CHEM EXAM 3 {NOTES}
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Bacillus & Pseudomonas perform:
anaerobic respiration (via NO₃⁻)
E. coli performs:
alcohol & lactic acid fermentation (heterolactic fermentation)
Enterobacter aerogenes performs:
alcohol & lactic acid fermentation
Saccharomyces cerevisiae performs:
alcohol fermentation
Streptococcus performs:
lactic acid fermentation
Lactobacillus acidophilis performs:
lactic acid fermentation
Micrococcus luteus performs:
aerobic respiration
metabolism:
all chemical reactions within a cell.
energy:
the ability to do work.
catabolism (decomposition):
form of metabolism which breaks down molecules & is energy releasing.
anabolism (synthesis):
form of metabolism which builds molecules & is energy requiring.
metabolic pathways:
sequence of chemical reactions.
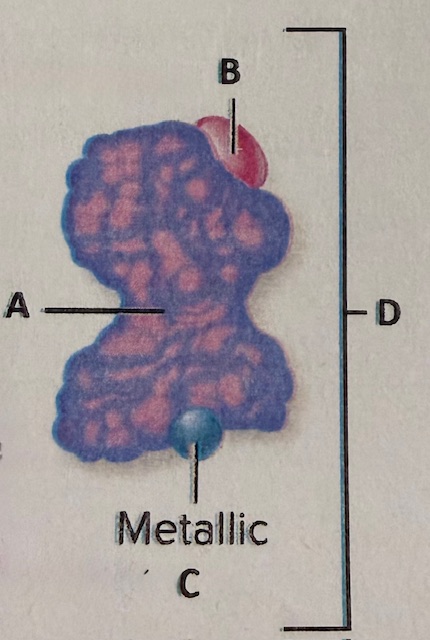
label A
apoenzyme
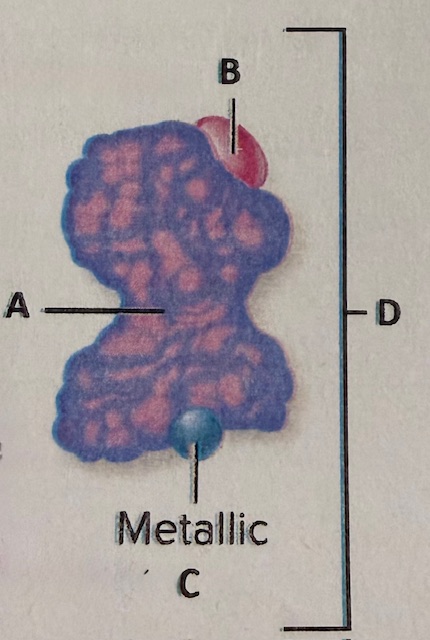
label B
coenzyme
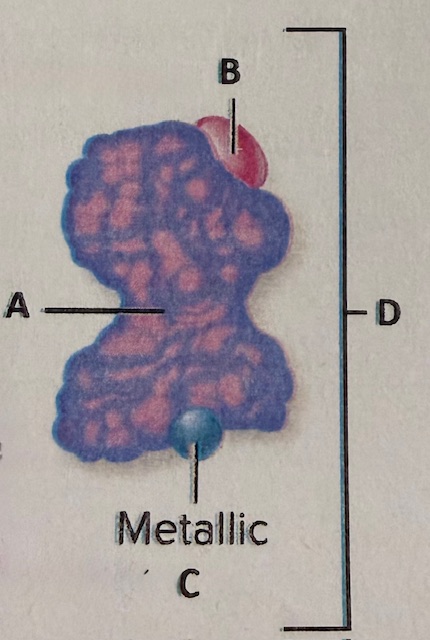
label C
cofactor
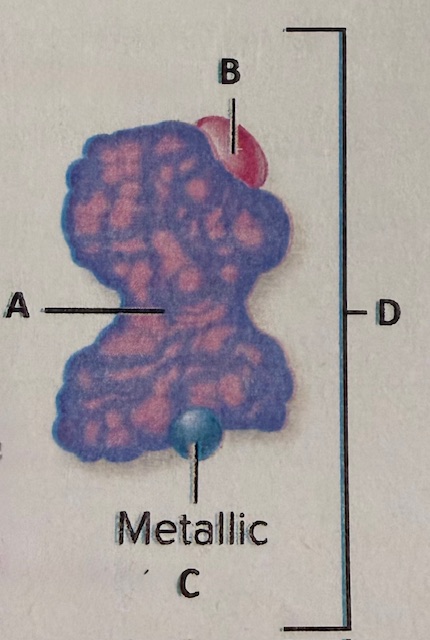
label D
enzyme
holoenzyme (conjugated enzyme):
enzymatic state required to function.
substrate:
any compound that reacts with an enzyme.
active site:
region on enzyme where a substrate binds.
function of catalase:
breaks down H₂O₂
function of amylase:
hydrolysis of starch
endoenzymes:
produced inside cells and function/work inside cells.
constitutive enzymes:
enzymes always present in constant amounts.
regulated enzymes:
enzymes produced only when needed.
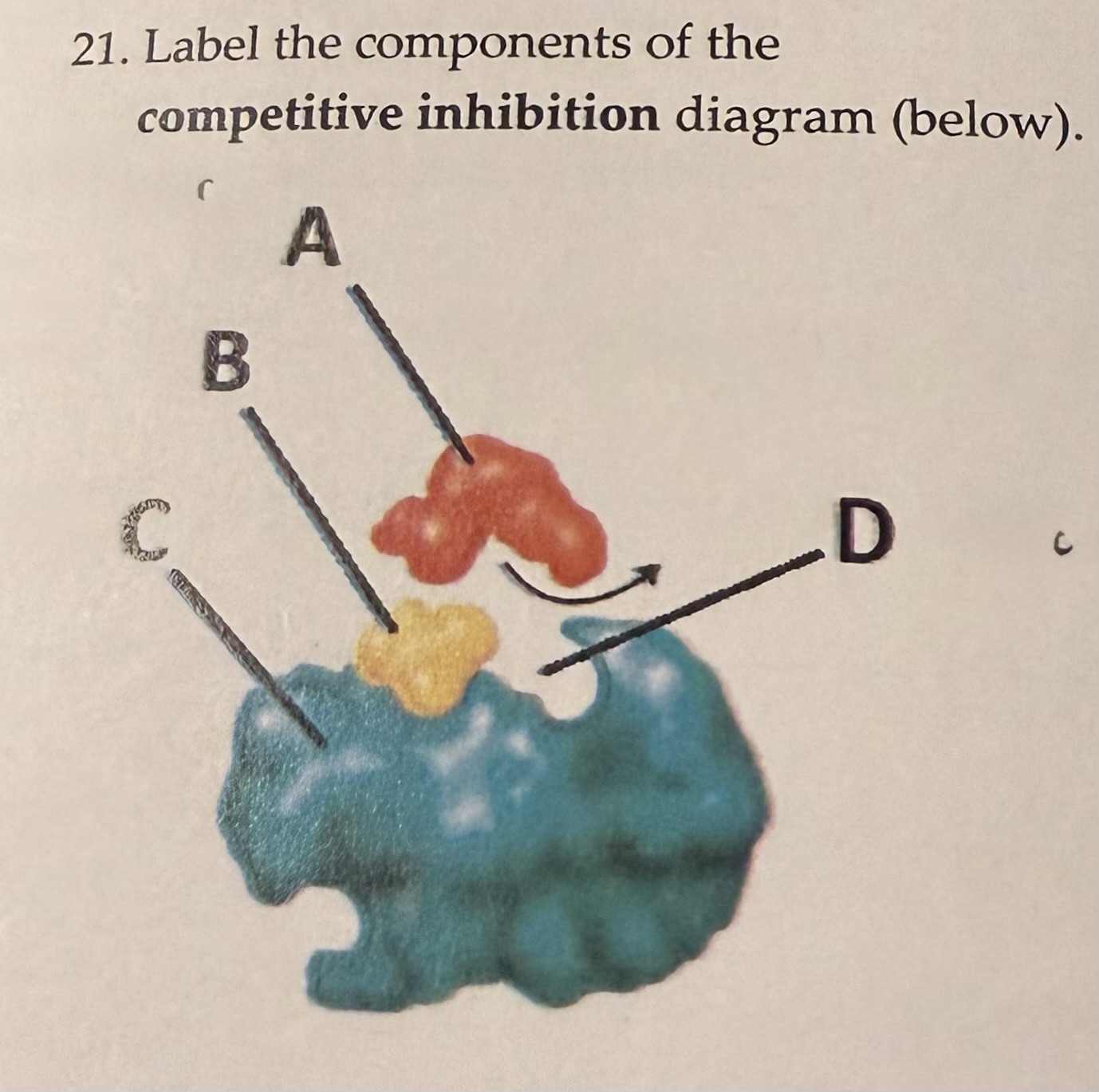
label the components
A) substrate B) competitive inhibitor C) enzyme D) active site
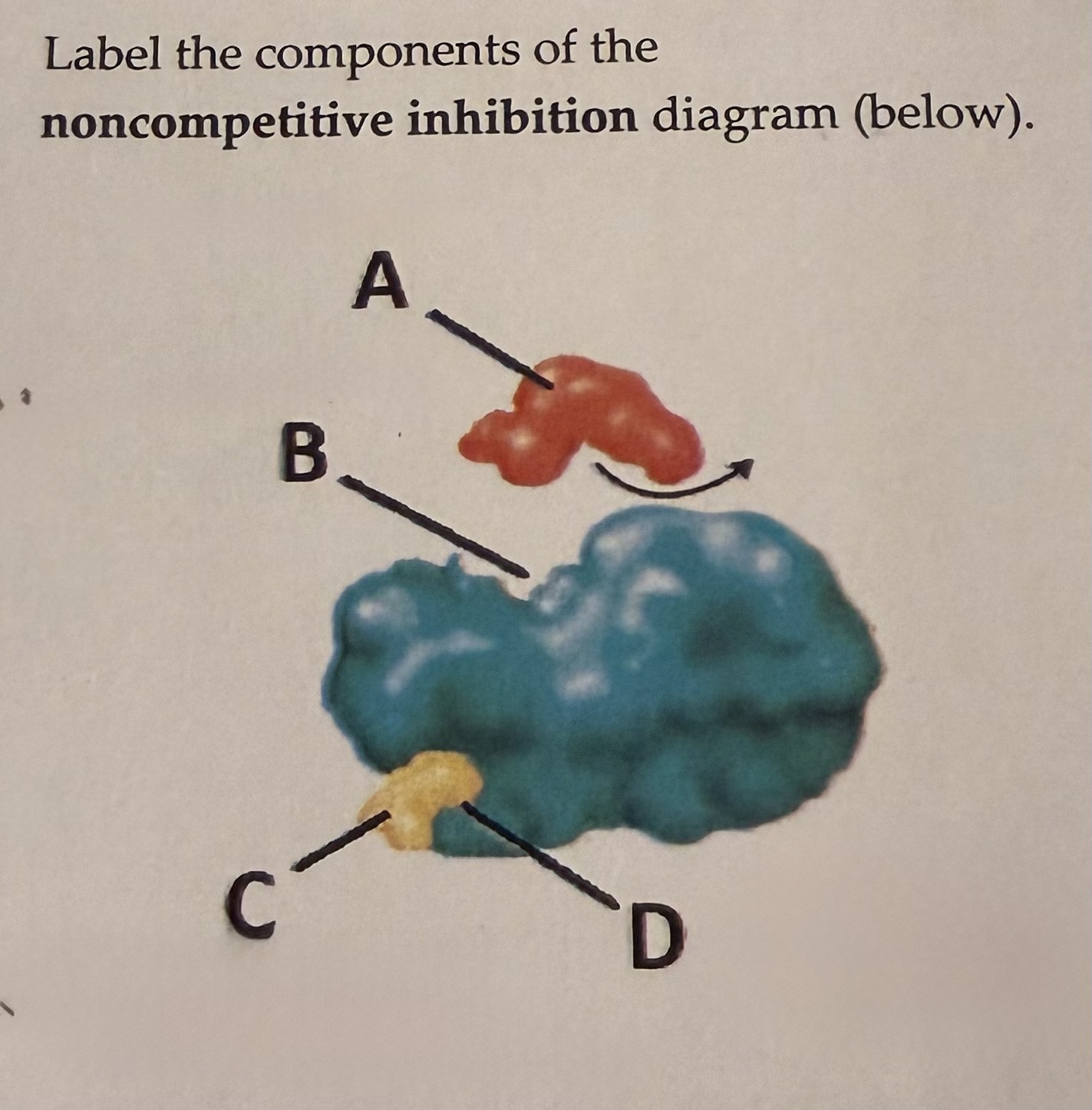
label the components
A) substrate B) altered active site C) non-competitive inhibitor D) allosteric site
how does feedback inhibition turn off a metabolic pathway:
when enough end product is needed.
redox reaction diagram
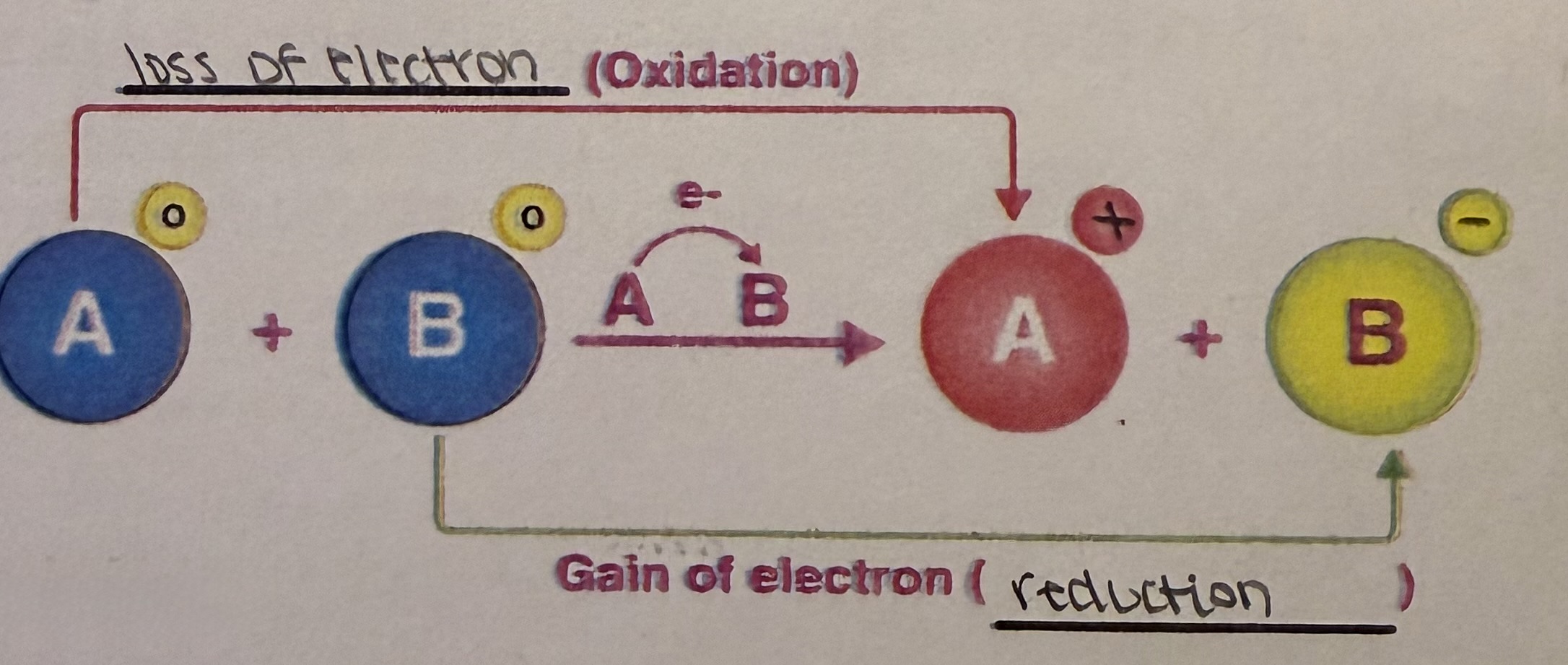
electron & proton carriers
molecules that load/unload electrons and/or protons (H+).
label the parts of the ATP molecule
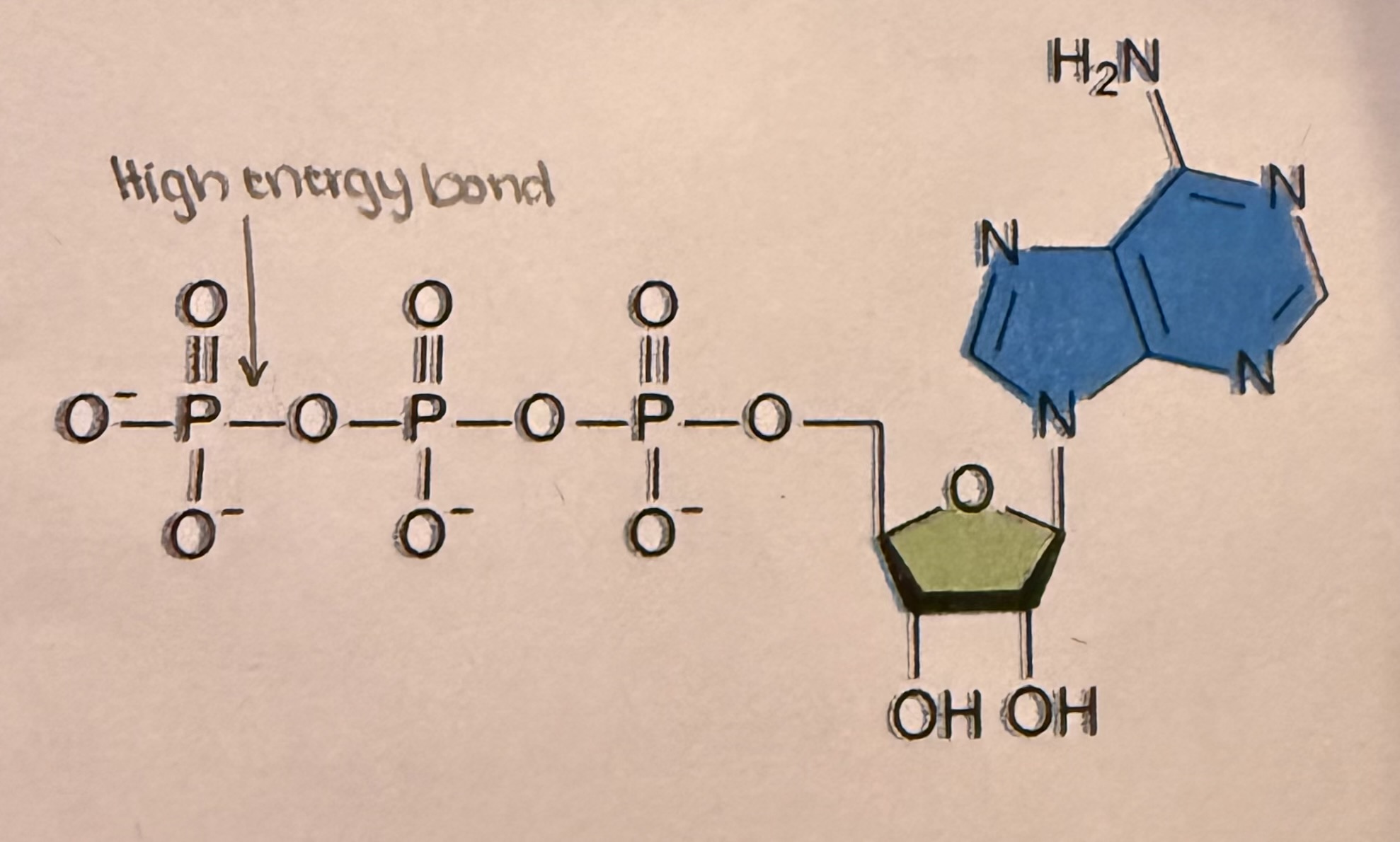
substrate-level phosphorylation:
form of ATP generation whereby inorganic phosphate (Pi) is transferred from a phosphorylated compound to ADP.
oxidative-phosphorylation:
form if ATP generation whereby electrons are transferred from organic compounds (NAD+ or FAD) to electron carriers to O₂.
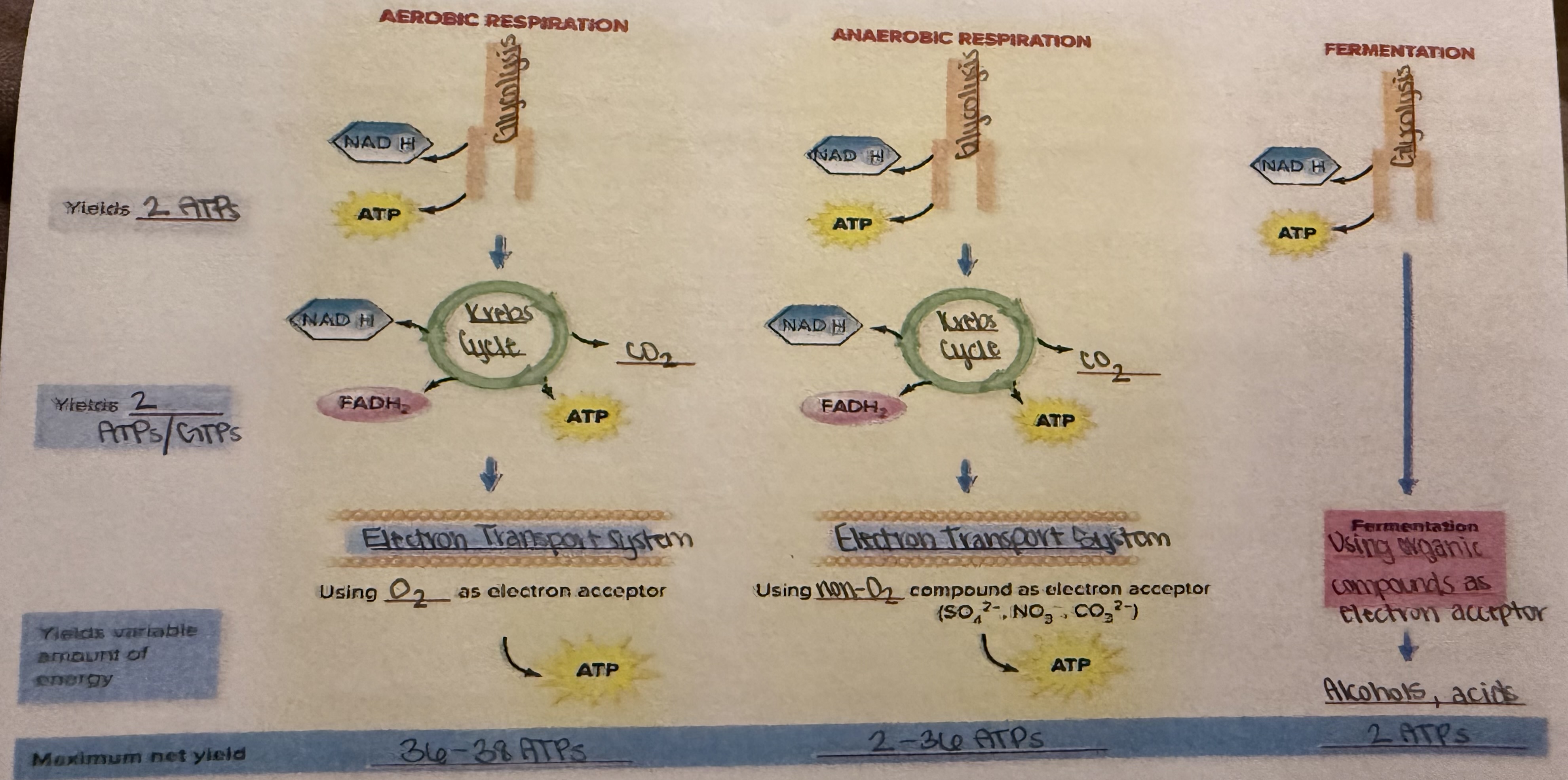
aerobic respiration equation in bacteria:
C6H12O6+6O2–>6CO2+6H2O+38ATP
glycolysis undergoing bacterial aerobic respiration:
cellular location- cytoplasm
net ATP produced- 2
O₂ required?- no
CO₂ produced- n/a
NADH produced- 2
FADH2 produced- n/a
“Prep step” undergoing bacterial aerobic respiration:
cellular location- cytoplasm
net ATP produced- 0
O₂ required?- no
CO₂ produced- 2
NADH produced- 2
FADH2 produced- n/a
Krebs cycle undergoing bacterial aerobic respiration:
cellular location- cytoplasm
net ATP produced- 2
O₂ required?- no
CO₂ produced- 4
NADH produced- 6
FADH2 produced- 2
electron transport chain undergoing bacterial aerobic respiration:
cellular location- outside cell membrane
net ATP produced- 28
O₂ required?- yes
CO₂ produced- n/a
NADH produced- n/a
FADH2 produced- n/a