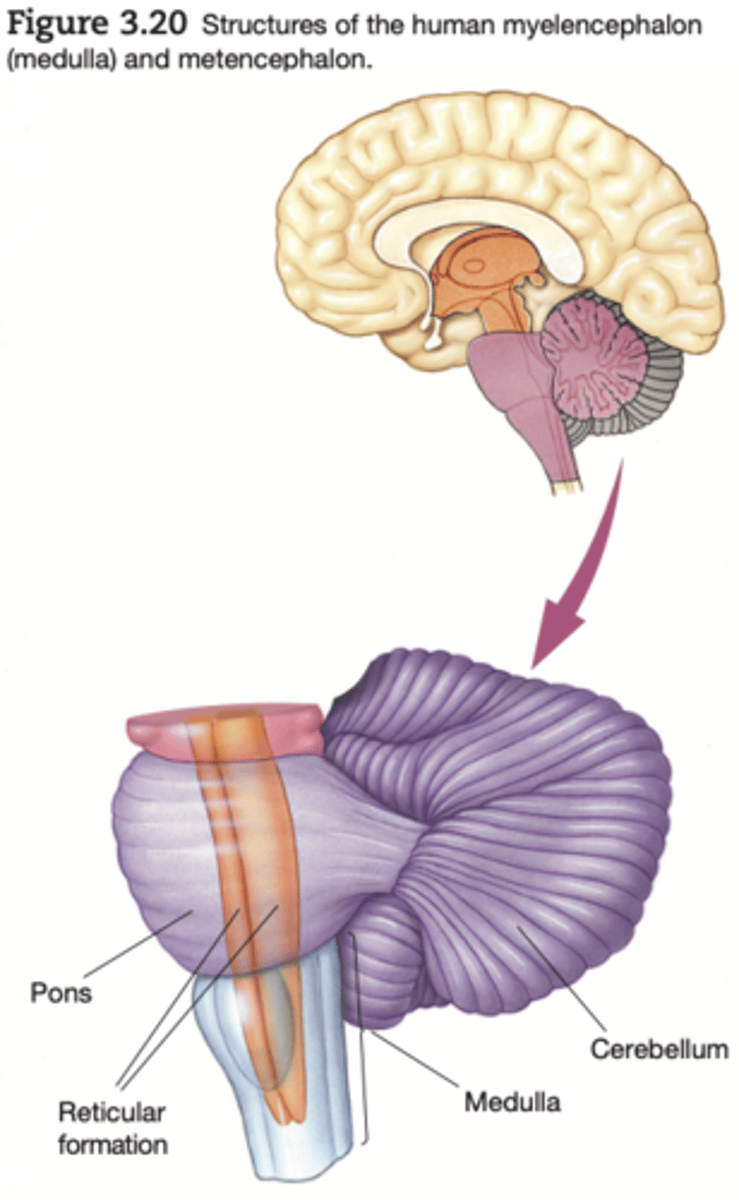
The _______ is the large, convoluted structure on the brain stem's dorsal surface. It is an important sensorimotor structure; cerebellar damage eliminates the ability to precisely control one's movements and to adapt them to changing conditions
cerebellum
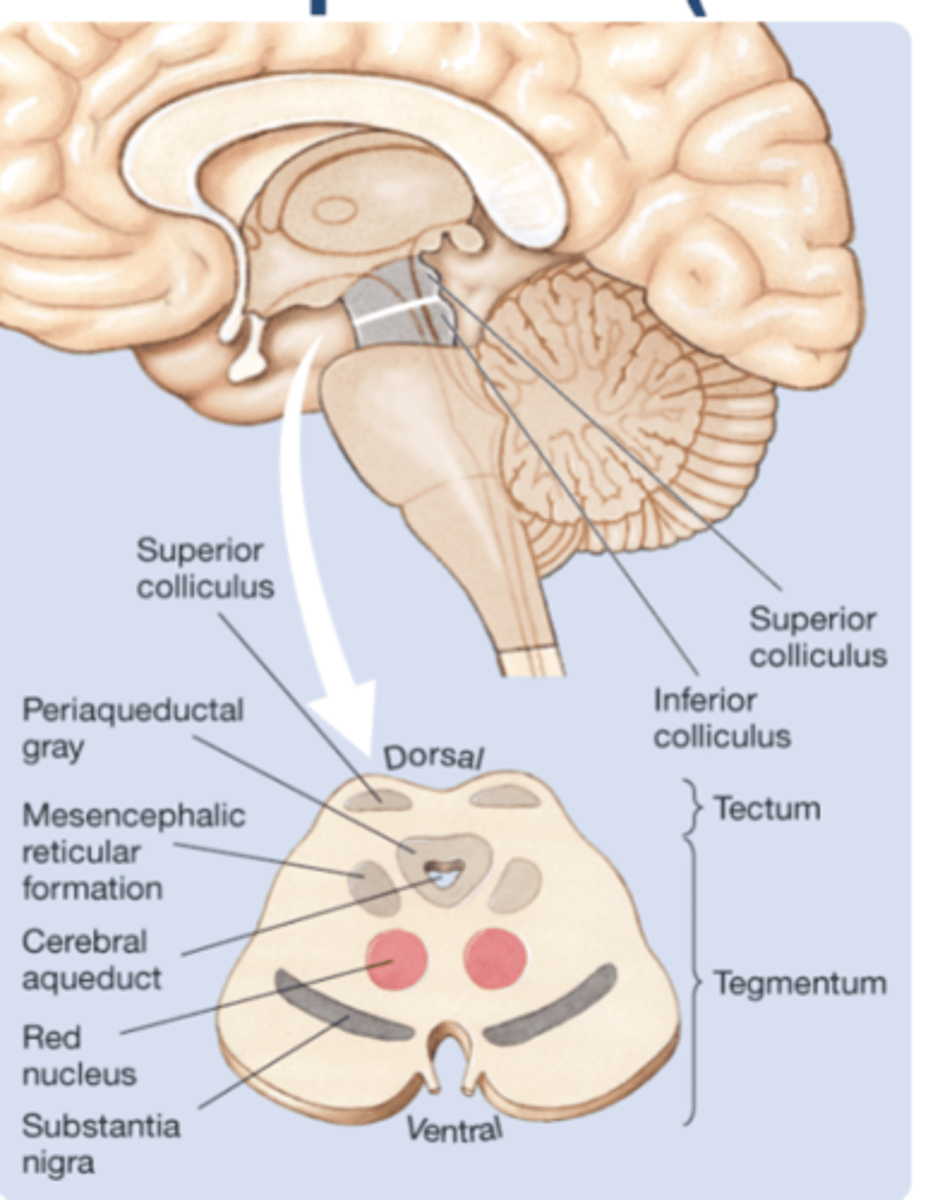
Mesencephalon
the midbrain; a region of the brain that surrounds the cerebral aqueduct; includes the tectum and the tegmentum
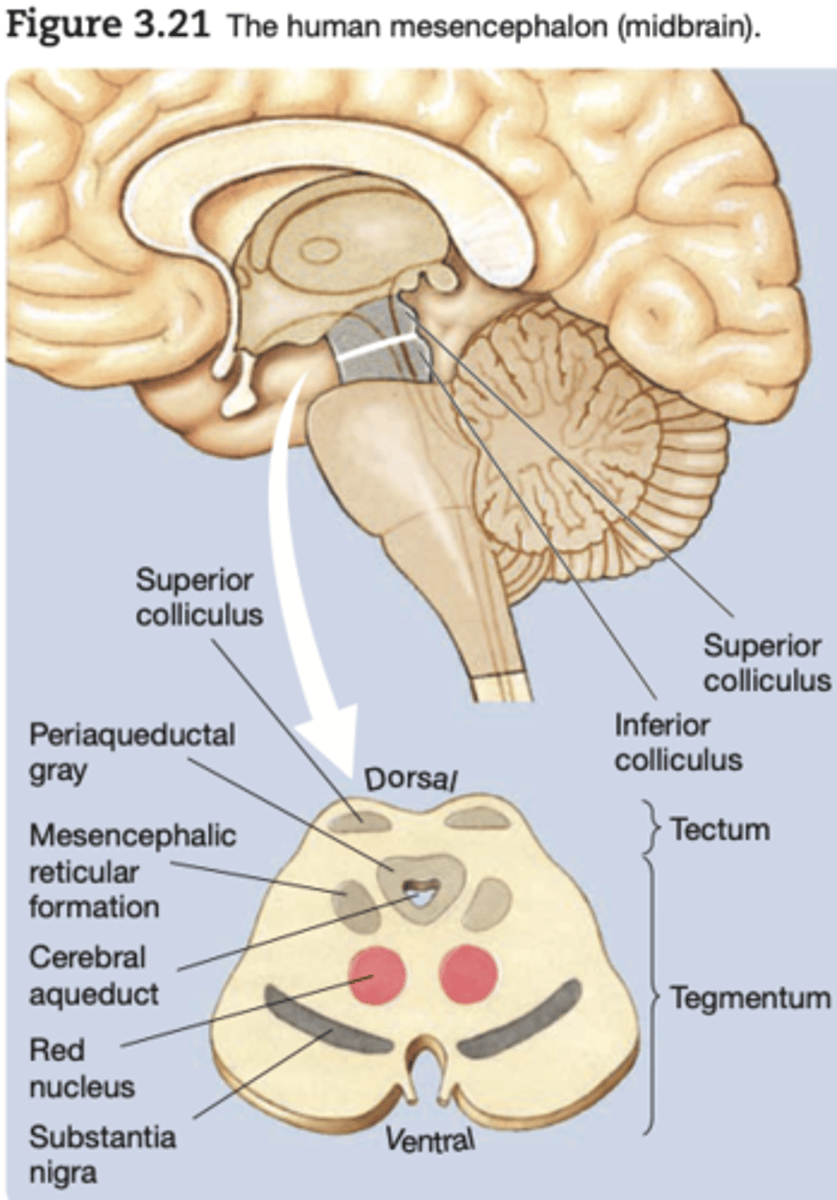
The ___ is the dorsal surface of the midbrain.
Tectum (roof)
The ________ is the division of the mesencephalon ventral to the tectum
tegmentum
The ____ (black substance) and the ______ are both important components of the sensorimotor system.
substantia nigral; red nucleus
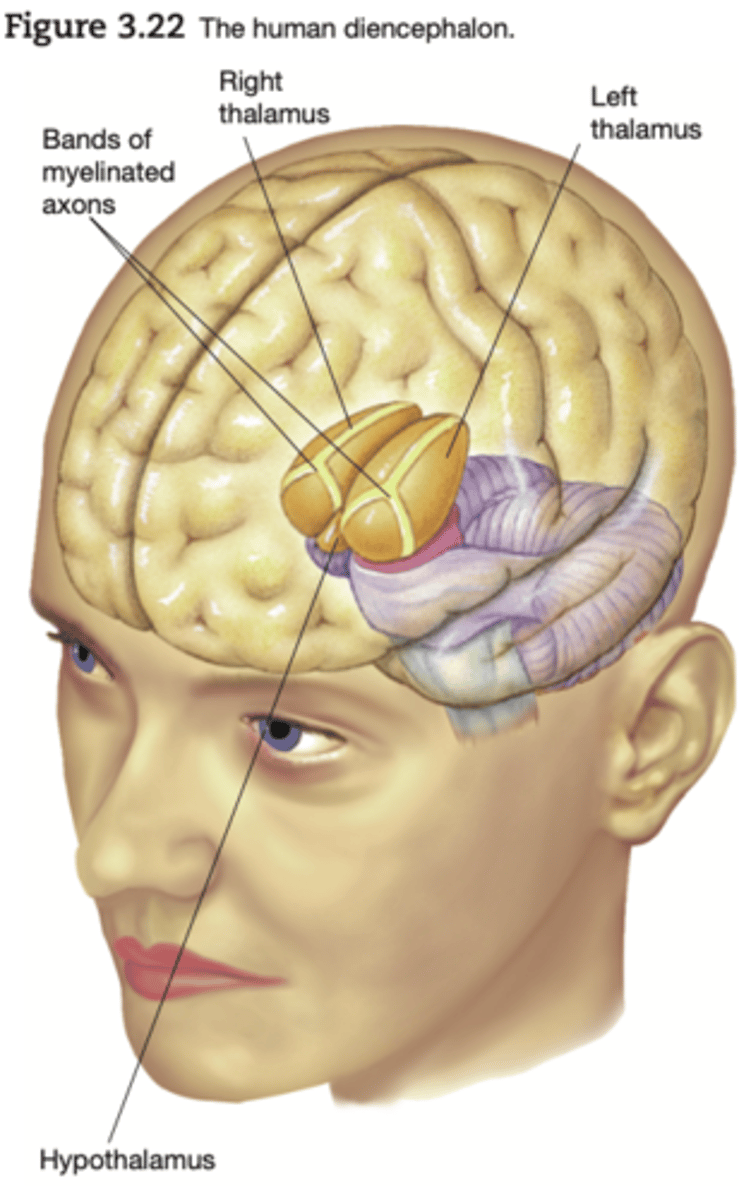
diencephalon
composed of two structures: the thalamus and the hypothalamus
The _____, the largest division of the human brain, mediates the brain’s most complex functions. It initiates voluntary movement, interprets sensory input, and mediates complex cognitive processes such as learning, speaking, and problem solving.
telencephalon
The cerebral hemispheres are covered by a layer of tissue called the _____
cerebral cortex
Major Divisions of the Cerebral Cortex: Motor cortex
Movement
Major Divisions of the Cerebral Cortex: Sensory Cortex
Sensations
Major Divisions of the Cerebral Cortex: Parietal Lobe
Perception, making sense of the world , arithemetic, spelling.
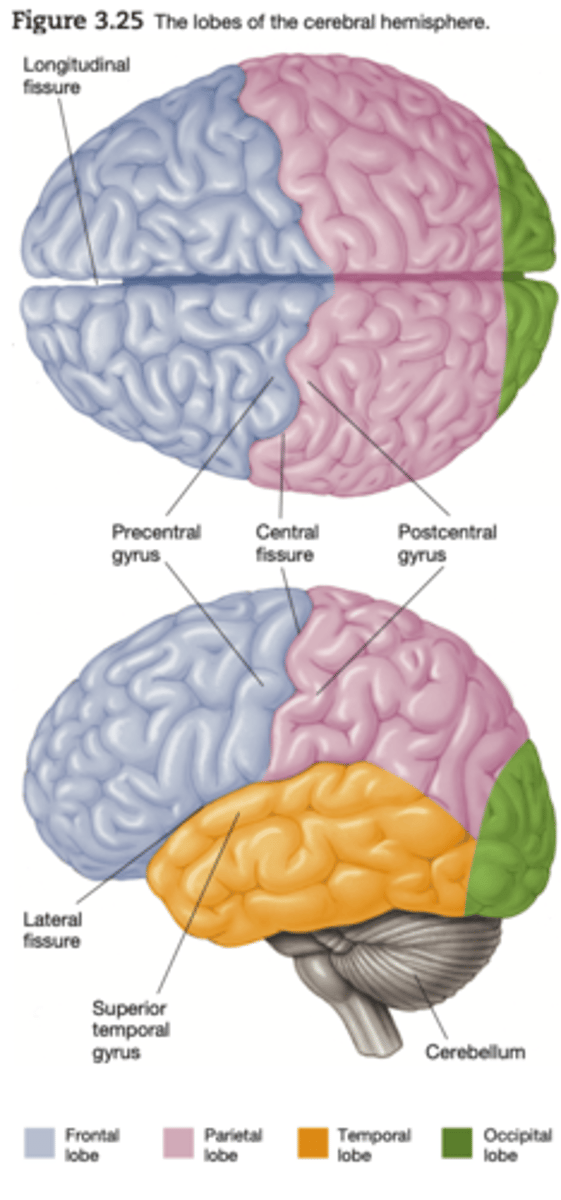
Major Divisions of the Cerebral Cortex: Occipital lobe
Vision
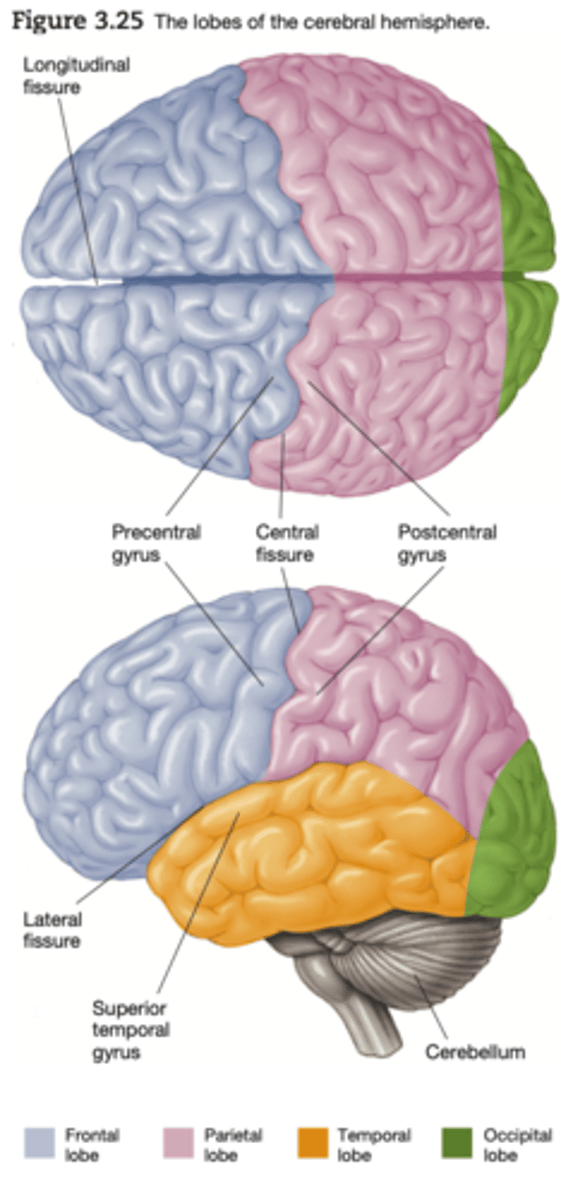
Major Divisions of the Cerebral Cortex: Temporal Lobe
memory, understanding and language.
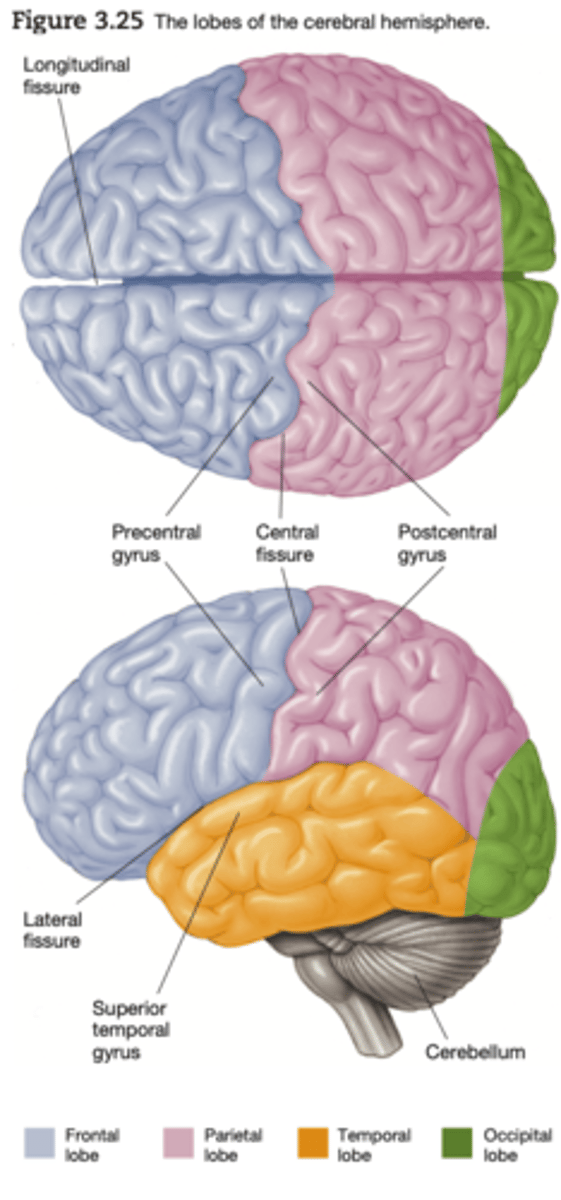
Limbic system
regulates motivated behaviours .
Structures include mammillary bodies, hippocampus, amygdala,fornix, cingulate cortex, septum
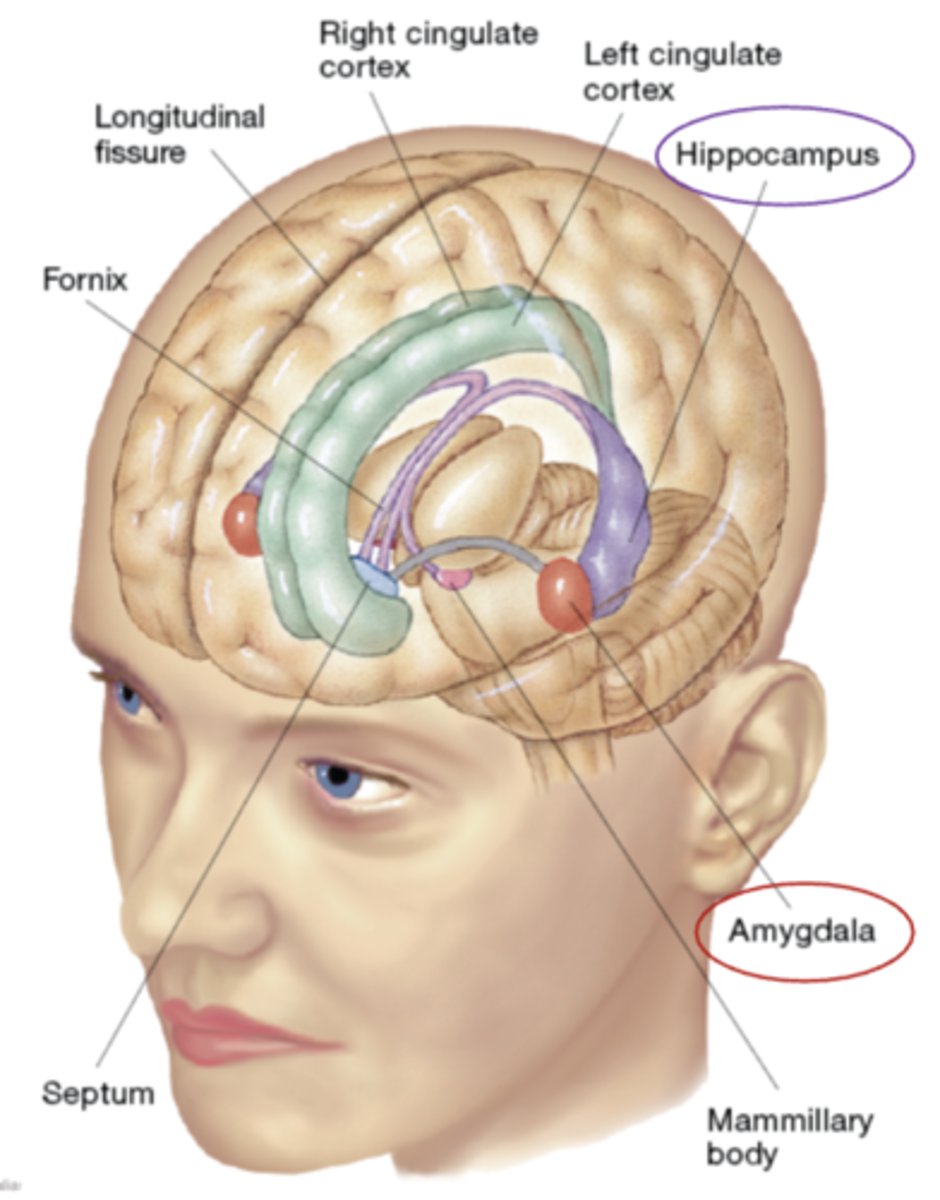
Basal Ganglia
regulates movement.
Structures include amygdala (again); the caudate & putamen(collectively called the striatum), & the globus pallidus
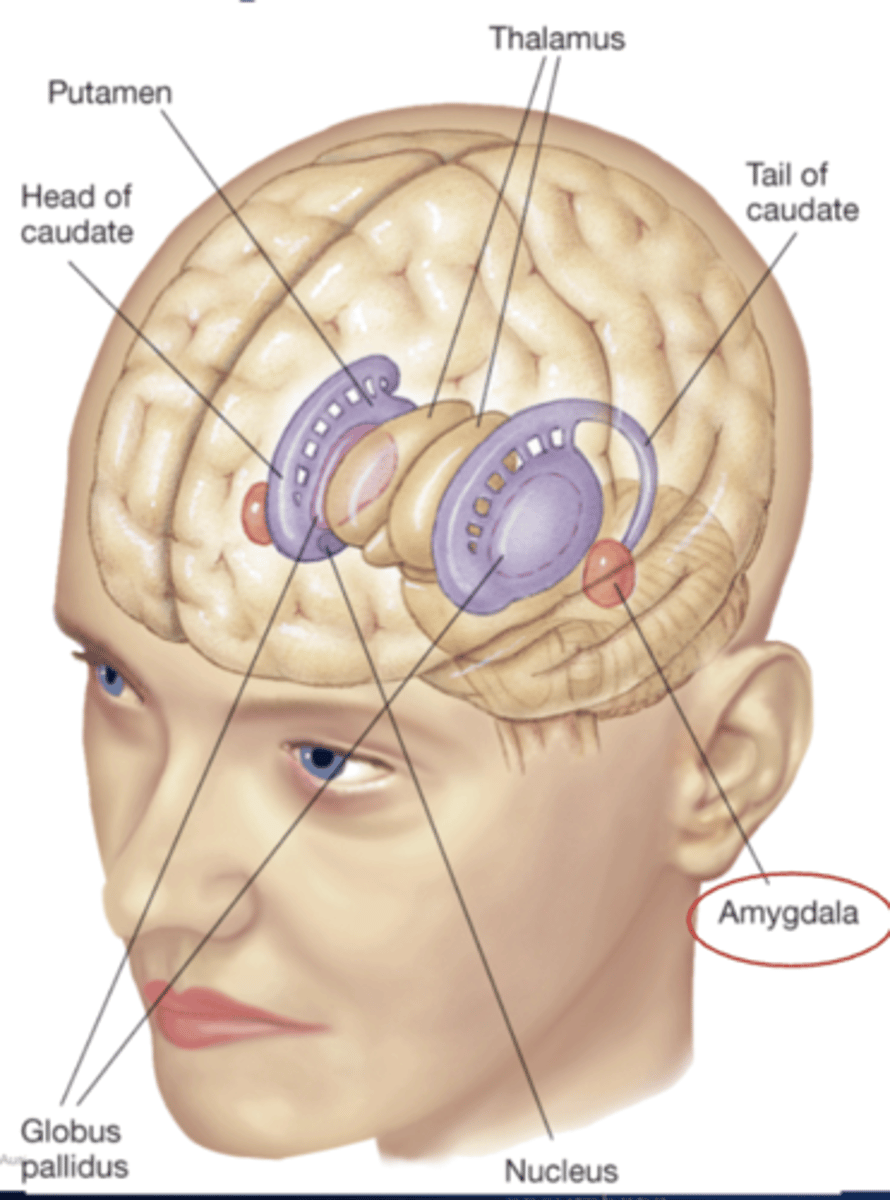
Hippocamus (limbic system)
plays a major role in some kinds of memory, located at themedial edge of the cerebral cortex as it folds back on itself in the medial temporal lobe
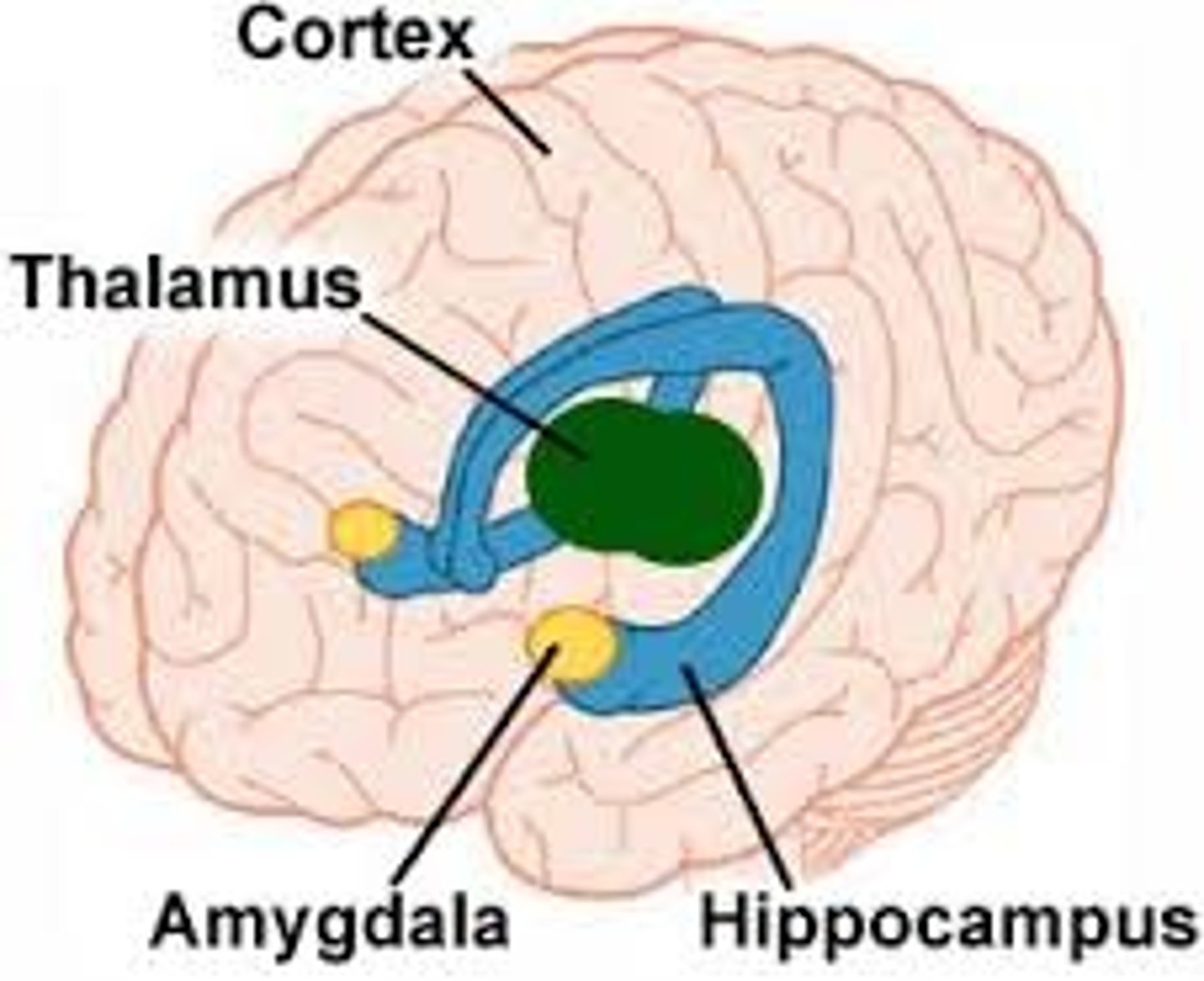
the almond-shaped nucleus in the anterior temporal lobe
amygdala

The _______, the major tract of the limbic system, also encircles the dorsal thalamus; it leaves the dorsal end of the hippocampus and sweeps forward in an arc coursing along the superior surface of the third ventricle and terminating in the septum and the mammillary bodies
fornix
The ______ is a midline nucleus located at the anterior tip of the cingulate cortex.
septum
The _____ is located medial to the putamen between the putamen and the thalamus.
globus pallidus
Thalamus
consists of sensory relaynuclei of visual, auditory, somatosensorysystems that project information in a two-way fashion: from and to the cortex
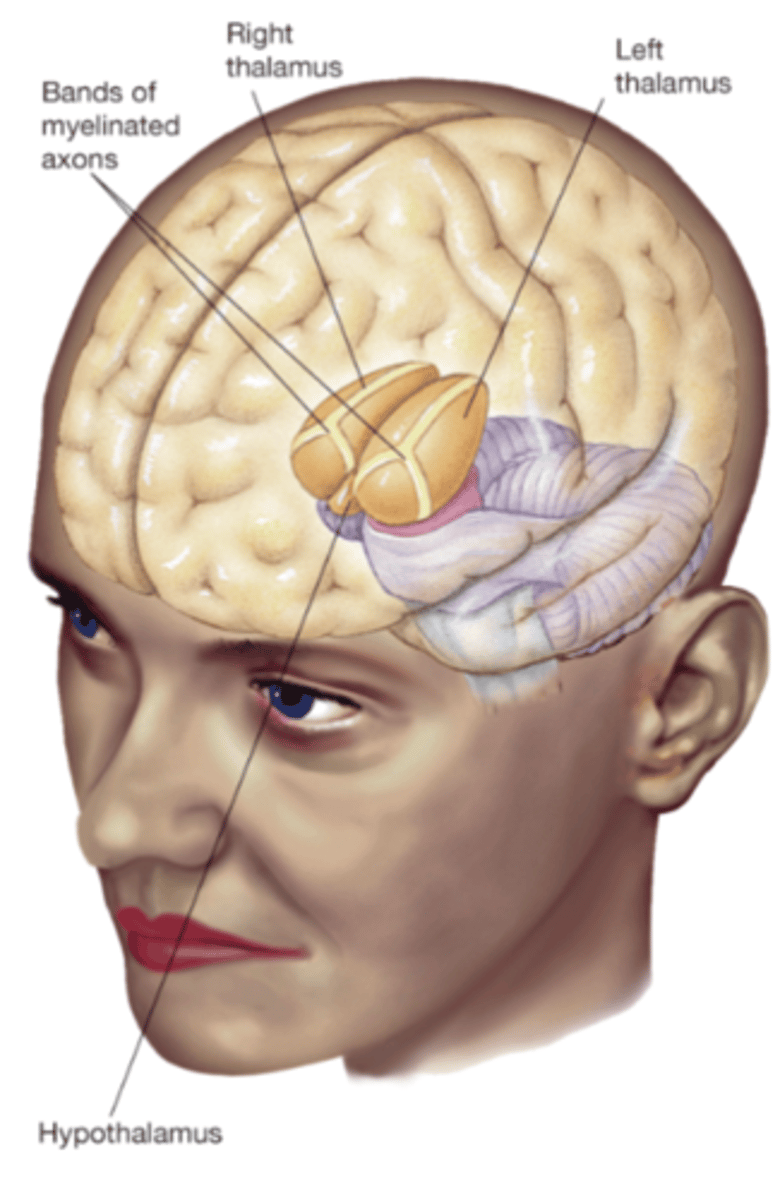
Hypothalamus
sits below the thalamus(hypo below) implicated in motivatedbehaviour (e.g., eating, sleeping, andsexual behaviour) through hormoneregulation interacting with pituitary gland.
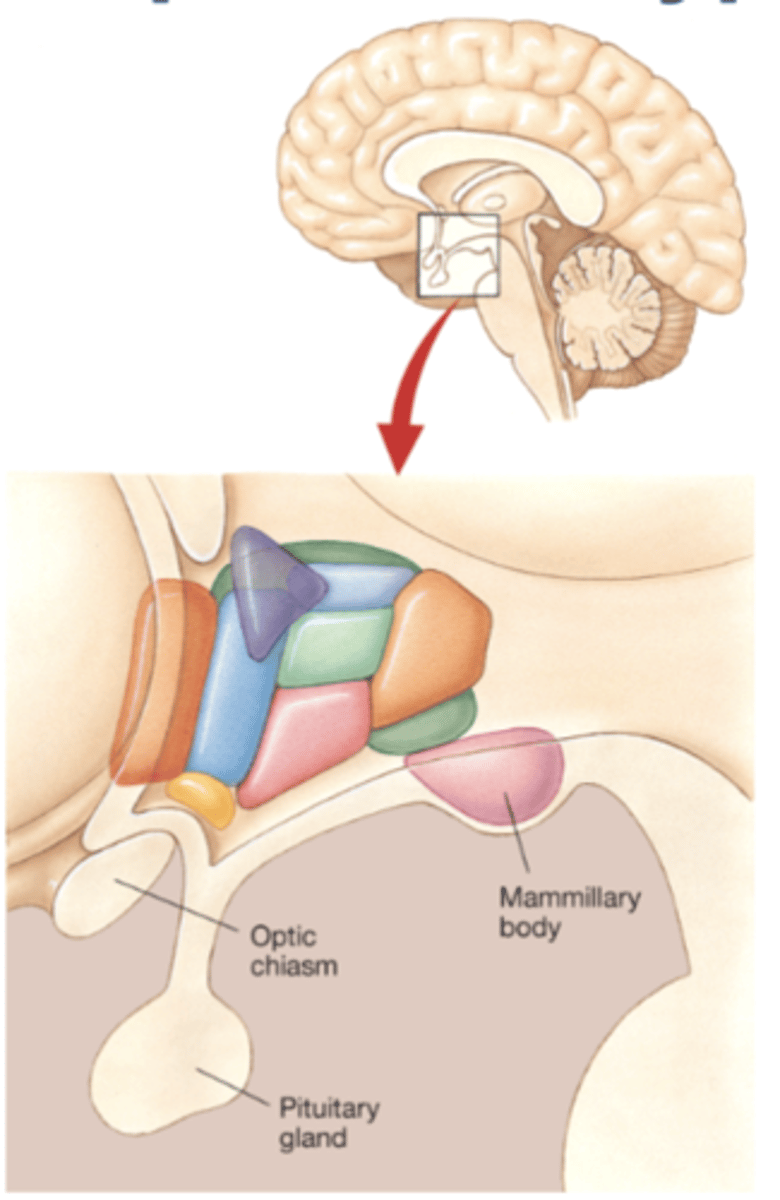
optic chiasm
points where optic nerves meet
Mammillary Bodies
considered to be part of the hypothalamus: recently associated with memory function
Tectum
→ Inferior Colliculi (auditory)
→ Superior Colliculi (visual+motor skills)
Mesencephalon
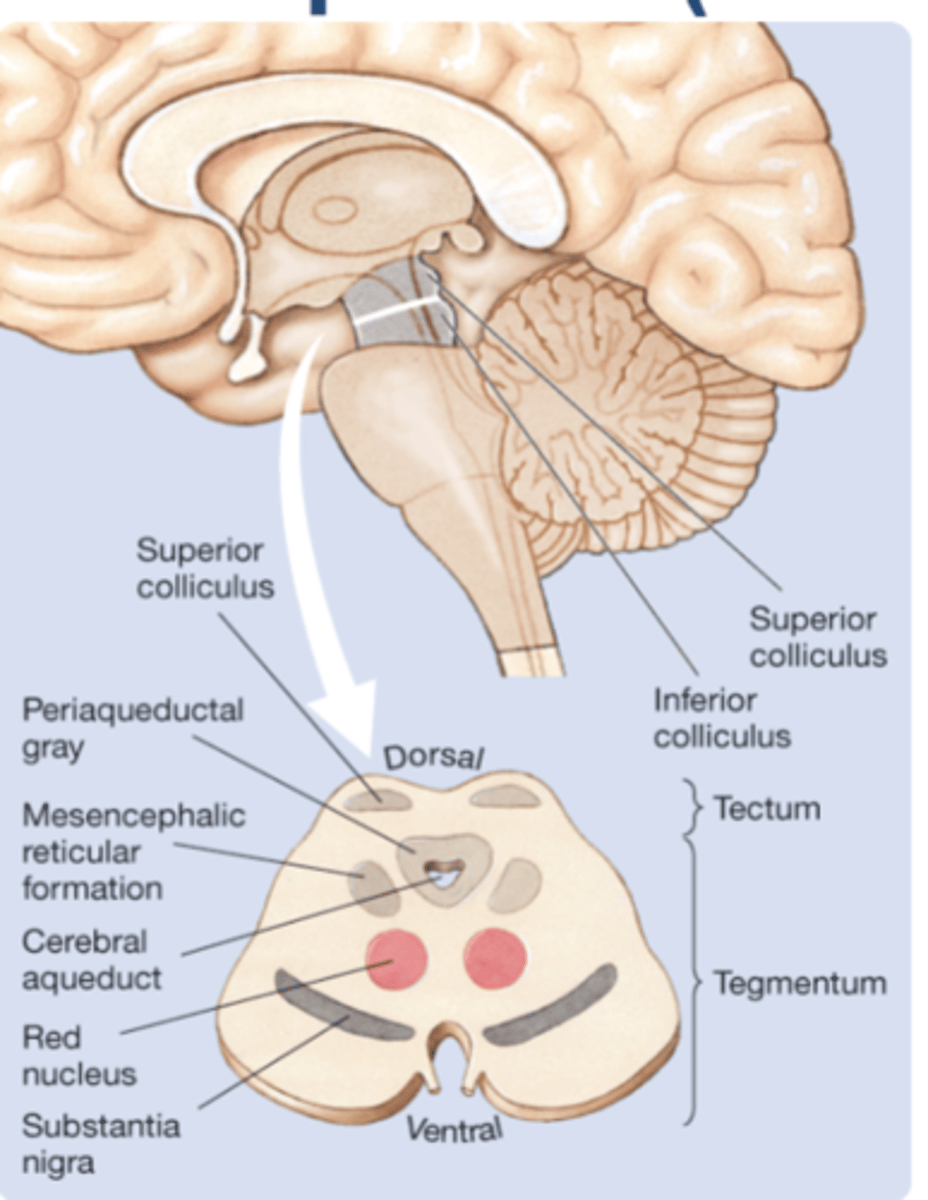
Tegmentum
→ Periaqueductal grey: grey matteraround aqueduct that connects 3rd and 4th ventricles; mediates analgesia → Substantia nigra
→ Red nucleus
→ Reticular formation
Pons
"Bridge"
bulge-like, contains theReticular formation (also part of the medulla and mesencephalon) - collection of nuclei withvariety of functions
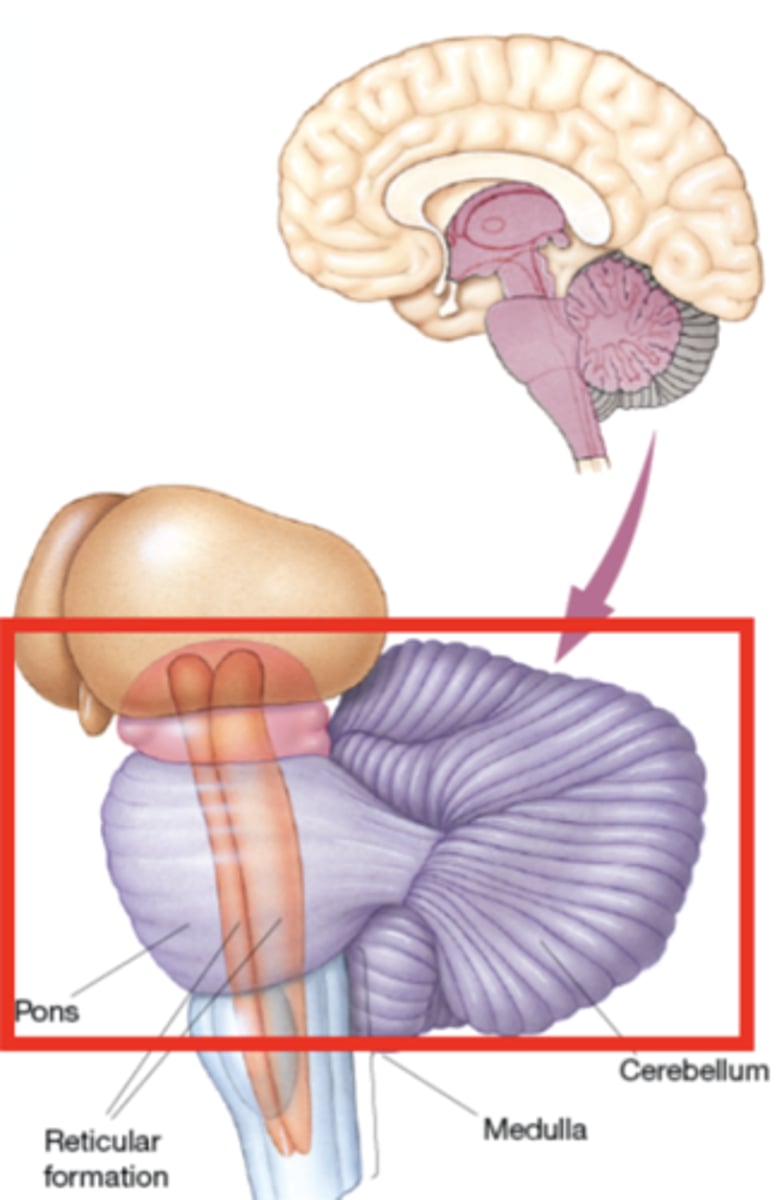
Cerebellum
little brain
important sensorimotor system; likely broader functiondue to observed cognitive deficits in cerebellar damage
neurons
cells that receive and transmit
electrochemical signals
The somatic nervous system includes _______ nerves that carry motor signals from the central nervous system
to the muscles.
efferent
The _______ is the part of the peripheral nervous system that regulates the body's internal environment.
ANS
The brain and the spinal cord are the only organs that are protected with three layers of protective membranes called _______.
meninges
_______ or "tough mother" is the outer meninx.
dura mater
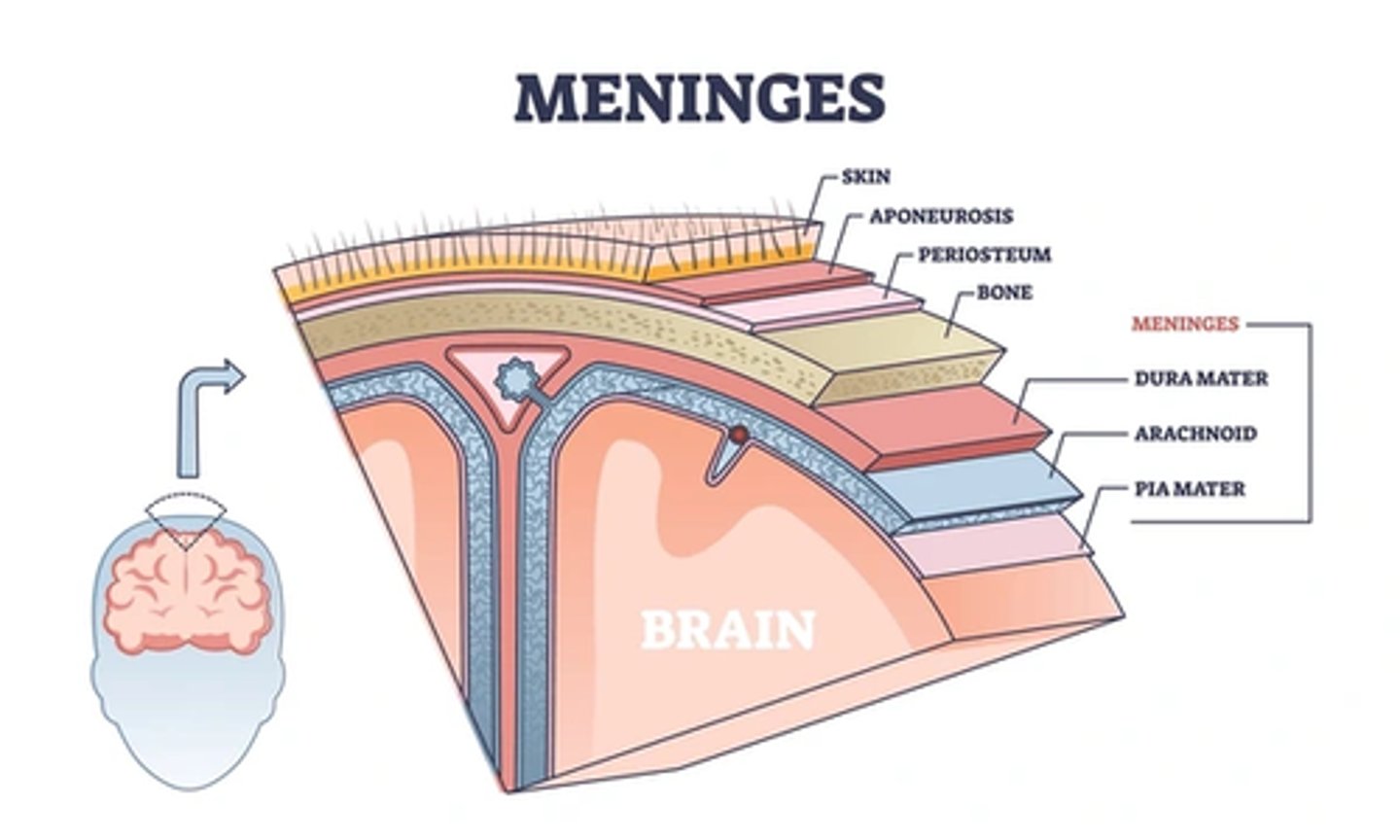
Immediately inside the dura mater is the fine
arachnoid membrane (spider-web-like membrane).
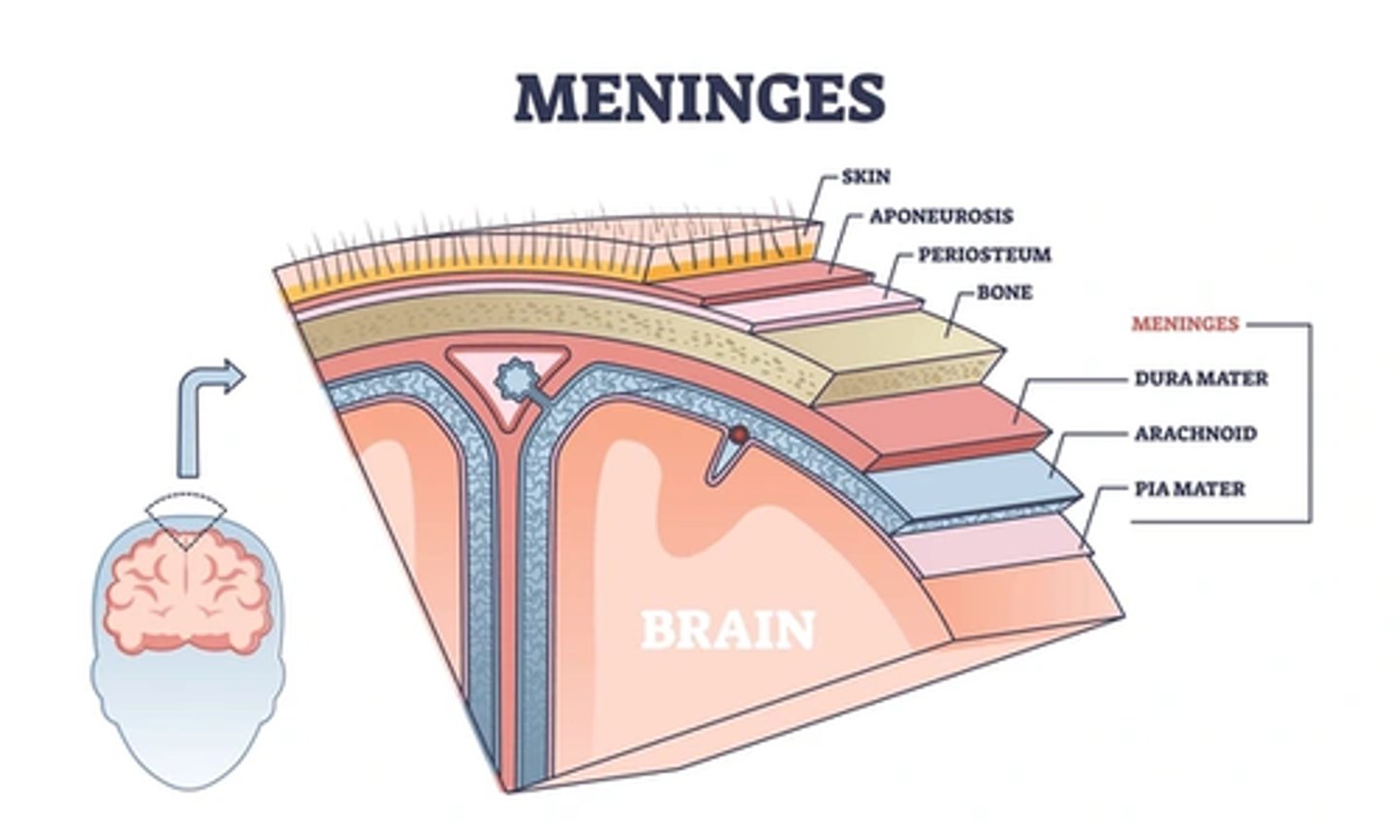
Beneath the arachnoid membrane is a space called the ___ which containes many large blood vessels and cerebrospinal fluid
subarachnoid space
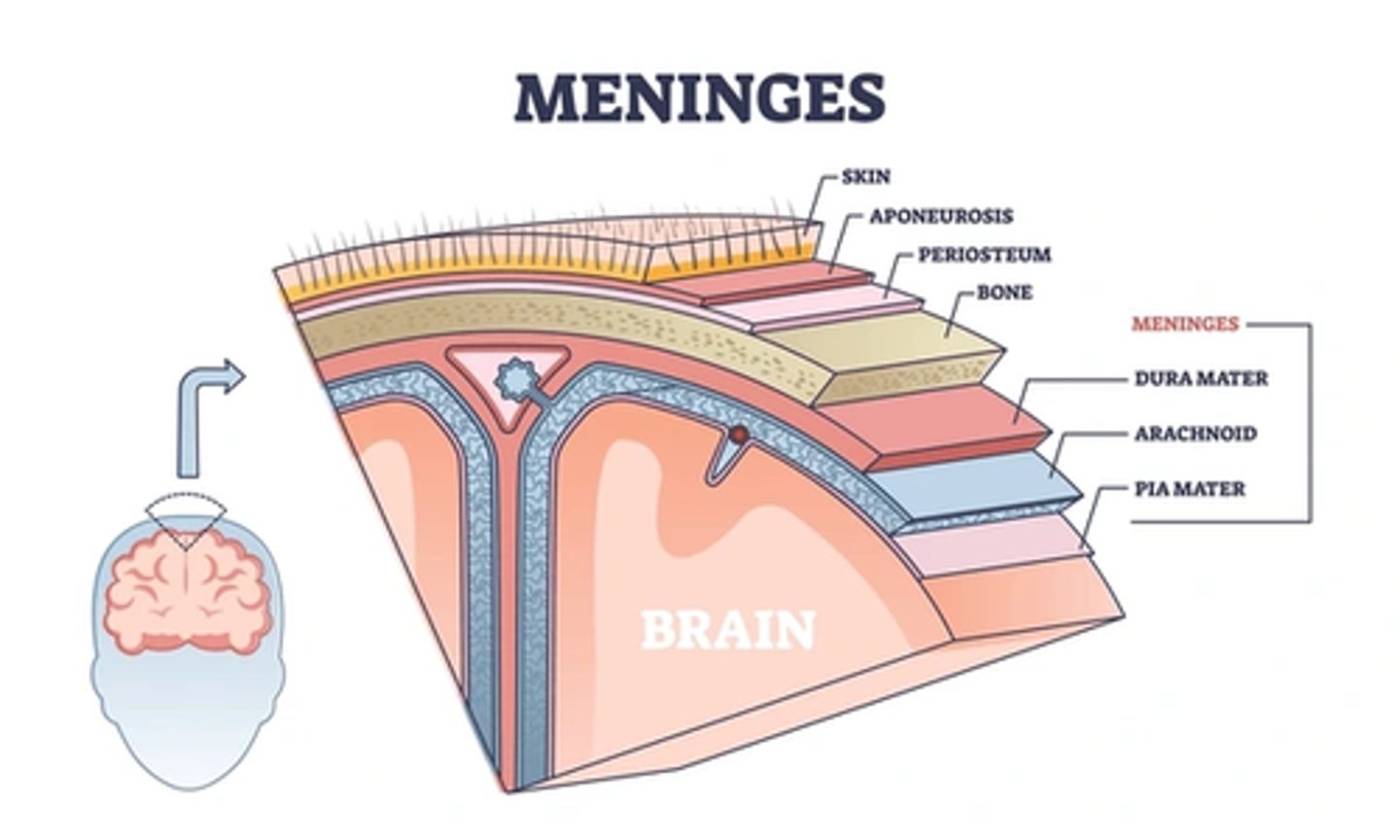
the innermost meninx, the delicate _____, which adheres to the surface of the CNS
pia matter (piou mother)
The _______ nervous system is activated when you encounter a threatening information such as a bear attacking you. This system is essential for the initiation of fight-or-flight responses.
sympathetic
Motor nerves that project from the brain and
the lower region of the spine are called _______
nerves.
parasympathetic
The _______ nerve is a purely sensory nerve that transfers visual information from the retina of the eye to the brain.
optic
The _______ nerve is the nerve cell that extends directly from the brain to the gut.
vagus
The _______ is a channel that connects the third and fourth ventricles in the brain.
cerebral aquduct
The ventricles of patients with a congenital condition called _______ build up fluid as a result of blocked channels in the brain.
hydrocephalus
The _____is a small central channel that runs the length of the spinal cord;
Central canal
Many toxic substances that are present in the
bloodstream are prohibited from entering the brain by a mechanism called the _______ where cells of blood vessel walls are tightly packed, forming a barrier to the passage of large proteins.
blood-brain barrier
Unlike large toxic molecules, _______, which is critical for the function of the brain, is actively transported through the vessel walls.
glucose
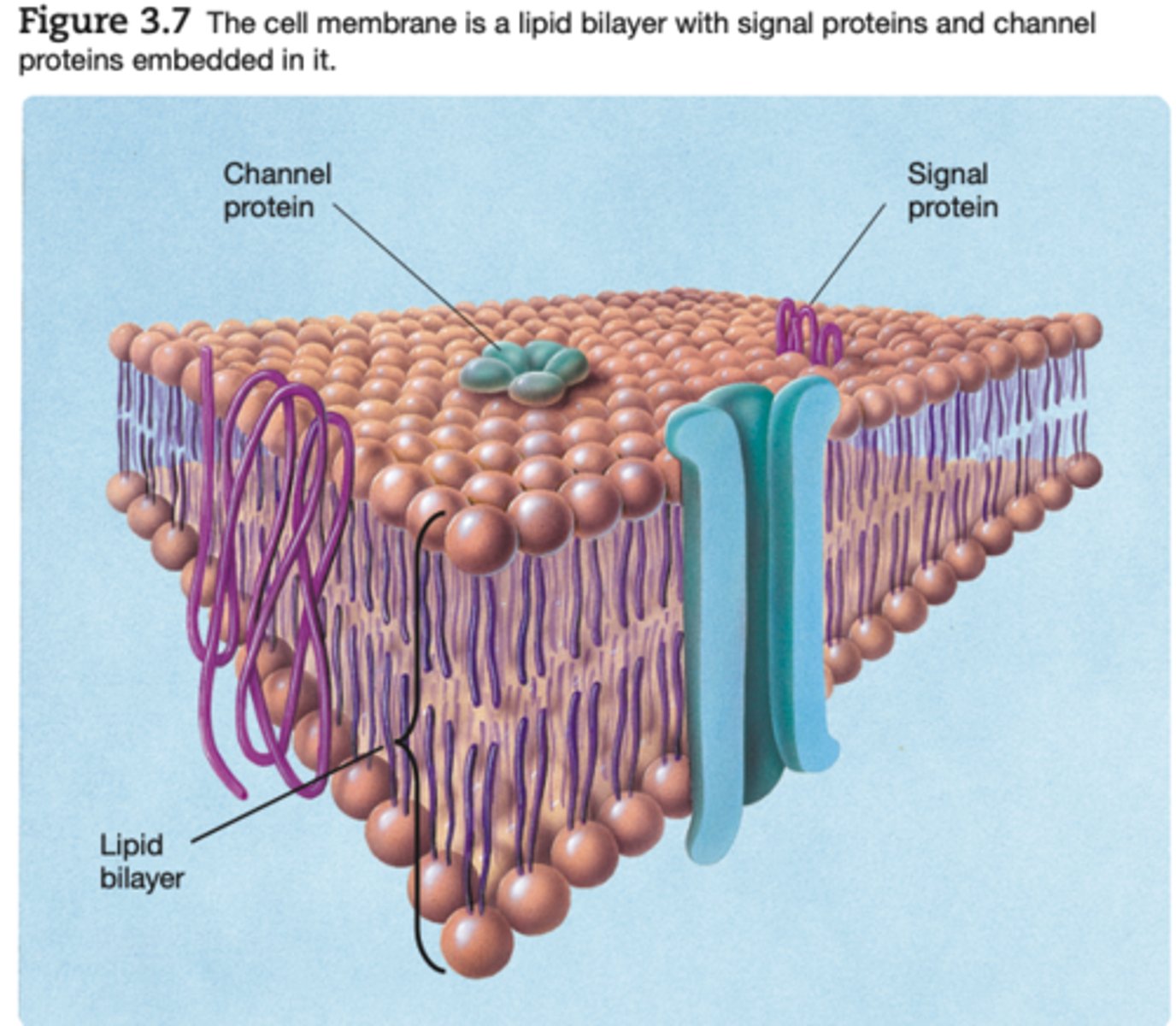
is composed of a lipid bilayer, or two layers of fat molecules
Neuron Cell Membrane
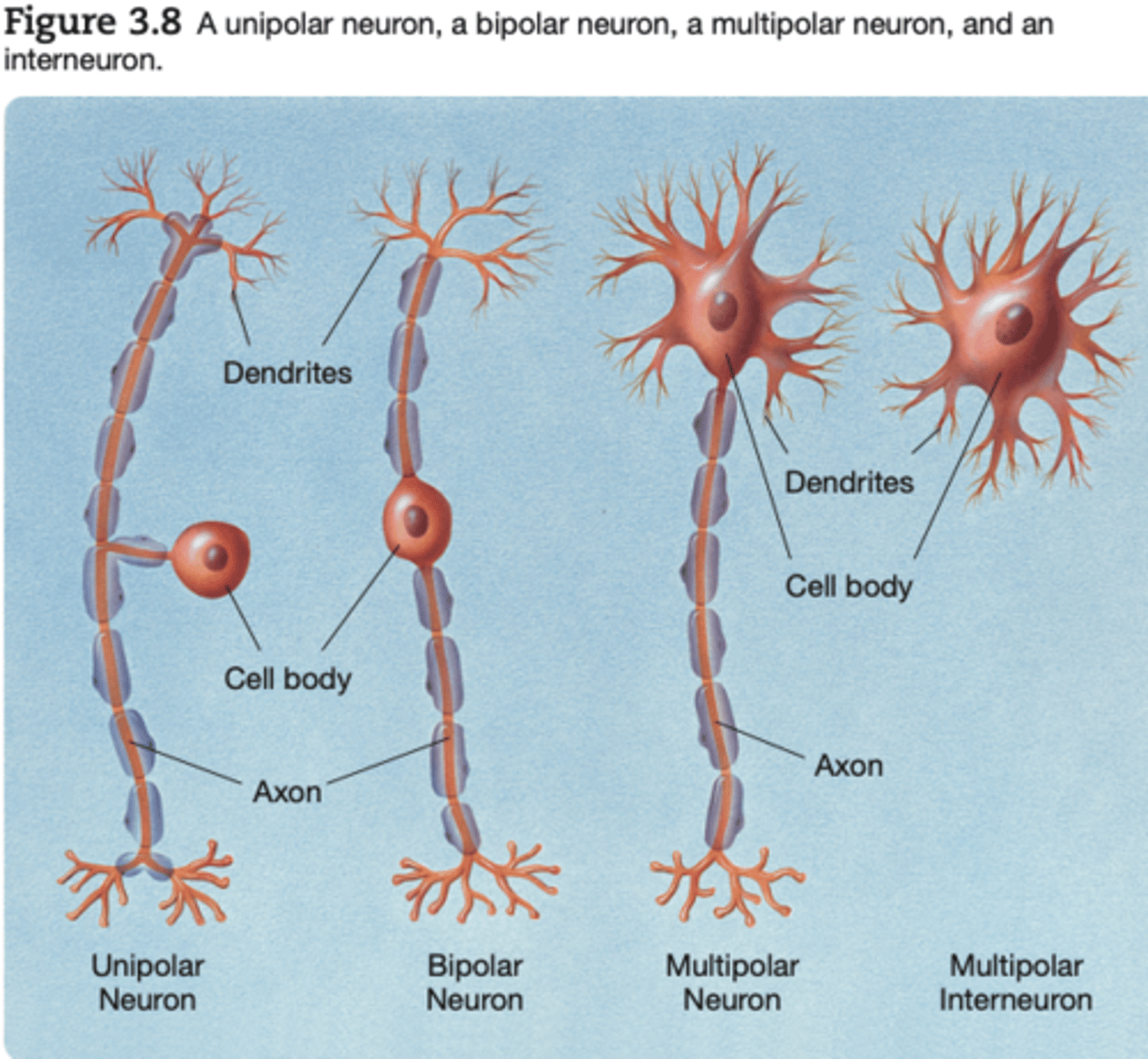
multipolar neuron
A neuron with more than two processes extending from its cell body
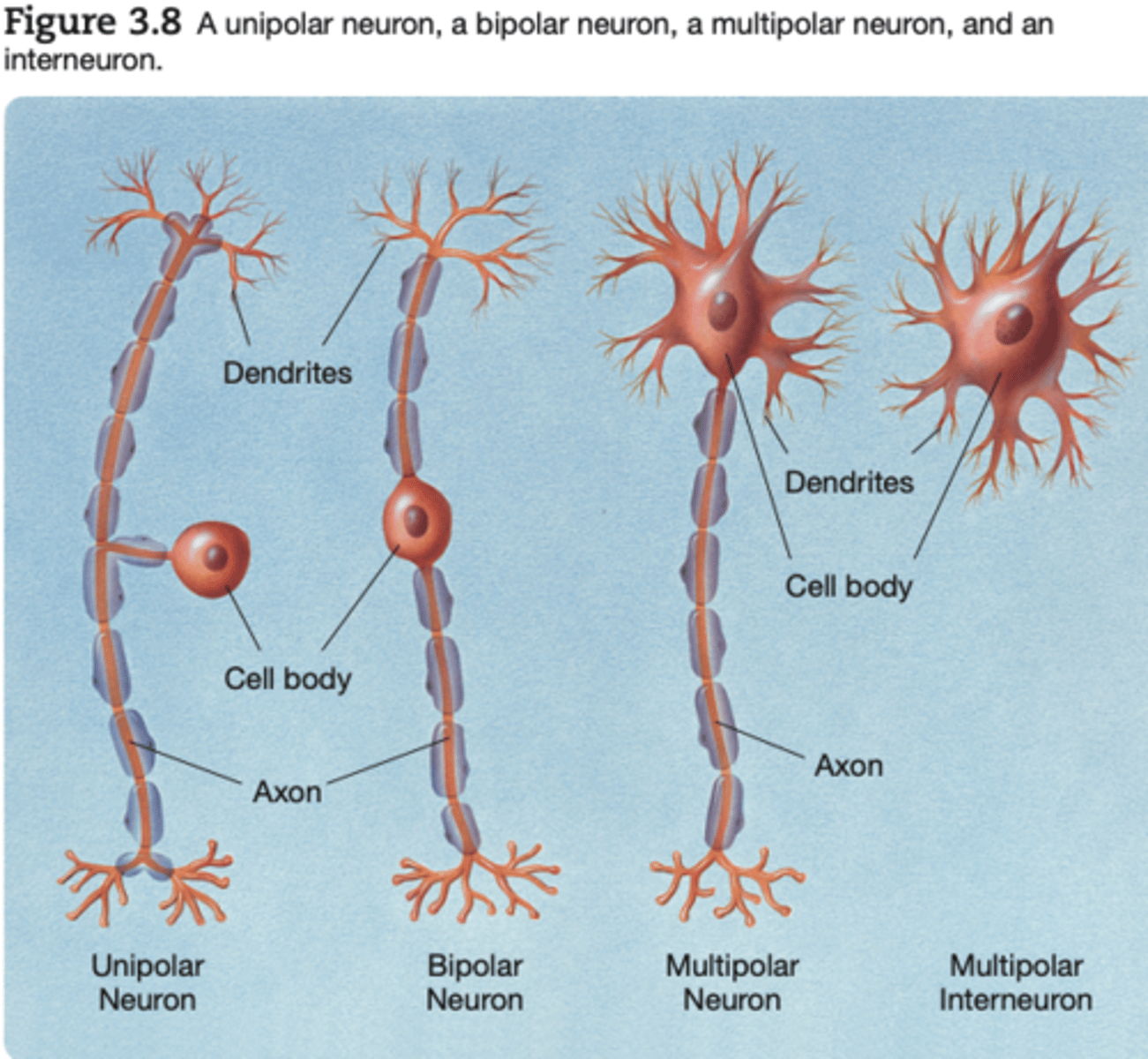
unipolar neuron
A neuron with one process extending from its cell body
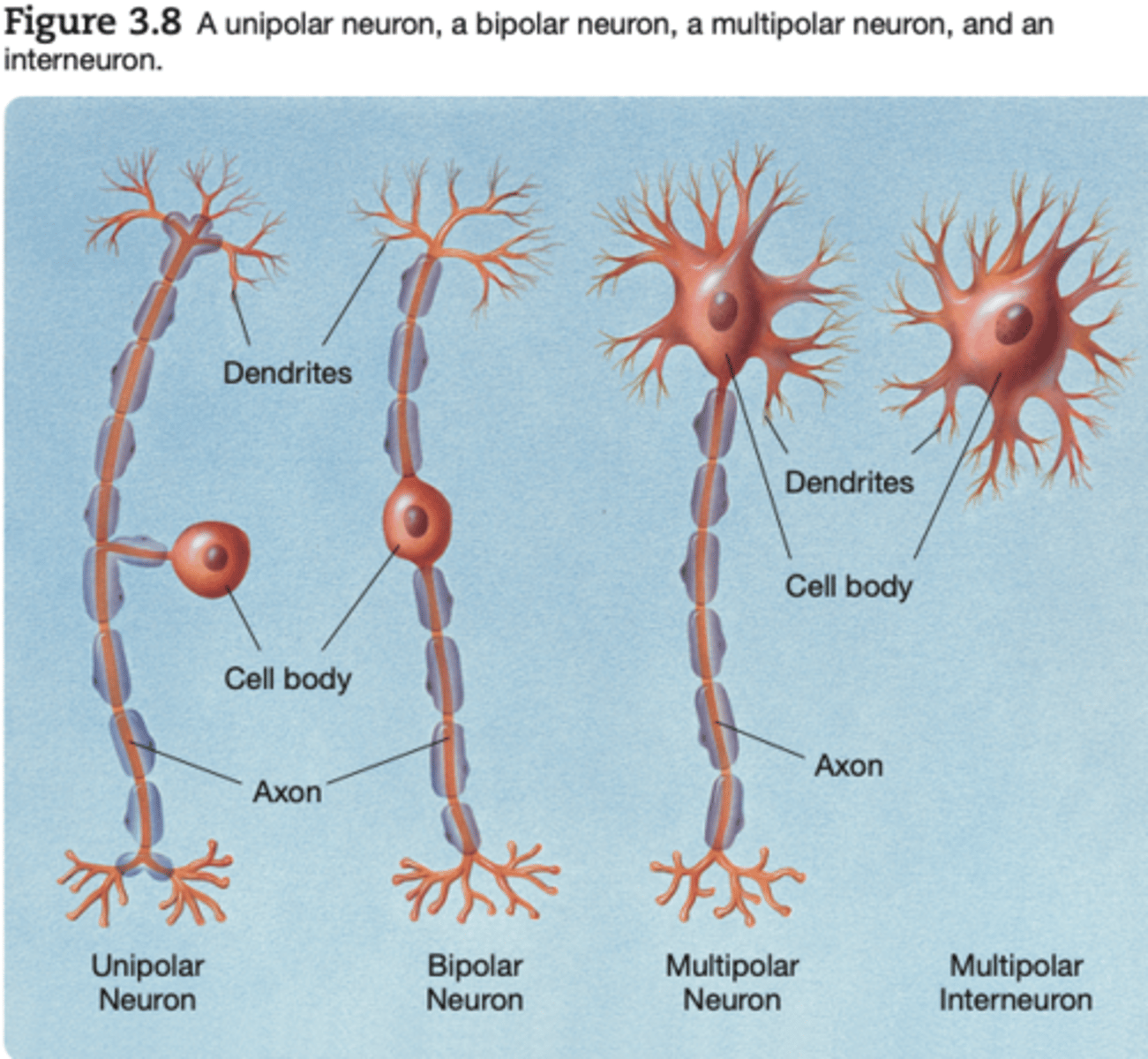
bipolar neuron
a neuron with two processes extending from its cell body
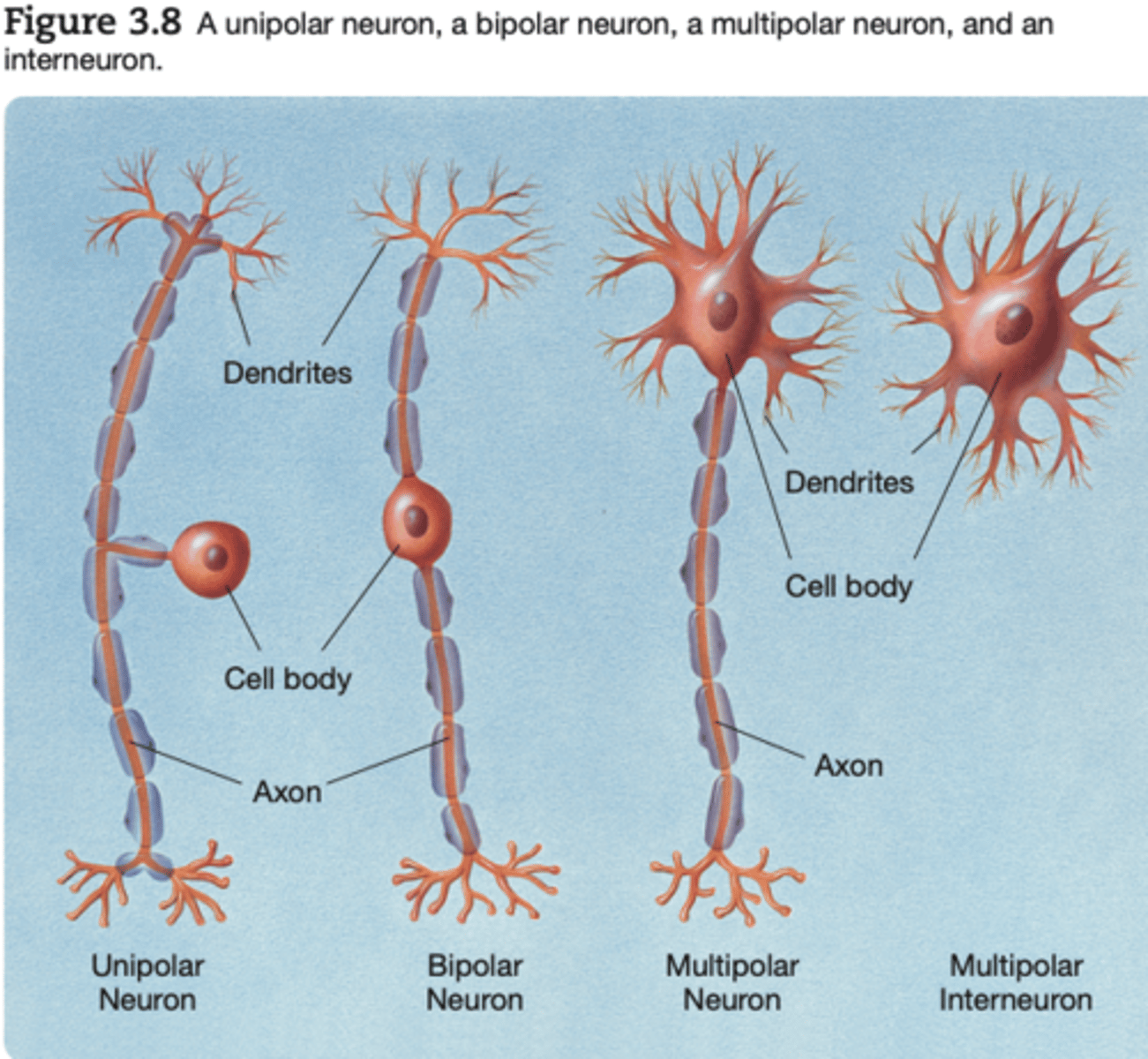
interneurons
Neurons with a short axon or no axon at all
In the central nervous system, bundles of axons are called ______and in the peripheral nervous system, they are called ____nerves
tracts ; nerves
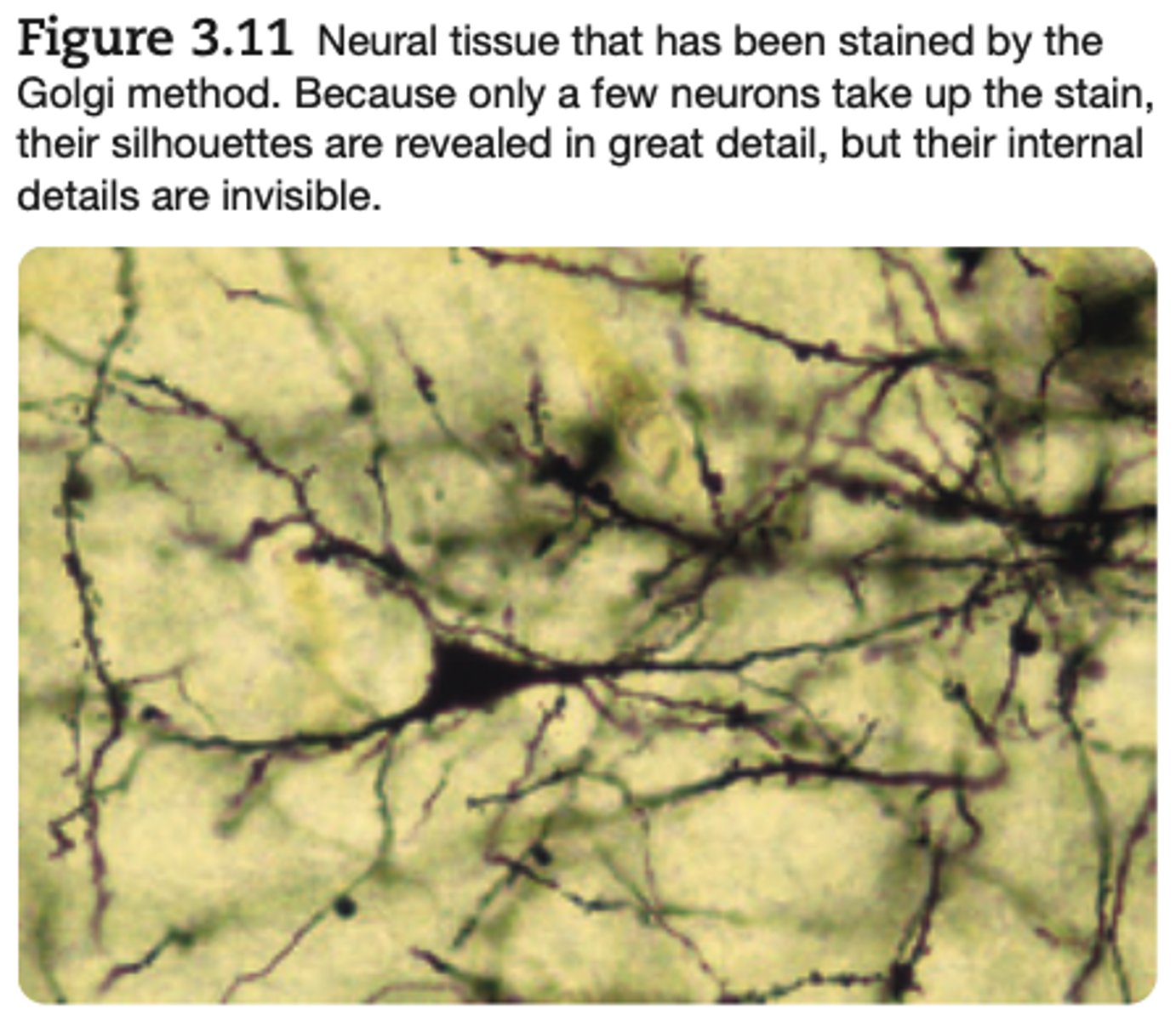
Golgi Stain is used to ?
Golgi stains are commonly used to discover the overall shape of neurons.