Bio1 Lab Midterm
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
What are the steps to the scientifc method?
question, research, hypothesis, experiment, gather data,draw conclusions,
a testable, educated guess or proposed explanation for a phenomenon, often stated as an "if/then" statement, that serves as a starting point for further investigation or experiments
hypothesis
Why must a hypothesis be falsifiable?
so it can be tested through experiments or observations that could prove it wrong
the variable that is deliberately changed or manipulated in an experiment.
independent variable
A variable that is kept constant throughout the experiment to ensure a fair test
control variable
the variable that is measured or observed; it changes
dependent variable
The group or sample that does not receive the experimental treatment; it serves as a baseline for comparison
control sample
A graph showing how much light a substance absorbs at different wavelengths
absorbance spectrum
What value can be determined from an absorption spectrum
wavelength of maximum absorbance
graph that shows the relationship between known concentrations of a substance and their corresponding absorbance value
standard curve
How do you determine an unknown concentration from a standard curve?
Plug in absorbance to y=mx +b
The movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached
diffusion
What does “diffusion down a concentration gradient” mean?
Molecules move from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated
the state where molecules continue to move but are evenly distributed; there is no net movement in any one direction
dynamic equilibrium
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
Higher temperature increases, lower temperature decreases
The diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from low solute concentration to high solute concentration
osmosis
the environment has a higher solute concentration than the cell; water leaves the cell — animal cells shrink, plant cells cytoplasm and plasma membrane shrink
hypertonic
The environment has a lower solute concentration than the cell; water enters the cell — animal cells swell or burst, plant cells swell within their walls
hypotonic
Solute concentration is equal inside and outside the cell; no net water movement — animal cells stay normal, plant cells become flaccid
isotonic
How do animal cells deal with osmosis
kidneys or other bodily systems
How do plant cells deal with osmosis?
cell walls prevent bursting
How do protists deal with osmosis?
contractile vacuoles to pump out water
How do bacteria deal with osmosis?
cell walls prevent bursting
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + energy (ATP)
aerobic celluar respiration
C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₂H₅OH + 2CO₂ + energy (ATP)
alcohol fermentation

Simple sugars made of one unit; basic building blocks of carbohydrates (examples: glucose, fructose, galactose)
monosaccharide
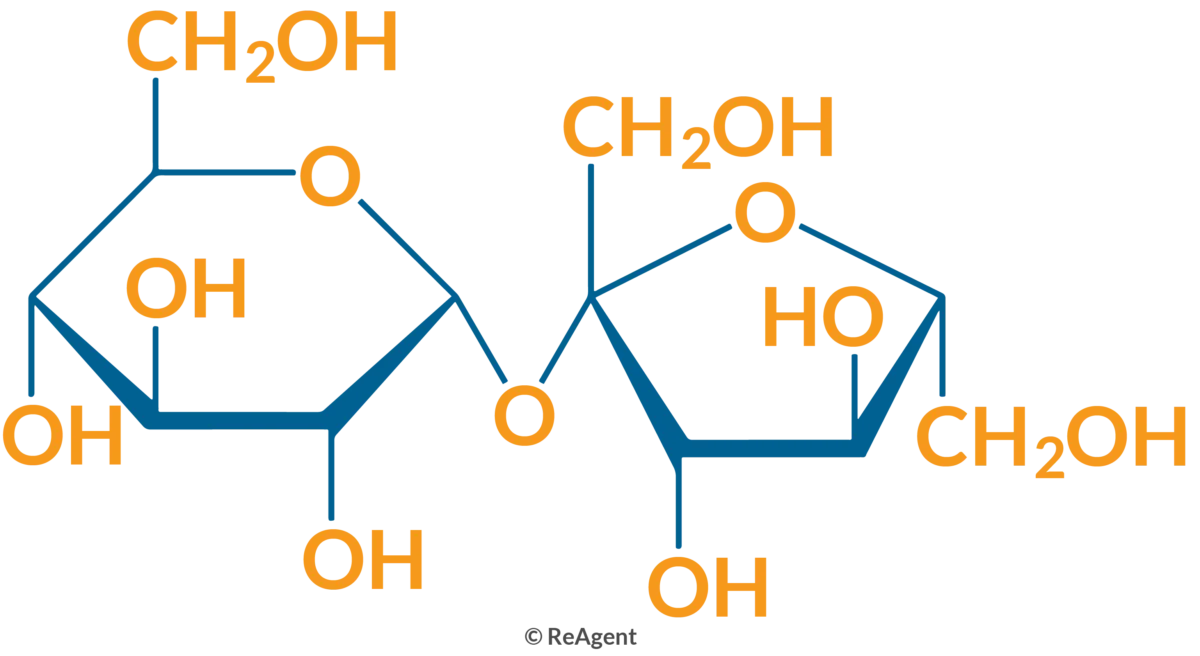
Sugars made of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond (examples: sucrose, lactose, maltose).
disaccharide
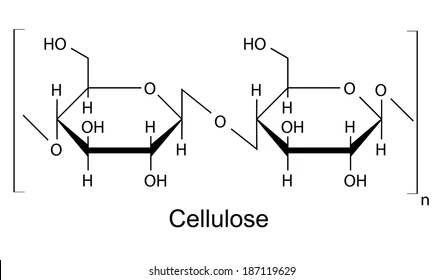
Large carbohydrate molecules made of many monosaccharides linked together (examples: starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin)
polysaccharide
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
photosynthesis
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
light dependent reaction and calvin cycle
occur in the stroma; use ATP and NADPH to fix CO₂ into glucose.
Calvin cycle
occur in the thylakoid membranes; convert light energy to ATP and NADPH and release O₂.
light dependent reaction
The continuous movement of carbon among the atmosphere, living organisms, oceans, and soil through processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion
carbon cycle
How do you calculate total magnification
objective x 10
What is the fov in mm for 40x, 100x, 400x, and 1000x
5 2 .5 .2
How do you convert from meters (m) to millimeters (mm)to micrometers(um)?
x 1000 each
How do you convert from liters (L) to milliliters (mL)to microliters(um)?
x 1000 each
What is the organism and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic? Say if photosynthetic
cyanobacteria anabaena (prokaryote, photosynthetic)

What is the organism and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
lactobacillus sp. (prokaryote)
What is the organism and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Paramecium sp. (eukaryote)

What is the organism and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic? State if photosynthetic
Elodea sp. (eukaryote, photosynthetic)
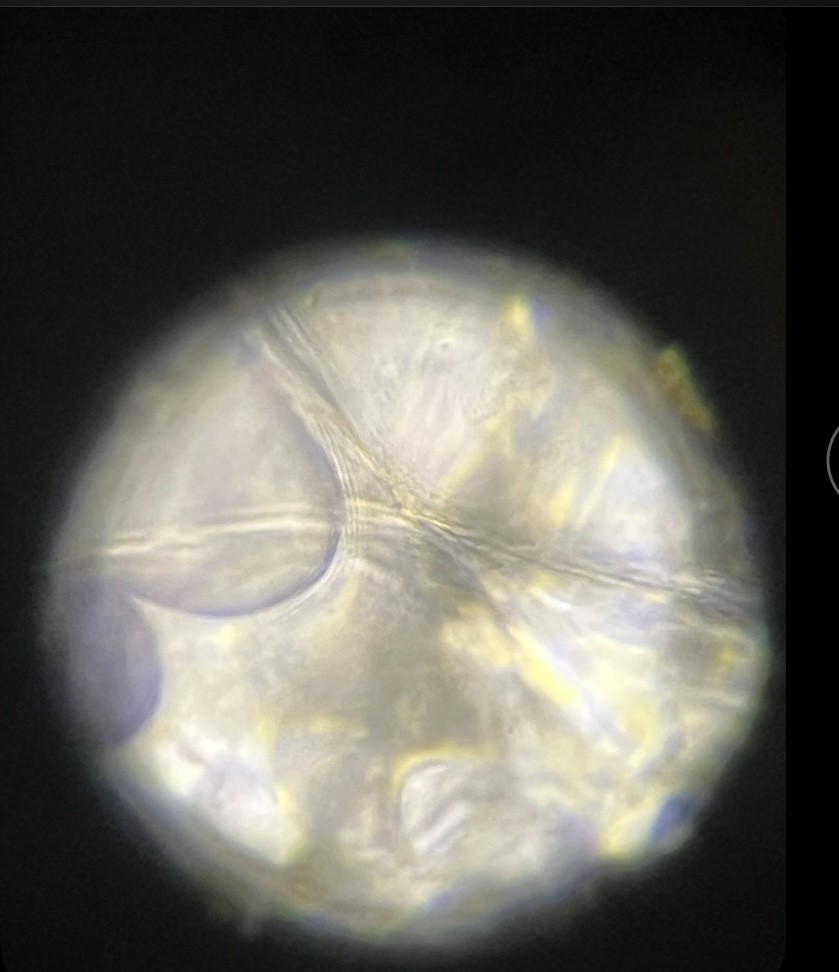
What is the organism and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic? State if photosynthetic
Solanum tuberosum/ potato (eukaryote, photosynthetic)

What is the organism and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic? State if photosynthetic
amoebae sp. (eukaryote)
How do you calculate cell size through a microscope?
fov (um)/ # of cells
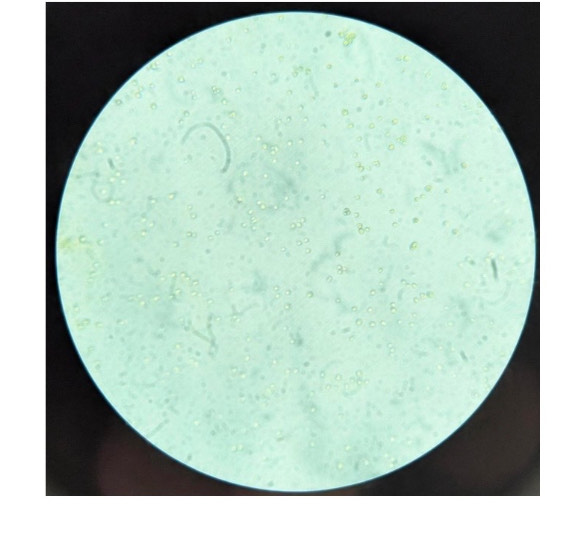
What is the organism and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Chlorella vulgaris (eukaryote)
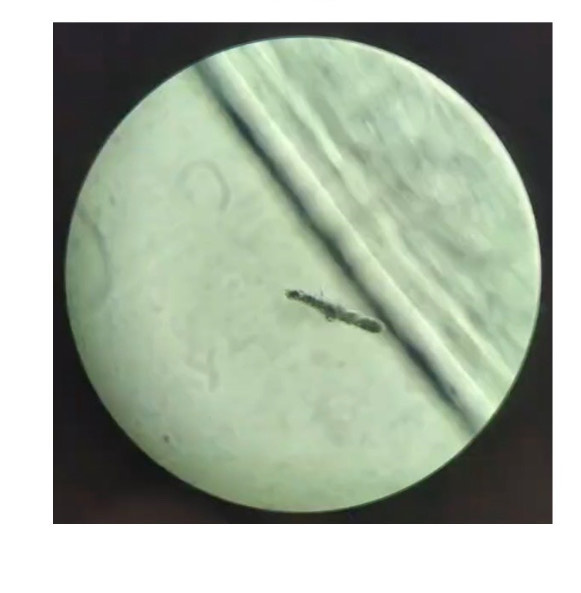

What is the organism and is it prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Amoeba proteus (eukaryote)
How do you find percent error
experimental-theoretical/theoretical
What are the requirements for a graph
Title, labeled x and y axis with name and units, tick marks on both axes, legend, caption
What are the requirements for a table
numbered, title, subheadings
What are the requirements for a drawing
title, total mag, estimated cell size, labeled cell strucutures
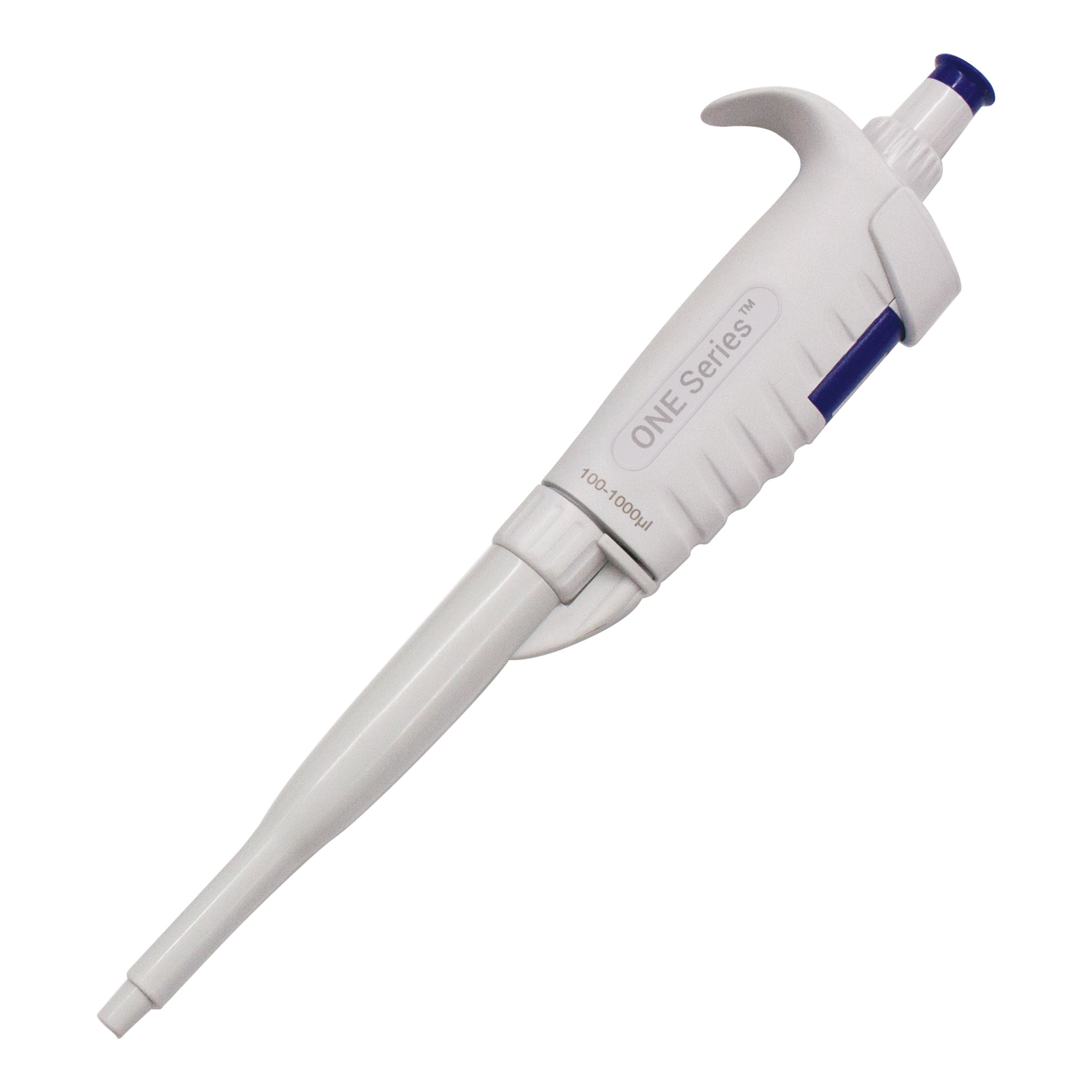
Whats this
micropipette
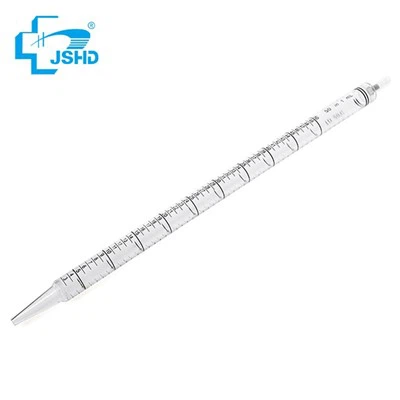

Whats this
serological pipette
In the egg lab when placed into a _____ solution it will gain mass
hypotonic
In the egg lab when placed into a _____ solution it will lose mass
hypertonic
In the egg lab when placed into a _____ solution its mass will stay the same
isotonic
the concentration of solute particles in a solution
osmolarity
the ability to distinguish two close objects as separate
resolution
difference in light intensity or color between an object and its background
contrast
thickness of the specimen that remains in sharp focus at one time
depth of field
Higher magnification = _______ depth of field
smaller
measure of how much a substance bends (refracts) light
index of refraction
simple, single-celled organism without a nucleus.
DNA is free in the cytoplasm
No membrane-bound organelles
Usually smaller (1–10 µm)
prokaryote
cell with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
DNA is inside the nucleus
Contains mitochondria, ER, etc.
Usually larger (10–100 µm)
eukaryote
d of fov1 X mag fov1/mag fov2=
d for fov2
What organelle can you expect to see in an ameobae
contractile vacuole
plant organelles that store starch.
Found in storage tissues like potatoes
A type of plastid
Can convert starch back into sugar when the plant needs energy
amyloplasts
How do ameobae move
pseudopodia and cytoplasmic streaming
How does paramecium move
cilia
why cell size is limited by the surface area-to-volume ratio
too much volume doesnt allow the export of materials
mitochondria and chloroplasts originated from free-living bacteria that were engulfed by an ancestral eukaryotic cell and became permanent organelles
endosymbiont theory
Whats the evidence for the endosymbiont theory
circular DNA
70S ribosomes, same as prokaryotes
Divide by binary fission
Double membranes
Similar size to bacteria
anaerobic respiration that converts pyruvate into lactic acid and regenerates NAD⁺
lactic acid fermentation
anaerobic process where pyruvate is converted into ethanol and CO₂, while regenerating NAD
alcohol fermentation
C6H12O6→2C3H6O3+Energy (2 ATP)
lactic acid fermentation
organism that obtains its energy and carbon by consuming other organisms
heterotroph
organism that produces its own food using energy from sunlight (photosynthesis) or chemical reactions (chemosynthesis)
autotroph
Where do the light reactions happen
thykaloids
Where does the Calvin cycle happen
stroma
Sugar forming step of photosynthesis is driven by ATP and NADH but can only occur while light is avaliable
calvin cycle
When light energy from photons is converted to electrochemical energy, water splits to give electrons to the system resulting in the formation of oxygen
light reactions
Does carbon dioxide or oxygen increase during photosynthesis
oxygen
What is DNA made of?
sugar, phosphate group, nitrogenous base
What are the pyrimidines
cytosine and thymine
What are the purines
adenine and guanine
Cut human DNA into fragments
restriction enzymes
How can restriction enzymes determine variation in DNA sequences
They cant cut where there is a mutation making the band longer for gel electrophoresis
What are the origins of restriction enzymes?
they were found in bacteria and cut out viruses
During gel electrophoresis DNA moves towards the positive end because it is ______ charged
negatively
During gel electrophoresis DNA is categorized by size as the ______ molecules travel faster and farther
smaller
A mixture of DNA with known sizes used in gel electrophoresis
marker
If I am preparing to cast a 100 mL 1% gel how much agrose would i need
1g/100 mL
A _____ agrose concentration is ideal when there are larger DNA fragments
lower
What is the purpose of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS PAGE)
to seperate proteins
Why do some use Polyacrylamide Instead of Agarose
the proteins are too small for agrose
The physical trait of an organism
phenotype
The genetic makeup of an organism
genotype
segment of DNA that contains the instructions to make a specific protein or RNA molecule
basic units of heredity
gene
alternative form of a gene.
arose because of mutations
allele
For F1 wheter monohybrid or dihybrid it is always…
heterozygous