STEM- Heredity Summative Test
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Heredity
the passing of physical characteristics from parents to offspring
Traits
Each specific characteristic passed down from parent to offspring.
Genetics
The scientific study of heredity
Fertilization
the process in which a new organism begins to form when egg and sperm cells join
purebred plants
The offspring of parents that have the same alleles of a trait. For example, (AA)
Genes
A word used to describe the factors that control a trait
Hybrid Plants
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait (Gg)
Alleles
Different forms of a gene. Expressed with uppercase and lowercase letters.
Dominant Alleles
An allele whose trait shows up in the organism when the allele is present.
Recessive Alleles
An allele that is hidden whenever the dominant allele is present and shows up when it is absent.
Probability
A number that describes how likely it is that an event will occur
Punnett Square
A chart that shows all the possible ways alleles can combine in a genetic cross
Phenotype
The physical appearance/visible traits of an organism
Genotype
An organism’s genetic makeup, otherwise known as alleles.
Homozygous
An organism that has two identical alleles for a trait.
(Also known as purebred)
Heterozygous
An organism that has two different alleles for a trait. (Also known as hybrid)
Incomplete Dominance (found in plants)
A form of phenotype when both are partially dominant, so they create a mix of both alleles. (e.g. white and red plants make pink plants)
Co-dominance (found in animals)
A form of phenotype when both alleles are shown equally instead of mixed, often uses superscripts to express the alleles.
Nitrogen Bases (Four Types)
Molecules that contain nitrogen and other elements. They make up the rungs of DNA
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
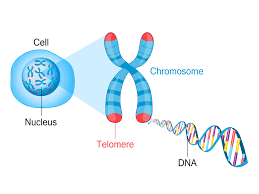
What are chromosomes?
Chromosomes are thread-like structures made of DNA and proteins found in the nucleus of cells. They carry genetic information and are passed from parents to offspring.
Mutations
Any change in the DNA of a gene or Chromosome that affect an offsprings traits. May be the removal of a nitrogen base, changes in the pairs of bases, or addition base added. Can cause diseases, including cancer.
What did Mendel Conclude?
he concluded that genes are inherited from two separate alleles, from each parent.