Chapter 10 - Chemical Bonding I: The Lewis Model
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Lewis Electron-Dot Structure
a structural formula that represents the element and its valence electrons
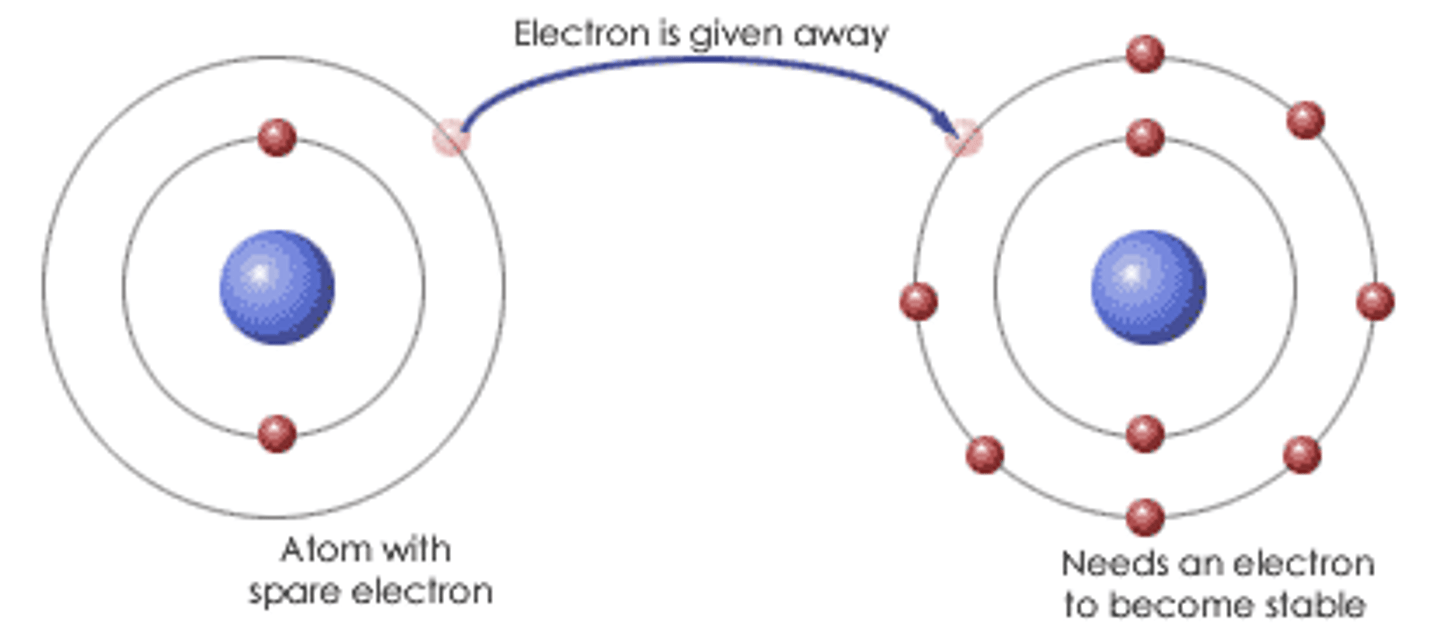
Ionic Bond
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
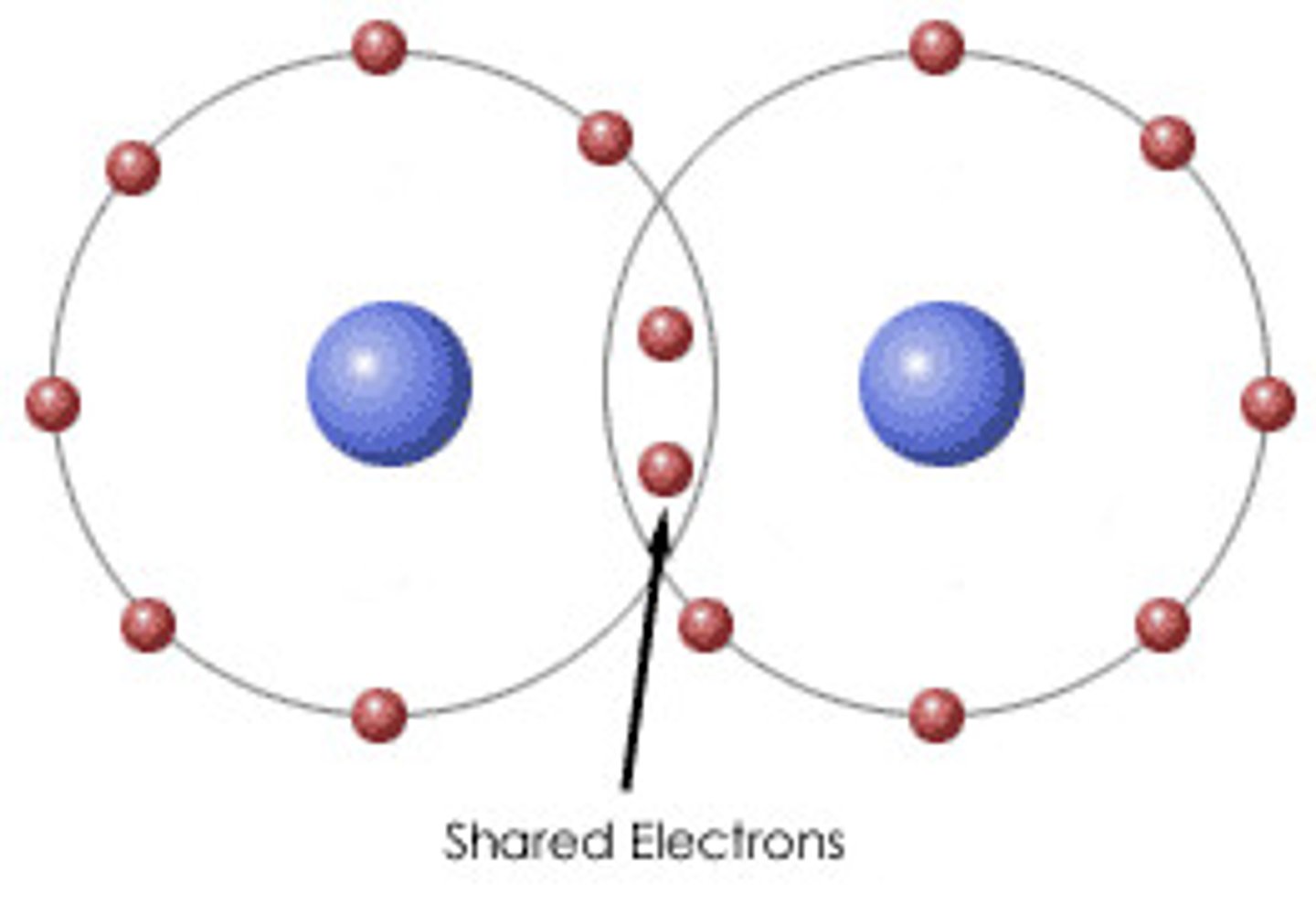
Covalent Bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
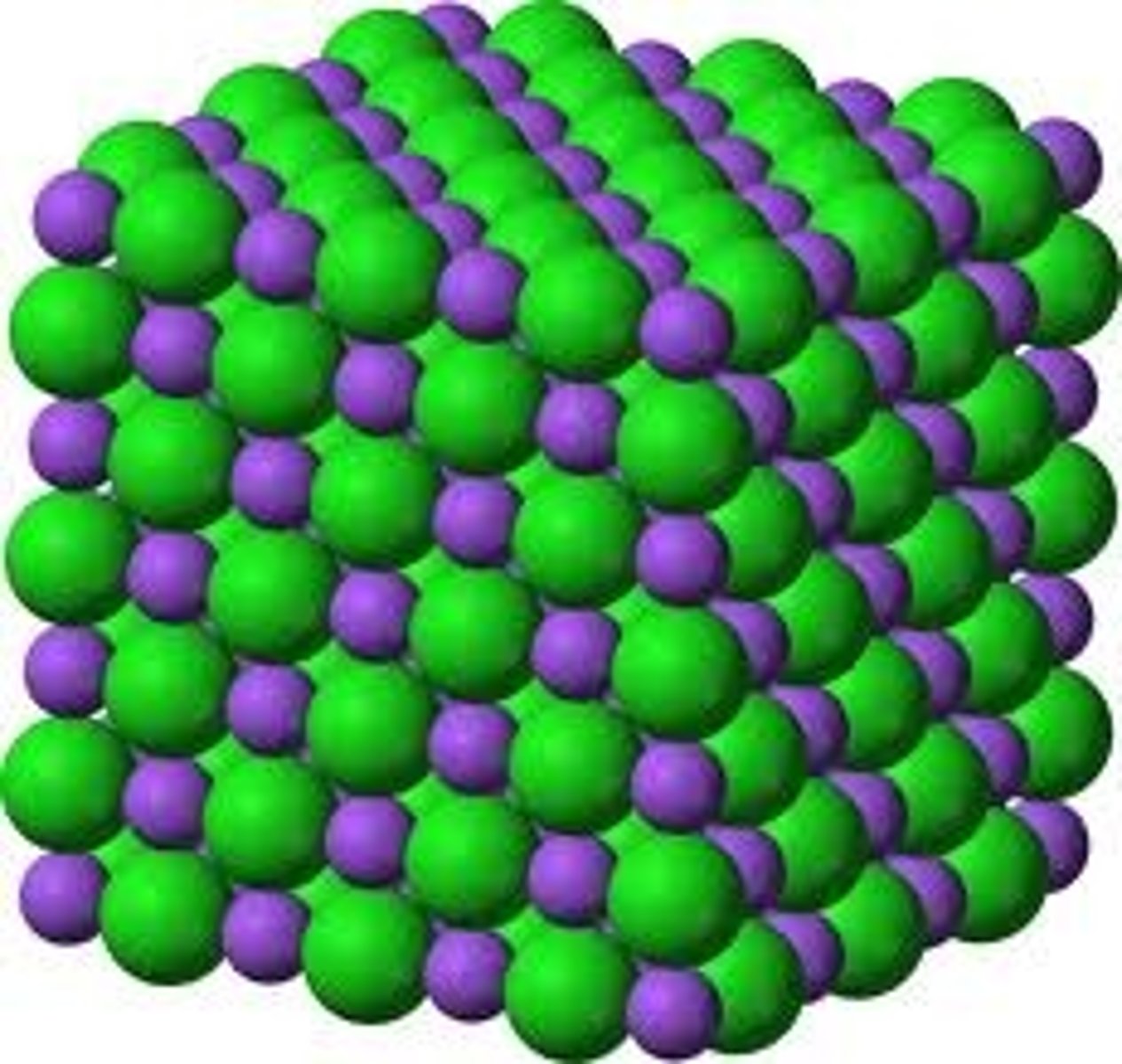
Metallic Bonding
the chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons; a pool of electrons
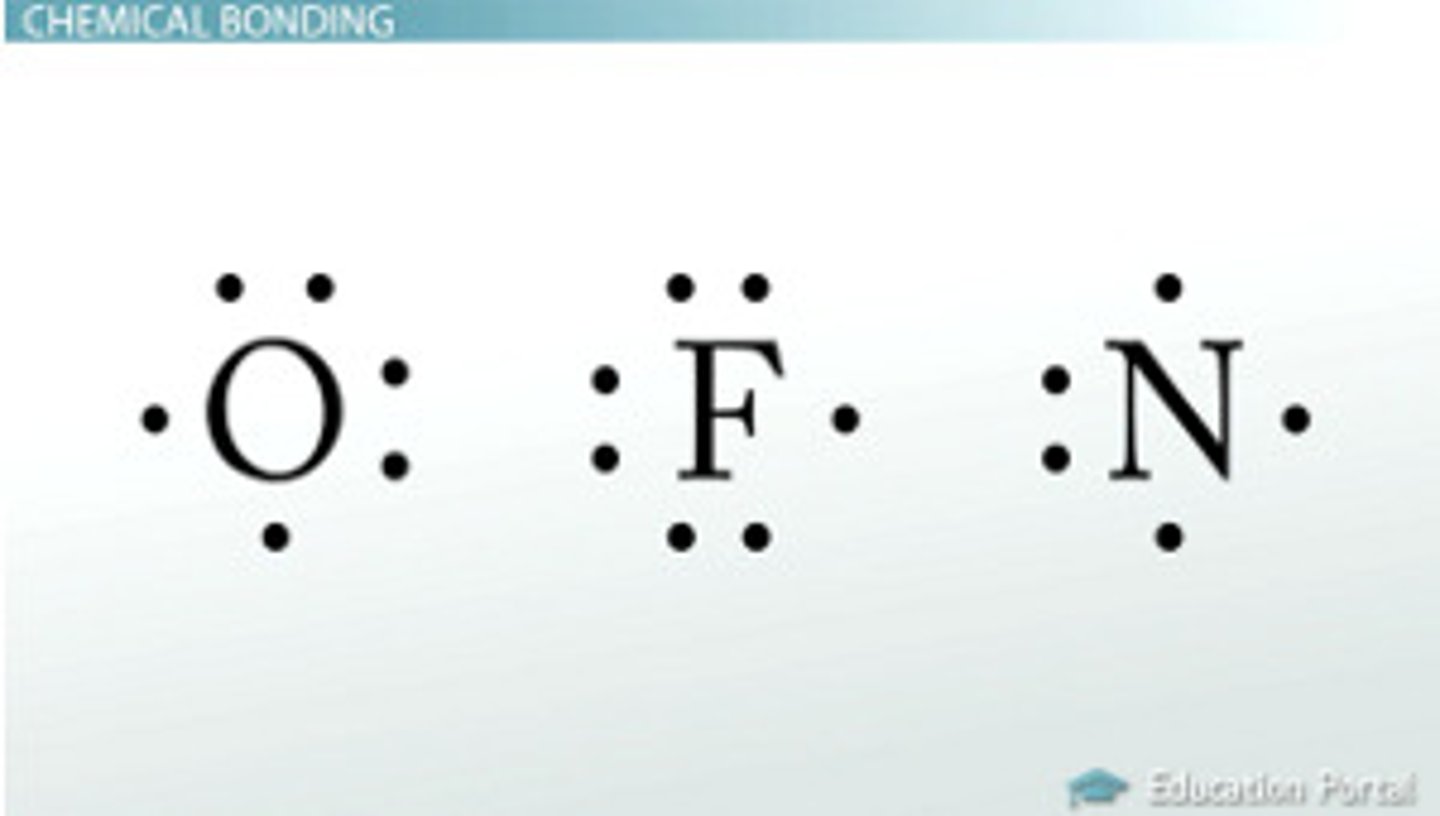
Lewis Symbol
representation of the valence electrons of main-group elements as dots surrounding the element symbol
Octect
atoms with eight valence electrons; full s and p sublevels; eight dots on the Lewis model
Duet
a Lewis structure with two dots, a filled outer later of valence electrons
Chemical Bond
sharing or transfer of electrons to attain stable electron configurations for the bonding atoms
Octect Rule
bonding atoms attain stable electron configurations; the stable configuration is usually eight electrons in the outermost shell
Lattice Energy
energy associated with the formation of a crystalline lattice of alternating cations and anions from the gaseous ions
Born-Haber Cycle
hypothetical series of steps that represents the formation of an ionic compound from its constituent elements
Bonding Pair
a shared pair of electrons
Lone Pair (Non-Bonding Electrons)
a pair of electrons that is associated with only one atom; not involved in bonding
Double Bond
when two atoms share two pairs of electrons
Triple Bond
shorter and stronger than double bonds
Polar Covalent Bond
intermediate in nature between a pure covalent bond and an ionic bond
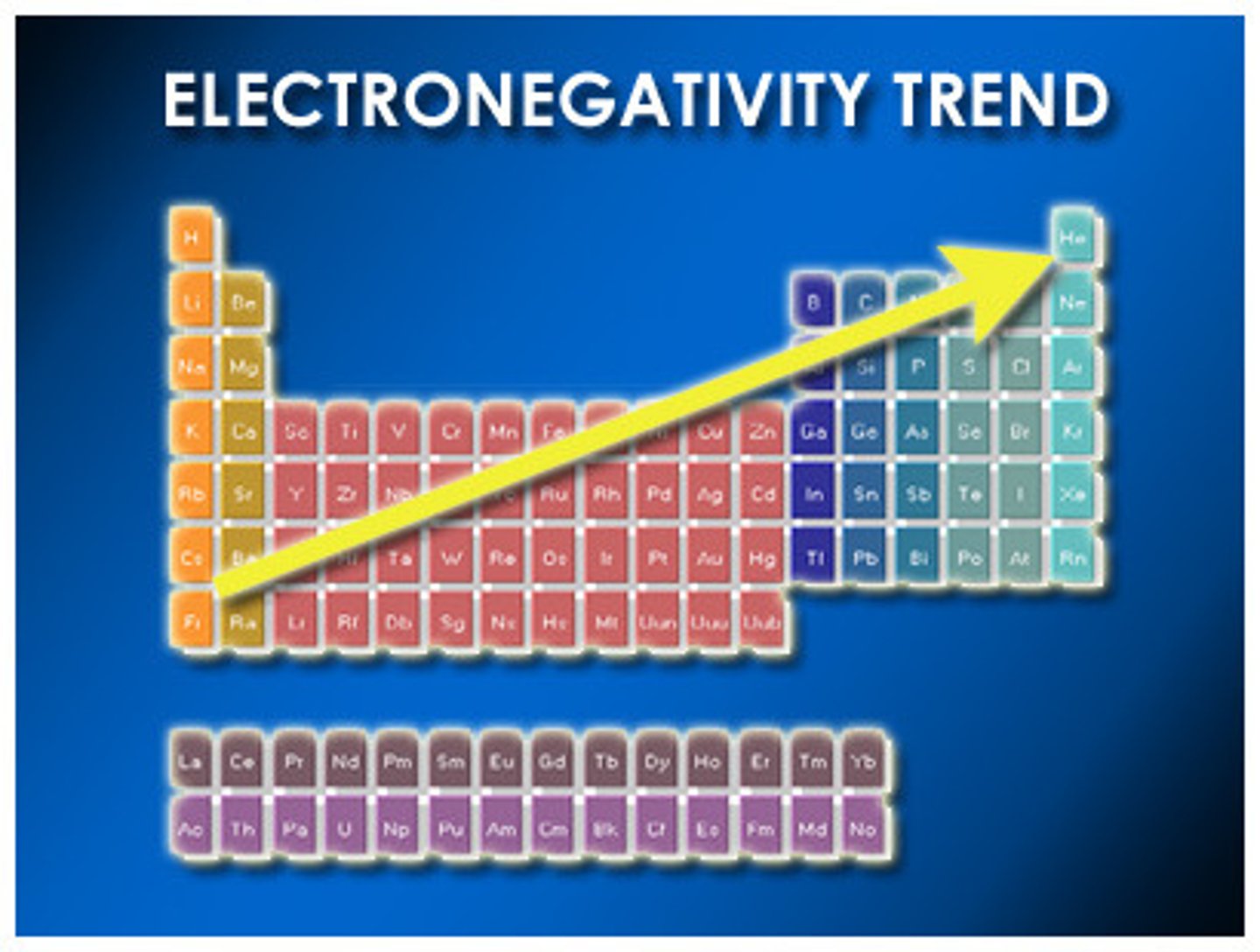
Electronegativity
the ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond; results in polar and ionic bonds
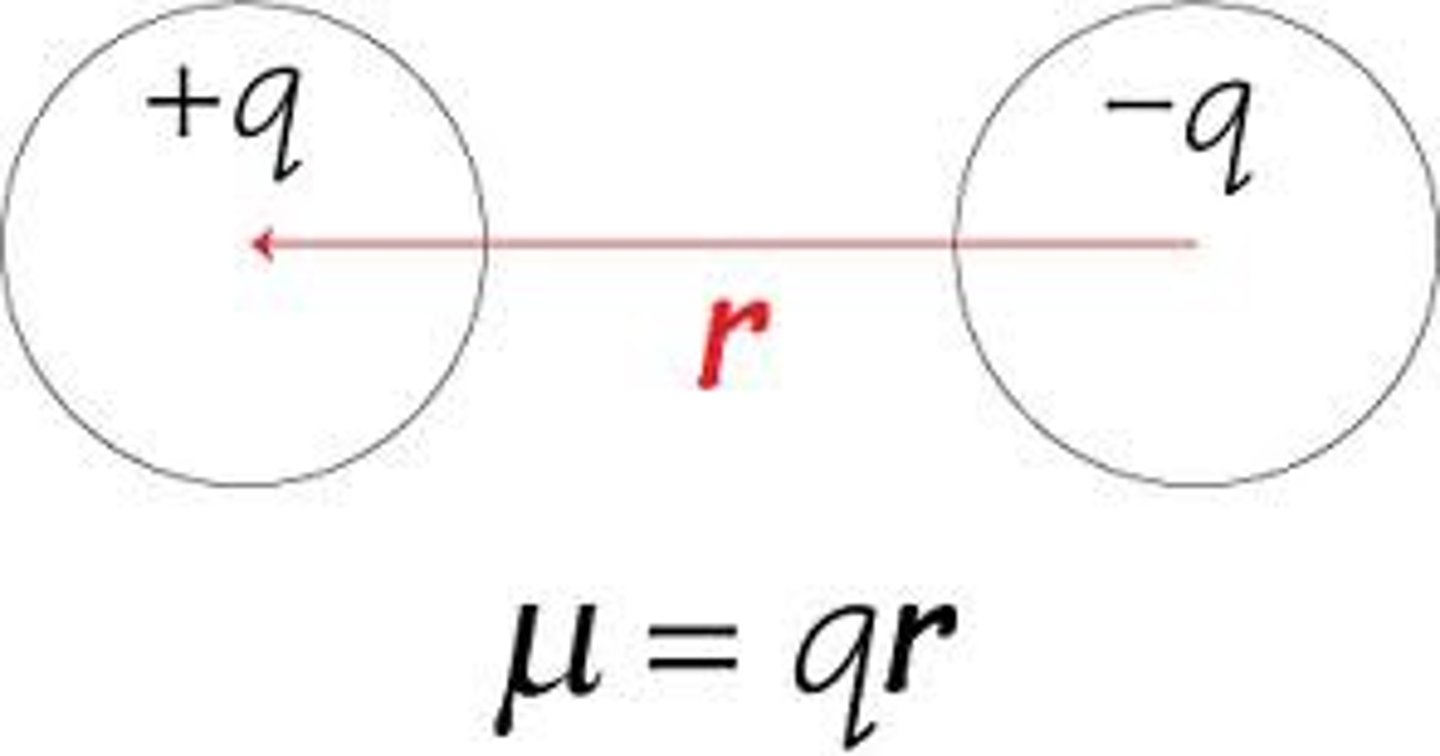
Dipole Movement
occurs any time there is a separation of positive and negative charge
Percent Ionic Character
ratio of a bond's actual dipole movement to the dipole movement it would have if the electron were completely transferred from one atom to the other, multiplied by 100%
Resonance Structure
one of two or more Lewis structures that have the same skeletal formula, but different electron arrangements
Resonance Hybrid
the actual structure of the molecule that is intermediate between two or more resonance structures
Formal Charge
fictitious charge assigned to each atom in a Lewis structure that helps us to distinguish among competing Lewis structures

Free Radicals
molecules and ions with an odd number of electrons in their Lewis structures
Bond Energy
energy required to break 1 mole of the bonds in the gas phase
Bond Length
represents the average length of a bond between two particular atoms in a large number of compounds