Environmental Science 8.3 Study Guide (Buie)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
wind, hydropower, geothermal, solar, biomass/biogas/biofuel, and hydrogen power
sustainable energy sources include all primary renewable energy sources which are...
wind power
power derived from the wind (as by windmills)

hydropower
electricity generated from the energy of moving water; a resource where falling water turns a turbine in a dam, which is connected to a generator that converts kinetic energy into electrical energy

geothermal power
a form of power obtained from steam or hot water coming from within the earth's interior; this is energy in underground thermal energy stores. It is possible in volcanic areas or where hot rocks lie close to the surface; the source of a lot of this energy is the slow decay of various radioactive elements deep inside the earth
solar power
energy from the sun that is converted into thermal or electrical energy

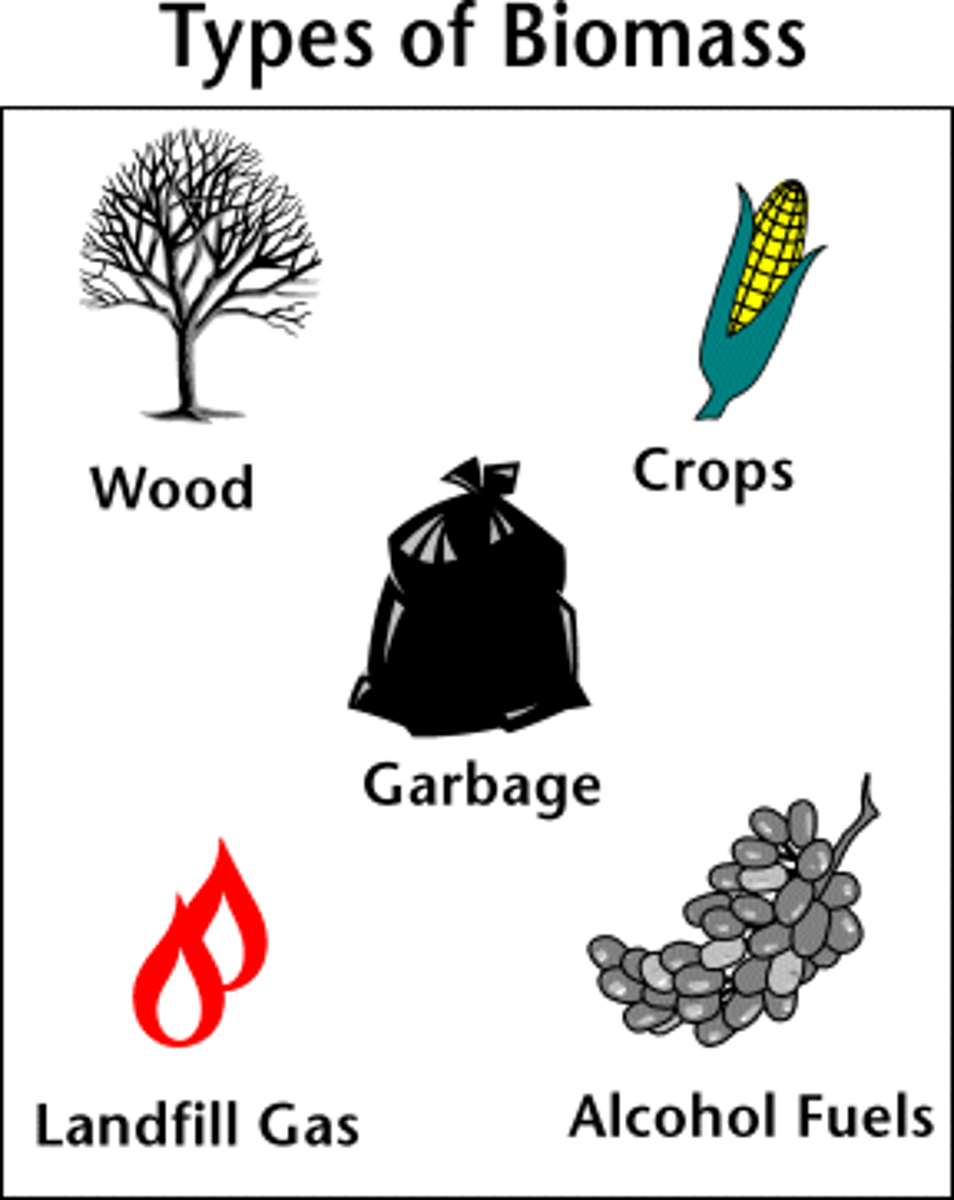
biomass
energy source that uses energy from organic matter (living things) to produce steam to spin a turbine when burnt (renewable); energy produced by burning organic matter, such as wood, food scraps, and alcohol

biofuel
liquid fuel created from processed or refined biomass

biogas
a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide produced by bacterial degradation of organic matter and used as a fuel; gaseous fuel, especially methane, produced by the fermentation of organic matter
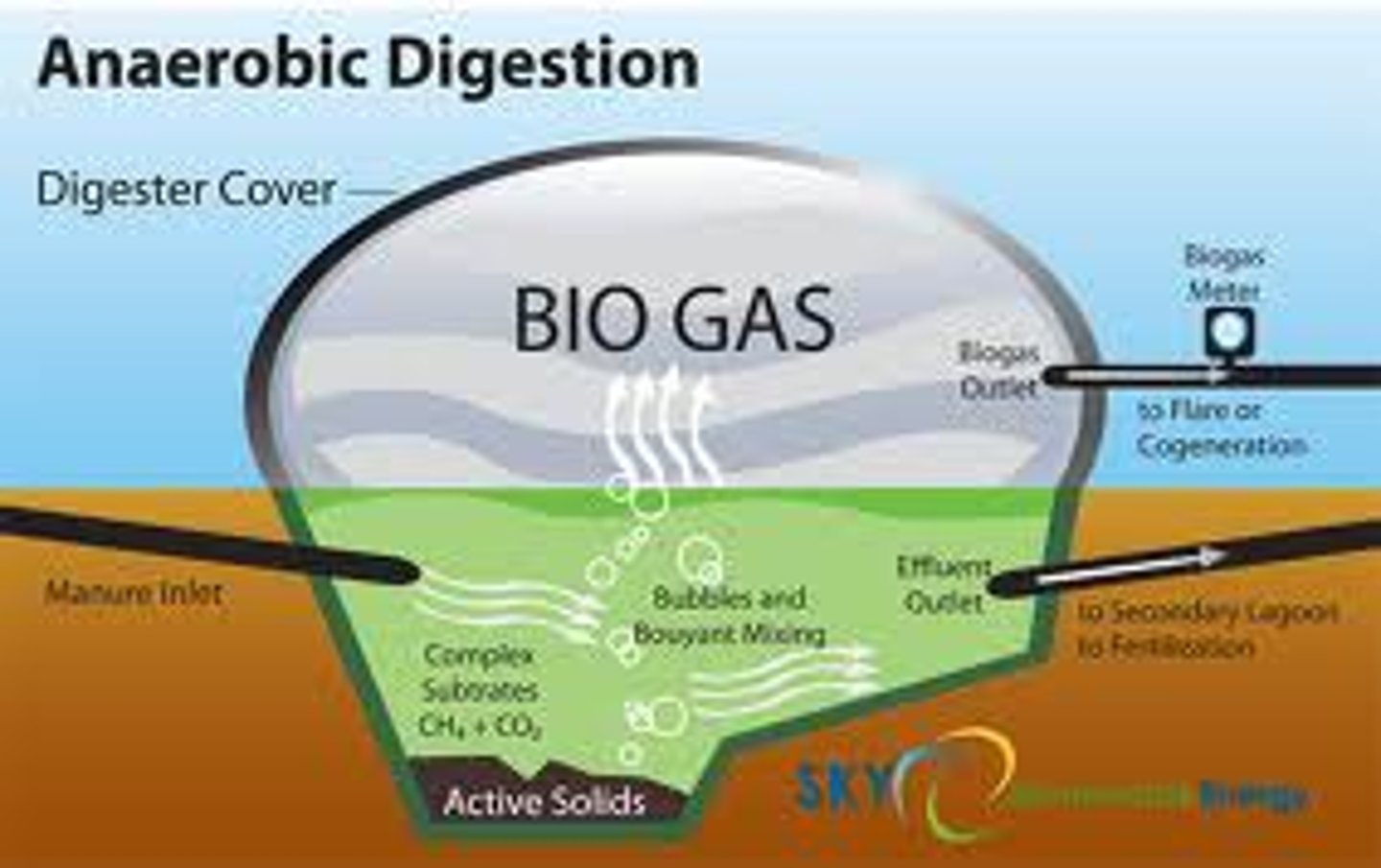
hydrogen power
energy produced by passing an electric current through water to burn hydrogen; the capture of energy from the reaction of hydrogen with oxygen (producing water); burn H to produce energy, plentiful and little pollution (water vapor) but currently expensive to separate H from water

supply-side policy
these aim to increase the production and availability of renewable resources and technologies by improving the supply side of the economy; applies to where the energy comes from
demand-side policy
these aim to influence consumer or business behavior to increase demand for renewable energy and eco-friendly practices; applies to the consumer and products that will use the energy
supply-side policies: increasing renewable supply and targets developers and producers; demand-side policies: increasing renewable demand and targets consumers and end-users
what is the difference between supply-side policies and demand-side policies?
together, they provide a balanced, effective push...the supply-side gets the green tech built and improved while the demand-side encourages people and businesses to actually use it--->creates a feedback loop
why do we want to make sure both policies (supply-side and demand-side) are put into place?
providing a balance between policies, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels (supply side), energy conservation and efficiency (demand side)
what are the goals of supply-side policies and demand-side policies when they are combined together?
global climate change and uncertainty surrounding fossil fuel supply
what two things are driving the push towards renewable energy sources?
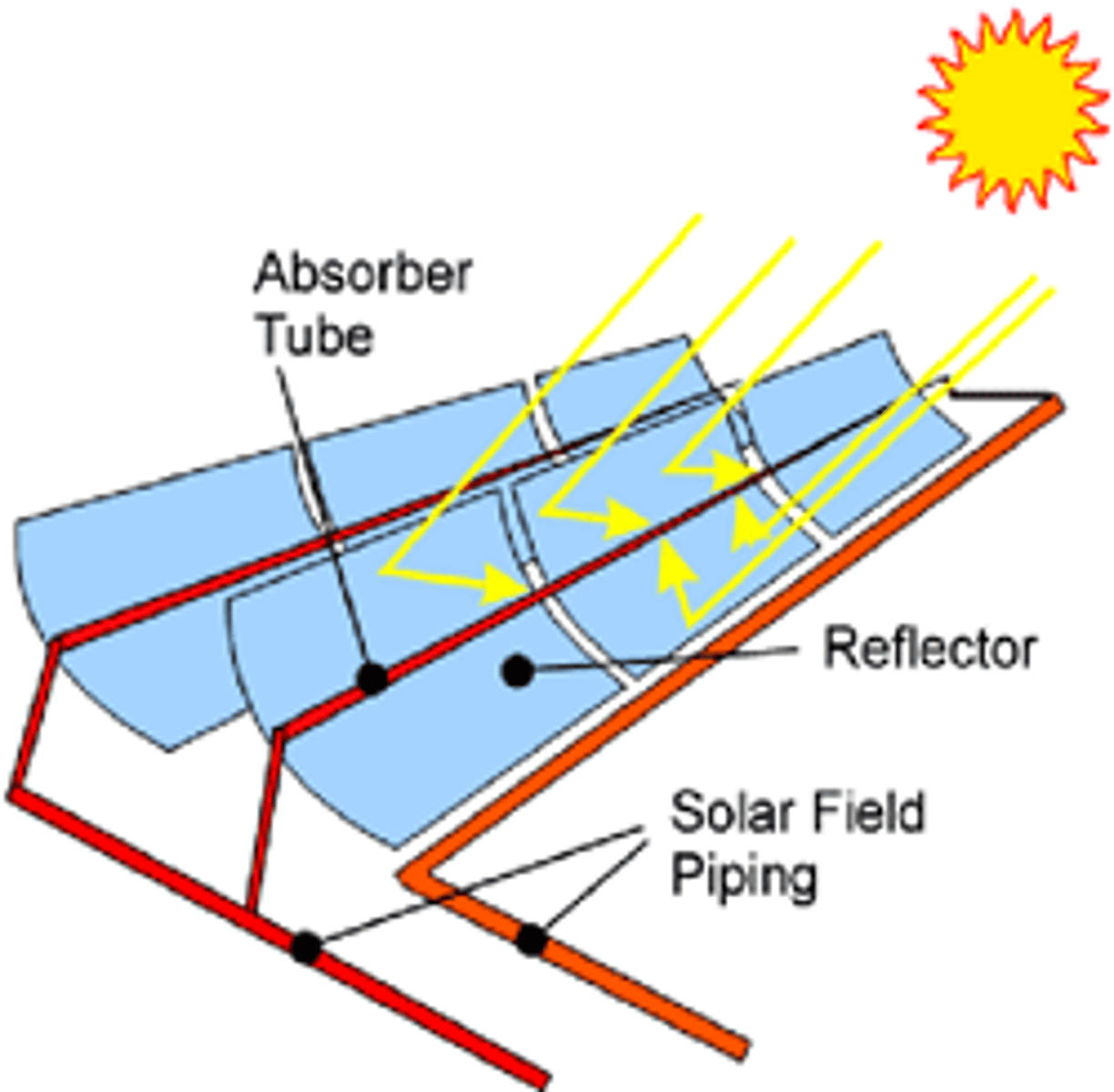
sunlight hitting the parabolic-shaped mirrors is reflected onto a central pipe, where it heats a fluid used to boil water and drive turbogenerators-reflect sunlight onto a center pipe
how does solar trough technology work?
solar troughs and power towers; all use mirrors + turbine
what are the two different versions of concentrated solar power? what do they have in common?

solar troughs
version of concentrated solar power; reflect sunlight onto a center pipe, heat-absorbing liquid is heated to high temperatures, boiling water to produce steam for a turbogenerator, energy can be stored for release at night
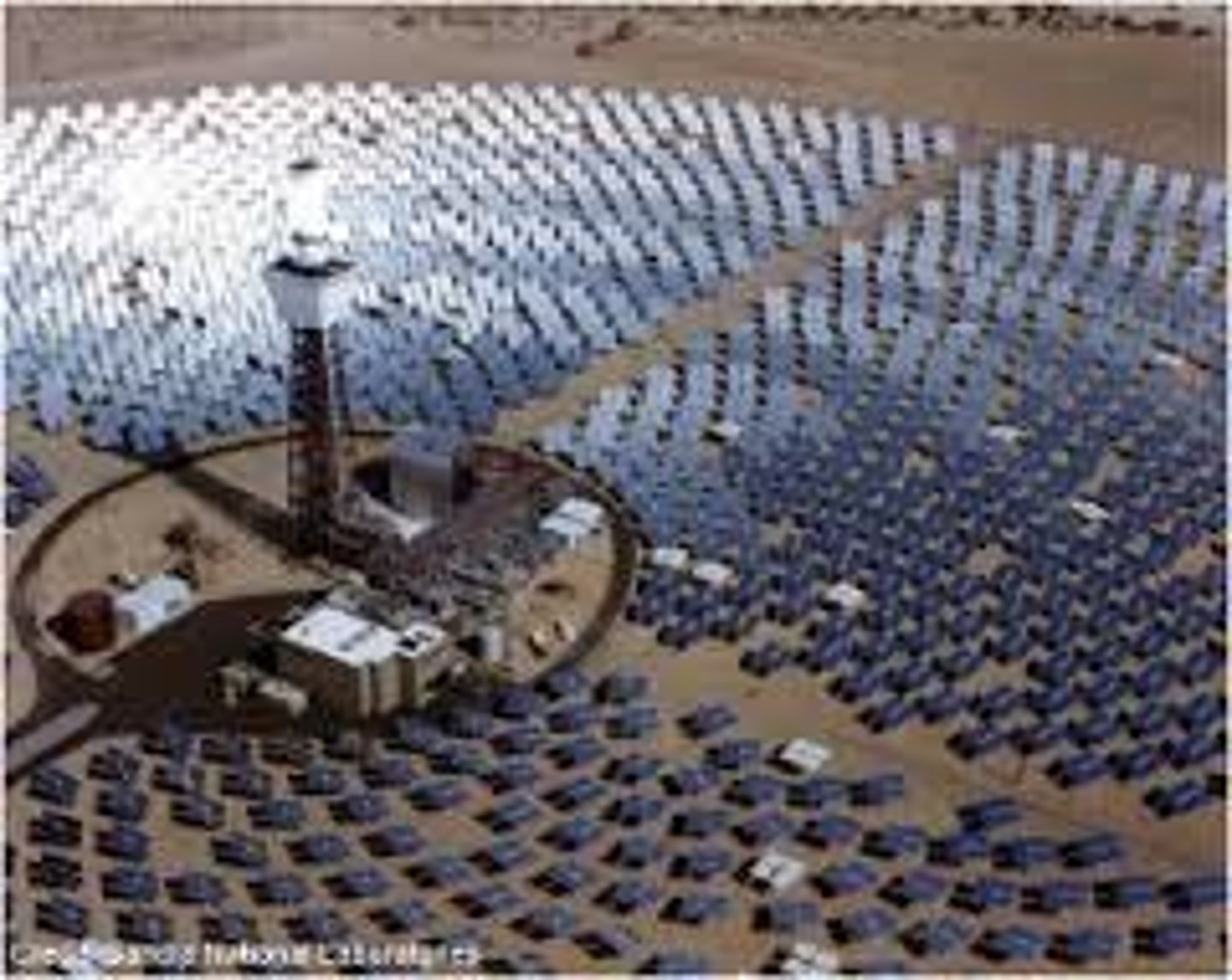
power towers
version of concentrated solar power; use fields of mirrors to concentrate sunlight on the top of central towers, in which the intense heat, generally carried by molten salts, boils water, and the steam then drives turbines

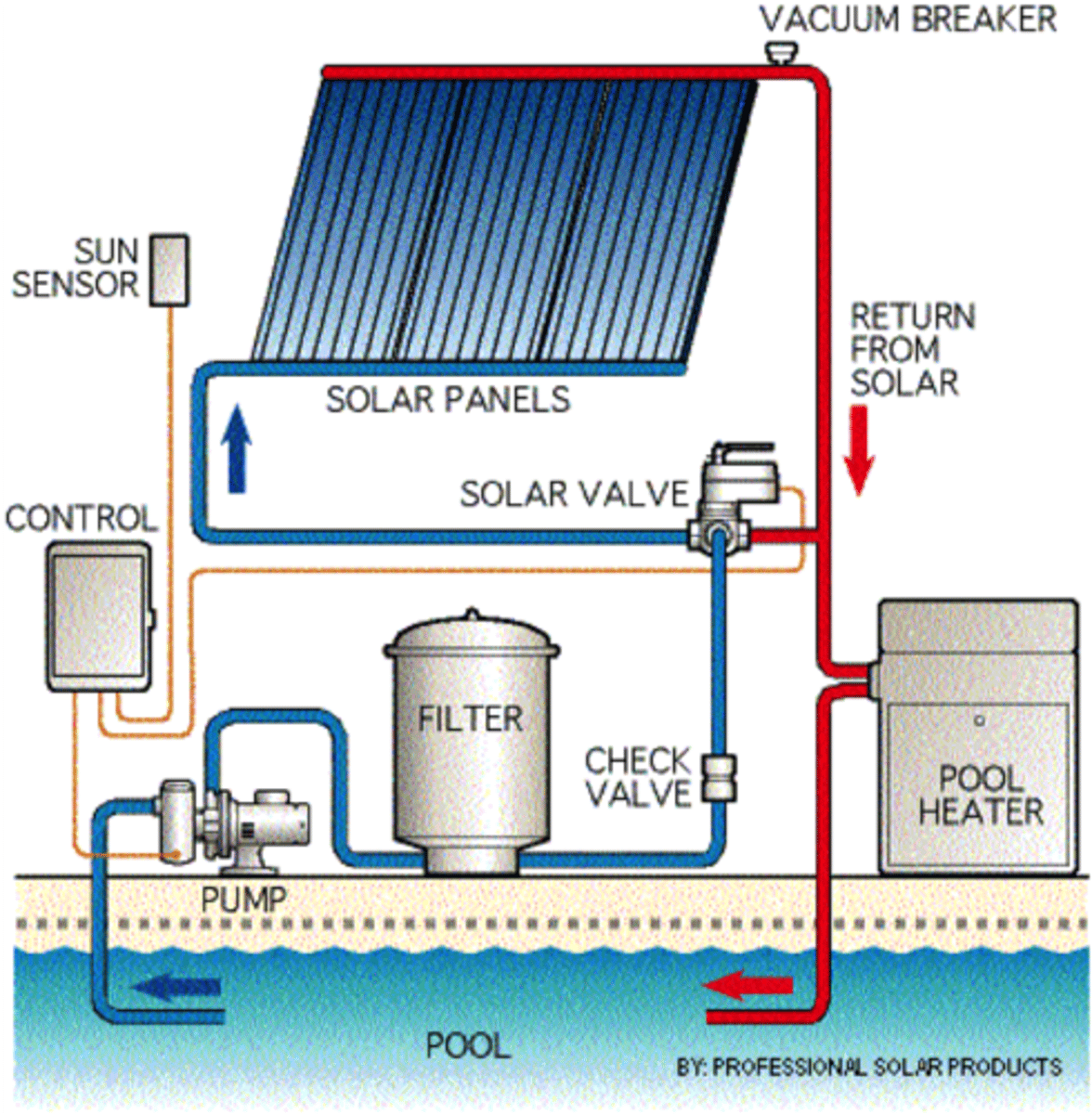
active heating systems
solar heating systems that use pumps to move heated water throughout a building
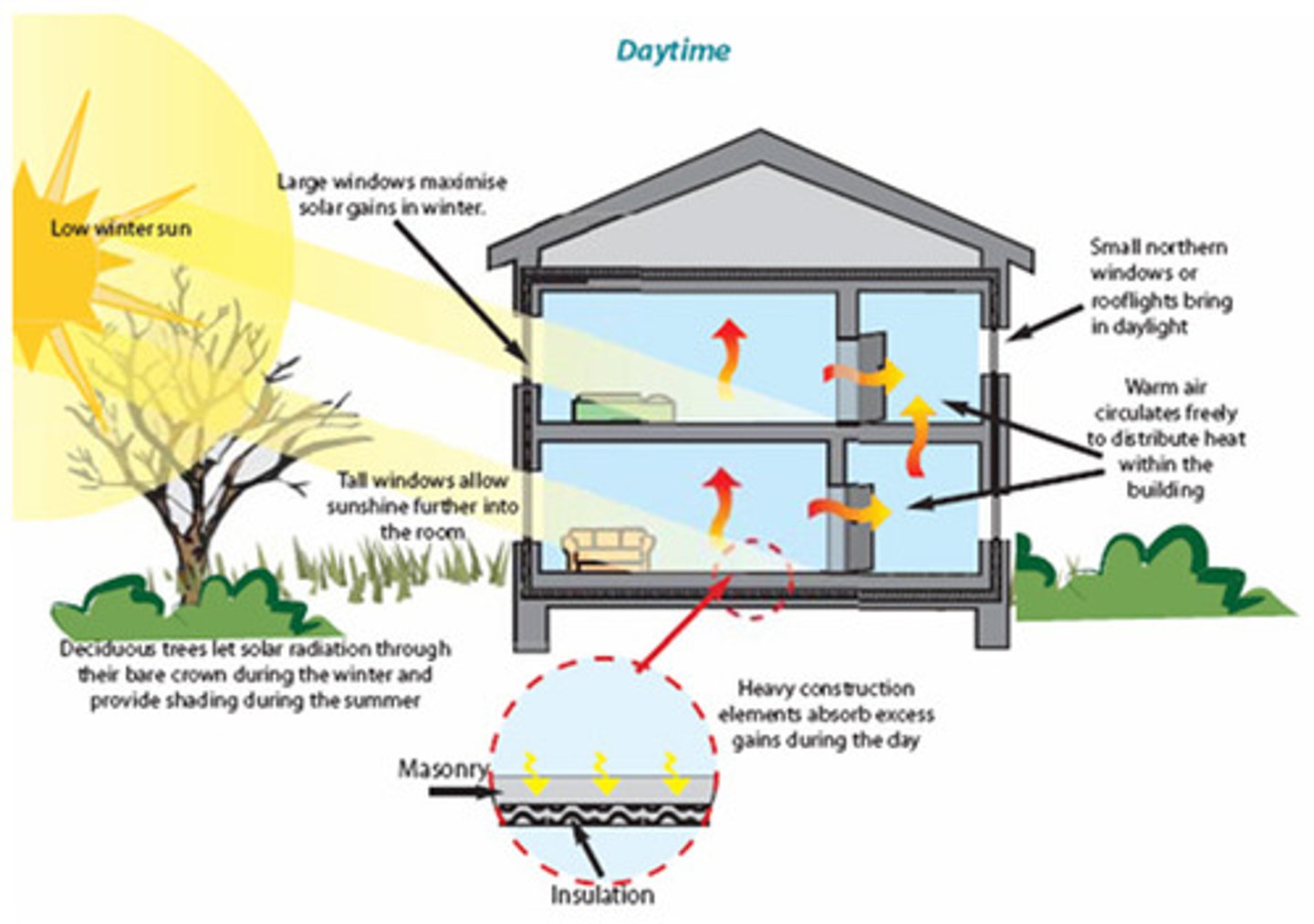
passive heating systems
solar heating systems that circulated heated water or air without using pumps
sunlight is converted to heat that warms air or water
how is solar power used for electricity and direct heating?
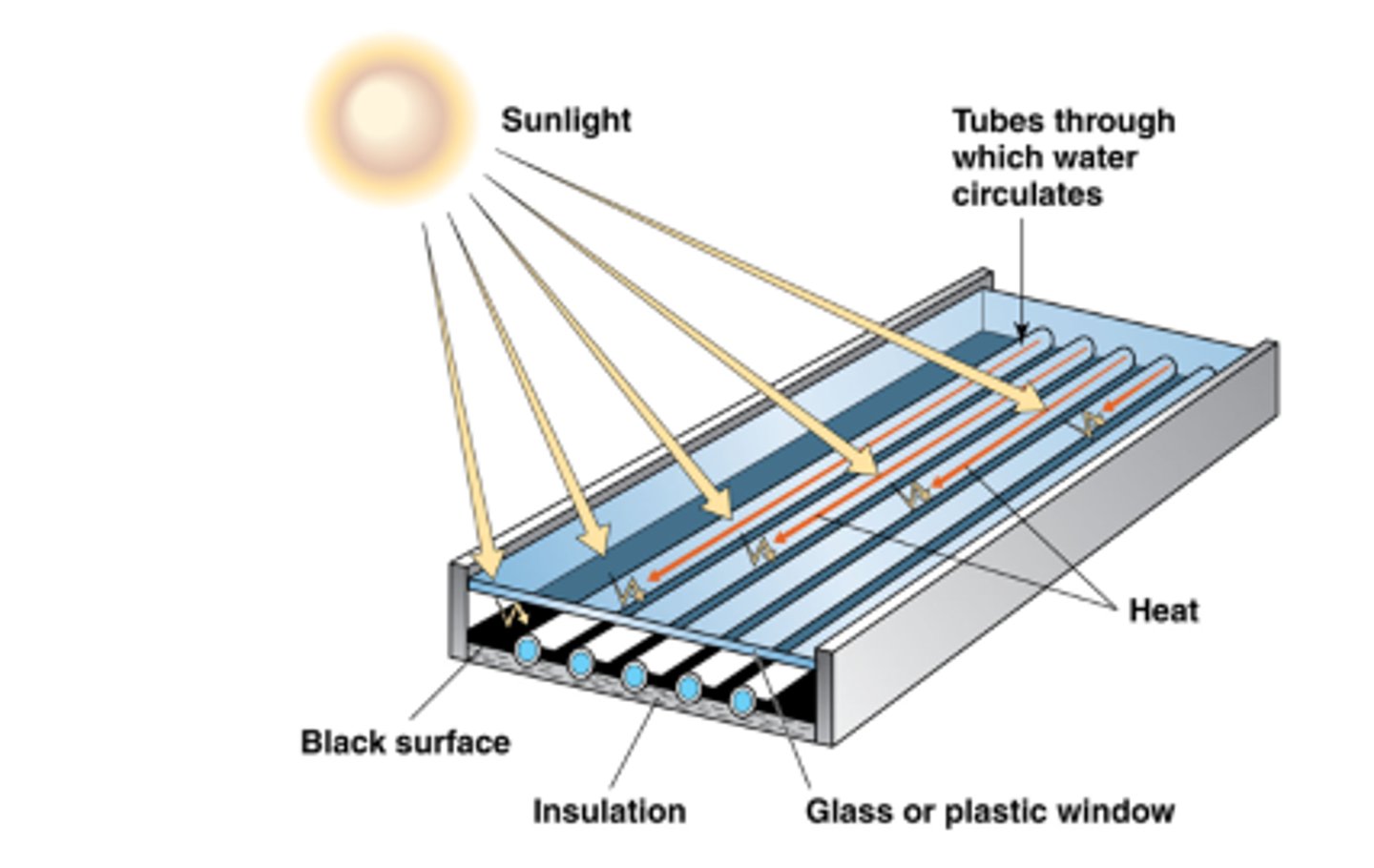
use mechanical parts like pumps or fans to collect heat (often from the sun) and move it through a building to provide warmth
how do active heating systems work?

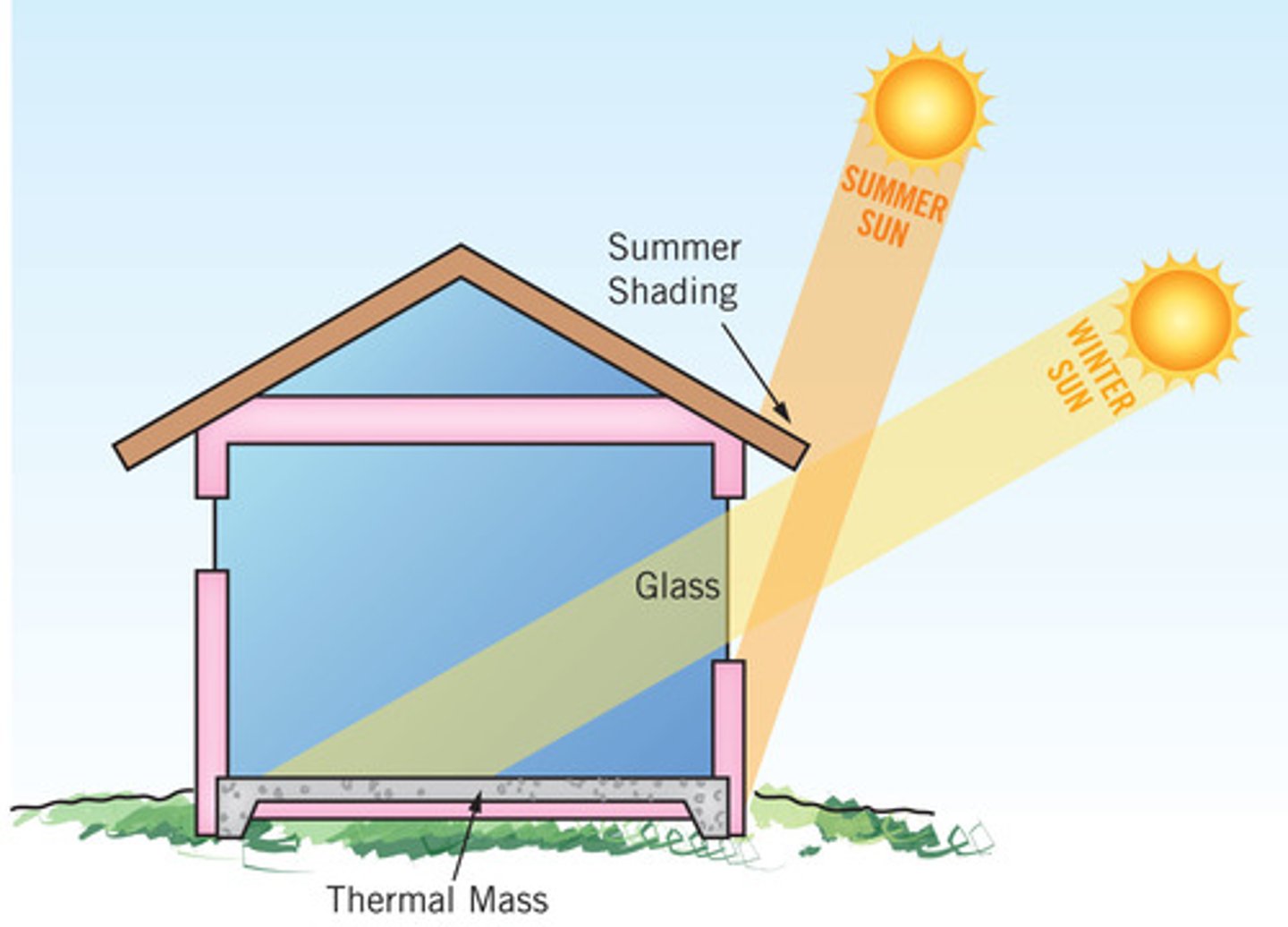
use the design of a building—like windows, walls, and floors—to collect and store heat from the sun without using mechanical devices
how do passive heating systems work?
active: uses pumps and external energy as an energy source (electricity), needs pumps, fans, or controllers, collects and moves heat using equipment, usually more expensive; passive: uses natural sunlight as an energy source, no mechanical parts needed, building design collects and stores heat, cheaper
what is the difference between active heating systems and passive heating systems?
active: solar water heating systems, forced-air heating systems, radiant floor heating, heat pumps; passive: south-facing windows, thermal mass, overhangs or shading devices, insulated windows and walls
give some examples of active heating systems and passive heating systems (4 each)
- PV panels are long lasting
- Materials used to make PV panels is abundant
- New PV panel technology is already in the works
- If placed correctly, it will not interfere with the environment
- No greenhouse gases/air pollution produced
what are the pros of solar power? (5)
- How do we collect the energy? Where can we? (some areas do not get as much sun as others)
- PV panels are only about 15% efficient at converting light energy to electricity
- Electricity storage (batteries) needed for nighttime
what are the cons of solar power? (3)
- Dams create reservoirs which can be used for recreational and tourist use (extra revenue; often why it is more used than other renewables)
- Dams provide flood control/irrigation water/drinking water
- No waste, air pollution, GHG production (once in use)
- Can be used on a large or small scale
what are the pros of hydropower? (4)
- Building can displace people and other organisms as the area floods to make the reservoir
- Building causes the release of GHG as organisms decay
- Impede or prevents fish migration; can hurt fishing up and down the river
- Only a few sites left in the US for large-scale dams
- Will not work if droughts are really bad
what are the cons of hydropower? (5)
- Reliable and efficient
- Farmers can make money from having wind turbines on their property, and only lose minimal farming space
what are the pros of wind power? (2)
- Can only be used in places with a consistent wind of a certain speed (although new technology is helping with this)
- Hurts birds? Impedes migration pathways for these bird or migratory birds
- Cannot yet recycle old blades (the other 90% of a turbine is recyclable/reusable), they must be stored in a landfill
what are the cons of wind power? (3)
- These sources are usually considered "carbon neutral" because what GHG you produce when burning is absorbed when growing the plants
- Can be a way to use wastes (like trash or waste from crops) instead of storing in a landfill
- Side product of biogas=fertilizer
- Can be used anywhere on a small or large scale
what are the pros of biomass/biogas/biofuel? (4)
- Do generate air pollutants and GHG
- Using wood for fuel can lead to deforestation
- If growing a specific crop, the growing of the crop could require the use of fossil fuels
- No more land left to expand crop production for biofuels
- Rising corn prices
what are the cons of biomass/biogas/biofuel? (5)
the only waste would be water
what is the pro of hydrogen fuel cells?
- supply hard to get
- hydrogen is hard to store
what are the cons of hydrogen fuel cells? (2)
no waste, air pollution, or GHG production
what is the pro of geothermal power?
unless there is something special around, this is only really useful for heating/cooling individual buildings
what is the con of geothermal power?
wind power (ex. Texas, Iowa, Oklahoma--->accounts for 10-11% of total electricity generation)
what renewable energy does the US utilize the most of?
solar power is the fastest growing renewable energy source (popular in sunny states such as California, Arizona, Florida--->solar panels, etc. are becoming more affordable and common)
which renewable energy source is growing fast in the US?
solar and wind due to falling costs, government incentives, and clean energy goals (battery storage helps manage this)
which renewable energy sources are likely to expand within the US?
because most big rivers are already dammed
even though hydropower is a major renewable energy source in the US, why is growth limited?
they are smaller portions of the renewable energy sources but are steady options
how is biomass and geothermal power used in the US?
biomass: organic material used directly as fuel; biogas: gas produced from decomposing organic matter; biofuel: liquid fuel made from organic sources
what are the differences between biomass, biogas, and biofuel?
ethanol
while this is a form of renewable energy we need to be cautious about its production
growing the corn
what could help utilize the use of fossil fuels for large scale agriculture with the production of ethanol?
by using heat from the Earth's interior--->they tap into hot water or steam from underground reservoirs, which is brought to the surface, where it drives a turbine connected to a generator...this converts thermal energy into electricity.
how do geothermal systems generate electricity?
uses hydrogen gas and oxygen gas to produce electricity; inputs: hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2); outputs: electricity and water (H2O)
what is used to create a hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell? What are the inputs and outputs from the reaction?
2H2+O2--->2H2O+energy
what is the chemical reaction for hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity?