Week 8-Lipids, Phospholipids, Their Biological Importance, and Solution Preparation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Lipids
main biological function of
includes energy storage along
the building blocks of living cells.
Lipids are insoluble in water
but are soluble in organic solvents
like ether and chloroform.
two categories of lipids:
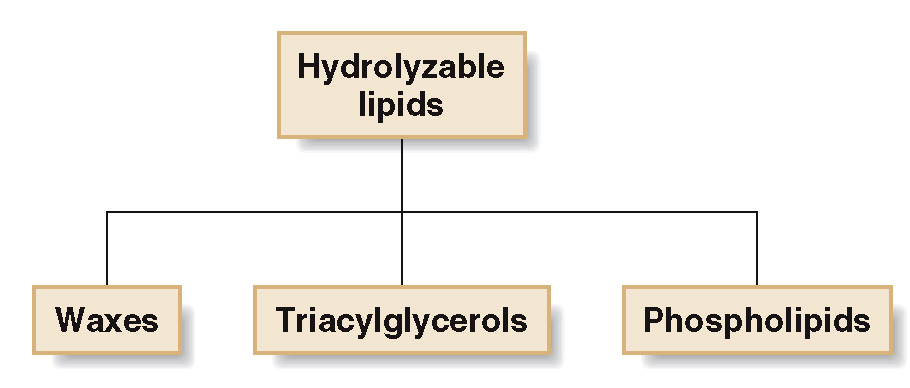
Hydrolyzable lipids
MADE OF fatty acids
polor/hyrdophilic end with carboxylic group
non-polar/hydrophobic end; the long hydrocarbon chain
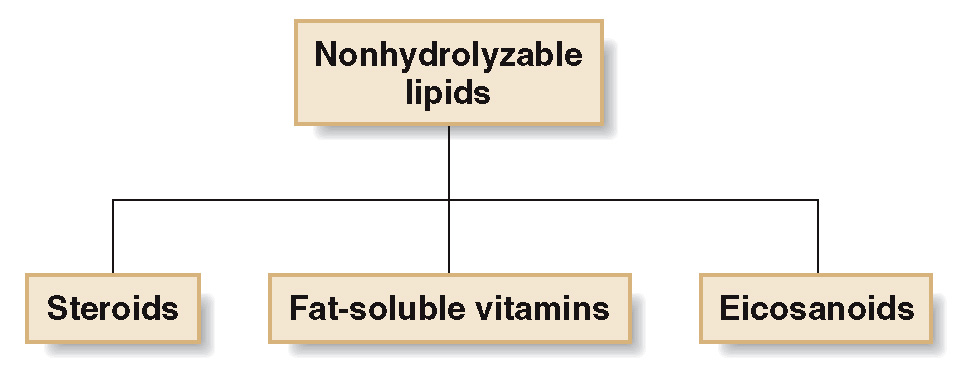
Nonhydrolyzable lipids
Hydrolyzable Lipids
lipids that can be converted to small molecules by hydrolysis with water.
are derived from fatty acids
Fatty acids are carboxylic acids (R-COOH) with long hydrocarbon chains of 12 to 20 carbon atoms.
They are the building blocks of fat in our body and in the food we eat.
Nonhydrolyzable Lipids
lipids that cannot be converted to small molecules by hydrolysis with water.
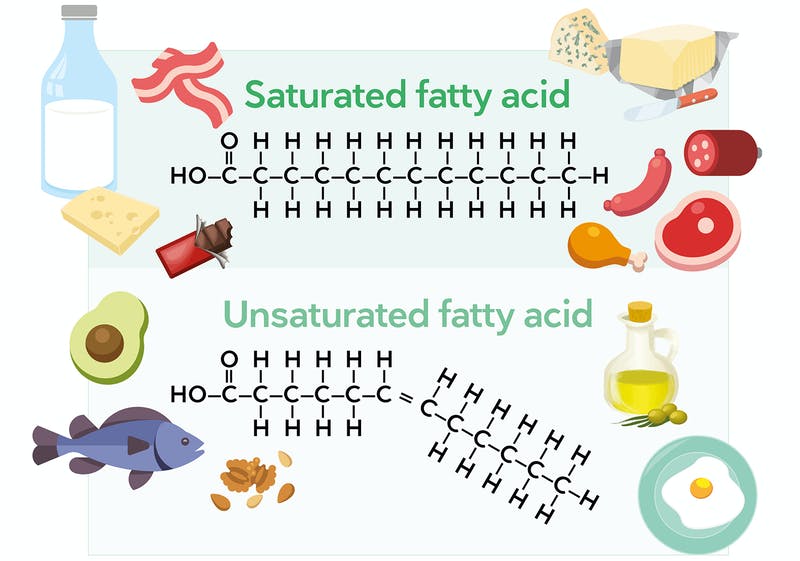
Fatty acids are of two types:
Naturally occurring fatty acids may be from plant or animal sources.
They have an
even number of carbon atoms in the chain,
and can -be either saturated or unsaturated
Some fatty acids cannot be produced by the body and are referred to as essential fatty acids
Linoleic (Omega-6 fatty acid) and Linolenic acids (Omega-3 fatty acid)
unsaturated fatty acids.
required for the growth and development of the body.
omega numbering is based on the appearance of the double bond on the carbon chain. The first carbon with a double bond in the chain is called the omega carbon.
Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds (C=C) in their long hydrocarbon chains.
Saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature and are generally obtained from animal source.
Unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds (C=C) in their long hydrocarbon chains.
Unsaturated fatty acids are liquid at room temperature and are generally obtained from plant source.
As the number of double bonds in the fatty acid increases, the melting point decreases
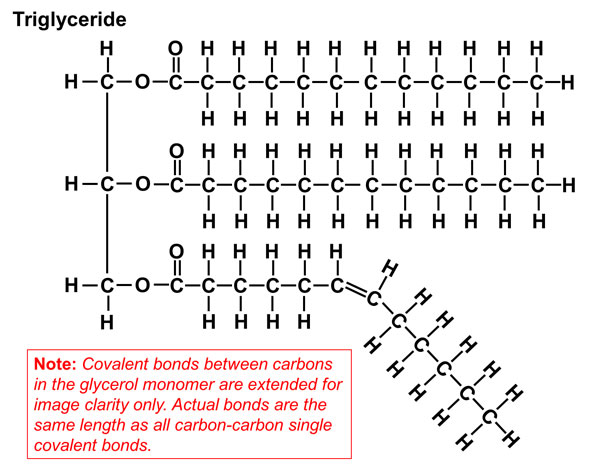
Triacylglycerols (Hydrolyzable Lipids)
are the building blocks of fat in our body and in the food we eat.
Fats and oils are made of triglycerides.
Hence fat and oil molecules are also known as triacylglycerol or triglycerides.
are formed when a glycerol molecule and three molecules of fatty acids are combined.
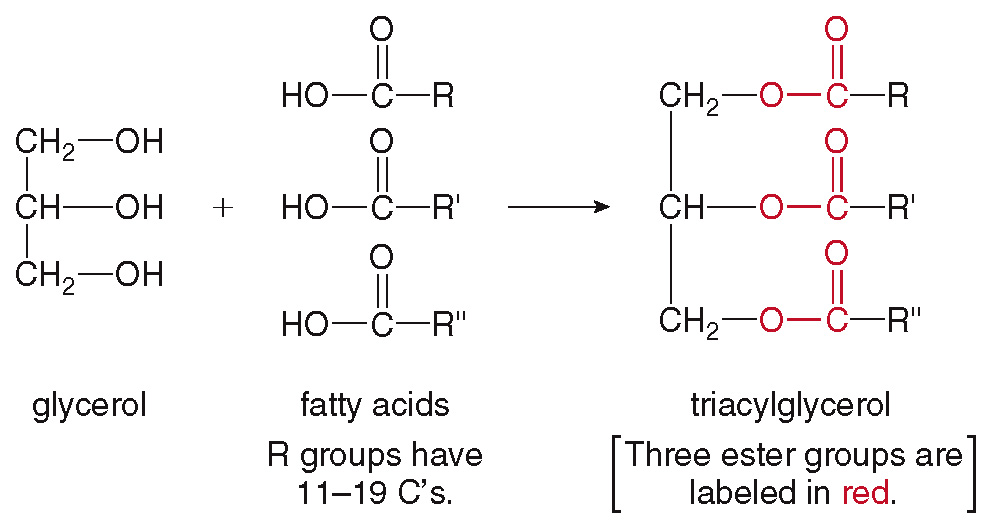
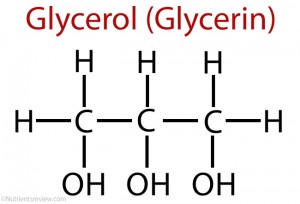
Glycerol
also known as glycerin
a three-carbon simple organic molecules, having three Hydroxyl (-OH) groups in the same molecule
It has a sweet taste.
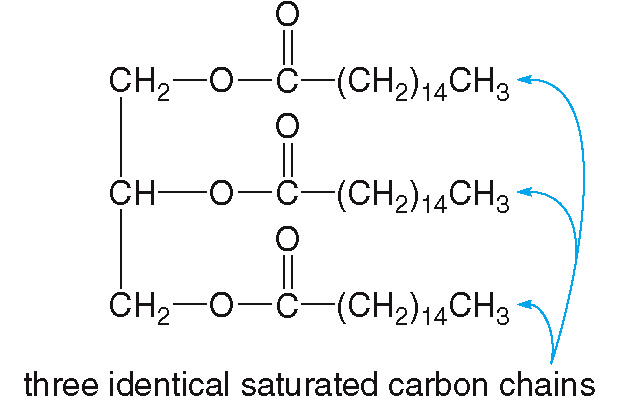
Simple Triglyceride
If the side chains (R, R’ and R’’) from the three fatty acid molecules are of the same kind
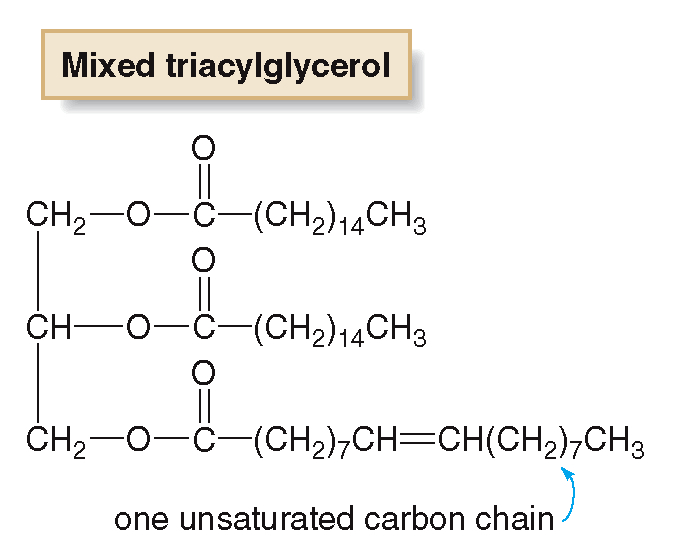
mixed triglyceride
if two or three fatty acids side chains are different,
Saturated triglycerides
contain only saturated fatty acids
They make up for most animal fat and are solid at room temperature.
They have a high melting point and are generally from animal source.
Unsaturated triglycerides
contain at least one unsaturated fatty acid.
They make up most vegetable oils and are liquid at room temperature.
They have a lower melting point are generally from plant source.
Oils are derived from fatty acids that have a larger number of double bonds.
Increasing the number of double bonds in the fatty acid chain decreases the melting point of the triglyceride.
monounsaturated triglycerides.
Triglycerides that have one carbon double bond (C=C)
polyunsaturated triglycerides.
Triglycerides that have two or more carbon double bonds (C=C)
Clinical Importance of Triglycerides
Fats are used to
build cell membranes
insulate the body
store energy for later use.
Humans store energy as triglycerides in adipose cells
below the surface of the
skin
breast area
surrounding internal organs.
The number of adipose cells is constant; weight gained or lost causes them to swell or shrink, but not decrease or increase in number
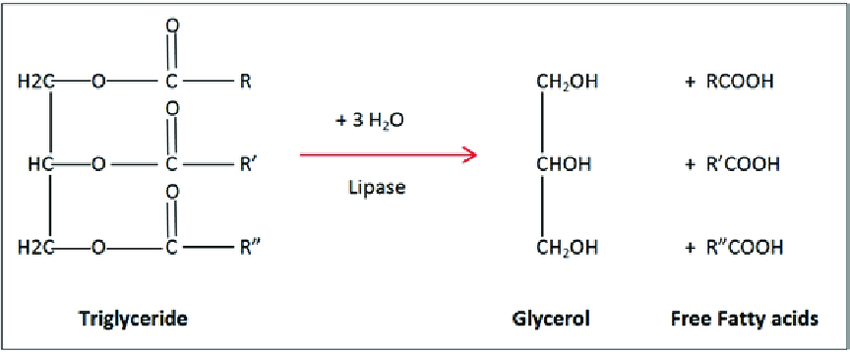
In order for the triglycerides to be used for energy in the body, they have to be hydrolyzed.
The esters in the triglycerides are hydrolyzed by enzymes called lipases.
Hydrolysis takes place in the presence of water molecules.
Triglycerides are hydrolyzed into glycerol and fatty acids as shown in the diagram below.
It is said that a high intake of saturated triglycerides is linked to heart disease.
Saturated fats stimulate cholesterol synthesis, which can lead to cholesterol building up inside arteries, known as cholesterol plaques.
This results in high blood pressure, heart attack, and even stroke
Triglycerides are usually measured along with cholesterol as part of a blood test known as Lipid Profile.
Phospholipids (Hydrolyzable lipids)
can be broken into simple molecules by hydrolysis with water
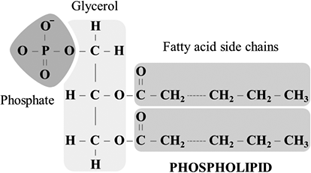
are lipids that contain a phosphate molecule
resemble triacylglycerols
Except in phospholipids,
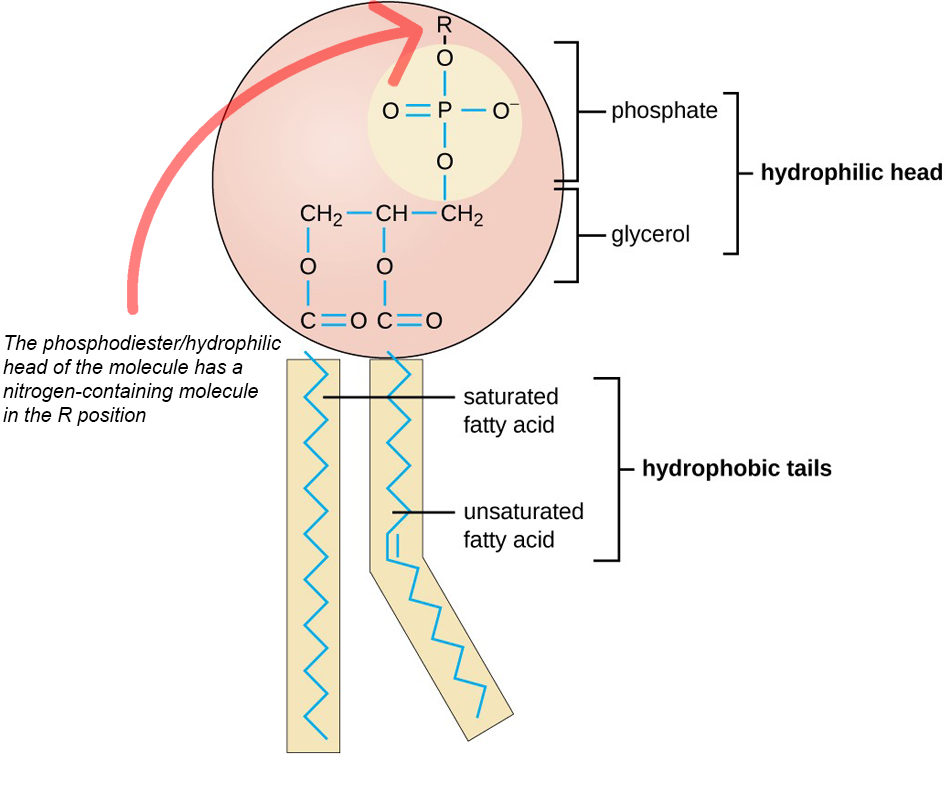
the third fatty acid is replaced with a phosphate group, which is bonded to the glycerol
The phosphodiester/hydrophilic head of the molecule has a nitrogen-containing molecule in the R position, which is attached to the oxygen of the phosphate group.
nitrogen-containing molecule can be of different kinds, such as Choline molecule, as shown in the following image.
also referred to as phosphoacylglycerols.
Phosphoacylglycerols are the main component of most cell membranes.
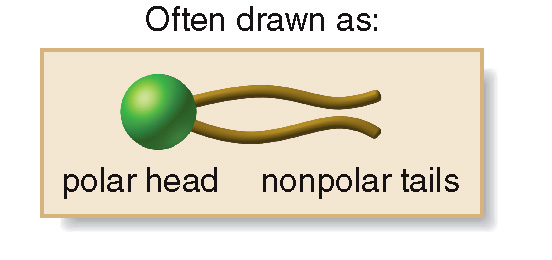
is made of a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head,
two fatty acid side chains form two nonpolar “tails” that lie parallel to each other.
This is known as the non-polar end or the hydrophobic (water not-liking) tail
The phosphodiester end of the molecule is a charged or polar “head”
also known as the hydrophilic (water-liking) head.
Cell Membrane Structure and the Role of Phospholipids
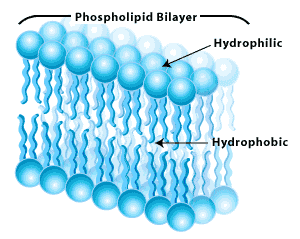
Phospholipids, the major component of cell membranes, contain a hydrophilic polar head and two hydrophobic nonpolar tail, which is often drawn as shown in the picture below.
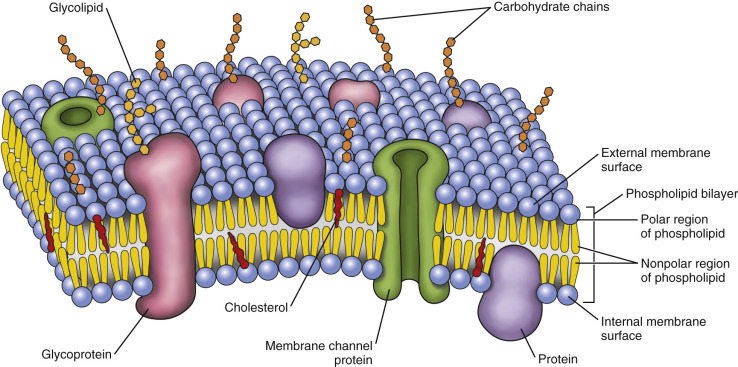
cell membranes are composed of two adjacent layers of phospholipids called phospholipid bilayers.
When phospholipids are mixed with water, they assemble in such a way that the hydrophobic (water-not liking) or nonpolar tails are towards the interior of the bilayer and the hydrophilic (water-liking) or polar heads are towards the exterior of the bilayer as seen in the diagram below.
Alongside the phospholipids, the cell membrane also has other molecules like proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol embedded in the lipid bilayer.
glycolipids
carbohydrates are attached to the exterior of the cell
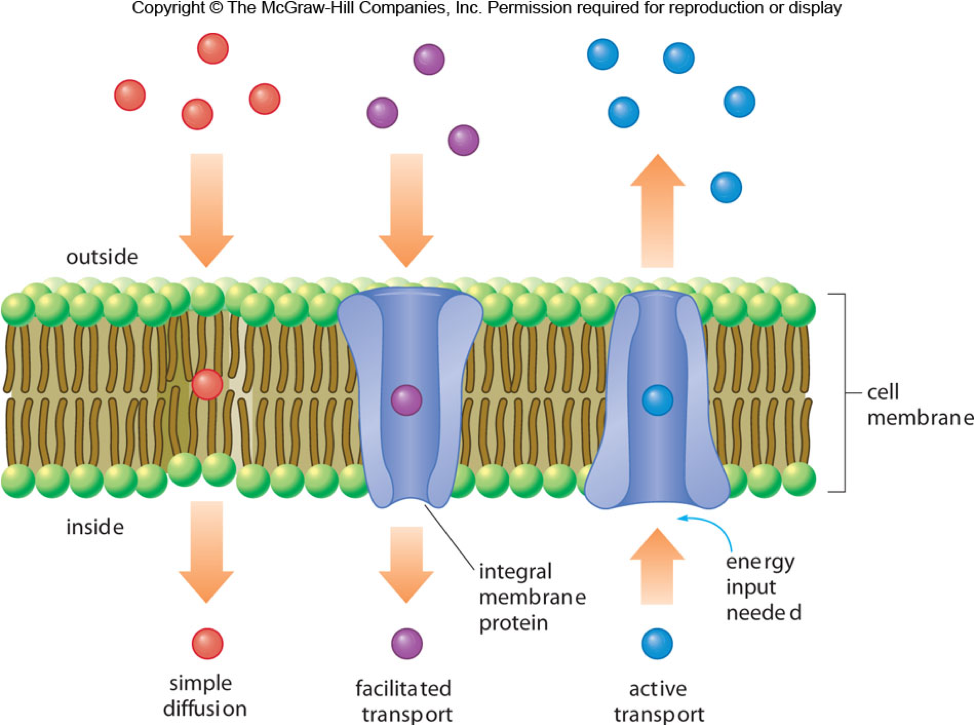
purpose of cell membrane
stop the passage of ions and molecules into or out of the cell.
transport of oxygen, carbon dioxide and other molecules through the membrane.
small molecules like O2 and CO2 can diffuse through the cell membrane, traveling from higher to lower concentration
larger polar molecules and ions like Cl− or HCO3−, travel through integral protein channels would facilitate their transport to cross the membrane efficiently.
For the movement of other ions such as Na+, K+, and Ca2+, some energy input is required and this is called active transport.
Steroids (Non Hydrolyzable Lipid)
are a type of non-hydrolyzable lipids that cannot be converted to small molecules by hydrolysis with water.
are a group of lipid characterized by a carbon skeleton with four fused rings (tetracyclic)
contain a significant amount of hydrocarbon character,
but unlike other lipids, they are not esters
Different steroids have different functional groups attached to this group of rings.
The most common steroid in the body is cholesterol.
Many steroid hormones are produced from cholesterol.

Cholesterol as a Steroid
is present in the cell membrane and is one of the most prominent steroids.
It is synthesized in the liver
is found in almost all body tissues.
obtained in the diet
meat
cheese
butter
eggs
is insoluble in the aqueous medium of blood.
transported through the bloodstream by lipoproteins,
are granules of phospholipids and proteins.
Two types
LDL (Low-density lipoproteins)
HDL (High-density lipoproteins).
Elevated levels of cholesterol in the bloodstream can lead to
coronary artery disease, heart attack, etc.
LDL (Low-density lipoproteins)
Transports cholesterol from the liver to the tissues
Deposits cholesterol on the walls of arteries,
when it carry more than is needed to form cell membranes.
This deposit forms plaque, which restricts blood flow;
thus, LDL cholesterol is called “bad” cholesterol.
HDL (High-density lipoproteins)
Transports cholesterol from tissues back to the liver
Reduces the level of cholesterol in the blood-stream by bringing excess back to the liver
thus HDL cholesterol is called “good” cholesterol
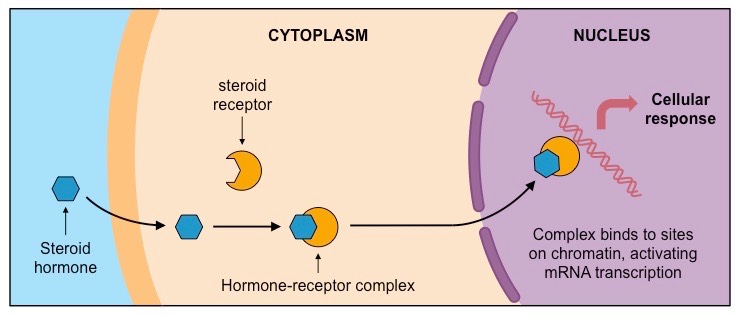
Steroid Hormones
Hormones are chemical molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body.
They are secreted directly in the blood, which carries them to other organs and tissues of the body.
There, they get attached to steroid receptors to form the hormone receptor compleX
allows the hormone to carry out its function
Two important classes of steroid hormones:
Sex hormones
Adrenal cortical steroids, also known as corticosteroids
Sex hormones
important role in the
sexual development
reproduction
general health.
They include
female sex hormones
estrogen
progesterone
male sex hormones
androgen.
They are typically made in the gonads or placenta.
Adrenal cortical steroids, also known as corticosteroids
are natural hormones and important in maintaining good health.
There are two types of corticosteroids which are
aldosterone
regulates blood pressure by controlling sodium and potassium levels in the blood and tissues
cortisol
Regulate metabolism, manage stress, and suppress the immune system
They are typically made in the adrenal cortex.