Lecture #14: Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Citrobacter
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
T/F: Klebsiella is belong to Enterobacteriaceae
True
Klebsiella:
Gram _
Motility
Special enzymes?
Agar colony description?
Gram -
Non-motile
Urease positive
Mucoid
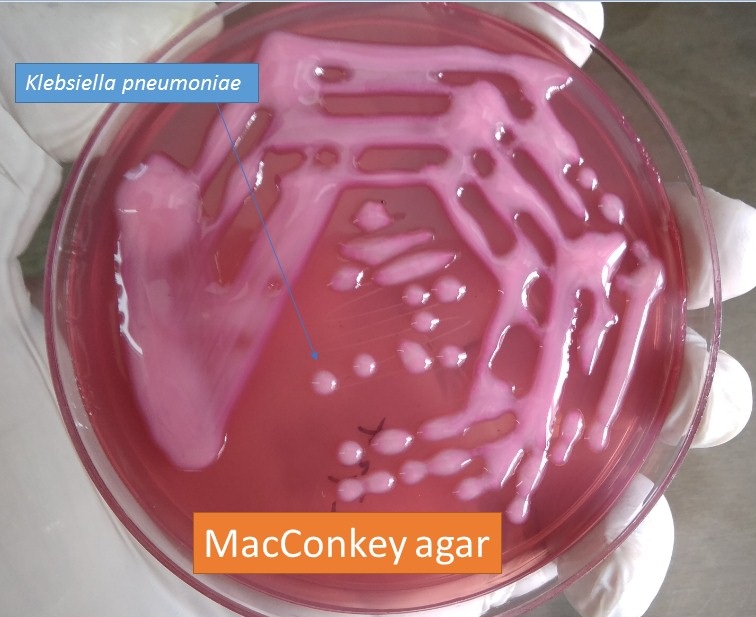
What are the Virulence factors associated with Klebsiella?
Capsule
Adhesin
Endotoxin (Coliform septicemia)
Urease
K. pneumoniae and K. oxytoca cause __________ infections
Opportunistic (they both are naturally found on animals but only cause disease in certain scenarios)
K. pneumoniae can cause Bovine ______, T/F: it cause this in many animals across the entire heard
Mastitis
False, it is usually associated with individual cases
What part of the environment of a dairy barn is Klebsiella associated with?
Sawdust and shavings
These are the normal sources of Klebsiella, when they get moist it creates an ideal environment

Which species of animals can Klebsiella infect? How does it infect them?
Equine
Colonizes the lower reproductive tract of mares
Vaginitis, metritis, infertility, abortion (repro related issues)
Canine
Companion Birds
Contaminant of bird seeds
Colonizes the cloaca and choana of healthy birds
Causes
Septicemia, respiratory signs, diarrhea
T/F: Stallions are reservoirs for K. pneumoniae/oxytoca
False, they can get infected and transmit but are not reservoirs
What is the most common infection site of Klebsiella in humans?
The urinary track
T/F: Klebsiella can be seen in reptiles
True
Enterobacter:
Gram_
Motility?
Enterobacter are Gram - and Motile
What are the 2 main species of Enterobacter to know?
Enterobacter cloacae complex
E. hormaechei
T/F: Both Klebsiella and Enterobacter are motile
False, Klebsiella is non-motile
Enterobacter are known to to have an innate ________ ________, what causes this?
Antimicrobial resistance, Beta-lactamase
What is the significance of Enterobacter in humans?
Common cause of nosocomial infections in health care facilities
What species of Citrobacter is known to infect turtles? What does it cause?
Citrobacter Freundii
Septicemia cutaneous ulcerative disease (SCUD)

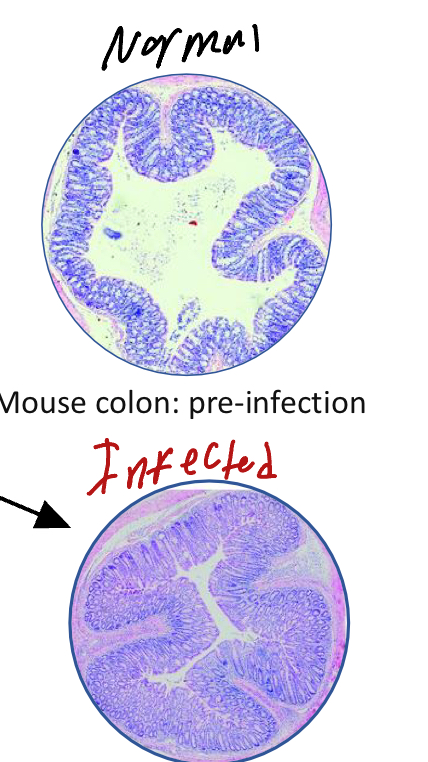
What disease does Citrobacter rodentium cause in rodents?
Murine Colonic Hyperplasia (Image)
C.S
Diarrhea, rectal prolapse
Effacement of the brush-border
What are the 2 main species of Proteus that we discuss? Are either strains associated with a particular disease process?
Proteus mirabilis
Common cause of UTIs
Proteus vulgaris
T/F: Proteus is urease negative
False, it is Urease positive
Proteus infections are a common cause of ____
UTIs
Proteus mirabilis performs “swarming. “What does this mean?
The coordinated, rapid movement of a bacterial population across a solid surface
Results in the formation of the odd shaped proteus colonies (circular)
__________ is the hallmark of a Proteus infection, how does Proteus cause this?
Urolithiasis (Struvite formation)
Urease (converts urea to CO2 and urine, increases pH, causes formation of struvites)

What are Superbugs?
Strains of bacteria that are resistant to several classes of antibiotics (multi- or pan- resistant)

Based on the growth on a BA plate, which of the bacteria that are in this Knowt (Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Citrobacter, Proteus) is this?
Proteus
What are the superbug species? (Use hint)
Enterococcus faecium
Staphylococcus aureus
Klebsiella species
Acinectobacter baumanni
Psuedomonas aeruginosa
Enterobacter spp.
What relationship do Hospitals have with Superbugs?
They are a breeding ground for Superbugs
How do superbugs resist the drugs that normally work to treat them?
They secrete Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs)
ESBL enzymes break down penicillins and cephalosporins
List the predisposing factors of Klebsiella-associated mastitis
Moist/wet sawdust and/or shaving bedding
T/F: Klebsiella, Morganella, and Enterobacter spp. cause opportunistic infections
True
Klebsiella-associated bacterimia can lead to which clinical/pathological condition?
Endotoxemia?
Citrobacter infection is a problem in which animal species?
Reptiles (C. freundii) and Rodents (C. rodentium)
List the virulence factors of Proteus
Endotoxin (Urease)
IgA protease
Fimbriae
Swarming Motility
Hemolysins
What is the advantage of the urease enzyme for a pathogen?
It allows it to survive in the Urinary tract and utilize urea to survive (decreases the pH to make the environment habitable)
How uroliths are formed in Proteus infected bladder?
Urease hydrolyzes Urea → Ammonia + CO2
Ammonia damages urinary epithelium
Urinary pH increases
Precipitate ions form calculi in the form of struvites
T/F: In bladder infections, bacteria can hide in struvites
True